Abstract
Phase contrast and epifluorescence microscopy were utilized to monitor morphological changes in human astrocytoma cells during a time-course exposure to single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) conjugates with different surfactants and to investigate sub-cellular distribution of the nanotube conjugates, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that cytotoxicity of the nanotube/surfactant conjugates is related to the toxicity of surfactant molecules attached on the nanotube surfaces. Both sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS) are toxic to cells. Exposure to CNT/SDS conjugates (0.5 mg/mL) for less than 5 min caused changes in cell morphology resulting in a distinctly spherical shape compared to untreated cells. In contrast, sodium cholate (SC) and CNT/SC did not affect cell morphology, proliferation, or growth. These data indicate that SC is an environmentally friendly surfactant for the purification and dispersion of SWCNTs. Epifluorescence microscopy analysis of CNT/DNA conjugates revealed distribution in the cytoplasm of cells and did not show adverse effects on cell morphology, proliferation, or viability during a 72-h incubation. These observations suggest that the SWCNTs could be used as non-viral vectors for diagnostic and therapeutic molecules across the blood–brain barrier to the brain and the central nervous system.
Keywords: Carbon nanotubes, Surfactants, Cytotoxicity, Astrocytoma cells, Blood–brain barrier, Brain tumors, Central nervous system, Gene therapy, Non-viral gene vector
Introduction
In recent years, increasing attention is being directed to the structure, maintenance, and pathological disturbance of the blood–brain barrier (BBB), particularly with regard to enlarging a conceptual understanding of the signaling pathways that exist between and among the constituent cells of the BBB (i.e., endothelial cells, astrocytes, perivascular cells, and pericytes) [1]. A tight BBB can effectively protect the brain from many common bacterial and selected, non-tissue specific viral infections, but can hinder also the delivery of many effective diagnostic and therapeutic agents to the brain. Defeating this latter capability of the BBB has been a particular interest of the pharmaceutical industry, especially with regard to delivery of successful chemotherapy against central nervous system (CNS) tumors and other CNS neuropathologies [2]. Recently, an increasing number of observations have demonstrated that nanoscale materials can be used as non-viral vectors to deliver therapeutic drugs and other small molecules across the plasma membrane [3] or putatively across the BBB [4-7]. The important implication of these studies is this: when researchers or workers in the manufacturing sector handle nanoscale materials, these nanomaterials may not only remain on the skin and be inhaled into the lungs, they could also be transported to the CNS. Therefore, a critical evaluation of the potential cytotoxicity of nanoscale materials on the brain must be executed before we can safely use nanomaterials as drug vectors or in the manufacture of nanoscale electronics and optoelectronic devices.
Carbon nanotubes, especially single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), are among the most promising nanoscale materials that have a broad range of applications, including building blocks for future nanoscale devices and vectors for drug delivery. Since their structures were revealed by transmission electron microscopy by Iijima et al. in 1993 [8], SWCNTs have been extensively investigated as building blocks for nanoscale electronics, such as field effect transistors (FET) [9,10], interconnects [11], and electron emitters [12]. In addition, a number of in vivo and in vitro experiments showed that SWCNTs can effectively deliver drugs, antibodies, and other biologically active molecules into cells and tissues [13,14]. In order to be useful for these promising applications, SWCNTs need to be purified and dispersed into individual nanotubes since synthesized nanotubes occur in the form of bundles with accompanying impurities such as metal catalyst particles and amorphous carbon debris. One method to do this is by surfactant stabilization of the hydrophobic nanotube surfaces, which overcomes the van der Waals forces among the nanotubes and results in suspensions of individual SWCNTs. Several surfactants, such as sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) [15,16], sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS) [16-19], and sodium cholate (SC) [20], have been demonstrated to efficiently disperse bundled nanotubes into aqueous suspensions of individual nanotubes. It is critical to understand the toxicity of the nanotube/surfactant conjugates since these reagents are increasingly being used in manufacturing industries and research laboratories. To our knowledge, there has been no systematic study concerning cytotoxicity of SWCNTs, especially carbon nanotube conjugates with the extensively used SDS, SDBS, and SC surfactants, on the brain and the CNS. In the brain, astrocytes serve important roles in the BBB [1] and their functional repertoire keeps expanding. For example, astrocytes are involved in regulating endothelial tight junctions [21], mediating cortical vasodilation during neural activity [22], and propagating intercellular Ca2+ signaling waves between astrocyte networks and distant neurons [23]. For this study exploring the cytotoxic effects of different surfactants conjugated to SWCNTs on the brain, we selected 1321N1 human astrocytoma cells because they model an important cell constituent of the BBB, and they avoid the difficulties with establishing and maintaining primary astrocyte cultures.
