Full text
PDF
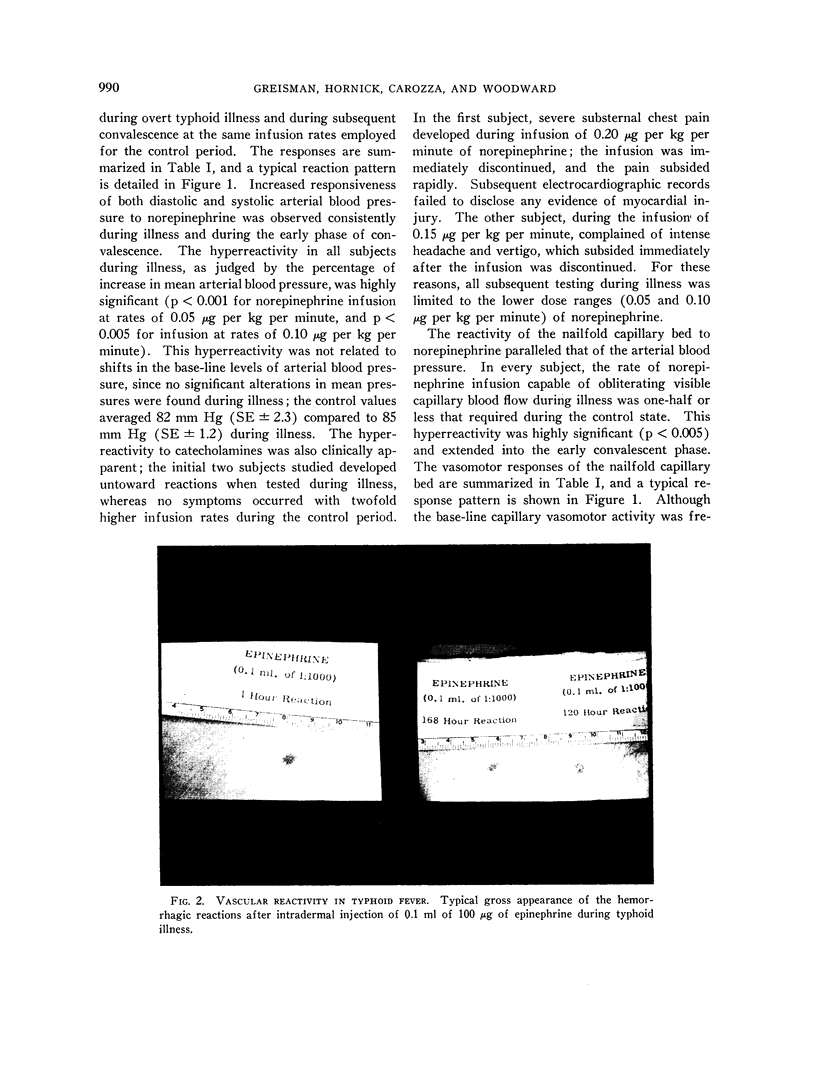

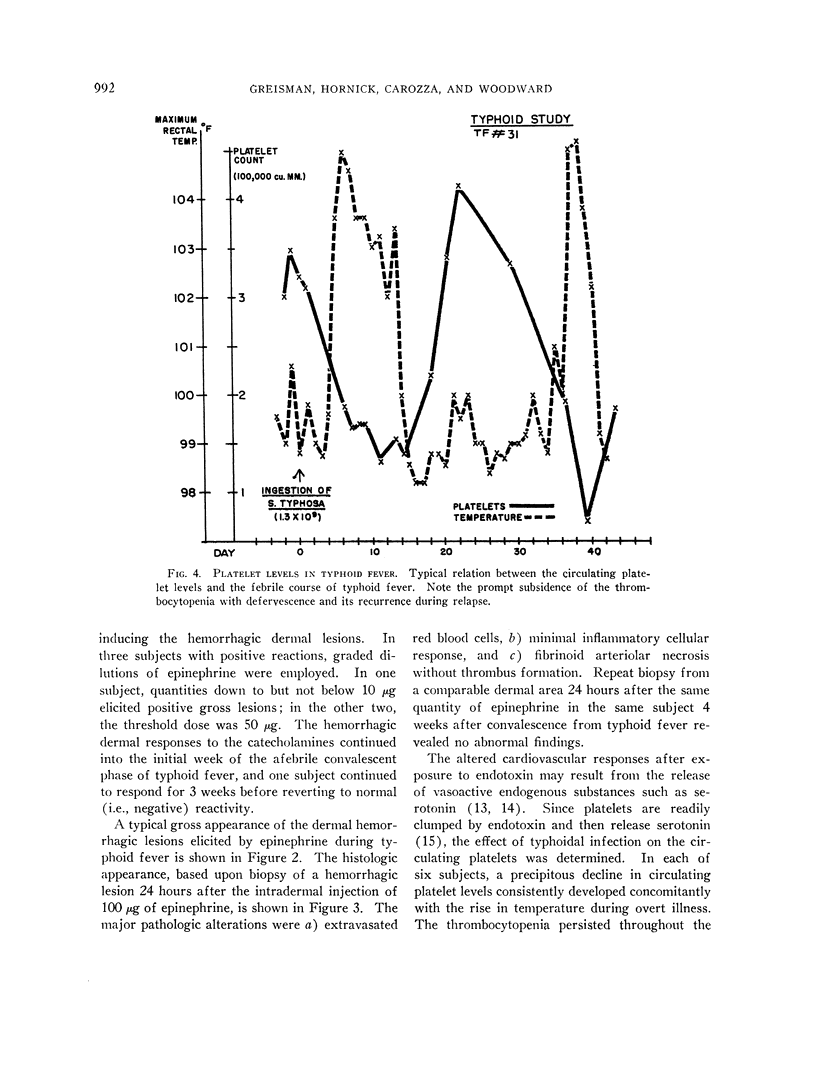
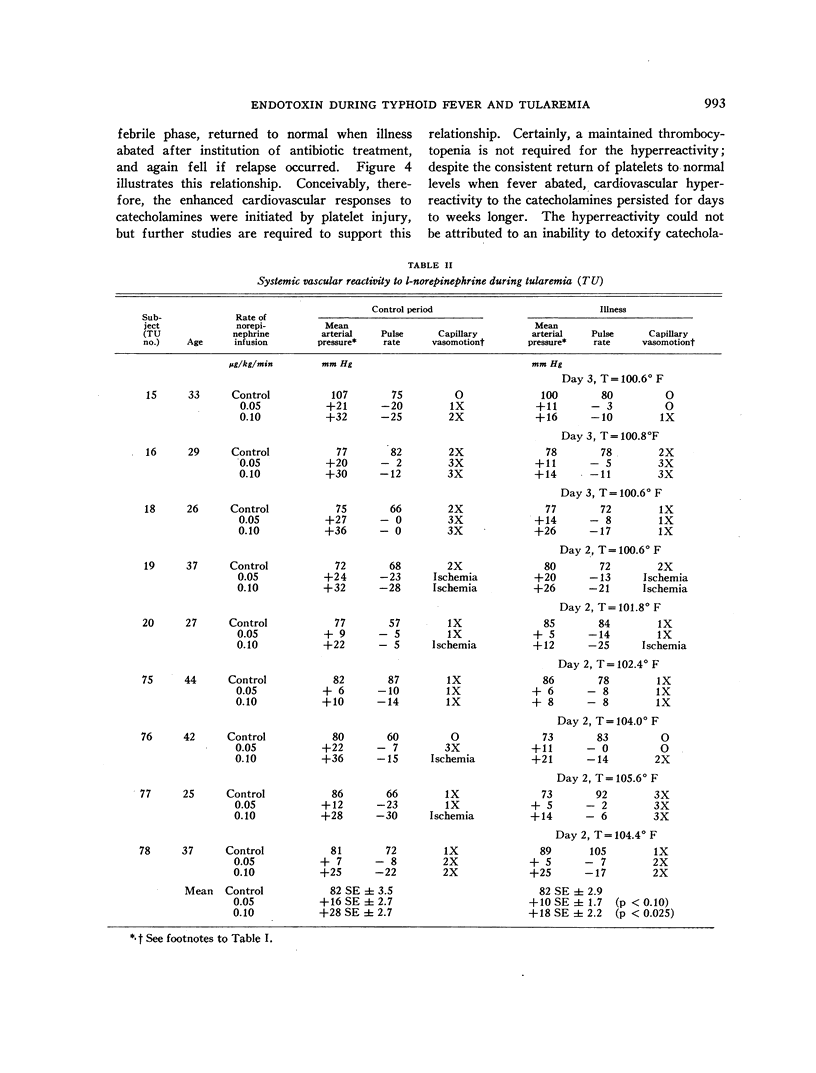
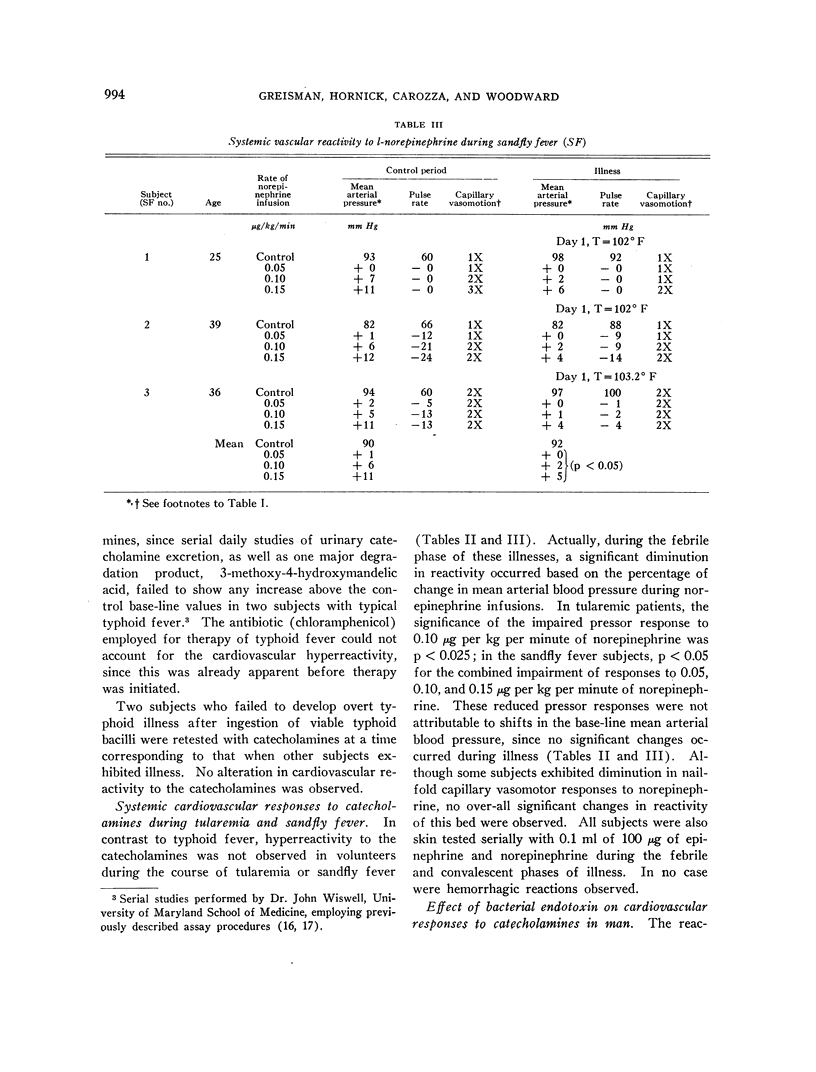
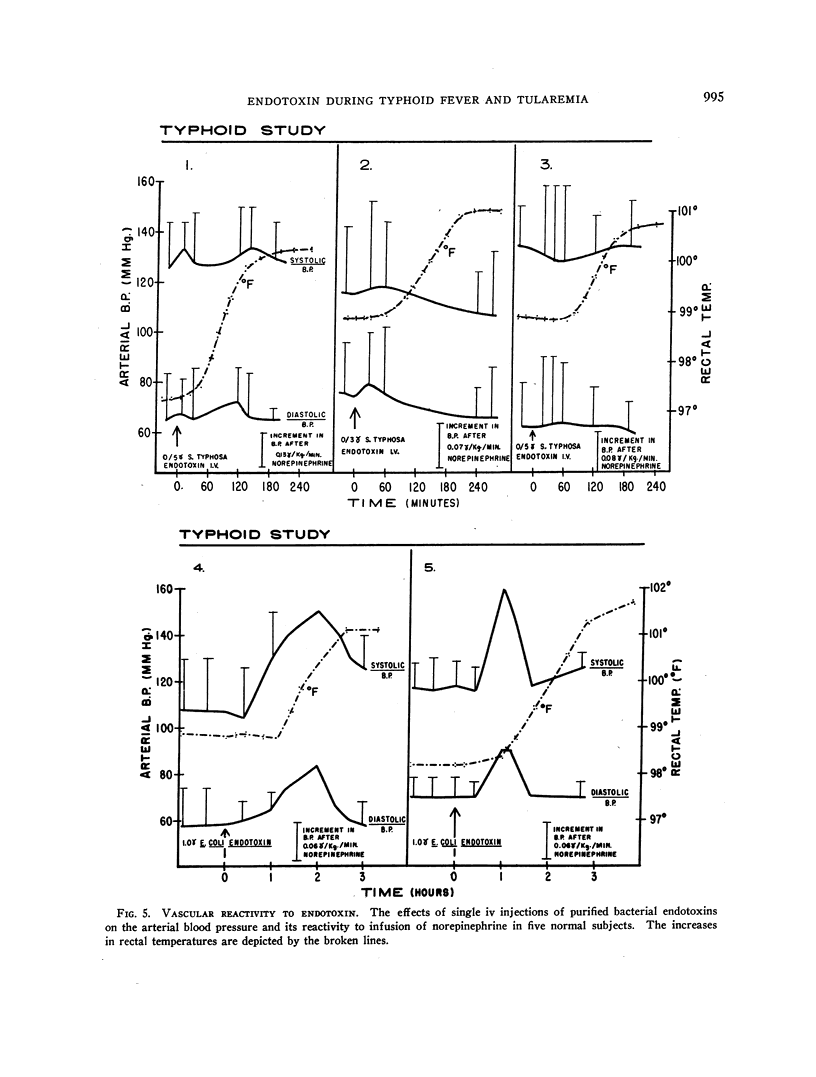




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG M. D., McMILLAN A., SHAW K. N. 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxy-D-mandelic acid, a urinary metabolite of norepinephrine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Aug;25(2):422–423. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90491-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCCINO R., LINGLEY J., ISRAEL J. Evaluation of the epinephrine skin test as a biological assay for endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Aug-Sep;110:724–726. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DES PREZ R. M., HOROWITZ H. I., HOOK E. W. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on rabbit platelets. I. Platelet aggregation and release of platelet factors in vitro. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:857–874. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., TOH C. C. Distribution of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin, enteramine) in the wall of the digestive tract. J Physiol. 1953 Feb 27;119(2-3):352–362. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRITZ H., HAGSTAM K. E., LINDQVIST B. Local reaction to epinephrine injected intradermally in man--a sign of endotoxinaemia? Acta Med Scand. 