Abstract
Excessive release of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) during loading and/or injury of the cartilage matrix may contribute to the onset or progression of osteoarthritis. This pathological role may be related to the ability of bFGF to decrease proteoglycan synthesis and to antagonize the activity of anabolic growth factors in cartilage such as insulin-like growth factor-1 and bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7 or OP-1). Matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13), a catabolic cartilage-degrading enzyme, is dramatically up-regulated by inflammatory cytokines or by fibronectin fragments in articular chondrocytes. In this study, we investigated MMP-13 production by bFGF using human articular chondrocytes. Endogenous concentration of bFGF in synovial fluids collected from arthritis patients and asymptomatic subjects showed a good linear correlation with the endogenous levels of MMP-13. bFGF stimulation of MMP-13 was mediated at the transcriptional level and, at least in part, by stimulation of interleukin-1 production. Also, our findings suggest that bFGF stimulation of MMP-13 required the activation of multiple MAPKs (ERK, p38, and JNK) by bFGF, and more importantly, bFGF activation of protein kinase C (PKC) δ played a key role in the MMP-13 stimulation. Indeed, PKCδ is the only isoform associated with MMP-13 stimulation among the PKC isoforms tested. PKCδ controls the bFGF response by regulating multiple MAPK pathways. Our results suggest that PKCδ activation is a principal rate-limiting event in the bFGF-dependent stimulation of MMP-13 in human adult articular chondrocytes. We propose that deregulation of cross-talk between MAPK and PKCδ signaling may contribute to the etiology of osteoarthritis in human patients.
Osteoarthritis (OA)2 involves the progressive destruction of the cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) by a pathological imbalance in the normal metabolic functions of articular chondrocytes. Under normal conditions, chondrocytes maintain a dynamic equilibrium between synthesis and degradation of ECM components. Although the causative events in the etiology of OA remain to be clearly defined, OA is characterized by a disruption of matrix equilibrium leading to progressive loss of cartilage tissue and clonal expansion of cells in the depleted regions. In the early stages of OA, cells respond with a transient induction of matrix synthesis (e.g. increases in the expression and/or protein secretion of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7 or OP-1)). This de novo ECM synthesis cannot overcome the concurrent catabolic processes (1, 2) that involve the excess production of matrix-degrading enzymes, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), aggrecanases, and other proteinases by chondrocytes. The resulting degradation of cartilage ECM may exacerbate the imbalance by enhancing the local activity of systemic regulatory factors, including growth factors and cytokines.
Matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13 or collagenase-3) is the most potent enzyme that degrades type II collagen (the principal component of articular cartilage) and is normally expressed during cartilage development and ECM remodeling. MMP-13 is highly expressed in several pathological contexts, including OA (3), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (4), and invasive cancer (5). In rabbit or rodent injury models of OA, MMP-13 expression was stimulated by injury and correlated with cartilage degradation (6, 7). Clinical studies in human patients have shown that MMP-13 is not expressed in normal adult cartilage but is highly expressed in OA at sites of cartilage degradation (8). Recently, transgenic mouse studies demonstrated that cartilage-targeted overexpression of activated MMP-13 alone is sufficient to cause the cartilage degradation characteristic of OA (9). However, despite evidence supporting a central role of MMP-13 in OA pathogenesis, the factors regulating MMP-13 production and the critical process governing stimulation of chondrocyte MMP-13 remain to be explored.
The important mitogenic roles of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF or FGF-2) in regulating cell proliferation in the growth plate and articular cartilage are well established. In contrast, bFGF appears to play a complex role in the synthesis and degradation of the ECM in adult articular cartilage. Evidence suggests that bFGF is pathologically associated with joint destruction (10, 11) and stimulation of MMP-13 (12). Chondrocyte proliferation resulting in cluster formation is a histological hallmark of OA cartilage. The mechanism that initiates cluster formation in OA cartilage is unknown, but it may be a consequence of cellular alterations that reduce the ability of cartilage to effectively establish normal repair tissue. Previous results from our laboratories (13) and others (14), using a three-dimensional cell culture system, suggest that bFGF plays a role in the formation of cell clusters similar to those seen in OA cartilage. Basic FGF also significantly reduces proteoglycan synthesis and antagonizes the biological effects mediated by cartilage anabolic growth factors such as BMP7 and IGF-1 (13). Antagonistic effects of bFGF on the cellular response to BMP/TGFβ in articular chondrocytes (15) and osteoblasts (16) have been attributed to the interruption of the Smad-mediated signaling.
Multiple factors operate in concert to control the overall metabolism of cartilage in vivo. Basic FGF is one of these factors. Joint damage by various causes such as obesity, mechanical joint injury, or simply aging may change the structure of cartilage (17). These structural changes alter the articular cartilage homeostasis (18) and may modulate chondrocyte-mediated gene expression, including growth factors and cytokines that may have impact on chondrocyte metabolism. Upon joint damage, continued use is likely to accelerate the pathological process, thus emphasizing the importance of prevention and early management of joint trauma. One of the factors that immediately responds to cartilage injury is bFGF (19). Basic FGF is produced by chondrocytes (20), stored in the ECM, and released from the cartilage matrix upon cartilage injury (19, 21). Thus, bFGF has a potential pathophysiological role in the development of arthritis where it may serve as link between altered cell signaling and mechanical damage to cartilage.
Basic FGF activates multiple signal transduction pathways, including mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), in various cell types. The MAPKs activate transcription factors by phosphorylation, which in turn regulates the expression of a broad spectrum of genes that modify cellular functions. Recent evidence suggests that mechanical injury of cartilage is associated with the release of bFGF from ECM (19). The released bFGF is thought to mediate an immediate response in articular cartilage by stimulating and sustaining ERK activation. Basic FGF-activated ERK1/2 results in the translocation of phosphorylated ERK1/2 into the nucleus followed by binding of Elk-1 to its response element in a number of target genes such as c-fos, which represents a critical transcriptional suppressor of ECM components in rat lung fibroblasts (22). More recently, Daouti et al. (23) reported the up-regulation of bFGF and its receptor in cells from osteoarthritic tissue compared with normal tissue. In this study, we addressed the molecular mechanisms and the signaling events that control MMP-13 production in response to bFGF signaling associated with human adult articular cartilage homeostasis.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Chondrocyte Isolation and Culture Conditions
Normal human ankle cartilage was obtained from tissue donors through the Gift of Hope Organ and Tissue Donor Network. Each donor specimen was graded for gross degenerative changes based on a modified version of the 5-point scale of Collins (24). Chondrocytes were isolated by enzymatic digestion of ankle articular cartilage (grade 0 or 1, which has no sign of cartilage degeneration) using Pronase followed by overnight digestion with collagenase-P as described previously (13, 25, 26). Isolated cells were resuspended in media at 2 × 106 per ml and plated on to 12-well plates at 1 ml/well. Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium/F-12 containing 10% fetal bovine serum and antibiotics (complete media) for 5 days before the experiments.
Chondrocyte Stimulation and Immunoblotting
Cells were serum-starved by changing media to serum-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium/F-12 with antibiotics for 1 day. For inhibitor studies, cells were preincubated with individual pathway-specific chemical inhibitors for 30 min before stimulation with bFGF or IL-1β. Experiments were terminated with removal of media and/or cell lysate preparation. The conditioned media were stored at 4 °C with 0.1% NaN3 and used for the experiments within 5 days. Cell lysates were prepared using modified cell lysis RIPA buffer: 20 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 1% Nonidet P-40, 0.25% deoxycholate, 2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM glycerol phosphate, 1 mM NaVO4, with 2 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (Sigma). Total protein concentrations of both media and cell lysates were determined by a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay (Pierce). An equal amount of protein was resolved by 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and was transferred to nitrocellulose membrane for immunoblot analysis as described previously (25, 26). Immunoreactivity was visualized using the ECL system (Amersham Biosciences) and the Signal Visual Enhancer system (Pierce), which magnifies the signal.
Reagents and Plasmids Constructs
Total and phospho-specific PKC isoforms antibodies, except anti-phospho-PKCε (Upstate), were purchased from BD Transduction Laboratories and Cell Signaling, respectively. Phospho-specific PKCε antibody was purchased from Upstate and Calbiochem. Total and phospho-specific PYK2 (Thr-402) and phospho-FAK were purchased from Upstate and Chemicon. Anti-MMP-13 and β-actin antibodies were purchased from R&D Systems and Abcam, respectively. Optimal doses were obtained for the chemical and peptide inhibitors used in our studies to ensure specific effects on signaling pathways operative in human adult articular chondrocytes. These inhibitors include bisindolylmaleimide I (BIM) (10 μM), rottlerin (PKCδ-specific inhibitor, 4 μM), and GÖ6976 (selective inhibitor of Ca2+-dependent PKC isozymes such as PKCα/β, 5 nM), PKC-ε translocation inhibitor peptide and a scrambled peptide (negative control) for PKC signaling studies. To study Raf-MAPK signaling cascades, we used the following agents: Raf1 kinase peptide inhibitor (20 μM) as an inhibitor of Raf, PD098059 (20 μM), which blocks activation of MEK1/2, SB203580 (10 μM) for p38, and SP600125 (20 μM) for JNK. All chemicals were purchased from Calbiochem. Basic FGF and IL-1β were kindly provided by the NCI, National Institutes of Health, and Amgen, respectively. MMP-13 promoter-reporter constructs were described previously (25, 26). Expression cDNA vectors for MEKK and pAP-1 Luc reporter vector were purchased from Clontech and Stratagene, respectively. Dominant negative forms of individual MAPK expression vectors (ERK-DN, p38-DN, and JNK-DN) were kindly provided by Dr. Ralf Janknecht (Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN).
