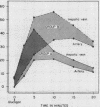
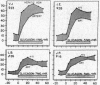
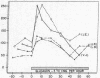
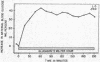
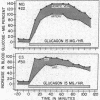
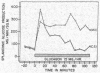
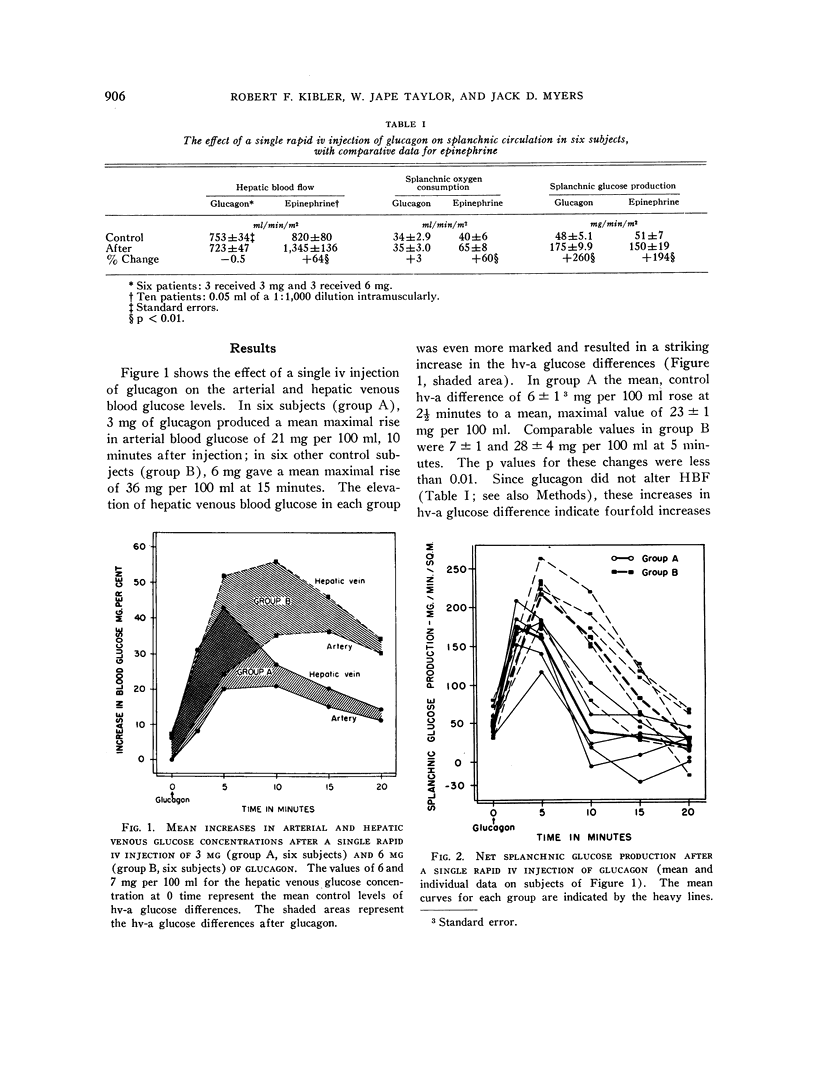
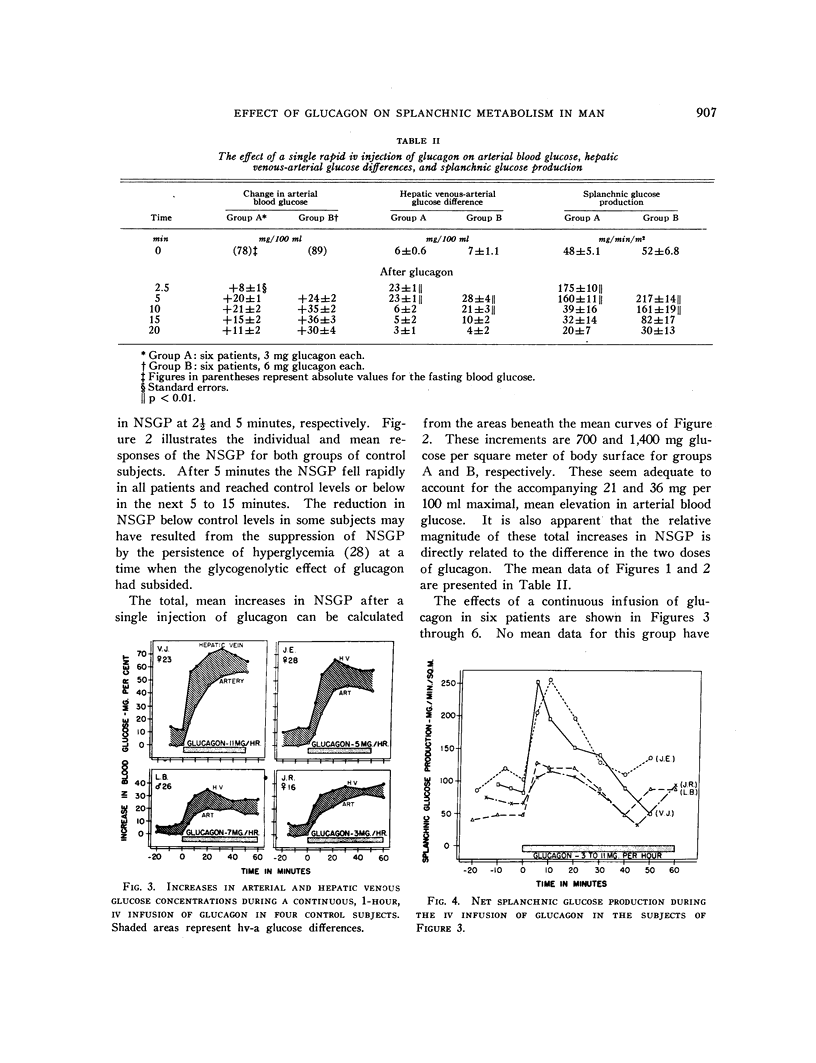
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELL D. M., BURNS T. Effect on femoral A-V glucose difference of insulin injected into an antecubital vein and into a femoral artery. J Clin Invest. 1952 Jul;31(7):717–720. doi: 10.1172/JCI102654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONDY P. K., CARDILLO L. R. The effect of glucagon on carbohydrate metabolism in normal human beings. J Clin Invest. 1956 May;35(5):494–501. doi: 10.1172/JCI103302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. E., Ingelfinger F. J., Bradley G. P., Curry J. J. THE ESTIMATION OF HEPATIC BLOOD FLOW IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1945 Nov;24(6):890–897. doi: 10.1172/JCI101676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAHILL G. F., Jr, EARLE A. S., ZOTTU S. In vivo effects of glucagon on hepatic glycogen, phosphorylase and glucose-6-phosphatase. Endocrinology. 1957 Feb;60(2):265–269. doi: 10.1210/endo-60-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAREN R., CORBO L. Glucagon and cholesterol metabolism. Metabolism. 1960 Oct;9:938–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARSON M. J., KOCH R. Clinical studies with glucagon in children. J Pediatr. 1955 Aug;47(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(55)80027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON I. W., SALTER J. M., BEST C. H. Calorigenic action of glucagon. Nature. 1957 Nov 23;180(4595):1124–1124. doi: 10.1038/1801124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREILING D. A., BIERMAN E. L., DEBONS A. F., ELSBACH P., SCHWARTZ I. L. Effect of ACTH, hydrocortisone, and glucagon on plasma nonesterified fatty acid concentration (NEFA) in normal subjects and in patients with liver disease. Metabolism. 1962 Jun;11:572–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRURY D. R., WICK A. N., SHERRILL J. W. The effect of the hyperglycemic factor on the metabolism of glucose by the extrahepatic tissues. Diabetes. 1954 Mar-Apr;3(2):129–132. doi: 10.2337/diab.3.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELRICK H., HLAD C. J., Jr, WITTEN T. The enhancement of peripheral glucose utilization by glucagon. J Clin Invest. 