Recently, we utilized the CellTiter 96 Aqueous One Solution (Promega) assay to study quantitatively the cytotoxicity of SWCNT conjugates with SC, SDS, SDBS, and single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) molecules on 1321N1 human astrocytoma cells [24]. Briefly, the toxicity of carbon nanotube conjugates was mainly controlled by the surfactant molecules attached to the nanotube surfaces. The conjugates of SWCNTs with SDS and SDBS were toxic to human astrocytoma cells, yet the nanotubes alone and the nanotube conjugates with SC and ssDNA did not generate obvious toxic responses. Since a cell viability or cytotoxicity assay requires at least 10 min to several hours of incubation to generate a measurable signal (1–2 h for the CellTiter 96 Aqueous One Solution), there could be some interactions of the nanotubes as well as their conjugates with the assay components. Consequently, we report here an attempt to assess the cytotoxicity of SWCNT conjugates for human astrocytoma cells by extending our previous observations to the sub-10 min reaction time, by direct observation with phase contrast light microscopy, and to confirm penetration and localization of an SWCNT conjugate (ssDNA labeled with Cy5 fluorochrome) in astrocytoma cell cytoplasm.
Materials and Methods
Preparation of SWCNT Conjugates
To prepare an aqueous SWCNT solution, 1 mg of nanotube powder (BuckyUSA Company) was dispersed in 1 mL of 1 wt% surfactant (SDS, SDBS, or SC) or Cy5-labeled single-stranded DNA [(GT)15, 1 mg/mL] solution. The suspension was sonicated (Branson Ultrasonic, 130 W) for 60 min and centrifuged (Eppendorf 5415R) at 16,000g for 60 min. After centrifugation, the supernatant, containing individual SWCNTs, was decanted. The precipitates, which contained catalyst particles, bundled nanotubes, and amorphous carbon debris, were discarded, and the nanotube concentration was determined by UV–Vis spectrophotometer.
Cell Culture and Microscopy
Human 1321N1 astrocytoma cells were maintained and assayed in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin, and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2incubator.
To assess cell morphology over an exposure time-course, 1,000 cells/well (estimated by a hemocytometer) were seeded in 100 μL/well of culture medium in 96-well culture plates and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2incubator for 24 h to allow the cells to settle and adhere to the wells. After the cells were established, 5.0 μL of 1% surfactant alone or nanotube/surfactant solution was added to selected wells in triplicate. Observation of morphological changes was conducted under ambient atmosphere at room temperature (22–24 °C) using an Olympus IX70 inverted microscope equipped with phase contrast optics.
For epifluorescence microscopy experiments, 2,000 cells/well in 500 μL/well of culture medium were seeded onto 11-mm glass coverslips in 24-well culture plates with 10.0 μL of CNT/DNA conjugate solution added to the wells. After a 72-h incubation, the cells were washed three times with standard phosphate-buffered saline, fixed with 4.0% paraformaldedyde for 5 min, counterstained with 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), and mounted on glass slides with Immunomount. Fixed cells were observed using an Olympus BX60 epifluorescence microscope equipped with a Retigia EX CCD camera. Images were acquired and processed with ImagePro Plus (Media Cybernetics) software.