Adenovirus Infection
For adenovirus infection, primary human chondrocytes were plated at a density of 2 × 106 cells per well in 12-well plates and incubated for >16 h in serum-free media by modifying our previous methodology (26–28) Briefly, cells were infected with a replication-defective adenovirus encoding PKC-δ wild type, PKC-δ DN, or dominant negative forms of other PKC isoforms (PKCα and PKCε) at a multiplicity of infection of 200. Adenovirus encoding GFP was infected in parallel as a control at a multiplicity of infection of 200. Four hours after the transduction, the cells were fed with complete media and incubated for 6 h at 37 °C in a humidified environment containing 5% CO2. The cells were then treated with bFGF at the concentration of 100 ng/ml in serum-free media followed by further incubation for 24 h.
Synovial Fluids
Normal synovial fluid was aspirated within 24 h of death from the knee joints of human organ donors (courtesy of the Gift of Hope Organ and Tissue Donor Network, Elmhurst, IL). Synovial fluid samples from organ donors with no documented history of joint diseases were used as controls for this study. With the approval of the Institutional Review Board for Human Investigations, synovial fluid was also collected from consenting OA and RA patients who were undergoing diagnostic or therapeutic arthrocentesis as part of their evaluation and therapy at the Section of Rheumatology, Rush University Medical Center. The patient cohort covered a broad spectrum of ages and disease severities for both OA and RA. OA was defined according to the classification criteria disseminated by the American College of Rheumatology (29). Samples were centrifuged to remove cells and cell debris, divided into aliquots, and immediately stored at −80 °C until the assay was performed.
Measurement of Endogenous bFGF and MMP-13 Concentrations
We used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with a sensitivity of <7 and 250 pg/ml for measuring endogenous concentrations of bFGF (BIOSOURCE International) and MMP-13 (R&D System), respectively, in synovial fluid samples according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, standard curves were generated in duplicate parallel to the preparation of mixtures containing 1 volume of standard diluent buffer (50 μl) and 1 volume of each sample of synovial fluid (50 μl). Multiple sample plates were then covered and incubated at room temperature for 2 h. Samples and standards were decanted, and the wells were washed four times with 400 μl of wash buffer. Biotinylated anti-bFGF or anti-MMP-13 (Biotin Conjugate) solution (100 μl) was pipetted into each well and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. After washing the wells again four times, 100 μl of streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase working solution was added to each well and incubated for 30 min at room temperature followed by the addition of stop solution. The absorbance of each well was read at 450 nm. A chromogen blank composed of 100 μl each of Stabilized Chromogen and Stop Solution was used to establish a zero base line for the plate reader. The bFGF or MMP-13 concentrations for samples were calculated from the standard curve.
Reverse Transcription and PCR
Reverse transcription (RT) was carried out with 500 ng of total cellular RNA using either real time or One-Step RT-PCR system (Invitrogen) following the instructions provided by the manufacturer. For all experiments, optimal conditions were determined by initially generating cycle number-dependent expression curves, and test reactions were performed in the linear range for the PCR amplification. The same amounts of total RNA or genomic DNA (25) were subjected to One-Step RT-PCR simultaneously to minimize experimental variation because of differences in amplification efficiency. The assessment for GAPDH was performed in parallel. The One-Step RT-PCR system was performed using 30 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s, 62 °C for 1 min, and 72 °C for 40 s in the presence of 50 pmol of sense and antisense primers. The primer sequences and the conditions for their use are summarized in Table 1. The resulting PCR products were resolved in 1.5% agarose gels and visualized by staining with ethidium bromide and UV transillumination. Integrated density values for test genes were normalized relative to GAPDH values to yield a semi-quantitative assessment. For real time PCR, the primer sets specific to human genes and optimized conditions were used to generate <200-bp coding regions, spanning two exons and an intron as we performed previously (30).
TABLE 1.
Primer sequence for semi-quantitative and real time RT-PCR
| Genes | Primer sequences (forward/reverse) (5′–3′) | Size | Annealing temperature | Ref./GenBank™ accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bp | °C | |||
| MMP-13 |
GGCTCCGAGAAATGCAGTCTTTCTT ATCAAATGGGTAGAAGTCGCCATGC |
337 | 64 |
25 NM_002427 |
| MMP-13 (real time) |
AAGGACCCTGGAGCACTCATGTTT TGGCATCAAGGGATAAGGAAGGGT |
178 | 62 | NM_002427 |
| bFGF |
GAG AAG AGC GAC CCT CAC A TAG CTT TCT GCC CAG GTC C |
276 | 62 | NM_002006 |
| IL-1β |
GAGCTCGCCAGTGAAATGATGGC CAAGCTTTTTTGCTGTGAGTCCCG |
387 | 58 |
25 NM_000576 |
| TNFα |
CTTCT CGAAC CCCGA GTGAC AAGCC TGTAG TGATC TCAGC GCTGA GTCGG TCACC CTTCT |
398 | 60 | NM_000594 |
| IL-6 |
GGATGCTTCCAATCTGGATTCAATGAG CGCAGAATGAGATGAGTTGTCATGTCC |
302 | 66 |
25 NM_000600 |
| IL-8 |
CGTGGCTCTCTTGGCAGCCTTCCTGAT TCAAAAACTTCTCCACAACCTTCTGCA |
270 | 68 |
25 NM_000584 |
| MCP-1 |
ATA GCA GCC ACC TTC ATT CC TTT CCC CAA GTC TCT GTA TCT |
480 | 55 | D29984 |
| GAPDH |
CTGAGAACGGGAAGCTTGTCATCA AGTTGTCATGGATGACCTTGGCCA |
318 | 58 | NM_002046 |
| GAPDH (real time) |
TCGACAGTCAGCCGCATCTTCTTT GCCCAATACGACCAAATCCGTTGA |
148 | 62 |
30 NM_002046 |
Transient Transfection by Nucleofection (Electroporation)
Nucleofection methods were optimized for use with human articular chondrocytes by minor modifications of the instructions for the Nucleofector™ kit (Amaxa Biosystems) as described previously (31, 32). The Renilla vector (pRL-TK) was co-transfected as an internal control, and the luciferase activity representing promoter activity was measured using the dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega) and a luminometer (Berthold). In samples containing combinations of plasmids (i.e. co-transfections with MEKK cDNA construct with MMP-13 promoter/luciferase reporter construct), we adjusted the total amount of DNA concentration to <5 μg per 100 μl of cell-nucleofector solution complex for the entire sets of experiments to minimize the toxic effect observed at higher DNA concentrations.
Immunohistochemistry
Full thickness cartilage slices from human ankle joints were cultured in 1.0 ml of Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium/F-12 containing 10% fetal bovine serum. Following a 2-day recovery period, the tissue explants were treated with or without bFGF (100 ng/ml) under serum-free conditions (mini-ITS). Following 9 days of incubation, the slices were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for overnight and embedded in paraffin, and 8 μM sections were prepared. The paraffin sections were deparaffinized and digested by chondroitinase ABC. The sections were then incubated with anti-MMP-13 antibody (mouse monoclonal, Cell Signaling) over-night after blocking endogenous peroxidase with 2% H2O2 in methanol and blocking nonspecific IgG binding with 10% goat serum. These antibodies were detected with horseradish peroxidase-labeled rabbit anti-goat IgG (1:20 dilution) and stained with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrachloride (FAST tablet set; Sigma).
Gel Shift Assay (Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays)
Gel shift assay was performed by using commercial AP-1 electrophoretic mobility shift assay kit (Panomics) for studying the formation of the specific nuclear DNA-AP-1 complex that represents AP-1 activation. Nuclear extracts prepared from human adult articular chondrocytes were incubated with the biotin-labeled double-stranded AP-1 consensus sequences (5′-CGCTTGATGACTCAGCCGGAA-3′). The mixture was separated on a nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel, and the shifted bands that correspond to the DNA-protein complexes were visualized by chemiluminescence imaging. Unlabeled double-stranded wild type oligonucleotides were used to determine the binding specificity of the assay.
Statistical Analyses
The statistical significance of results was determined by analysis of variance, using StatView 5.0 software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). Data interpretation was performed by statistical normalization as assessed with histograms, and a 0.05 significance level was used for all statistical tests.
