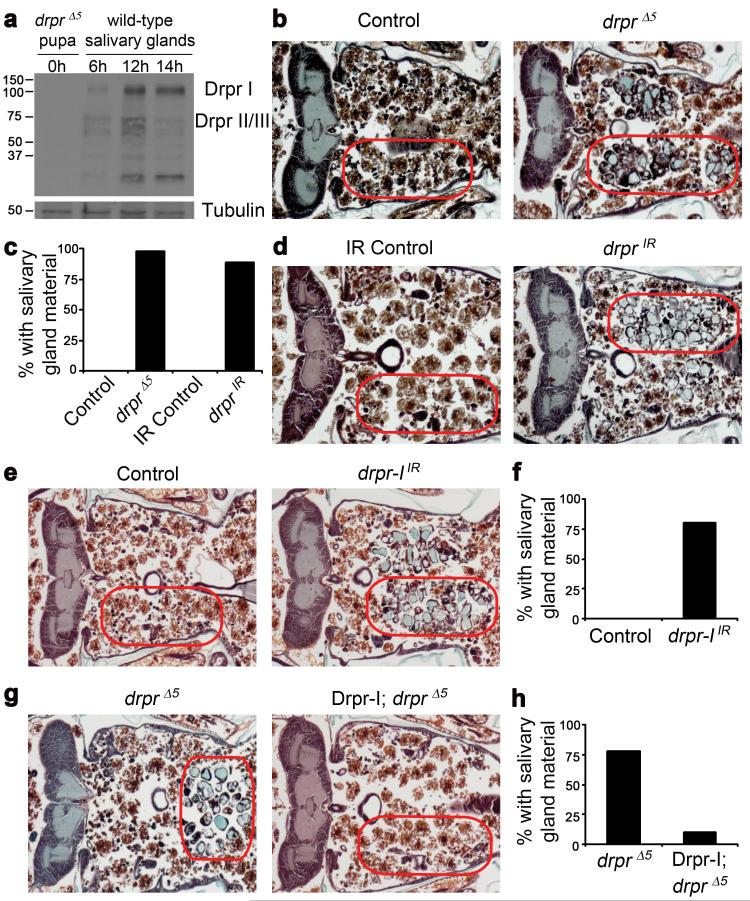
Figure 1. Draper is required for salivary gland cell degradation.
a, Protein extracts from drpr null (w; drprΔ5/drprΔ5) pupae at puparium formation (0h) and wild type (Canton-S) salivary glands 6h, 12h, and 14h after puparium formation, were analyzed by Western Blotting with anti-Drpr antibody. b, Control animals (+/w; +/drprΔ5), n=12, and drpr null mutants (w; drprΔ5/drprΔ5), n=47, were analyzed by histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red circles) 24h after puparium formation. c, quantification of data from b and d. d, Control animals (+/w; +/UAS-drprIR), n=11, and those with salivary gland-specific knockdown of drpr (fkh-GAL4/w; UAS-drprIR/+), n=19, were analyzed by histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red circles) 24h after puparium formation. e, Control animals (+/w; +/UAS-drpr-IIR), n=9, and those with salivary gland-specific knockdown of drpr-I (fkh-GAL4/w; UAS-drpr-IIR/+), n=20, were analyzed by histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red circles) 24h after puparium formation. f, quantification of data from e. g, drpr null animals (+/w; +/UAS-Drpr-I; drprΔ5/drprΔ5), n=9, and those with salivary gland-specific expression of Drpr-I (fkh-GAL4/w; UAS-Drpr-I/+; drprΔ5/drprΔ5), n=20, were analyzed by histology for the presence of salivary gland material (red circles) 24h after puparium formation. h, quantification of data from g.