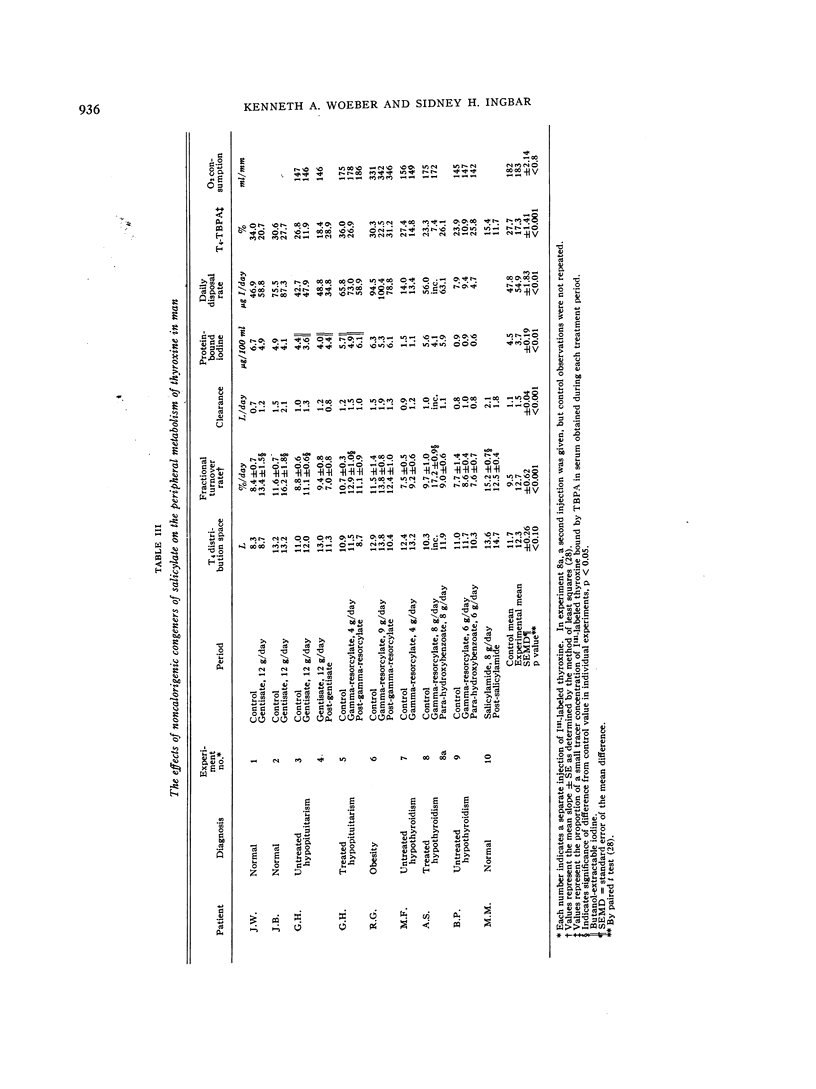
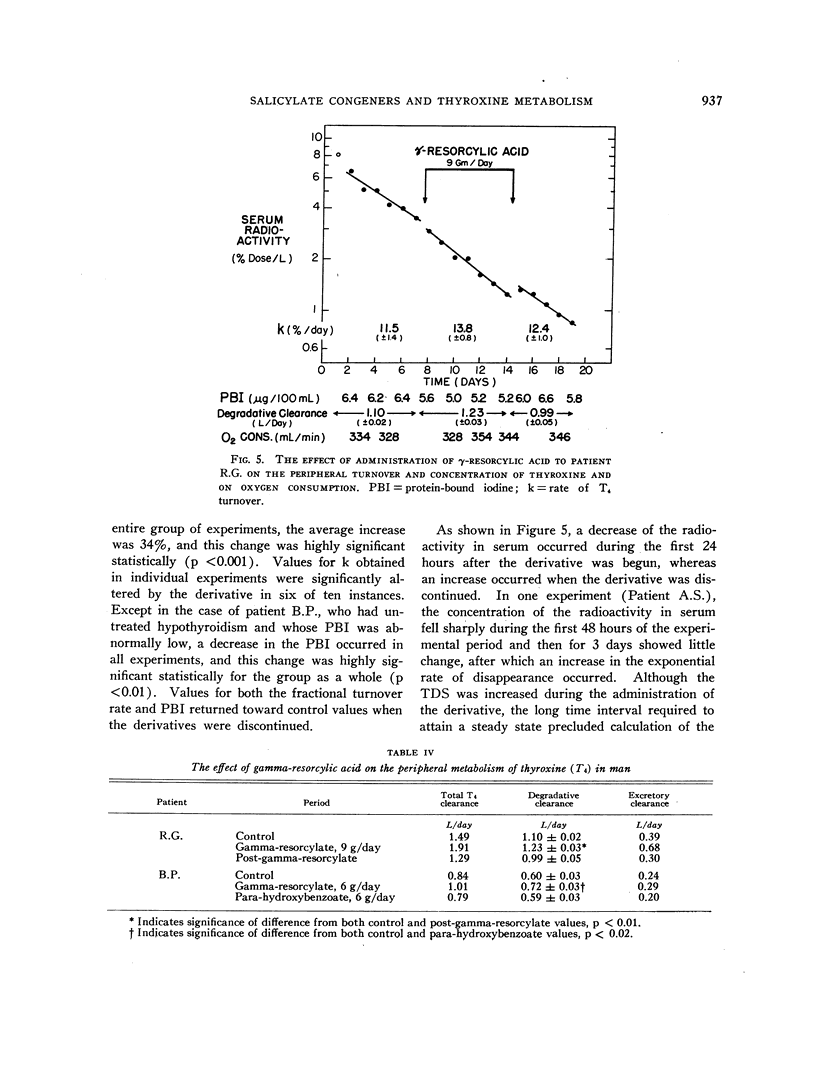
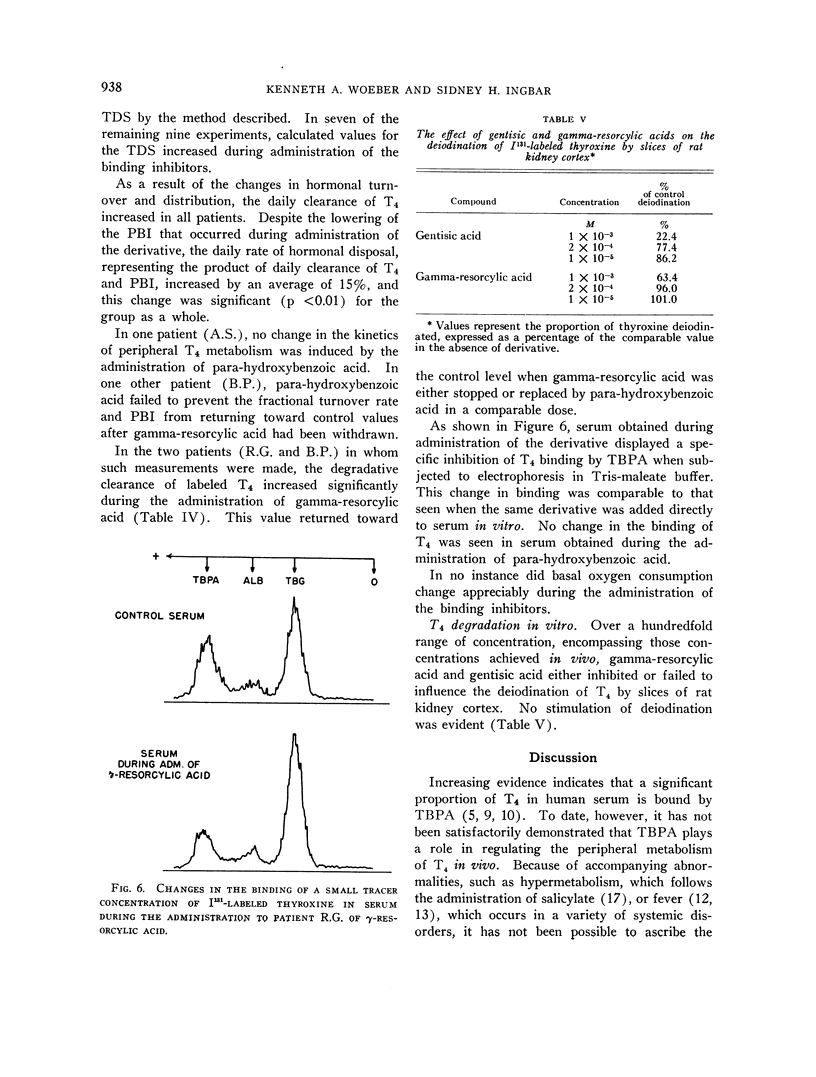
Full text
PDF

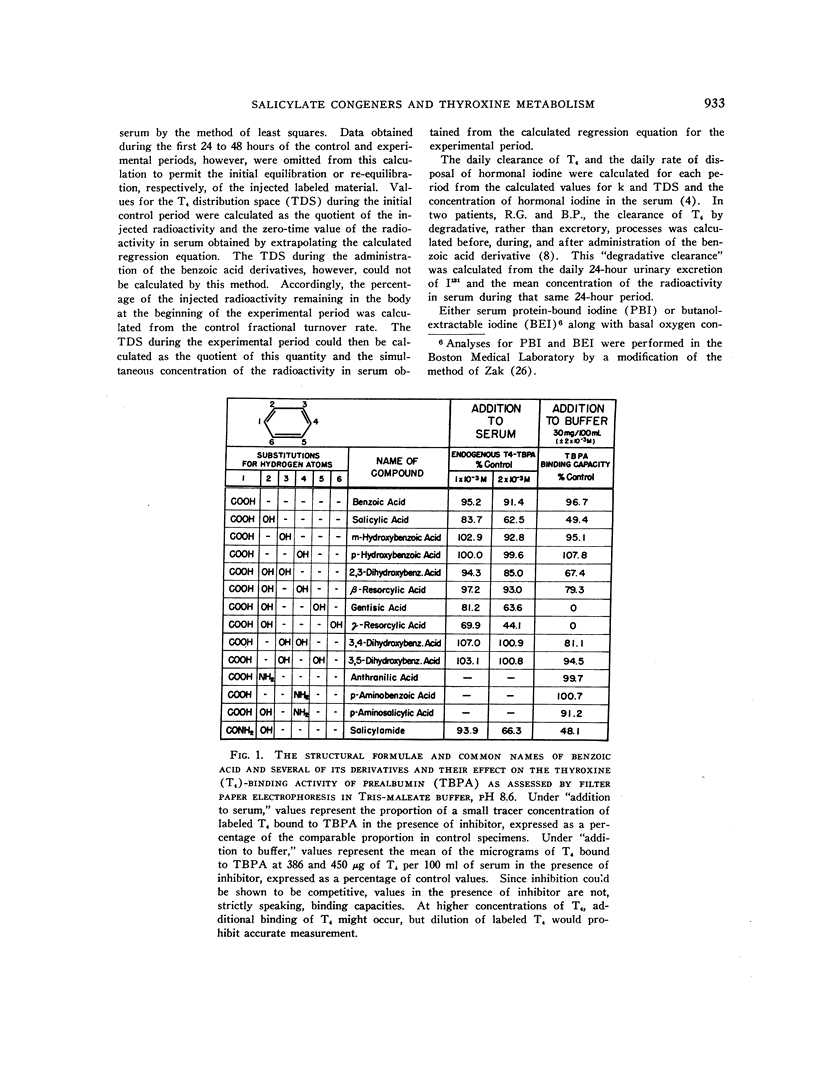
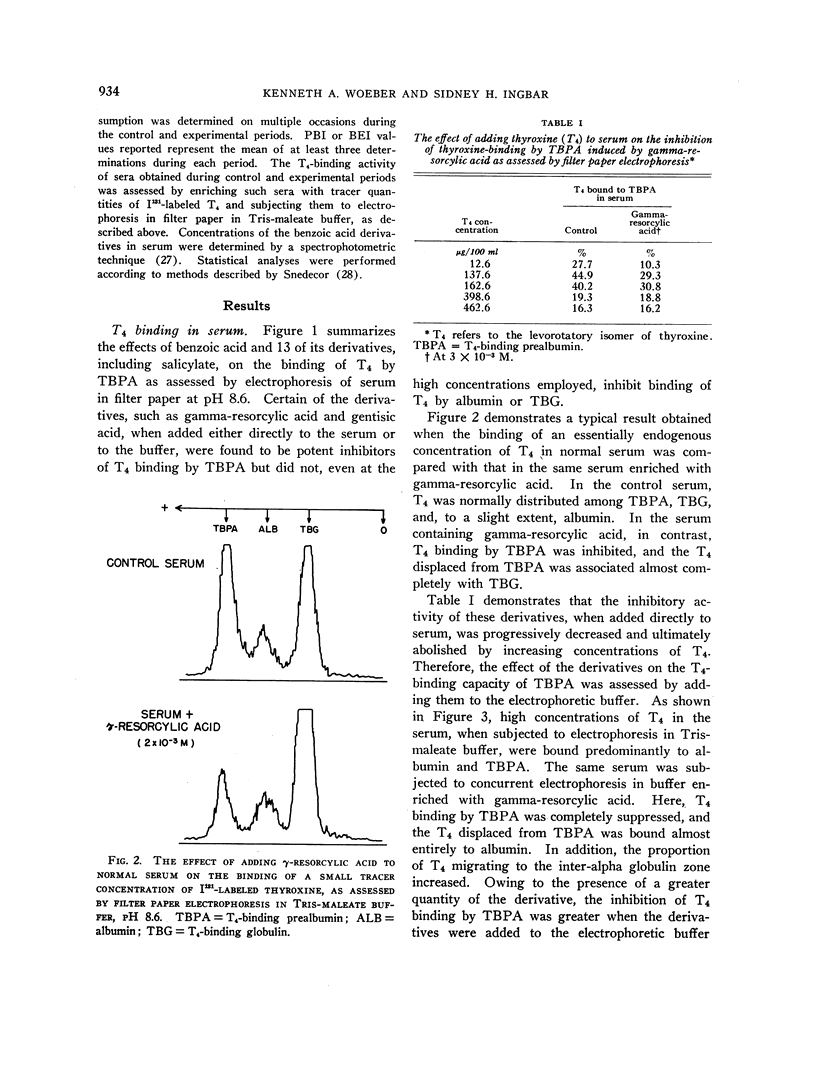
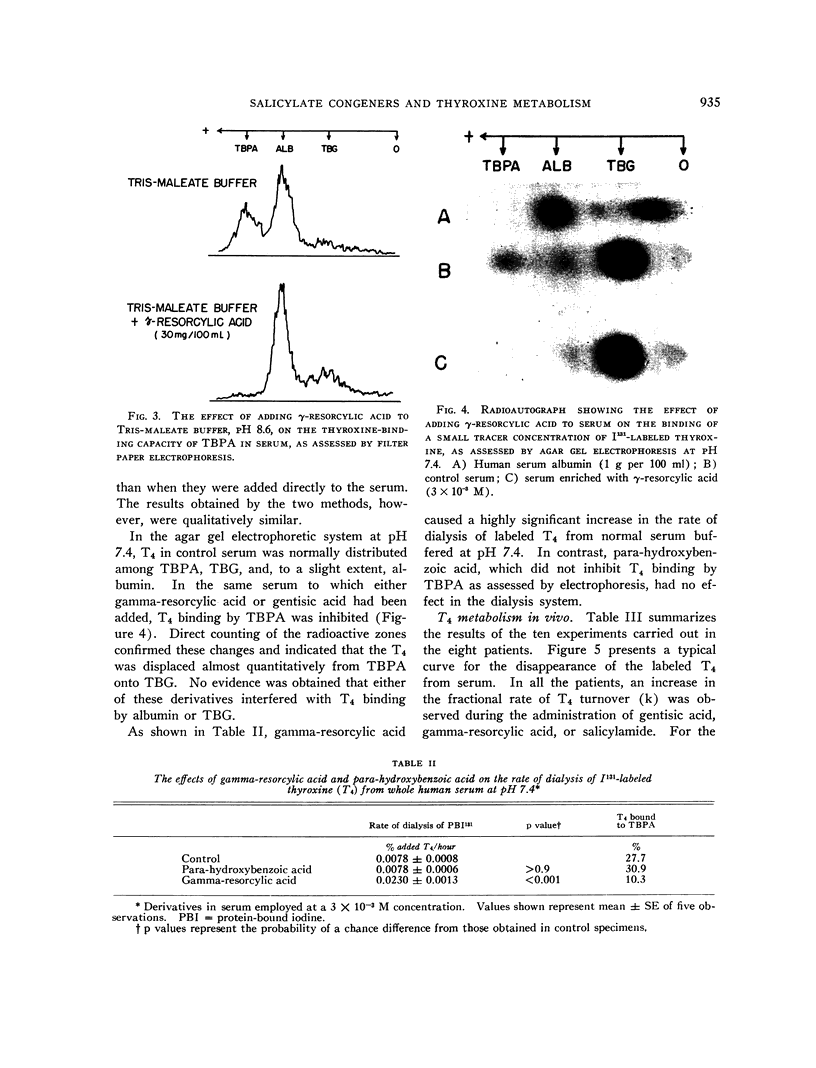




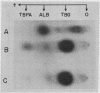
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDREWS M. M. The relative potencies of some substituted salicylic acids as metabolic stimulants in the intact rat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Dec;13(4):419–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00232.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUSTEN F. K., RUBINI M. E., MERONEY W. H., WOLFF J. Salicylates and thyroid function. I. Depression of thyroid function. J Clin Invest. 1958 Aug;37(8):1131–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI103703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENOTTI J., BENOTTI N. PROTEIN-BOUND IODINE, TOTAL IODINE, AND BUTANOL-EXTRACTABLE IODINE BY PARTIAL AUTOMATION. Clin Chem. 1963 Aug;12:408–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODY T. M. Action of sodium salicylate and related compounds on tissue metabolism in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 