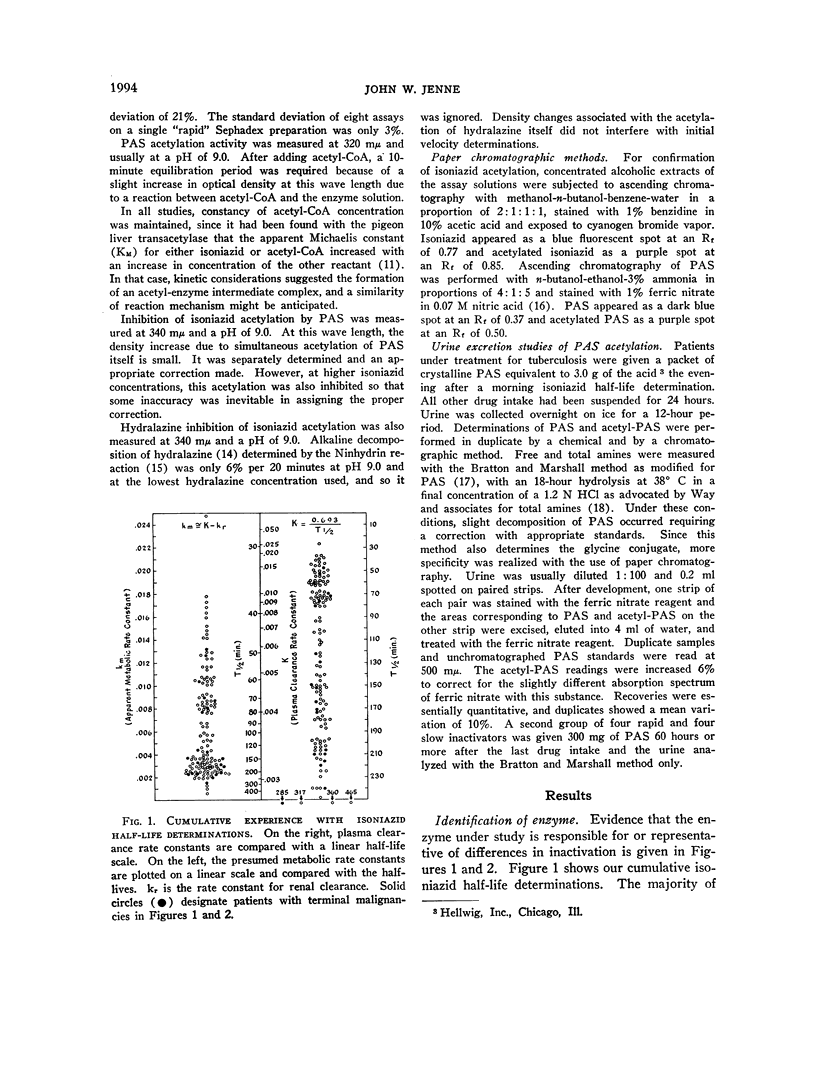