RESULTS
Endogenous Levels of bFGF and MMP-13 Are Increased in Arthritic Patients
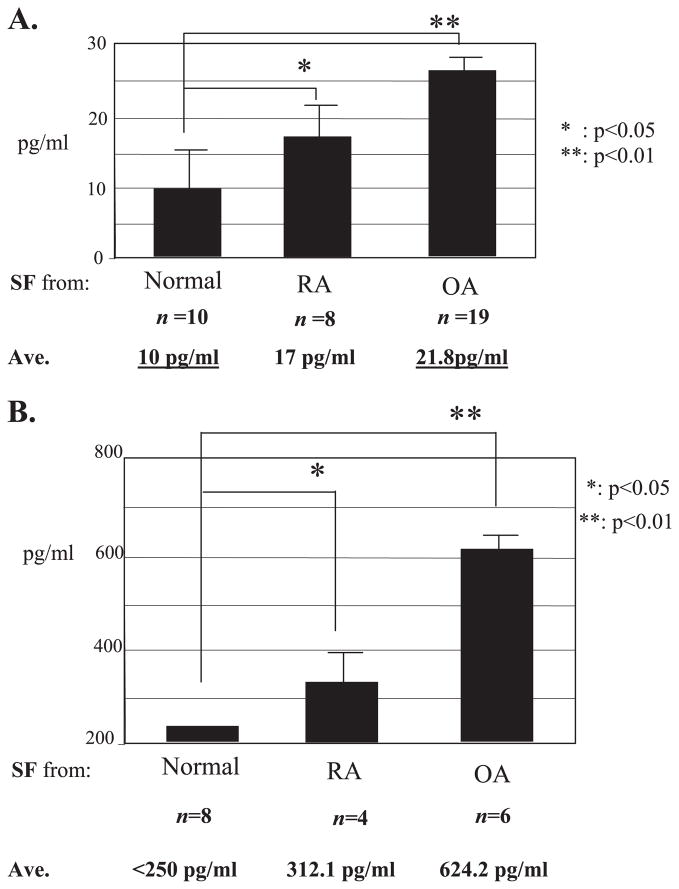
Evidence suggests that bFGF is pathologically associated with joint destruction and MMP-13 stimulation (10–12). We further addressed the links of bFGF signals to the pathogenesis of cartilage degeneration by measuring the level of bFGF in human synovial fluid collected from normal and OA patients. Initially, we used synovial fluid from RA patients as positive controls for our bFGF ELISAs based on the known increase observed in RA patients (33). Our data show that bFGF levels are clearly elevated (~2-fold) in the synovial fluids from OA patients compared with normal subjects. Surprisingly, the endogenous level of bFGF in OA samples was even higher than those levels in RA samples (Fig. 1A). The endogenous levels of MMP-13 were also increased in synovial fluids from RA and OA patients, concomitant with an increase in the levels of bFGF (Fig. 1B). These data reinforce the potential clinical relevance of bFGF and MMP-13 in adult articular cartilage homeostasis.
FIGURE 1. Endogenous concentrations of bFGF (A) and MMP-13 (B) in human synovial fluids.
The concentrations of bFGF and MMP-13 were measured by ELISA in synovial fluid samples collected from asymptomatic donors (Normal), from osteoarthritis (OA), and from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. The data are means ± S.E., and statistical significance was determined by analysis of variance.
Basic FGF Stimulates MMP-13 Expression in Human Adult Articular Chondrocytes
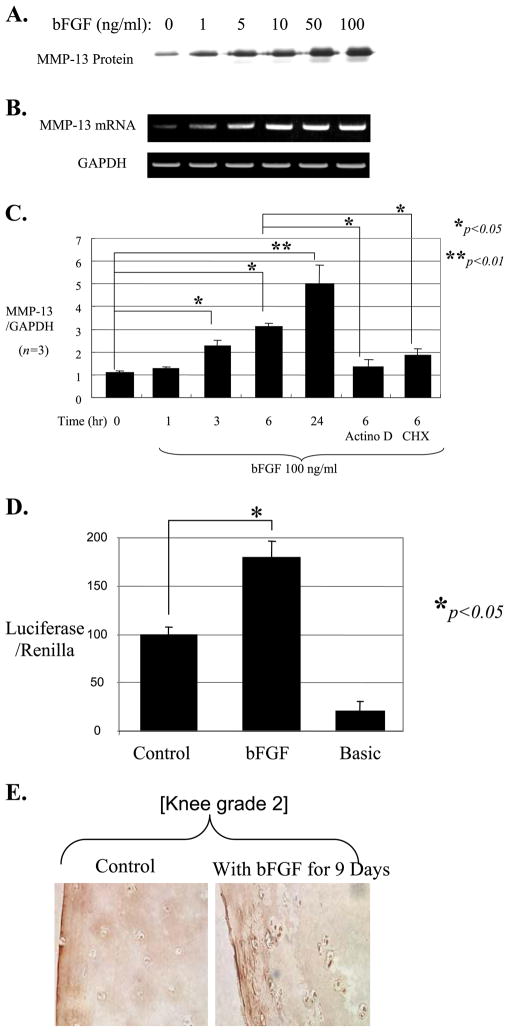
We tested whether bFGF stimulates MMP-13 using chondrocytes isolated from human adult articular cartilage. Treatment of cells in monolayer with bFGF significantly stimulated MMP-13 production, and the induction occurred in both mRNA and protein levels in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2, A and B). Increased mRNA levels of MMP-13 are evident within 3 h by real time RT-PCR after stimulation with bFGF in time course experiments, and this induction was blocked by either the transcriptional inhibitor actinomycin D or the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (Fig. 2C). Our results suggest that bFGF-modulated MMP-13 induction is direct, occurring mainly by transcriptional stimulation, and is dependent on de novo protein synthesis.
FIGURE 2. Basic FGF stimulates MMP-13 expression.
Human adult articular chondrocytes cultured in monolayer were serum-starved and then treated with bFGF at gradually increasing concentrations (0 –100 ng/ml). The conditioned media were collected after 24 h and used for immunoblotting for MMP-13 protein (A), and the cells were used for total RNA extraction to perform semi-quantitative RT-PCR (B). C, real time RT-PCR was performed using total RNA extracted from cells treated with bFGF (100 ng/ml) in a time course (1–24 h). Cells were also preincubated for 30 min with either the transcriptional inhibitor actinomycin D (Actino D, 5 μM) or the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX, 10 μM) prior to stimulation with bFGF for 6 h. The mRNA level of GAPDH was evaluated as an internal control for the mRNA level of MMP-13. D, −1600MMP-13 promoter-reporter construct was transiently transfected into human adult articular chondrocytes. The transfected cells were incubated in the presence or absence of bFGF (100 ng/ml) for an additional 24 h, and the luciferase activity representing MMP-13 promoter activity was measured. A Renilla vector was co-transfected as an internal control for normalization. The data represent four different donors measured in triplicate for each experiment. E, human cartilage explants were incubated in mini-ITS in the presence or absence of bFGF (100 ng/ml) for 9 days. Tissue sections were stained with an anti-MMP-13 antibody. The picture is representative of experiments performed with tissue from five different donors.
These results were further supported by transient transfection studies using primary human articular chondrocytes. A transfected full-length MMP-13 promoter-reporter construct (−1600 MMP-13) exhibited increased luciferase activity after stimulation with bFGF (Fig. 2D). The up-regulation of the intracellular level of MMP-13 in the presence of bFGF was further visualized by histological examination within the context of cartilage explants. Human adult articular cartilage tissue (same grades of knee or ankle) was cultured in an ex vivo system in the presence or absence of bFGF. Initially, we performed time course experiments (0, 3, 6, 9, 14, and 21 days). MMP-13 gradually increased from day 0 to 9. After day 9, an expression level reached a plateau up to day 21, suggesting that MMP-13 production by bFGF may be saturated after 9 days of incubation. Thus, the immunohistochemistry was performed using an anti-MMP-13 antibody after 9 days of incubation of explants with bFGF. Our histology data further supported the up-regulation of the MMP-13 by bFGF in human articular chondrocytes within the context of explants (Fig. 2E). There were no significant differences in the bFGF-mediated stimulation of MMP-13 between knee and ankle as we observed similar results for both tissue parts using same grade of knee and ankle, suggesting the universal impact of bFGF in different joint cartilage homeostasis.