Results and Discussion
Cytotoxicity of SWCNT Conjugates with Different Surfactants
The morphology of human astrocytoma cells exposed to the SWCNT/surfactant conjugates, CNT/SC, CNT/SDBS, or CNT/SDS, was similar to the cellular morphology demonstrated by exposure to the corresponding surfactant solution cargoes SC, SDBS, or SDS, respectively (Fig. 1). Without the introduction of any surfactants or surfactant/nanotube conjugates, control cells exhibit normal morphology and growth even under ambient atmosphere at room temperature for several hours (Fig. 1a, taken at 1 h of incubation under ambient atmosphere). Cells exposed to DNA, SC, and CNT/SC (Fig. 1b–d) demonstrate normal cell morphology when compared to the control conditions (Fig. 1a). Cells undergoing mitosis are indicated by arrows. Phase contrast images in Fig. 1suggest that SC and the nanotube conjugates with DNA and SC had no effect on proliferation or viability of human astrocytoma cells within 60 min.
Figure 1.
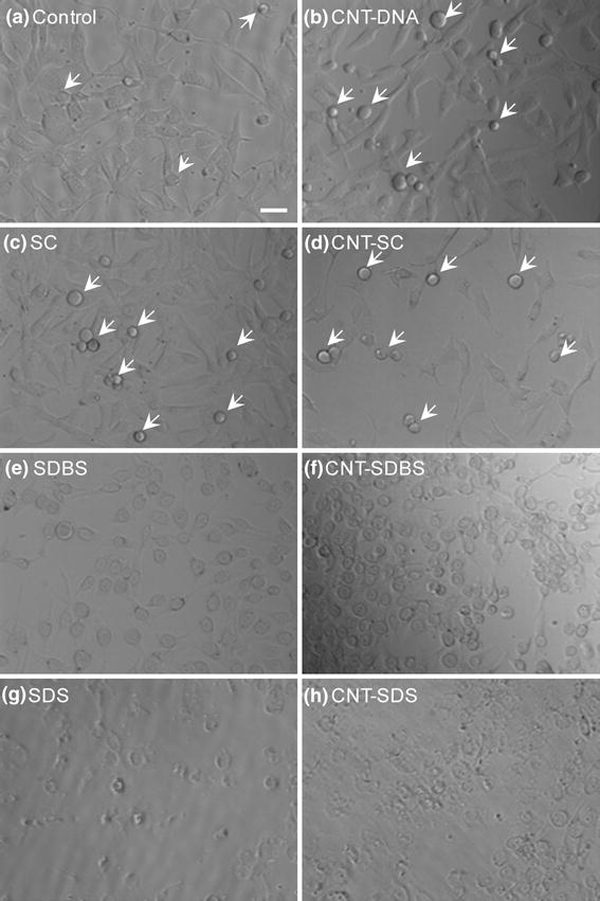
Digital phase contrast images of human astrocytoma cells exposed to surfactants or nanotube/surfactant conjugate solutions under ambient atmosphere at room temperature:acontrol, 60 min;bCNT/DNA, 60 min;cSC, 60 min;dCNT/SC, 60 min;eSDBS, 30 min;fCNT/SDBS, 30 min;gSDS, 30 min; andhCNT/SDS, 30 min. The concentrations of surfactants (b–h) and the SWCNTs (b,d,f, andh) were 0.5 mg/mL and 2 μg/mL, respectively.Arrowsindicate proliferating cells. All images were acquired at 200× magnification directly from the wells.Scale bar: 100 μm
In contrast, cells exposed to SDBS, CNT/SDBS, SDS, and CNT/SDS demonstrate irregular cell morphology at the 30 min time point, and no mitotic cells were observed. Cells exposed to SDBS (Fig. 1e) and CNT/SDBS (Fig. 1f) for 30 min show a distinct spherical morphology with cytoplasmic processes apparently retracted compared to untreated or SC-exposed cell morphology. Cells exposed to SDS (Fig. 1g) and CNT/SDS (Fig. 1h) for 30 min exhibit a similar spherical morphology with cellular debris visible in the medium. The phase contrast images in Fig. 1suggest that SDBS and SDS and their nanotube conjugates adversely affected cell morphology and growth within 30 min of exposure.