1955 Dec;34(12):1830–1838. doi: 10.1172/JCI103239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EZRIN C., SALTER J. M., OGRYZLO M. A., BEST C. H. The clinical and metabolic effects of glucagon. Can Med Assoc J. 1958 Jan 15;78(2):96–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASSER S. R., IZZO J. L. The influence of adrenalectomy on the metabolic actions of glucagon in the fasted rat. Endocrinology. 1962 Jan;70:54–61. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-1-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUGAARD E. S., HAUGAARD N. The effect of hyperglycemic-glycogenolytic factor on fat metabolism of liver. J Biol Chem. 1954 Feb;206(2):641–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMER O. M., ROOT M. The effect of ACTH and cortisone on the hyperglycemic response to glucagon. Endocrinology. 1954 Mar;54(3):338–342. doi: 10.1210/endo-54-3-338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN D. H., SHOEMAKER W. C. Effect of glucagon and epinephrine on regional metabolism of glucose, pyruvate, lactate, and citrate in normal conscious dogs. Endocrinology. 1961 Jun;68:889–898. doi: 10.1210/endo-68-6-889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IZZO J. L., GLASSER S. R. Comparative effects of glucagon, hydrocortisone and epinephrine on the protein metabolism of the fasting rat. Endocrinology. 1961 Feb;68:189–198. doi: 10.1210/endo-68-2-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IZZO J. L. Metabolic effects of continued administration of sulfonylurea derivatives in selected diabetic subjects: interrelations with glucagon. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 30;74(3):582–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb39584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALANT N. The effect of glucagon on metabolism of glycine-1-C14. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Dec;65(2):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU B. R., LEONARDS J. R., BARRY F. M. A quantitative study of glucagon-induced hepatic glycogenolysis. Am J Physiol. 1960 Aug;199:231–234. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUBE S. D., CAMPBELL E. D., MIRSKY I. A. Administration of the hyperglycemic-glycogenolytic factor of the pancreas to non-anesthetized and anesthetized subjects. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Oct;75(1):161–164. doi: 10.3181/00379727-75-18131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS J. D. Net splanchnic glucose production in normal man and in various disease states. J Clin Invest. 1950 Nov;29(11):1421–1429. doi: 10.1172/JCI102380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALOYAN E., HARPER P. V., Jr Glucagon as a regulating factor of plasma lipids. Metabolism. 