Basic FGF Induces MMP-13 Indirectly via an IL-1β-dependent Pathway
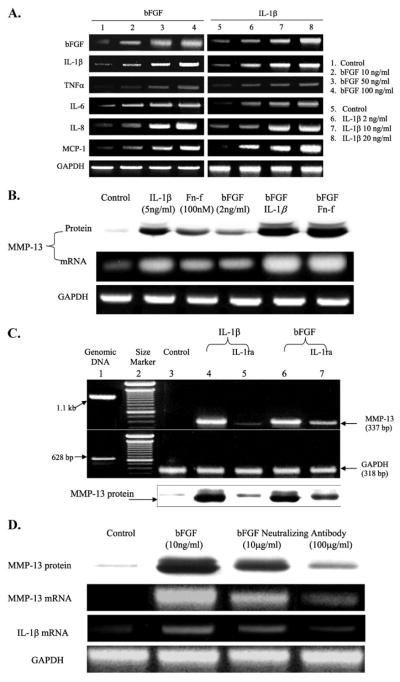
Proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, are well known inducers of MMPs, including MMP-13 (34, 35). We explored whether bFGF plays a role in stimulating other pro-inflammatory cytokines by which it may stimulate MMP-13 indirectly. Our data show that bFGF induces various inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1, and the stimulation patterns occur in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 3A). As shown in IL-1β, bFGF stimulates itself suggesting that bFGF may exert its biological effect through the autocrine and paracrine loop. In addition, combination of bFGF with IL-1β or Fn-f appeared to have a synergistic effect on the stimulation of MMP-13 expression at both mRNA and protein levels (Fig. 3B). IL-1β-mediated MMP-13 production was significantly reduced in the presence of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra), and to a lesser extent, bFGF induced MMP-13 expression at mRNA and protein levels (Fig. 3C). Furthermore, pretreatment of the cells with bFGF-neutralizing antibody prior to stimulation with bFGF dose-dependently decreased expression of MMP-13 as well as IL-1β (Fig. 3D). These results suggest that bFGF-mediated up-regulation of MMP-13 occurs indirectly through, in part, the IL-1β-dependent signaling pathway in human articular chondrocytes.
FIGURE 3. IL-1β-dependent stimulation of MMP-13 by bFGF.
A, cells in monolayer were serum-starved overnight and treated with varied concentrations of bFGF or IL-1β as indicated for 24 h. The cells were then harvested and subjected to total RNA extraction. Modulation of various pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1, were analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. B, cells in monolayers are incubated with cytokines, growth factor, and/or Fn-f for 36 h as indicated. The conditioned media were used to analyze MMP-13 protein production, and the cells were harvested and subjected to total RNA extraction for mRNA levels of MMP-13. Lower concentrations of bFGF (2 ng/ml instead of 100 ng/ml), IL-1β (2 ng/ml instead of 5–10 ng/ml), and Fn-f (100 nM instead of 250 nM to 1 μM) were used to observe additive and/or synergistic effects after combination of these factors. C, modulation of MMP-13 levels of mRNA and protein secretion by bFGF or IL-1β in the presence of IL-1ra was analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and immunoblotting, respectively. Cells stimulated with bFGF (10 ng/ml) or IL-1β (5 ng/ml) were treated with IL-1ra (100 ng/ml) for 36 h. The cells were harvested, and the total RNA was extracted for RT-PCR analysis. Lane1, genomic DNA;lane2, 100-bp DNA size marker; lane 3, control (untreated cells); lane 4, IL-1β treatment; lane 5, IL-1β with IL-1ra; lane 6, bFGF treatment; lane 7, bFGF with IL-1ra. D, cells were preincubated with FGF-neutralizing antibody (10 and 100 μg/ml concentrations) prior to stimulation with bFGF (10 ng/ml) for 36 h. Basic FGF-mediated stimulation of MMP-13 (protein and mRNA levels) and IL-1β was determined by immunoblot and RT-PCR. The picture represents two individual donors with duplicates.
bFGF Stimulation of MMP-13 Requires the Activation of Multiple MAPKs
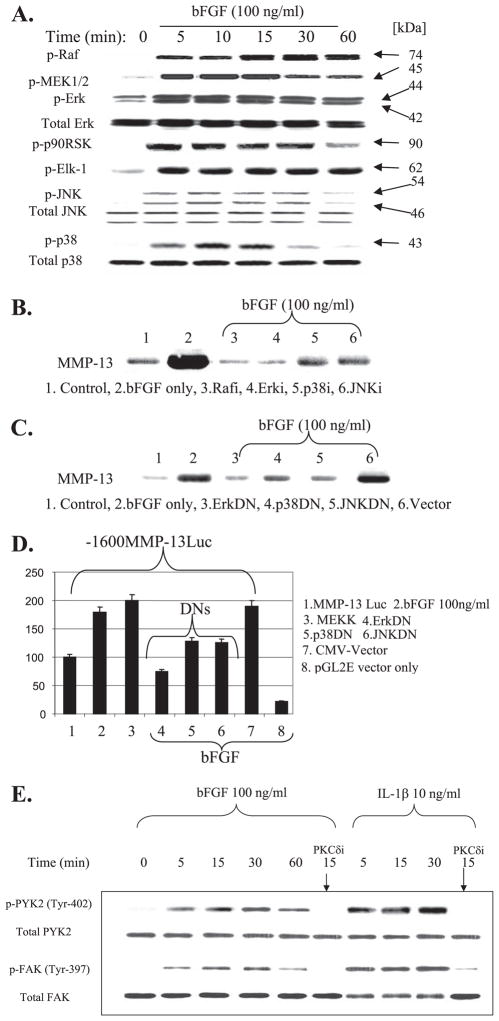
Basic FGF activates all three MAPK subgroups (ERK1/2, p38, and JNK) within 5 min as reflected by their phosphorylation in response to bFGF treatment. Among the MAPK subgroups, the activation of ERK1/2 by bFGF was most rapid (<5 min) and sustained (>60 min) (Fig. 4A). The activation of ERK1/2 was prolonged beyond 24 h after the initial bFGF stimulus (data not shown). The strong up-regulation of the ERK pathway by bFGF was also reflected by the potent activation of its upstream (Raf and MEK1/2) as well as its downstream signaling regulators (i.e. p90 RSK kinase and transcription factor Elk-1). The inhibition of Raf (Rafi, Raf1 kinase peptide inhibitor) and distinct MAPK subgroups using selective chemical inhibitors (e.g. MEK1/2 inhibitor PD98059, JNK inhibitor SP600125, and p38 inhibitor SB203580) efficiently blocked bFGF stimulation of MMP-13 at the protein level (Fig. 4B) as well as the mRNA level (data not shown). These chemical inhibitor studies were further confirmed by transient transfection studies using individual dominant negative (DN) expression vectors of ERK, p38, and JNK. Forced expression of individual DN forms of MAPK subgroups significantly reduced (i) endogenous MMP-13 production (Fig. 4C) and (ii) promoter activity of a co-transfected MMP-13 promoter/luciferase reporter (Fig. 4D). The overexpression of MEKK, which can activate all three MAPK subgroups, with different preferences was able to stimulate the luciferase activity driven by the MMP-13 promoter by mimicking bFGF stimulation. These results suggest that the multiple MAPK pathways may significantly contribute to bFGF stimulation of MMP-13 expression and that MMP-13 expression is tightly regulated within the chondrocyte cell signaling network.
FIGURE 4. Basic FGF activates multiple MAPK pathways.
A, cells in monolayer were serum-starved overnight and treated with a 100 ng/ml concentration of bFGF in a time course (0 – 60 min). Cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with phospho-specific antibodies for Raf, MEK1/2, ERK, p90 RSK, Elk-1, JNK, and p38. After stripping of the membranes, immunoreactivity using total antibodies for each molecule was detected for normalization. B, co-incubation of bFGF with the chemical inhibitors of Raf (Rafi, Raf1 kinase peptide inhibitor, 20 μM), ERK activation by MEK (ERKi, PD098059, 20 μM), p38 (p38i, SB203580, 10 μM), and JNK (JNKi, SP600125, 20 μM) for 24 h significantly reduced bFGF-induced MMP-13 production. C, human articular chondrocytes were transfected to overexpress dominant negative forms of MAPK subgroups (ERKDN, p38DN, and JNKDN). After incubation for 48 h, the conditioned media were analyzed for MMP-13 production by immunoblotting. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) vector was overexpressed as a control. D, −1600MMP-13 promoter-reporter construct was transiently co-expressed with MEKK and DN forms of MAPK subgroups (ERKDN, p38DN, and JNKDN). Cytomegalovirus vector (backbone of the DN constructs) and pGL2E vector (MMP-13 construct backbone) were used for controls. E, monolayer cultures of chondrocytes were serum-starved overnight and treated with bFGF (100 ng/ml) or IL-1β (10 ng/ml) in a time course (0 – 60 min) in the presence or absence of selective inhibitor of PKCδ (rottlerin). Cell lysates were then prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with phospho-specific antibodies for FAK and PYK-2. The membranes were stripped and reprobed with total antibodies for normalization purpose.