The anionic surfactants SC, SDBS, and SDS exhibited different influences on cell morphology and viability. This indicates that the toxicity of nanotube/surfactant conjugates was controlled by the surfactant molecules attached on the nanotube surface, but was not related to their anionic characteristics. The SC molecules alone had no effect on cell morphology or growth; apparently, the conjugates of CNT/SC are not toxic to the cells. Human astrocytoma cells did demonstrate a toxic response to conjugates of CNT/SDBS and CNT/SDS because both SDBS and SDS are toxic to the cells. Preliminary observations indicate that SDS (Fig. 1g, h) may be more toxic to the astrocytoma cells than SDBS (Fig. 1e, f) since the phase contrast observations demonstrate cellular debris, possibly indicating cell lysis, at 30 min exposure.
Time-Course Morphological Changes Induced by an Exposure to CNT/SDS Conjugates
CNT/SDS conjugates affected cell viability within 30 min of exposure (Fig. 1h). To further understand the earliest appearance of morphological changes induced by nanotube/conjugate exposure, a time-course study of changes was recorded starting at time 0 min, at which time the CNT/SDS conjugates were introduced into the growth medium (Fig. 2a). Cells were observed at 2 min after introduction of the CNT/SDS conjugates, at which time a few cells demonstrated retraction of their cytoplasmic processes (Fig. 2b). After 5 min, a majority of cells assumed a nascent spherical morphology with accompanying process retraction (Fig. 2c). At 10 min, virtually all cells demonstrated reduced contact with the substratum and assumption of a spherical morphology (Fig. 2d). Observations at 25 and 75 min revealed cellular debris in the culture medium (Fig. 2e).
Figure 2.
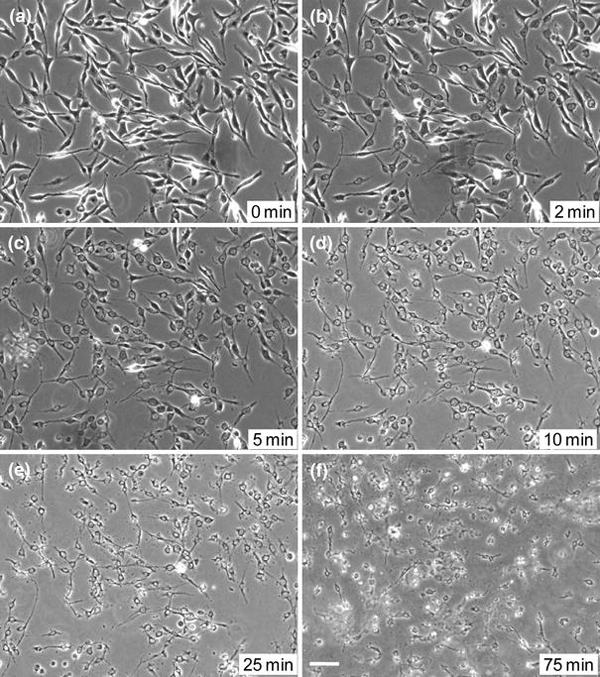
Phase contrast images of a time-course of morphological events observed in astrocytoma cells after exposure to 0.5 mg/mL CNT/SDS conjugate solutions fora0 min;b2 min;c5 min;d10 min;e25 min; andf75 min. All images were acquired at 100× magnification.Scale bar: 200 μm
The time-course analysis shows that exposure to CNT/SDS conjugates rapidly (within 2 min) and distinctly affected cell morphology. Observations included potential loss of membrane integrity, retraction of cytoplasmic processes, reduced cell-to-substratum adhesion, putative cell shrinkage, and generation of cellular debris. Astrocytoma cells exposed to CNT/SDS conjugates demonstrate characteristic morphological changes that are reminiscent of apoptosis [25].
There are alternative interpretations regarding the toxicity of carbon nanotubes for both in vivo and in vitro generated data. Some experimental results indicate that introduction of carbon nanotubes into the growth medium does not affect cell proliferation and viability [26-35], yet other experiments demonstrate that structural variants of carbon nanotubes do affect cell proliferation [36-39]. Our time-course analysis (Figs. 12) demonstrates that the cytotoxicity of the tested nanotube conjugates was controlled by the surfactants attached to the nanotube surface, and nanotubes alone do not affect cell proliferation and growth.