1962 Oct;172:463–472. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1962.tb07180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT R. P. Mechanisms of the hemodynamic effects of endotoxin. Physiol Rev. 1960 Apr;40:245–279. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOURZIS J. T., HOLLENBERG M. W., NICKERSON M. Involvement of adrenergic factors in the effects of bacterial endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:593–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E. Capillary observations in patients with hemorrhagic fever and other infectious illnesses. J Clin Invest. 1957 Dec;36(12):1688–1700. doi: 10.1172/JCI103570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E., HORNICK R. B., CAROZZA F. A., Jr, WOODWARD T. E. Effect of endotoxin tolerance on human typhoid fever. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1962;75:170–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E., HORNICK R. B., CAROZZA F. A., Jr, WOODWARD T. E. The role of endotoxin during typhoid fever and tularemia in man. I. Acquisition of tolerance to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1064–1075. doi: 10.1172/JCI104792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E. The reaction of the capillary bed of the nailfold to the continuous intravenous infusion of levo-nor-epinephrine in patients with normal blood pressure and with essential hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1954 Jul;33(7):975–983. doi: 10.1172/JCI102975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E., WISSEMAN C. L., Jr Studies of rickettsial toxins. IV. Cardiovascular functional abnormalities induced by Rickettsia mooseri toxin in the white rat. J Immunol. 1958 Oct;81(4):345–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREISMAN S. E., WOODWARD T. E., HORNICK R. B., SNYDER M. J. Role of endotoxin in typhoid fever. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1961 Jul;37:493–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDISTY R. M., STACEY R. S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine in normal human platelets. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):711–720. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANOFF A., NAGLER A. L., BAEZ S., ZWEIFACH B. W. Pathogenesis of experimental shock. III. A lethal factor in the blood of rabbits following occlusion of the superior mesentric artery. J Exp Med. 1961 Aug 1;114:205–216. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGLER A. L., THOMAS L., ZWEIFACH B. W. The role of epinephrine in the reactions produced by the endotoxins of gram-negative bacteria. II. The changes produced by endotoxin in the vascular reactivity to epinephrine, in the rat mesoappendix and the isolated, perfused rabbit ear. J Exp Med. 1956 Dec 1;104(6):881–896. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.6.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGLER A. L., ZWEIFACH B. W. Pathogenesis of experimental shock. II. Absence of endotoxic activity in blood of rabbits subjected to graded hemorrhage. J Exp Med. 1961 Aug 1;114:195–204. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RESNICK R. H., GRAY S. J. Distribution of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) in the human gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1961 Aug;41:119–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. The role of epinephrine in the reactions produced by the endotoxins of gram-negative bacteria. I. Hemorrhagic necrosis produced by epinephrine in the skin of endotoxin-treated rabbits. J Exp Med. 1956 Dec 1;104(6):865–880. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.6.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L., ZWEIFACH B. W., BENACERRAF B. Mechanisms in the production of tissue damage and shock by endotoxins. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1957;70:54–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., SAGIN J. F., LANDY M., JOHNSON A. G. Studies on the O antigen of Salmonella typhosa. I. Purification of the antigen. J Immunol. 1955 Jun;74(6):455–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von EULER U., LISHAJKO F. Improved technique for the fluorimetric estimation of catecholamines. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Apr;51:348–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]