Focal adhesion kinase family members such as focal adhesion kinase (FAK) or proline-rich tyrosine kinase-2 (PYK2) are activated by Fn-f (26) or IL-1β (36), leading to the activation of the Ras/ERK MAPK signaling pathway. Thus, we examined whether bFGF activates these FAK family members. Rapid (within 5 min) and sustained (>60 min) activation of both PYK2 (Tyr-402) and FAK (Tyr-397) was observed by bFGF, and this activation was abolished by preincubation with the selective PKCδ pathway inhibitor rottlerin (Fig. 4E). Similar results were obtained in the presence of IL-1β. These results suggest that integrin-associated focal adhesion molecules may cooperate with the bFGF-generated cell signaling pathway, and as we have seen by Fn-f (26), the PKCδ pathway may play a role in controlling focal adhesion molecule activity to regulate MMP-13 in human adult articular chondrocytes.
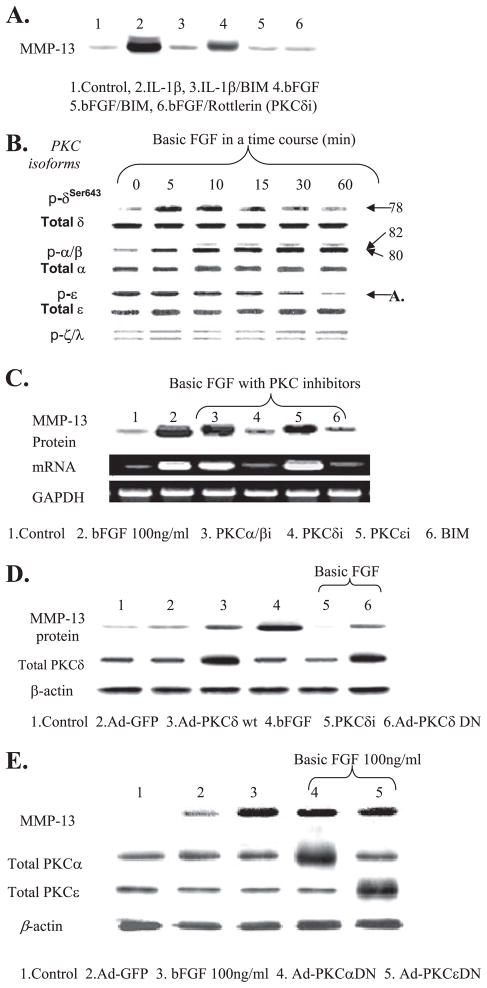
The Selective PKCδ Pathway Is Required for MMP-13
We observed that bFGF-up-regulated MMP-13 production is abolished in the presence of the broad spectrum PKC inhibitor (BIM) and a selective inhibitor of PKCδ (rottlerin), suggesting the involvement of a PKC pathway in the production of MMP-13 by bFGF (Fig. 5A). Similar results were obtained when the cells were treated with IL-1β. Thus, we explored the role of PKC signaling in the bFGF-dependent stimulation of MMP-13 expression. First, we determined whether bFGF activates specific PKC isoforms in human adult articular chondrocytes. Our time course experiments using phospho-specific antibodies for each PKC isoform suggested that bFGF activates PKCδ and PKCα/β but not PKCξ/λ. PKCε appeared to be dephosphorylated in the presence of bFGF (Fig. 5B). The chemical inhibitor studies suggested that among the PKC isoforms that are modulated by bFGF (PKCα/β, -δ, and -ε), only PKCδ is specifically associated with MMP-13 induction by bFGF (Fig. 5C). The chemical inhibitor studies were further confirmed by adenovirus-based overexpression strategies. Previously, we successfully enhanced and/or blocked the PKCδ-mediated signaling pathway by using these adenoviruses encoding PKCδ-WT or dominant form of PKCδ (26–28). Cells were infected with adenovirus encoding wild type (PKCδ-WT) or dominant negative forms of PKCδ (Ad-δDN), respectively. Exogenous expression of PKCδ-WT itself partially induced MMP-13 production without bFGF stimulation. Ad-δDN, on the other hand, reduced the bFGF-stimulated MMP-13 production. Increased intracellular levels of total PKCδ protein indicates the successful adenovirus-based expression of PKCδ-WT and Ad-δDN proteins, relative to cells infected with control adenovirus encoding GFP (Ad-GFP) (Fig. 5D). Adenovirus vectors encoding the dominant negative forms of PKCα (Ad-αDN) or PKCε (Ad-εDN) were also tested. Consistent with our chemical inhibitor results, the infection with Ad-αDN or Ad-εDN did not prevent stimulation of MMP-13 by bFGF (Fig. 5E). Taken together, these results indicate that bFGF-mediated enhancement of MMP-13 gene expression requires activation of PKCδ in human adult articular chondrocytes.
FIGURE 5. Basic FGF activation of PKCδ is associated with the stimulation of MMP-13 expression.
A, cells were serum-starved overnight and treated with bFGF (100 ng/ml) or IL-1β (10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of a broad spectrum PKC inhibitor (BIM, 10 μM) and PKCδ-specific inhibitor, rottlerin (4 μM). The conditioned media were collected and immunoblotted for the production of MMP-13. B, serum-starved cells were treated with bFGF (100 ng/ml) in a time course. Cell lysates were immunoblotted using phospho-specific anti-PKCδ, -α/β, -ε, and -ξ/λ. The membrane was re-stripped and blotted with anti-total PKC antibodies for each isoform. C, specific chemical inhibitors of PKCα/β (α/βi, GÖ6976, 5 nM), PKCδ (δi, rottlerin, 5 μM), PKCε (εi, 5 μM), and BIM were co-incubated with bFGF (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. Conditioned media and cells were used for immunoblotting and RT-PCR for protein and mRNA levels of MMP-13, respectively. D, cells were infected with adenovirus encoding PKCδ-WT (Ad-PKCδ-WT, lane 3) or Ad-PKCδ DN (lane 6). Infected cells were treated with bFGF (100 ng/ml). Conditioned media were analyzed for MMP-13 protein production, and the cells were extracted and immunoblotted using anti-total PKCδ to validate the overexpression of PKCδ-WT and DN via adenovirus infection. In parallel, the addition of PKCδi (rottlerin, 5 μM, lane 5) and infection with adenovirus encoding GFP (Ad-GFP, lane 2) were included as controls. E, adenoviruses encoding DN forms of PKCα (α DN) and -ε (ε DN) were infected. These infected cells were stimulated with bFGF (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. The conditioned media were analyzed for immunoblotting for MMP-13 production by using an anti-MMP-13 antibody.
bFGF Activation of PKCδ Controls MMP-13 via Regulating the MAPK Pathway
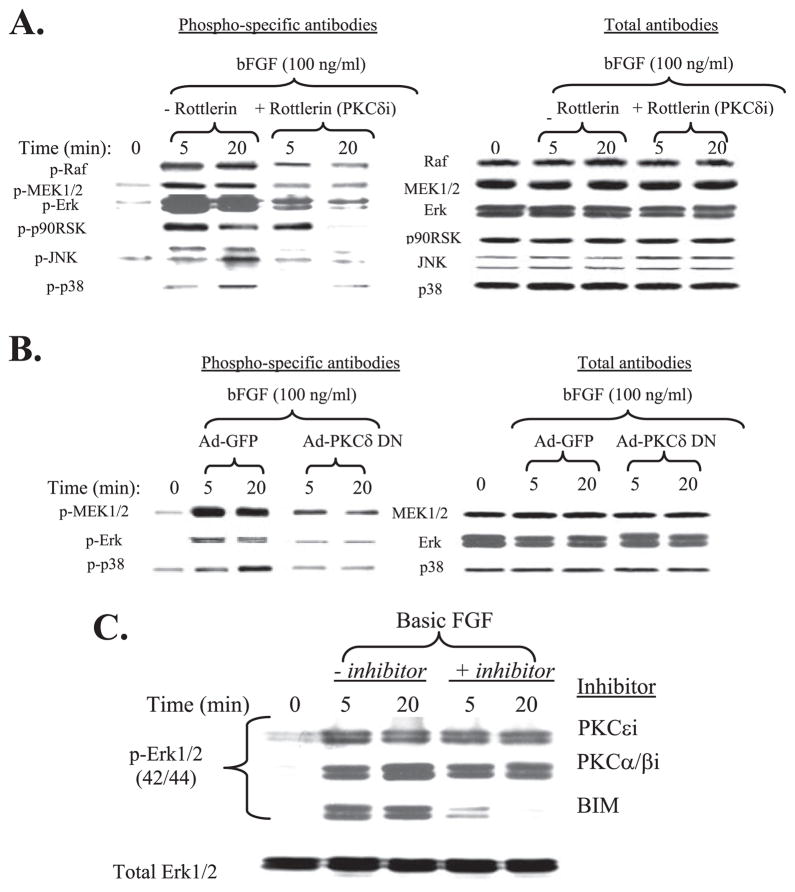
Our results show that bFGF activation of both MAPK and PKCδ pathways are critical for MMP-13 expression in human adult articular chondrocytes. We therefore addressed whether these pathways are mutually required for bFGF stimulation or perhaps can compensate for each other. Because we observed that PKCδ is the only PKC-related pathway capable of modulating MMP-13 expression among other PKC isoforms that we tested, we examined potential molecular cross-talk between PKCδ and MAPKs in control of MMP-13 expression in human adult articular chondrocytes.