Cellular Distribution of CNT/DNA Conjugates
The nanotube conjugates with SC and ssDNA did not affect cell proliferation and growth. These observations could be attributed to the conjugates remaining in the extracellular environment and not being taken into astrocytoma cell cytoplasm. In order to explore whether the nanotube conjugates can enter the cells or not, as well as cellular distributions of the conjugates if they enter the cells, we utilized epifluorescence microscopy to initiate the exploration, and the Cy5 fluorochrome attached to the CNT/DNA conjugate was used to monitor the uptake of these nanotube conjugates.
When the cells were exposed to the CNT/DNA conjugates for a time period less than 24 h, the fluorescence signal was quite weak. In order to obtain a strong signal and to investigate cytotoxicity of the nanotube conjugates for a longer time period, adhering astrocytoma cells were exposed to CNT/DNA-Cy5 conjugates for 72 h. After the 72-h incubation, the cells exhibit normal morphology and proliferation (Fig. 3a). The CNT/DNA-Cy5 conjugates were observed within the cytoplasm (Fig. 3b–d), indicating that the conjugates were effectively transported into the astrocytoma cells. Infrequently, fluorescence was detected in a punctate pattern within the cell cytoplasm, with fluorescence signal detected over the nuclear region of some cells (Fig. 3d). The question about the entry of the labeled conjugate into, or exclusion from, the nuclear compartments could not be resolved from these images at this time. No fluorescence was detected from untreated control cells (data not shown). Some cytoplasmic regions demonstrate more intense fluorescence; this focal intensity may represent clusters or bundles of the conjugates. The fluorescence microscopy analysis demonstrates that CNT/DNA-Cy5 conjugates were distributed within the cytoplasm and did not affect cell morphology. These results suggest that SWCNTs could be used as vectors for diagnostic and imaging contrast agent molecules into the brain and the CNS across the blood–brain barrier since carbon nanotubes can convey the ssDNA molecules into the cells, and their conjugates did not affect the proliferation and growth of astrocytoma cells. The next step is to investigate how to target delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents and how to release agent molecules inside the cells.
Figure 3.
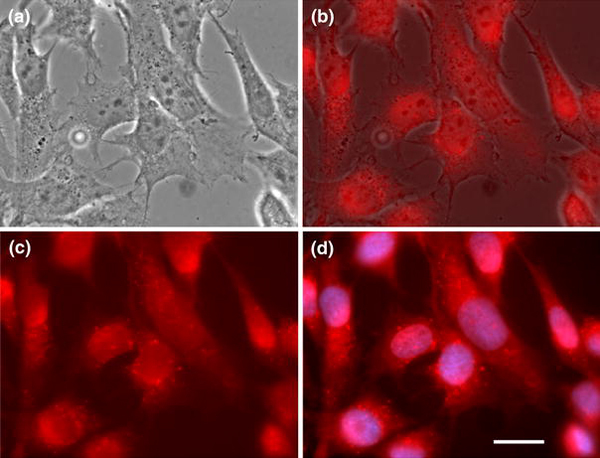
Epifluorescence microscopy of human astrocytoma cells exposed to CNT/DNA-Cy5 conjugates:aphase contrast image;bmerged image of the phase contrast and Cy5 images;cCNT/DNA-Cy5 (red) fluorescence image; anddmerged image of the CNT/DNA-Cy5 and DAPI-stained cells (blue). The concentration of the CNT/DNA-Cy5 was 2 μg/mL. Images demonstrate that nanotube/DNA conjugates (red) can enter astrocytoma cells and were localized in the cytoplasm. Uptake of the nanotube/DNA conjugate did not affect cell proliferation and viability. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). All images were acquired at 1,000× magnification.Scale bar: 50 μm
Conclusions
Time-course microscopy analysis demonstrates that the cytotoxicity of nanotube/surfactant conjugates is related to the toxicity of the surfactant molecules attached on the nanotube surfaces. Human astrocytoma cells, exposed to SDBS or SDS in the growth medium, experienced morphological changes including potential loss of plasma membrane integrity, altered attachment, putative cell shrinkage, and generation of cellular debris. Cells exposed to 0.5-mg/mL CNT/SDS conjugates exhibited nascent morphological alterations within 2 min. Our data indicate that SC could be used as an environmentally