May;117(1):39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTOR C. W., BEIERWALTES W. Effect of 2, 4-dinitrophenol on thyroid function in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956 Aug;16(8):1026–1031. doi: 10.1210/jcem-16-8-1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE N. E., CLARKE C. N., MOSHER R. E. Phenolic compounds in chemotherapy of rheumatic fever. Am J Med Sci. 1958 Jan;235(1):7–22. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195801000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE N. E., MOSHER R. E., CLARKE C. N. Phenolic compounds in the treatment of rheumatic fever. I. A study of gentisic acid derivatives. Circulation. 1953 Feb;7(2):247–257. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.7.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWLING J. T., FREINKEL N., INGBAR S. H. The effect of estrogens upon the peripheral metabolism of thyroxine. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1119–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI104127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEDERMAN D. D., ROBBINS J., RALL J. E. Effects of methyl testosterone on thyroid function, thyrozine metabolism, and thyroxine-binding protein. J Clin Invest. 1958 Jul;37(7):1024–1030. doi: 10.1172/JCI103683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERALD P. S., KAGAN B. M. A method for the determination of gentisic acid in serum. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON A. H., GROSS J., O'CONNOR D., PITT-RIVERS R. Nature of the circulating thyroid hormone-plasma protein complex. Nature. 1952 Jan 5;169(4288):19–20. doi: 10.1038/169019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLANDER C. S., ODAK V. V., PROUT T. E., ASPER S. P., Jr An evaluation of the role of prealbumin in the binding of thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Jun;22:617–622. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-6-617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Regulation of the peripheral metabolism of the thyroid hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1960;16:353–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Simultaneous estimation of rates of thyroxine degradation and thyroid hormone synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):808–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI103136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Studies of thyroid function and the peripheral metabolism of I 131-labeled thyroxine in patients with treated Graves disease. