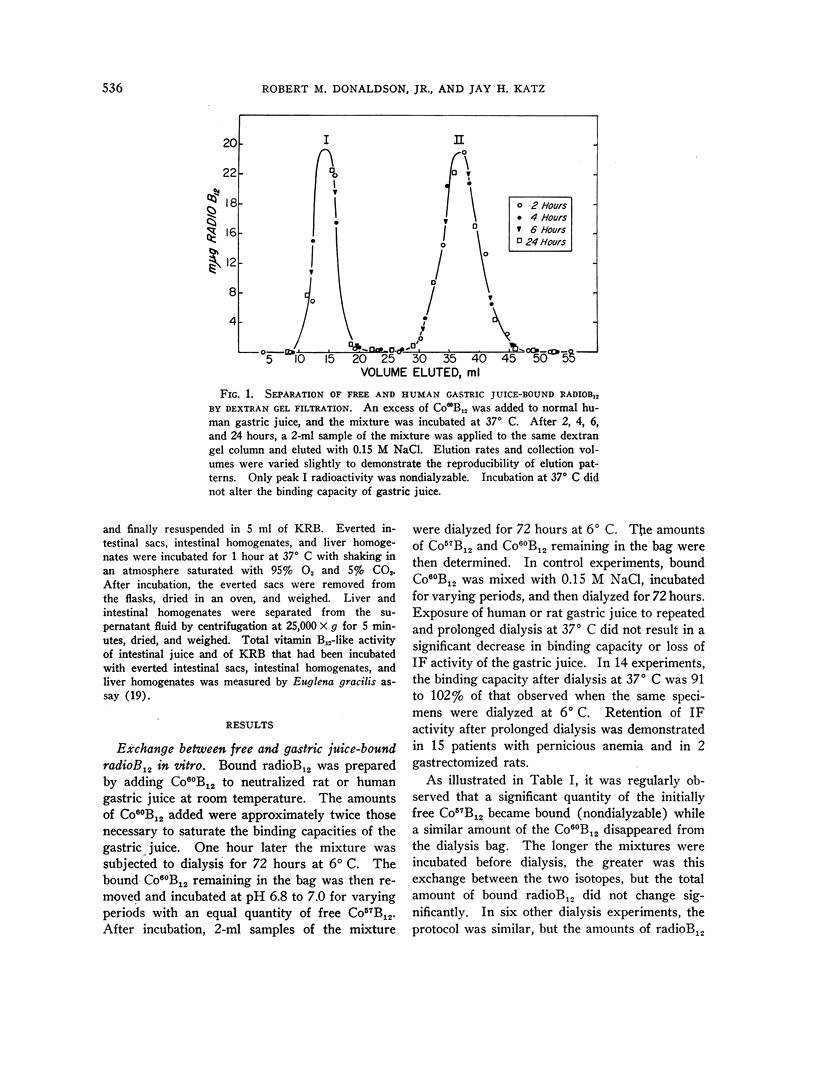
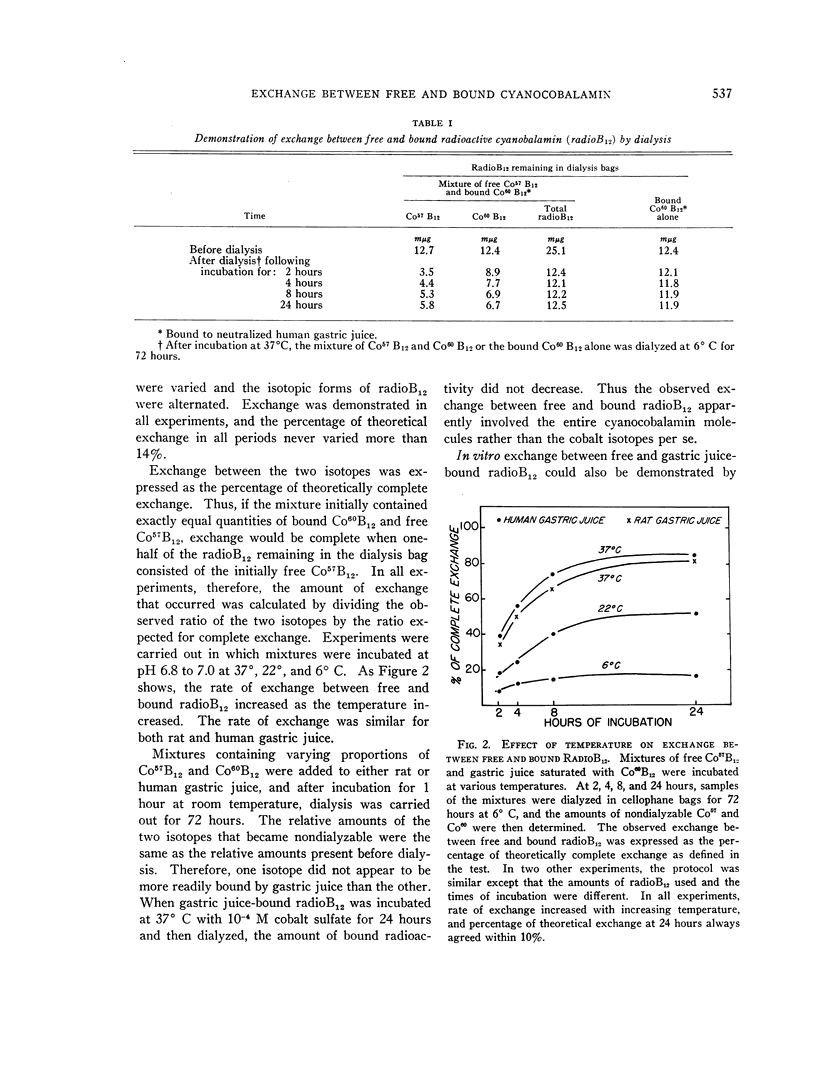
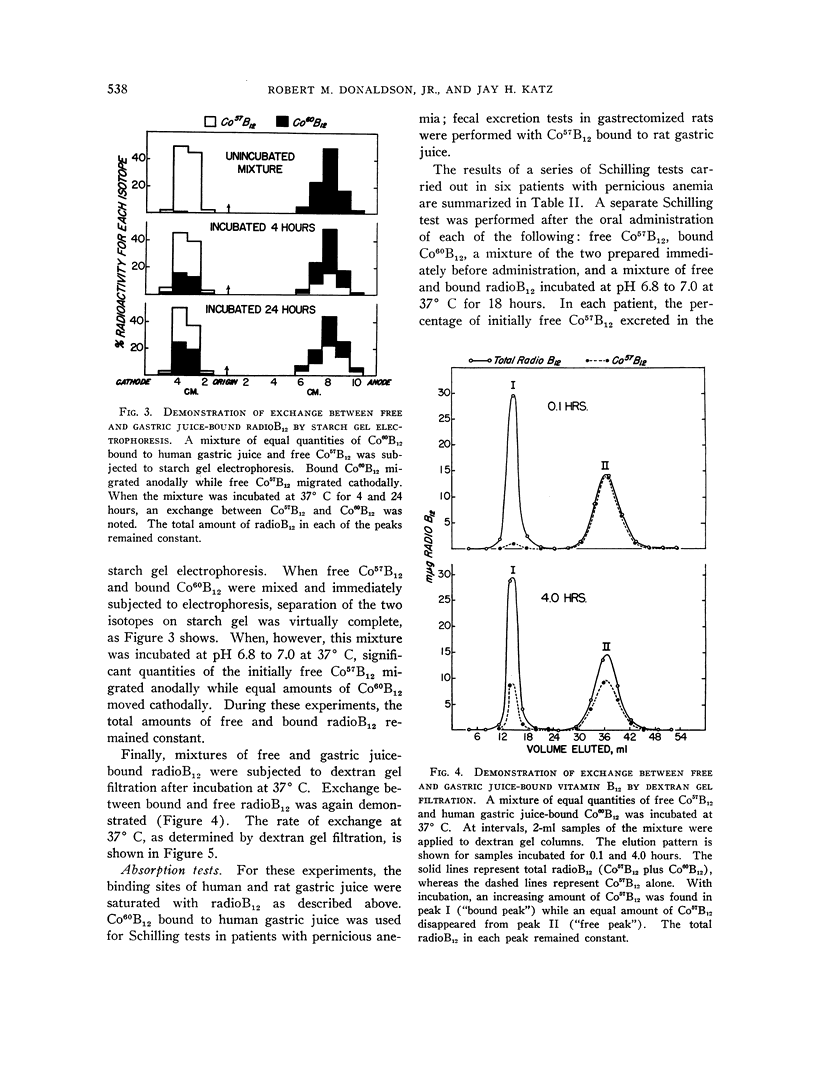
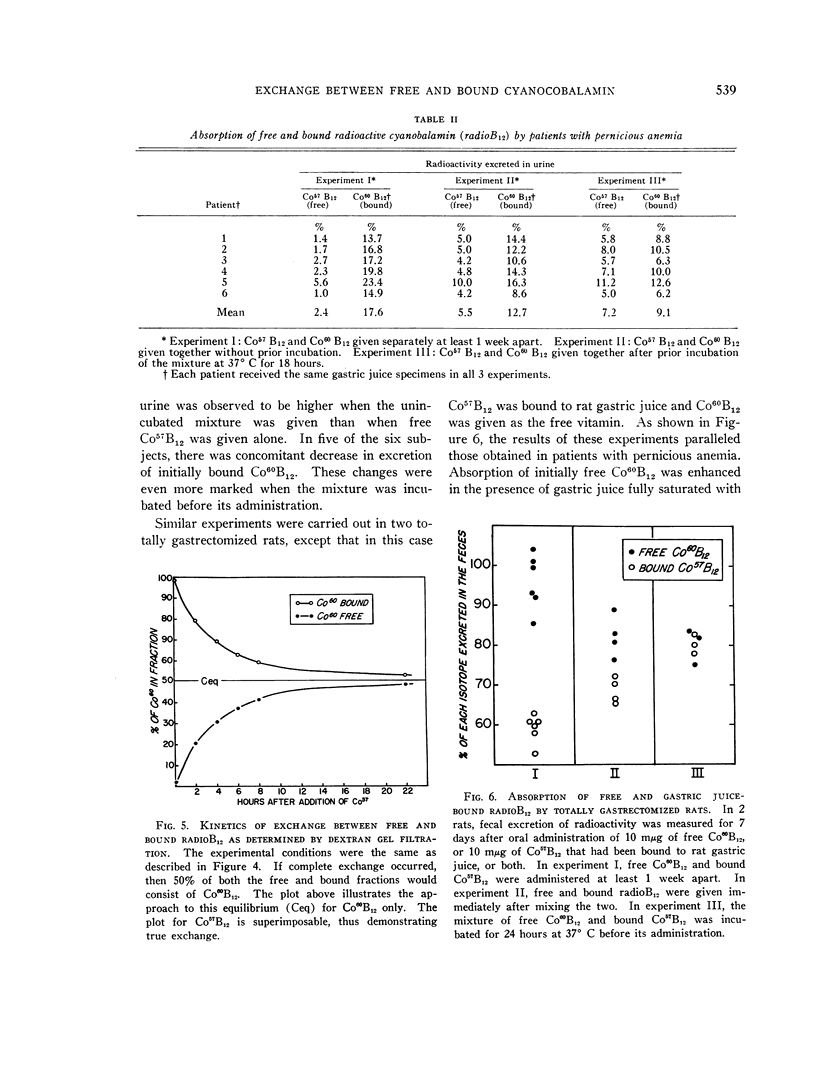
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER S. J., MOLLIN D. L. The relationship between intrinsic factor and the intestinal absorption of vitamin B12. Br J Haematol. 1955 Jan;1(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECK W. S. The metabolic function of vitamin B. N Engl J Med. 1962 Apr 5;266:708–714. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196204052661407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRD O. D., HOEVET B. The vitamin B12 binding power of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1951 May;190(1):181–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUNGE M. B., SCHILLING R. F., SCHLOESSER L. L. Intrinsic factor studies. IV. Selective absorption and binding of cyanocobalamin by gastric juice in the presence of excess pseudovitamin B12 or 5, 6-dimethylbenzimidazole. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 Nov;48(5):735–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLENDER S. T., EVANS J. R. The urinary excretion of labelled vitamin B12. Clin Sci. 1955 May;14(2):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., CASTLE W. B. Sequential mechanisms in the enhanced absorption of vitamin B12 by intrinsic factor in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:199–214. doi: 10.1172/JCI104019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., PARANCHYCH W., LOWENSTEIN L. Studies on the absorption by guinea pig intestine of cyanocobalamin incubated with intrinsic factor. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:370–377. doi: 10.1172/JCI104491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD J. E., HUTNER S. H. Role of vitamin B12 in the metabolism of microorganisms. Vitam Horm. 1955;(13):101–136. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)61024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASS G. B. J., BOYD L. J., STEPHANSON L. Intestinal absorption of vitamin B12 in man. Science. 1954 Jul 9;120(3106):74–75. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3106.74-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASBECK R. Physiology and pathology of vitamin B12 absorption, distribution, and excretion. Adv Clin Chem. 1960;3:299–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY M. E. The microbiological assay of vitamin B12 in the milk different animal species. Br J Nutr. 1954;8(4):340–347. doi: 10.1079/bjn19540051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. Divalent cation and pH dependence of rat intrinsic factor action in everted sacs and mucosal homogenates of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1978–1983. doi: 10.1172/JCI104423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., COOPER B. A., CASTLE W. B. The site of vitamin B12-intrinsic factor complex "releasing factor" activity in the rat small intestine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jun;110:315–317. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Development of a possible in vitro assay for intrinsic factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Mar;97(3):668–671. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., KAPLAN M. E. Studies suggesting the presence of intrinsic factor in bile. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Aug-Sep;107:900–904. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Mechanism of absorption of vitamin B12. Fed Proc. 1960 Dec;19:884–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Mechanism of intrinsic factor action in everted sacs of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):102–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI103779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Studies on the role of intrinsic factor in vitamin B12 absorption, transport, and storage. Am J Clin Nutr. 1959 Jul-Aug;7:433–443. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/7.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGHLEY D. R., ELLENBOGEN L. Studies on the mechanism of vitamin B12 absorption: in vivo transfer of vitamin B12 to intrinsic factor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Oct;99:126–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFRIES G. H., SMITH F. W., HOSKINS D. W., SLEISENGER M. H. Fractionation of the nondialyzable components of normal human gastric juice by starch gel electrophoresis. Gastroenterology. 1961 Nov;41:467–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAY A. W. Effect of large doses of histamine on gastric secretion of HCI; an augmented histamine test. Br Med J. 1953 Jul 11;2(4827):77–80. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4827.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOERTEL C. G., SCUDAMORE H. H., OWEN C. A., Jr, BOLLMAN J. L. Intestinal absorption of cobalt60-labeled vitamin B12 in the normal male albino rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Aug;197:347–350. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.2.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEWEG H. O., ARENDS A., MANDEMA E., CASTLE W. B. Enhanced absorption of vitamin B12 in gastrectomized rat by rat intrinsic factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):328–332. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REIZENSTEIN P. G. Excretion, enterohepatic circulation, and retention of radiovitamin B12 in pernicious anemia and in controls. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:703–707. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS G. I. M. Vitamin B12 assay in body fluids using Euglena gracilis. J Clin Pathol. 1952 Aug;5(3):250–256. doi: 10.1136/jcp.5.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILLING R. F. Intrinsic factor studies II. The effect of gastric juice on the urinary excretion of radioactivity after the oral administration of radioactive vitamin B12. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Dec;42(6):860–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. An improved procedure for starch-gel electrophoresis: further variations in the serum proteins of normal individuals. Biochem J. 1959 Mar;71(3):585–587. doi: 10.1042/bj0710585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS E. W., DONALDSON R. M., Jr, GARDNER F. H. A relationship between intestinal bacteria and the absorption of vitamin B12 in rats with diverticula of the small bowel. Lancet. 1961 Sep 30;2(7205):736–738. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90687-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOOHEY J. I., BARKER H. A. Isolation of coenzyme B12 from liver. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:560–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOPOREK M. The relation of binding power to intrinsic factor activity. Effect of pseudovitamin B12 on absorption of vitamin B12. Am J Clin Nutr. 1960 May-Jun;8:297–300. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/8.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER J. B., HUGHES D. E. The absorption of some B-group vitamins by surviving rat intestine preparations. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1962 Apr;47:107–133. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1962.sp001582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON G. M., FLOREY H. W. The absorption of vitamin B12 in gastrectomised rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Oct;36(5):479–486. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H., WISEMAN G. The use of sacs of everted small intestine for the study of the transference of substances from the mucosal to the serosal surface. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):116–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