friendly reagent for the dispersion and purification of SWCNTs. Epifluorescence microscopy analysis of CNT/DNA conjugates indicates that these conjugates were efficiently delivered into cells and distributed within the cytoplasm, although the question of CNT conjugate penetration into nuclei remains unresolved at this time. The precise mechanism for uptake of SWCNTs and SWCNT conjugates into the cytoplasm of any cell type also remains unelucidated. Since toxicity questions exist for the surfactants used to disperse other nanoscale materials [40], the experimental approach outlined in our study can be used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of other nanoscale particles as well. SWCNTs could be developed as non-viral vectors for diagnostic and therapeutic molecules into the brain and the CNS across the blood–brain barrier since their conjugates with ssDNA do not affect the proliferation and growth of astrocytoma cells.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by a Faculty Research Grant and a Summer Faculty Fellowship from Missouri State University. The authors would like to thank Dr. Richard Garrad for providing the 1321N1 human astrocytoma cell line and for providing suggestions and expertise regarding culture methods and Hannah E. Gann and Jenna L. Chase for their involvement in some of the experiments. Acknowledgment is also made to the Donors of the American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund (47532-GB10) for partial support of this research.
References
- Wolburg H, Noell S, Mack A, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fallier-Becker P. Cell Tissue Res. 2009. p. 75. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Deeken JF, Löscher W. Clin. 2007. p. 1663. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXivV2gtrg%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Murakami T, Ajima K, Miyawaki J, Yudasaka M, Iijima S, Shiba K. Mol. 2004. p. 399. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXnslGqsbs%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Schroeder U, Sommerfeld P, Ulrich S, Sabel BA. J. 1998. p. 1305. COI number [1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlsV2jsrc%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kreuter J. Adv. 2001. p. 65. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhvVajsrk%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Faraji AH, Wipf P. Bioorg. 2009. p. 2950. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1MXksVWlur0%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh R, Lillard JW. Exp. 2009. p. 215. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1MXlslWhtrs%3D] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Iijima S, Ichihashi T. Nature. 1993. p. 603. COI number [1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXltVOrs7o%3D]; Bibcode number [1993Natur.363..603I] [DOI]
- Tans SJ, Verschueren ARM, Dekker C. Nature. 1998. p. 49. COI number [1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjt1aitb8%3D]; Bibcode number [1998Natur.393...49T] [DOI]
- Martel R, Schmidt T, Shea HR, Hertel T, Avouris Ph. Appl. 1998. p. 2447. COI number [1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXms1eqsrc%3D]; Bibcode number [1998ApPhL..73.2447M] [DOI]
- Dong LF, Youkey S, Bush J, Jiao J, Dubin VM, Chebiam RV. J. 2007. p. 024320. Bibcode number [2007JAP...101b4320D] [DOI]
- Dong LF, Jiao J, Pan CC, Tuggle DW. Appl. Phys. A. 2004. p. 9. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXot1erurg%3D]; Bibcode number [2004ApPhA..78....9D] [DOI]
- Kam NW, Liu Z, Dai HJ. Angew. 2005. p. 1. [DOI]
- Lacerda L, Raffa S, Prato M, Bianco A, Kostarelos K. Nanotoday. 2007. p. 38.