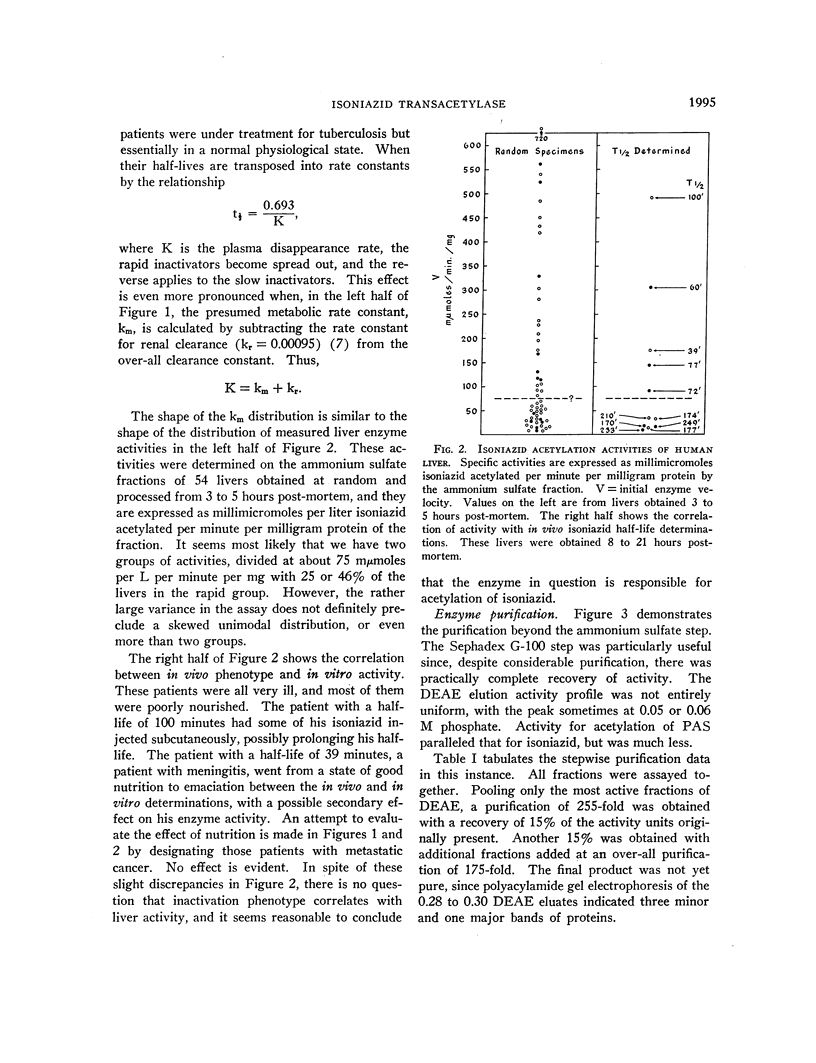
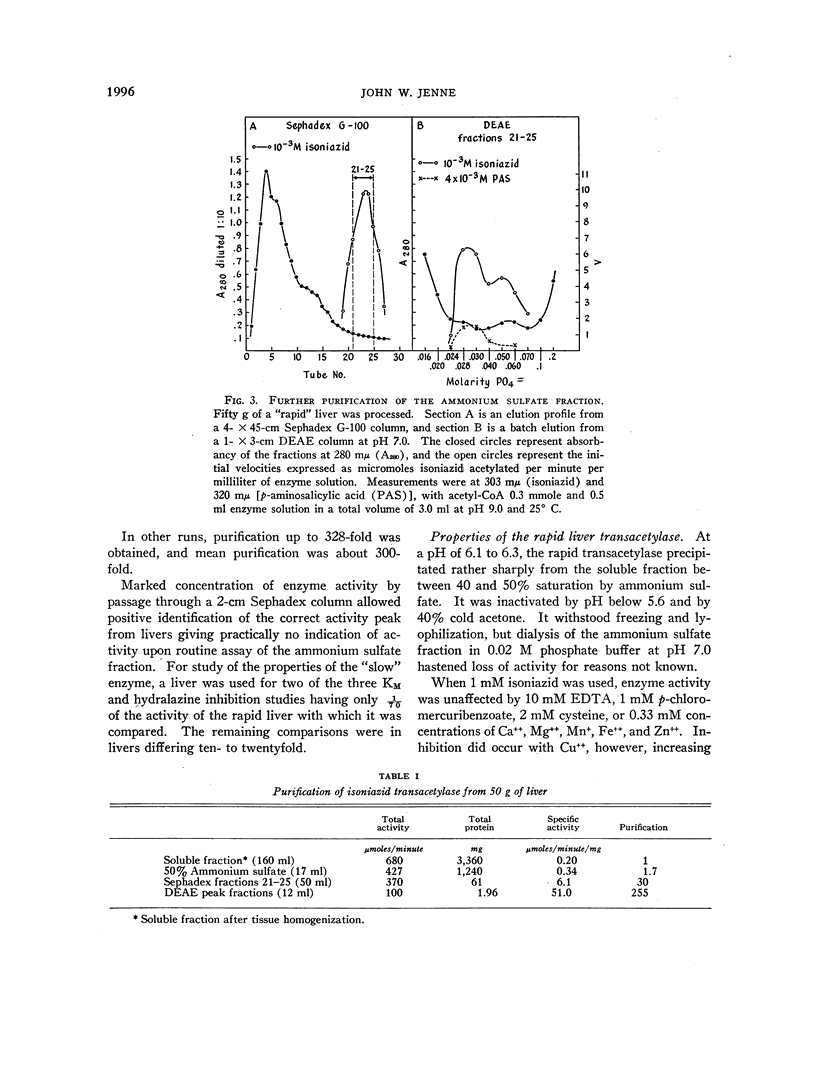
