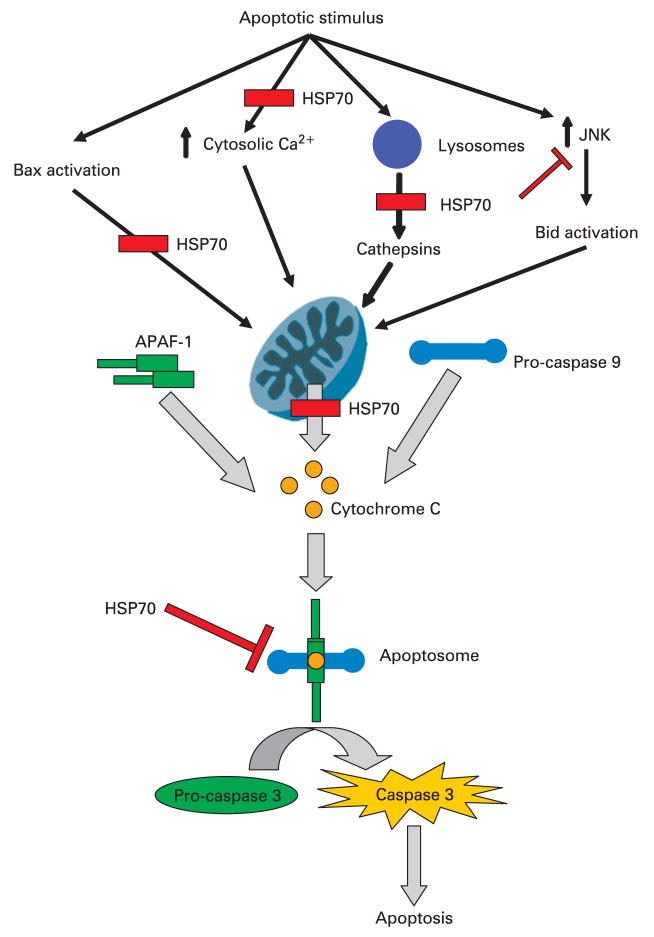
Figure 7.
A schematic diagram of the possible sites where heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) inhibits intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. It is believed that mitochondrial permeabilisation and subsequent cytochrome c release, along with other apoptosis-inducing factors, constitute central steps in apoptotic cell death. Multiple mechanisms of this mitochondrial permeabilisation have been proposed, including Bax, increased cytosolic calcium, lysosomal enzymes, and cJun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Once cytochrome c is released from the mitochondria it interacts with apoptosis protease-activating factor-1 (APAF-1) and pro-caspase 9 in the cytosol leading to formation of caspase 9 which then activates the effector caspases. These events result ultimately in apoptosis. HSP70 has been shown to inhibit apoptosis by participating in events both before and after mitochondrial membrane permeabilisation, as depicted in the figure.