1961 Apr;10:315–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINCUS I. J. A hyperglycemic factor extracted from the pancreas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1950 May;10(5):556–571. doi: 10.1210/jcem-10-5-556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTER J. M., DAVIDSON I. W., BEST C. H. The pathologic effects of large amounts of glucagon. Diabetes. 1957 May-Jun;6(3):248-52; discussion, 252-5. doi: 10.2337/diab.6.3.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTER J. M., EZRIN C., LAIDLAW J. C., GORNALL A. G. Metabolic effects of glucagon in human subjects. Metabolism. 1960 Aug;9:753–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOEMAKER W. C., VAN ITALLIE T. B. The hepatic response to glucagon in the unanesthetized dog. Endocrinology. 1960 Feb;66:260–268. doi: 10.1210/endo-66-2-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOEMAKER W. C., VAN ITALLIE T. B., WALKER W. F. Measurement of hepatic glucose output and hepatic blood flow in response to glucagon. Am J Physiol. 1959 Feb;196(2):315–318. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART R. D., ROITMAN E. Effect of pancreatic extracts on ketone body production of rat liver. Endocrinology. 1953 Aug;53(2):192–197. doi: 10.1210/endo-53-2-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., CORI C. F. Effect of hyperglycemic-glycogenolytic factor and epinephrine on liver phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):531–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg P., Stead E. A. THE CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW IN MALE SUBJECTS AS MEASURED BY THE NITROUS OXIDE TECHNIQUE. NORMAL VALUES FOR BLOOD FLOW, OXYGEN UTILIZATION, GLUCOSE UTILIZATION, AND PERIPHERAL RESISTANCE, WITH OBSERVATIONS ON THE EFFECT OF TILTING AND ANXIETY. J Clin Invest. 1949 Sep;28(5 Pt 2):1163–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI102150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNGER R. H., EISENTRAUT A. M., McCALL M. S., MADISON L. L. Measurements of endogenous glucagon in plasma and the influence of blood glucose concentration upon its secretion. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:682–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI104525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ITALLIE T. B., MORGAN M. C., DOTTI L. B. Effect of glucagon on peripheral utilization of glucose in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955 Jan;15(1):28–35. doi: 10.1210/jcem-15-1-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERK E. E., Jr, McPHERSON H. T., HAMRICK L. W., Jr, MYERS J. D., ENGEL F. L. Studies on ketone metabolism in man. I. A method for the quantitative estimation of splanchnic ketone production. J Clin Invest. 1955 Aug;34(8):1256–1267. doi: 10.1172/JCI103172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]