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1603–1614. doi: 10.1172/JCI103753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H. Observations concerning the binding of thyroid hormones by human serum prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:143–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI104701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H. Pre-albumin: a thyroxinebinding protein of human plasma. Endocrinology. 1958 Aug;63(2):256–259. doi: 10.1210/endo-63-2-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H. CLINICAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS IN A PATIENT WITH AN IDIOPATHIC DECREASE IN THE THYROXINE-BINDING GLOBULIN OF PLASMA. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40(11):2053–2063. doi: 10.1172/JCI104431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEADE B. W. Effect of certain hydroxybenzoic acids on the oxygen consumption of Wistar rats. Ann Rheum Dis. 1954 Mar;13(1):60–62. doi: 10.1136/ard.13.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYANT N. B. Relation between the biliary clearance rate of thyroxine and the binding of thyroxine by the serum proteins. J Physiol. 1957 Feb 15;135(2):426–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K., Ragan C. The Antirheumatic Effect of Sodium Gentisate. Science. 1948 Sep 10;108(2802):281–281. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2802.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SQUEF R., SURKS M. I., HAUER H. BINDING OF THYROXINE BY SERUM PROTEINS EVALUATED BY EQUILIBRUM DIALYSIS AND ELECTROPHORETIC TECHNIQUES. ALTERATIONS IN NONTHYROIDAL ILLNESS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1769–1782. doi: 10.1172/JCI104862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS J. B., INGBAR S. H. The effects of propylthiouracil and perchlorate on the biogenesis of thyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1959 Aug;65(2):198–207. doi: 10.1210/endo-65-2-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., RALL J. E. Proteins associated with the thyroid hormones. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:415–489. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs D. S., Man E. B., Winkler A. W. SERUM IODINE OF EUTHYROID SUBJECTS TREATED WITH DESICCATED THYROID. J Clin Invest. 1945 Sep;24(5):722–731. doi: 10.1172/JCI101657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEFER L. E., RASHKOFF I. A., MEGIBOW R. S. Sodium gentisate in the treatment of acute rheumatic fever. Circulation. 1950 Aug;2(2):265–270. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.2.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., CHODOS R. B. Radiothyroxine turnover studies in myxedema, thyrotoxicosis, and hypermetabolism without endocrine disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jul;35(7):806–813. doi: 10.1172/JCI103333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUROG A. Deiodination of [131-I] thyroxine on filter paper. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 18;60:197–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOEBER K. A., INGBAR S. H. Effect of salicylate on the binding of thyroxine by human serum proteins at pH 7.4. Endocrinology. 1963 Jul;73:118–119. doi: 10.1210/endo-73-1-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF J., AUSTEN F. K. Salicylates and thyroid function. II. The effect on the thyroid-pituitary interrelation. J Clin Invest. 1958 Aug;37(8):1144–1152. doi: 10.1172/JCI103704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF J., STANDAERT M. E., RALL J. E. Thyroxine displacement from serum proteins and depression of serum protein-bound iodine by certain drugs. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1373–1379. doi: 10.1172/JCI104368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]