Cells were incubated in the presence or absence of rottlerin, a selective inhibitor of PKCδ, for 1 h prior to stimulation with bFGF. Basic FGF rapidly activated the MAPK pathways (Raf-MEK1/2-ERK-p90 RSK, JNK, and p38) as expected. The activation of Raf and MAPK subgroups was significantly reduced and/or abolished by blocking the PKCδ pathway (Fig. 6A), whereas blocking the Raf-MAPK pathway has no effect on PKCδ activation (data not shown). We further confirmed these chemical inhibitor studies by overexpressing PKC-δDN using adenovirus-based infection as we described above and previously (26–28) prior to stimulation with bFGF. Consistent with our chemical inhibitor studies, the rapid activation of MEK1/2 and MAPK subgroups by bFGF was again significantly reduced by forced expression of a dominant negative PKC-δ mutant (Ad-PKCδ DN) (Fig. 6B). We wondered if the pathways generated by the PKC isoforms such as PKCα/β,ε, which do not stimulate MMP-13 expression, have any impact on the activation of MAPKs. Serum-starved cells were preincubated with selective inhibitors of PKCε, PKCα/β, and a broad spectrum PKC inhibitor, BIM, prior to stimulation with bFGF. The resulting cell lysates were analyzed for activation of ERK1/2 MAPK. The presence of the general PKC inhibitor BIM and ERK1/2 inhibitor U0126, which can directly acts on inhibiting MEK1/2, abolished the bFGF-mediated activation of ERK, whereas the cells incubated with the selective inhibitors of PKCε or -α/β failed to modulate the phosphorylation of ERK (Fig. 6C).
FIGURE 6. PKCδ activation by bFGF is required for MAPK signaling.
A, serum-starved cells were co-incubated with a specific chemical inhibitor of PKCδ for 30 min prior to the stimulation with bFGF (100 ng/ml) in two time intervals (5 and 20 min). The cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting for the activation of Raf, MEK1/2, ERK1/2, p90 RSK, JNK, and p38 using phospho-specific antibodies. For loading normalization, corresponding total antibodies were used, and the resulting immunoblots are shown in the right panel. B, cells were infected with adenovirus encoding PKCδ DN in the presence of bFGF (100 ng/ml) at two time intervals (5 and 20 min). Cells were infected with Ad-GFP as control. Cell lysates were used for immunoblotting for the activation of MEK1/2, ERK, and p38. For loading normalization, corresponding total antibodies were used, and the resulting immunoblots are shown in the right panel. C, cells were incubated with selective PKC isoforms of ε (PKCεi), α/β (PKCα/βi), or a broad spectrum PKC inhibitor (BIM) for 30 min prior to the stimulation with bFGF in two time intervals (5 and 20 min). and the cell extracts were immunoblotted with a phospho-specific ERK1/2 antibody. Representative immunoblotting results using anti-total ERK antibody for loading normalization is shown in the lower panel.
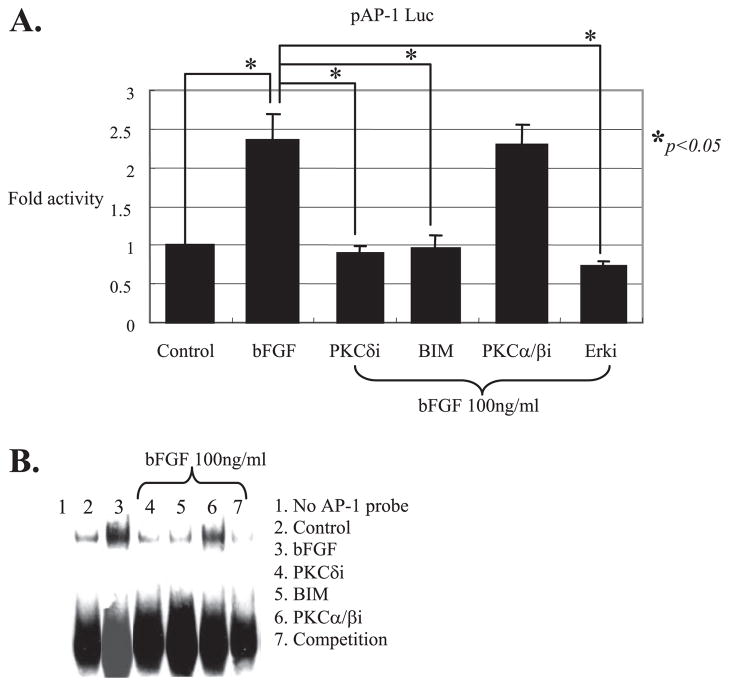
PKCδ Controls AP-1 Regulating MMP-13 Expression
AP-1 is a well known core transcriptional stimulator required for the induction of MMP-13 by pro-inflammatory cytokine or fibronectin fragment in human adult articular chondrocytes (25). Because bFGF activates multiple MAPKs, and the activation of MAPKs are controlled by the PKCδ pathway, we expected to see the inhibition of MAPK and its downstream target, such as AP-1 when the PKCδ pathway is blocked. To test our hypothesis, we first examined whether the increased activity of AP-1 after stimulation with bFGF can be attenuated in the presence of specific inhibition of PKCδ. Cells were transiently transfected with pAP-1 Luc (Stratagene), which contains seven tandem repeats of AP-1 recognition consensus sequences. The transfected cells were incubated with and without bFGF stimulation for 24 h in the presence or absence of selective inhibitors of PKCδ, PKCα/β, or BIM, the broad spectrum inhibitor of PKC. The cell lysates were used to measure a luciferase activity, which represents the AP-1 activity. Stimulation of cells with bFGF increased (~2-fold) the luciferase activity driven by the pAP-1Luc reporter plasmid compared with cells with no treatment (Fig. 7A). This increased AP-1 activity in the presence of bFGF was abrogated by rottlerin, BIM, or MEK inhibitor that can block the activity of its downstream transcription factor AP-1 component. There was no significant modulation of AP-1 activity in the presence of the PKCα/β-selective inhibitor. These transient transfection studies were further confirmed by measurement of AP-1 factor-DNA binding activity by gel shift. Cells were incubated with the general inhibitor of PKC (BIM) and selective inhibitors for each isoform (PKCδI and PKCα/βi) prior to the stimulation with bFGF for 45 min. Consistent with our transient transfection results, the increase in AP-1 factor-DNA binding activity by bFGF was significantly reduced by inhibitors of PKC (BIM) and PKCδ but not by PKCα/βi. Competition studies using an excess amount of cold unlabeled probes suggested that the protein-DNA binding activity was specific (Fig. 7B). Collectively, our data establish that bFGF-activation of MAPK signaling and its downstream transcription factor AP-1 are regulated by the PKCδ pathway and that the integration of molecular cross-talk in these pathways controls MMP-13 expression in human adult articular chondrocytes.
FIGURE 7. PKCδ activation by bFGF is required for the activation of AP-1, a direct downstream transcriptional regulatory factor of MAPK signaling.
A, cis-acting control plasmid, pAP-1 Luc, which contains seven tandem repeats of AP-1 consensus sequences was transiently transfected (2 μg per reaction) into human primary adult articular chondrocytes with and without bFGF (100 ng/ml) and in the presence or absence of a general inhibitor of PKC, BIM, or selective inhibitors of PKCδ or PKCα/β. The luciferase activity was calculated by comparing with the luciferase activity of a control plasmid, pAP-1 Luc (assigned as 1). A Renilla vector (100 ng per reaction) was co-transfected as an internal control for normalization. The data represent the means of three independent experiments in duplicate. B, serum-starved cells (>16 h) in monolayer that were stimulated with and without bFGF (100 ng/ml) for 45 min were subjected to nuclear preparation and incubated with biotin-labeled double-stranded AP-1 consensus sequences. Shifted AP-1 protein-DNA complex band was visualized by chemiluminescence imaging. Unlabeled double-stranded AP-1 oligonucleotides were used for competition assays to determine the binding specificity of the assay.
DISCUSSION
Accumulated evidence has indicated that in arthritic cartilage the overproduction of collagenases, in particular MMP-13, by chondrocytes plays a central role in cartilage degeneration. Thus, it has become important to determine the signaling pathways that control chondrocyte collagenase expression. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β or Fn-f are reported as stimulators of collagenase production (25, 26). This study provides evidence for a pathway by which bFGF induces MMP-13 expression through activation of multiple MAPKs. Our findings also suggest that bFGF activation of PKCδ plays a key regulatory role in the activation of multiple MAPKs via molecular cross-talk to modulate MMP-13 expression in human adult articular chondrocytes.
