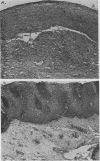
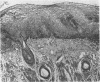
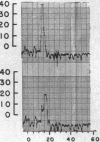
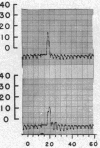
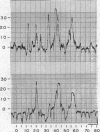
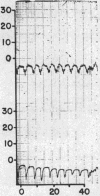
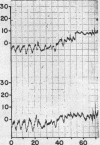
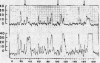
Full text
PDF


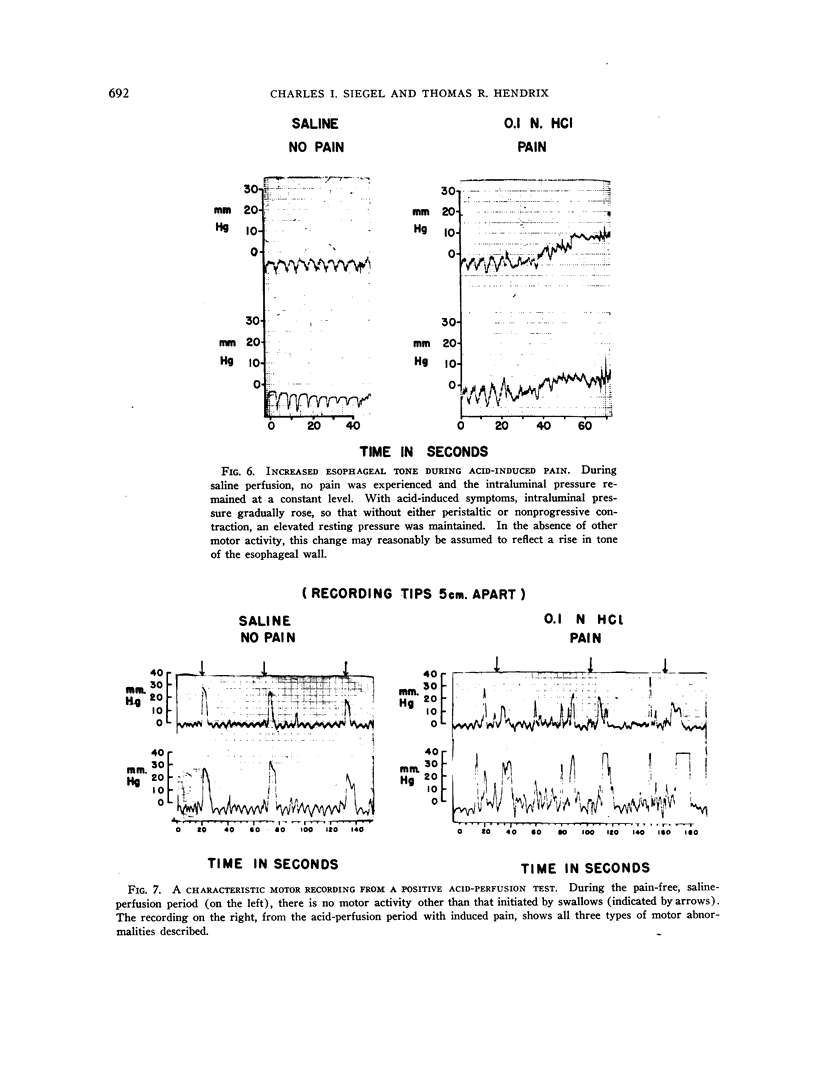



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON M., EDWARDS D. A., HONOUR A. J., ROWLANDS E. N. Comparison of cardiac and pyloric sphincters; a manometric study. Lancet. 1957 Nov 9;273(7002):918–922. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATKINSON M., EDWARDS D. A., HONOUR A. J., ROWLANDS E. N. The oesophago-gastric sphincter in hiatus hernia. Lancet. 1957 Dec 7;273(7006):1138–1142. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSTEIN L. M., BAKER L. A. A clinical test for esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1958 May;34(5):760–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSTEIN L. M., PACINI R., FRUIN R. C., GORVETT E. Esophagitis as a cause of upper abdominal pain. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Sep 6;168(1):27–33. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.03000010079007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTHA G. S. M. Mucosal folds at the cardia as a component of the gastro-oesophageal closing mechanism. Br J Surg. 1958 May;45(194):569–580. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004519402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAASCH J. W., ELLIS F. H., Jr The gastroesophageal sphincter mechanism: an experimental study. Surgery. 1956 Jun;39(6):901–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CODE C. F., FYKE F. E., Jr, SCHLEGEL J. F. The gastroesophageal sphincter in healthy human beings. Gastroenterologia. 1956;86(3):135–150. doi: 10.1159/000200544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER B., HENDRIX T. R., KRAMER P., INGELFINGER F. J. Resistance and reflex function of the lower esophageal sphincter. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Mar;12(2):339–342. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.12.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGELFINGER F. J. Esophageal motility. Physiol Rev. 1958 Oct;38(4):533–584. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM P. R., KESWANI R. K., MULLER W. H., Jr A correlative histopathologic study of experimental surgical reflux esophagitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1960 Oct;111:403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM P. R., RESPESS J. C., MULLER W. H., Jr The role of an intrinsic sphincter mechanism in the prevention of reflux esophagitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1959 Dec;109:659–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGLER R., SPIRO H. M. Heartburn in late pregnancy. Manometric studies of esophageal motor function. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jun;40:954–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI104335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER E. D. Subacute eroive ("peptic") esophagitis associated with achlorhydria. N Engl J Med. 1960 May 5;262:927–929. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196005052621807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERT J. H., DAVIDSON M., ALMY T. P., SLEISENGER M. H. Esophageal catheterization studies. I. The mechanism of swallowing in normal subjects with particular reference to the vestibule (esophago-gastric sphincter). J Clin Invest. 1959 Feb;38(2):397–406. doi: 10.1172/JCI103814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUTTLE S. G., BETTARELLO A., GROSSMAN M. I. Esophageal acid perfusion test and a gastroesophageal reflux test in patients with esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1960 Jun;38:861–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUTTLE S. G., RUFIN F., BETTARELLO A. The physiology of heartburn. Ann Intern Med. 1961 Aug;55:292–300. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-2-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANTRAPPEN G., TEXTER E. C., Jr, BARBORKA C. J., VANDEN-BROUCKE J. The closing mechanism at the gastroesophageal junction. Am J Med. 1960 Apr;28:564–577. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]