- Islam MF, Rojas E, Bergey DM, Johnson AT, Yodh AG. Nano Lett. 2003. p. 269. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjsFKrug%3D%3D]; Bibcode number [2003NanoL...3..269I] [DOI]
- Moore VC, Strano MS, Haroz EH, Hauge RH, Smalley RE. Nano Lett. 2003. p. 1379. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnt1OnsrY%3D]; Bibcode number [2003NanoL...3.1379M] [DOI]
- O’Connell MJ, Bachilo SM, Huffman CB, Moore VC, Strano MS, Haroz EH, Rialon KL, Boul PJ, Noon WH, Kittrell C, Ma J, Hauge RH, Weisman RB, Smalley RE. Science. 2002. p. 593. Bibcode number [2002Sci...297..593O] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Richard C, Balavoine E, Schultz P, Ebbesen TW, Mioskowski C. Science. 2003. p. 775. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjtlSkt78%3D]; Bibcode number [2003Sci...300..775R] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dong LF, Chirayos V, Bush J, Jiao J, Dubin VM, Chebiam RV, Ono Y, Conley JF, Ulrich BD. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2005. p. 13148. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXlt1Shsbk%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Arnold MS, Green AA, Hulvat JF, Stupp SI, Hersam MC. Nat. 2006. p. 60. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XhtFCisrvF]; Bibcode number [2006NatNa...1...60A] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L, Hansson E. Nat. 2006. p. 41. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtlaktbjP] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Takano T, Tian G-F, Peng W, Lou N, Libionka W, Han X, Nedergaard M. Nat. 2006. p. 260. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XotVegtw%3D%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Araque A, Carmignoto G, Haydon PG. Ann. 2001. p. 795. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtFKmuro%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dong LF, Joseph KL, Witkowski CM, Craig MM. Nanotechnology. 2008. p. 255702. Bibcode number [2008Nanot..19y5702D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lawen A. BioEssays. 2003. p. 888. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXns1Sis7s%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kam NWS, Dai HJ. J. 2005. p. 6021. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXislChtL4%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liu Z, Winters M, Holodniy M, Dai HJ. Angew. 2007. p. 2023. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXjsFyntLo%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kam NWS, Jessop TC, Wender PA, Dai HJ. J. 2004. p. 6850. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjvVCltbY%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kam NW, Liu Z, Dai HJ. Angew. 2006. p. 577. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XpvVequg%3D%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cherukuri P, Bachilo SM, Litovsky SH, Weisman RB. J. 2004. p. 15638. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXpsFKkurc%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lu Q, Moore JM, Huang G, Mount AS, Rao AM, Larcom LL, Ke PC. Nano Lett. 2004. p. 2473. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXovFKrt78%3D]; Bibcode number [2004NanoL...4.2473L] [DOI]
- Singh R, Pantarotto D, Lacerda L, Pastorin G, Klumpp C, Prato M, Bianco A, Kostarelos K. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006. p. 3357. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XksF2ktbY%3D]; Bibcode number [2006PNAS..103.3357S] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Liu Z, Cai W, He L, Nakayama N, Chen K, Sun X, Chen X, Dai HJ. Nat. 2007. p. 47. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXhtVWqtbc%3D]; Bibcode number [2007NatNa...2...47L] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tejral G, Panyala NR, Havel J. J. 2009. p. 1. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1MXms1Ogsb8%3D]
- Koyama S, Kim YA, Hayashi T, Takeuchi K, Fujii C, Kuroiwa N, Koyama H, Tsukahara T, Endo M. Carbon. 2009. p. 1365. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1MXjt1Sluro%3D] [DOI]
- Jia G, Wang HF, Yan L, Wang X, Pei RJ, Yan T, Zhao YL, Guo XB. Environ. 2005. p. 1378. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXht1Grtw%3D%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kagan VE, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Konduru NV, Potapovich AI, Osipov AN, Kisin ER, Schwegler-Berry D, Mercer R, Castranova V, Shvedova A. Toxicol. 2006. p. 88. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Warheit DB, Laurence BR, Reed KL, Roach DH, Reynolds GAM, Webb TR. Toxicol. 2004. p. 117. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXnslKl] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lam CW, James JT, McCluskey R, Hunter RL. Toxicol. 2004. p. 126. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXnslKk] [DOI] [PubMed]
- Colvin VL. Nat. 2003. p. 1166. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXns1Cltr8%3D] [DOI] [PubMed]