In joint synovial fluids, various metabolic factors such as growth factors and pro-inflammatory cytokines have been suggested to have important roles in cartilage metabolism and, subsequently, in the onset and/or progression of OA (40, 41). Our ELISA results show that concentrations of endogenous bFGF and the corresponding MMP-13 are increased in synovial fluids collected from OA and RA patients compared with normal subjects, suggesting the clinical relevance of bFGF in arthritis. One striking finding of our studies is that the level of bFGF in OA is higher than RA. RA synovial fluid samples were initially included as a positive control for bFGF levels, because elevated bFGF have been detected in synovial fluids and/or serum of RA patients (42, 43). Our data are consistent with those previously reported by Orito et al. (33) that measured bFGF concentrations in human joint fluids from patients having mild (characteristic of early OA) or severe degenerative symptoms. They showed a positive correlation between “mild” and “severe” conditions with correspondingly elevated bFGF levels (>2-fold). Our data reinforced the clinical and pathological links between bFGF and human cartilage degeneration. We anticipate that future expansion of the sample pool (e.g. with more precise and strict criteria for categorizing synovial fluid samples) may validate measurements of bFGF as valuable prognostic or diagnostic parameters for the assessment of arthritic conditions to complement existing markers for cartilage degenerative diseases.
Qualitative and quantitative changes in chondrocyte gene expression contribute to the onset and progression of OA. Our findings suggest that bFGF could be an important physiological regulator of MMP-13 expression in human adult articular cartilage. The stimulation of MMP-13 by bFGF was dose-dependent suggesting that the induction of MMP-13 results from a bFGF-mediated chondrocytic cellular response. Our histological examination using an ex vivo cell culture system further supported the stimulation of MMP-13 by bFGF in the context of articular cartilage explants. Elevated MMP-13 mRNA level by bFGF was evident within 3 h. This relatively rapid induction could result from the activation, by bFGF, of transcription factors involved in the immediate early response, such as AP-1, known as a downstream target of MAPKs and PKC (38, 44, 45). In particular, AP-1 is a direct downstream heterodimeric transcriptional regulator of the ERK and JNK pathway leading to the activation of c-Fos and c-Jun, respectively. AP-1 may act as a proxy factor for bFGF to control MMP-13 gene transcription. Along with Runx2 and PEA-3, AP-1 is a positive regulator of MMP-13 gene expression through interactions at regulatory elements in the proximal core promoter of the MMP-13 gene.
Our real time PCR results in the presence of the transcriptional inhibitor actinomycin D suggest that bFGF regulates MMP-13 expression principally at the level of transcriptional control. Basic FGF induces IL-1β expression which in turn stimulates MMP-13. The presence of IL-1ra partially attenuated bFGF-mediated MMP-13 induction. Collectively, these results indicate the stimulation of MMP-13 by bFGF is via both direct and indirect mechanisms. Nevertheless, the fact that the preincubation of bFGF-neutralizing antibody abolishes the entire biological impact mediated by bFGF, such as induction of IL-1β and MMP-13 gene expression, further enhances our hypothesis that bFGF-induced MMP-13 is initially mediated by a direct mechanism in human adult articular chondrocytes.
Extracellular signals from FGF to the cells are transduced through members of the FGF receptor family FGFR1–4 (46–50). It is well established in the literature that FGFR1 and FGFR3 play a critical role in the growth plate cartilage biology in which FGFR1 and FGFR3 play opposite roles. Basic FGF is shown to interact with both FGFR1 and FGFR3 (51, 52). Basic FGF binding to FGFR1 has been demonstrated to increase proliferation of growth plate chondrocytes, whereas bFGF binding to FGFR3 inhibits proliferation and therefore promotes differentiation (51, 52). In human adult articular chondrocytes, FGFR1 is the major FGF receptor that is responsible for the biological consequences after stimulation with bFGF.3 The activation of FGFR1, represented by the phosphorylation of the receptor at the tyrosine amino acid residues, was specific to the presence of bFGF as we did not observe the activation of FGFR1 in the presence of FGF18, another member of the FGF superfamily which is shown to signal through FGFR3 and a tropic factor promoting articular cartilage repair (53). Interestingly, Valverde-Franco et al. (54) recently demonstrated that the absence of signaling from fgfr3 results in defective articular cartilage characterized by increased MMP-13 expression leading to increased cleavage product from type II collagen and aggrecan, which resembled those changes seen in mice overexpressing MMP-13. This result may be attributed from compensatory signaling by bFGF interacting with FGFR1, which is up-regulated in the absence of fgfr3 (55), thus increasing MMP-13 expression.
We have demonstrated that activation of multiple MAPKs is required for MMP-13 expression in response to Fn-f (26). Here we show that activation of multiple MAPK pathways is also required for the expression of MMP-13 after stimulation with bFGF in human adult articular chondrocytes. The shared requirement of activation of all three MAPK subgroups to achieve stimulation of MMP-13 expression suggests an important mechanistic explanation for the observation that some growth factors, such as insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) (56) or FGF-18,3 do not stimulate chondrocyte MMP-13 expression although they are capable of activating ERK MAPK signaling. Our data further suggest that the absence of concomitant activation of other MAPK subgroups (p38 and JNK) by these growth factors (57) may restrict expression of MMP-13. Similarly, selective inhibition of the ERK or p38 MAPK pathways alleviates joint disease in an experimental OA model (58) or IL-1β-generated cartilage degeneration in a cartilage explant system (59). Stringent regulation of MMP-13 within the chondrocytic cell signaling network, through a complex interplay of regulatory factors and elements, may be necessary, especially considering the fact that MMP-13 has a potent degrading activity against a wide spectrum of substrates in ECM.
The precise roles of PKC isoforms associated with articular cartilage homeostasis are not understood. More recently, Ca2+ influx-dependent PKCα-MAPK signaling cascades have been implied to be activated in the experimental dog OA model system, suggesting that the PKCα pathway may mediate development and progression of OA (60). Our data showed that stimulation with bFGF also phosphorylated PKCα and -β isoforms, but they did not appear to be associated with MMP-13 stimulation. Furthermore, blocking the PKCα/β or the PKCε pathway had no significant influence on the activation of ERK or p38 MAPKs (data not shown) in human adult articular chondrocytes. Again, these results are consistent with our working hypothesis that MMP-13 production in articular chondrocytes is tightly regulated because the activation of all three MAPKs is required.
Our study suggests that bFGF activation of the PKCδ pathway may influence the signaling pathways of Raf-MEK1/2 and three MAPK subgroups (ERK, JNK, and p38) as downstream target regulatory molecules, which in turn control the expression of MMP-13. The specific PKCδ-driven signaling cascades by bFGF appeared to be different from those we previously observed upon PKCδ-dependent activation by Fn-f, in which PKCδ regulates mainly the JNK pathway, without significantly affecting the p38 or ERK pathways (26). These differences are perhaps because of the slightly different activation pattern of upstream signaling molecules, such as integrin-associated regulators. Unlike Fn-f, we found in the cells stimulated with bFGF that the activation of FAK was evident within 5 min as represented by the FAK (Tyr-397) phosphorylation status. The activation patterns of PYK2 and FAK by bFGF were similar to those in the presence of IL-1β in which both focal adhesion molecules were activated in a rapid and sustained manner as shown by bFGF not by Fn-f. Our results from the use of the pathway-specific inhibitor of PKCδ also suggest that both PYK2 and FAK activities may be under the control of the PKCδ activity after stimulation with bFGF or IL-1β. Although bFGF and Fn-f utilize similar downstream signaling pathways to control MMP-13 expression, a subset of transducing molecules and co-factors may direct the responses through distinct pathways.
We also observed that blocking PKCδ, but not PKCα/β, correspondingly shut down the bFGF-mediated activation of AP-1 factors. These results further supported that controlling PKCδ activation could be the principal rate-limiting event for the cellular response to bFGF, because a blockade in PKCδ signaling prevents the activation of the multiple MAPK pathways and their downstream target transcriptional regulatory factors, which are required for the biological action of bFGF to stimulate MMP-13. Collectively, our data suggest that an increased level of bFGF in synovial fluid, which is evident in joints of arthritic patients with OA or RA, may acutely and chronically modulate the activities of cartilage-degrading enzymes (i.e. MMP-13). Based on our studies, we conclude the role of bFGF can be defined as “catabolic” in human adult articular cartilage by enhancing MMP-13 gene expression at the transcriptional level.
Acknowledgments
We thank the tissue donors, Dr. Arkady Margulis, and the Gift of Hope Organ and Tissue Donor Network for tissue samples. We thank Larry Madsen for preparing human synovial fluids collected from OA and RA patients, and Carol Pacione for technical assistance. Dr. Ralf Janknecht (Mayo Clinic) kindly provided DN forms of MAPKs plasmid vectors and greatly assisted the study by in-depth discussion. We also thank the NCI, National Institutes of Health, and Amgen for providing bFGF and IL-1β, respectively.
Footnotes
The abbreviations used are: OA, osteoarthritis; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; IL, interleukin; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ECM, extracellular matrix; DN, dominant negative; BIM, bisindolylmaleimide I; RT, reverse transcription; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IL-1ra, IL-1 receptor antagonist; MEK, MAPK/ERK kinase; MEKK, MEK kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; Fn-f, fibronectin fragments.
H.-J. Im, P. Muddasani, V. Natarajan, T. M. Schmid, J. A. Block, F. Davis, A. J. van Wijnen, and R. F. Loeser, unpublished data.
This work was supported by the Falk Foundation, a UCR grant from the Rush University Medical Center, The Arthritis National Research Foundation, The Arthritis Foundation (Chicago Chapter grant), National Institutes of Health Grant AR053220 (to H. J. I.), and National Institutes of Health Grant AR49003 (to R. F. L.).
References
- 1.Middleton JF, Tyler JA. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992;51:440–447. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keyszer GM, Heer AH, Kriegsmann J, Geiler T, Keysser C, Gay RE, Gay S. J Rheumatol. 1995;22:275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Salminen HJ, Saamanen AM, Vankemmelbeke MN, Auho PK, Perala MP, Vuorio EI. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:591–597. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.7.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Smeets TJ, Barg EC, Kraan MC, Smith MD, Breedveld FC, Tak PP. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:635–638. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.7.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pendas AM, Uria JA, Jimenez MG, Balbin M, Freije JP, Lopez-Otin C. Clin Chim Acta. 2000;291:137–155. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(99)00225-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.van den Berg WB. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001;13:452–456. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200109000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bluteau G, Gouttenoire J, Conrozier T, Mathieu P, Vignon E, Richard M, Herbage D, Mallein-Gerin F. Biorheology. 2002;39:247–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mitchell PG, Magna HA, Reeves LM. J Clin Investig. 1996;97:761–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI118475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Neuhold LA, Killar L, Zhao W, Sung ML, Warner L, Kulik J, Turner J, Wu W, Billinghurst C, Meijers T, Poole AR, Babij P, De-Gennaro LJ. J Clin Investig. 2001;107:35–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI10564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Qu Z, Huang XN, Ahmadi P, Andresevic J, Planck SR, Hart CE, Rosenbaum JT. Lab Investig. 1995;73:339–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tchetina EV, Squires G, Poole AR. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:876–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang X, Manner PA, Horner A, Shum L, Tuan RS, Nuckolls GH. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12:963–973. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2004.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Loeser FR, Chubinskaya S, Pacione C, Im HJ. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3910–3917. doi: 10.1002/art.21472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Quintavalla J, Kumar C, Daouti S, Slosberg E, Uziel-Fusi S. J Cell Physiol. 2005;204:560–566. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sonal D. Matrix Biol. 2001;20:233–242. doi: 10.1016/s0945-053x(01)00140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nakayama K, Tamura Y, Suzawa M, Harada SI, Fukumoto S, Kato M, Miyazono K, Rodan GA, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:827. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.5.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lohmander LS, Felson D. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12:S49–S52. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2003.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Iannone F, Lapadula G. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2003;15:364–372. doi: 10.1007/BF03327357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vincent T, Hermansson M, Bolton M, Wait R, Saklatvala J. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:8259–8264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.122033199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shida JI, Jingushi S, Izumi T, Ikenoue T, Iwamoto Y. J Orthop Res. 2001;19:259–264. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(00)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vincent TL, Hermansson MA, Hansen UN, Amis AA, Saklatvala J. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:526–533. doi: 10.1002/art.20047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Carreras I, Rich CB, Jaworski JA, Dicamillo SJ, Panchenko MP, Goldstein R, Foster JA. Am J Physiol. 2001;281:L766–L775. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.281.4.L766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Daouti S, Latario B, Nagulapalli S, Buxton F, Sziel-Fusi S, Chim GW, Bodian D, Song C, Labow M, Lotz M, Quintavalia J, Kumar C. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13:508–518. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2005.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Collins DH, editor. Osteoarthritis: The Pathology of Articular and Spinal Diseases. Edward Arnold; London: 1949. pp. 74–115. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Im HJ, Pacione C, Chubinskaya S, van Wijnen AJ, Sun Y, Loeser FR. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:25386–25394. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302048200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Loeser FR, Forsyth CB, Samarel AM, Im HJ. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:24579–24585. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304530200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cummings R, Zhao Y, Jacoby D, Spannhake EW, Ohba M, Garcia JGN, Watkins T, He D, Saatian B, Natarajan V. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:41085–41094. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404045200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhao Y, He D, Saatian B, Watkins T, Spannhake EW, Pyne NJ, Natarajan V. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:19501–19511. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511224200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G, Borenstein D, Brandt K, Christy W, Cooke TD, Greenwald R, Hochberg M. Arthritis Rheum. 1986;29:1039–1049. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yang G, Im HJ, Wang JH. Gene (Amst) 2005;363:166–172. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pulai JI, Chen H, Im HJ, Dumar S, Hanning C, Loeser FR. J Immunol. 2005;174:5781–5788. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.9.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Loeser FR, Yammani R, Carlson CS, Chen H, Cjole A, Im HJ, Bursch LS, Yan DS. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2376–2385. doi: 10.1002/art.21199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Orito K, Koshino T, Saito T. J Orthop Sci. 2003;8:294–300. doi: 10.1007/s10776-003-0647-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mengshol JA, Vincenti MP, Coon CI, Barchowsky A, Brinckerhoff CE. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:801–811. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<801::AID-ANR10>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liacini A, Sylvester J, Li WQ, Ahmad M, Zafarullah M. Matrix Biol. 2002;21:251–262. doi: 10.1016/s0945-053x(02)00007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sawai H, Okada Y, Funahashi H, Matsuo Y, Takahashi H, Takeyama H, Manabe T. Mol Cancer. 2005;4:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Deleted in proof
- 38.Mengshol JA, Vincenti MP, Brinckerhoff CE. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:4361–4372. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.21.4361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Deleted in proof
- 40.Bottomley MJ, Webb NJ, Watson CJ, Holt L, Bukhari M, Denton J, Freemont AJ, Brenchley PE. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000;119:182–188. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Manicourt DH, Poilvache P, Van Egeren A, Devogelaer JP, Lenz ME, Thonar EJ. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:281–288. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<281::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nedvetzki S, Golan I, Assayag N, Gonen E, Caspi D, Gladnikoff M, Yayon A, Naor D. J Clin Investig. 2003;111:1211–1220. doi: 10.1172/JCI17100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sharaki OA, Il-Guiziry DA, Abou-Zeid AA, El-Noueam KI, Helal AE, Gaballah AE. Egypt J Immunol. 2004;11:91–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Harris VK, Liaudet-Coopman ED, Boyle BJ, Wellstein A, Riegel AT. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19130–19139. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.30.19130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Li TF, Zuscik MJ, Ionescu AM, Zhang X, Rosier RN, Schwarz EM, Drissi H, O’Keefe RJ. Exp Cell Res. 2004;300:159–169. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Coughlin SR, Barr PJ, Cousens LS, Fretto LJ, Williams LT. J Biol Chem. 1998;263:988–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Johnson DE, Williams LT. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;60:1–41. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60821-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mohammadi M, McMahon G, Li S, Tang C, Hirth P, Yeh BK, Hubbard SR, Schlessinger J. Science. 1997;276:955–960. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5314.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Jaye M, Schlessinger J, Dionne CA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1135:185–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90136-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ornitz DM. BioEssays. 2000;22:108–112. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(200002)22:2<108::AID-BIES2>3.0.CO;2-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kilkenny DM, Hill DJ. Endocrinology. 1996;137:5078–5089. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.11.8895382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nicole BW, Gregory PL, Eric SR, William AH. Biochem J. 1999;342:677–682. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ellsworth JL, Berry J, Bukowski T, Claus J, Feldhaus A, Holderman S, Holdren MS, Lum KD, Moore EE, Raymond F, Ren H, Shea P, Sprecher C, Storey H, Thompson DL, Waggie K, Yao L, Fernandes RJ, Eyre DR, Hughes SD. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10:308–320. doi: 10.1053/joca.2002.0514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Valverde-Franco G, Binette JS, Li W, Wang H, Chai S, Laflamme F, Tran-Khanh N, Quenneville E, Meijers T, Poole AR, Mort JS, Buschmann MD, Henderson JE. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1783–1792. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Davidson D, Blanc A, Filion D, Wang H, Plut P, Pfeffer G, Buschmann MD, Henderson JE. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:20509–20515. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410148200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Starkman BG, Cravero JK, Delcarlo M, Loeser RF. Biochem J. 2005;389:723–729. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Geng Y, Valbracht J, Lotz M. J Clin Investig. 1996;98:2425–2430. doi: 10.1172/JCI119056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Pelletier JP, Fernandes JC, Brunet J, Moldevan F, Schrier D, Flory C, Martel-Pelletier J. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:1582–1593. doi: 10.1002/art.11014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Radons J, Bosserhoff AK, Grassel S, Falk W, Schubert TE. Int J Mol Med. 2006;17:661–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Boileau C, Martel-Pelletier J, Brunet J, Schrier D, Flory C, Boily M, Pelletier JP. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:573–580. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.041855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]