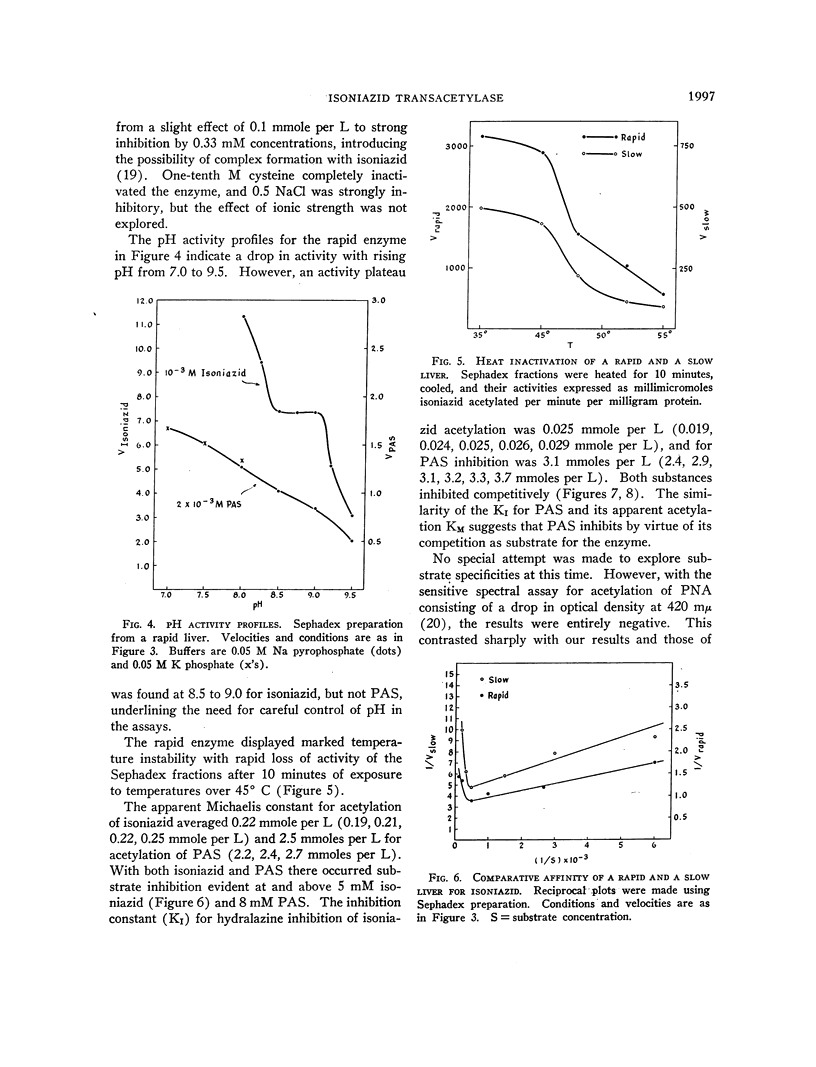
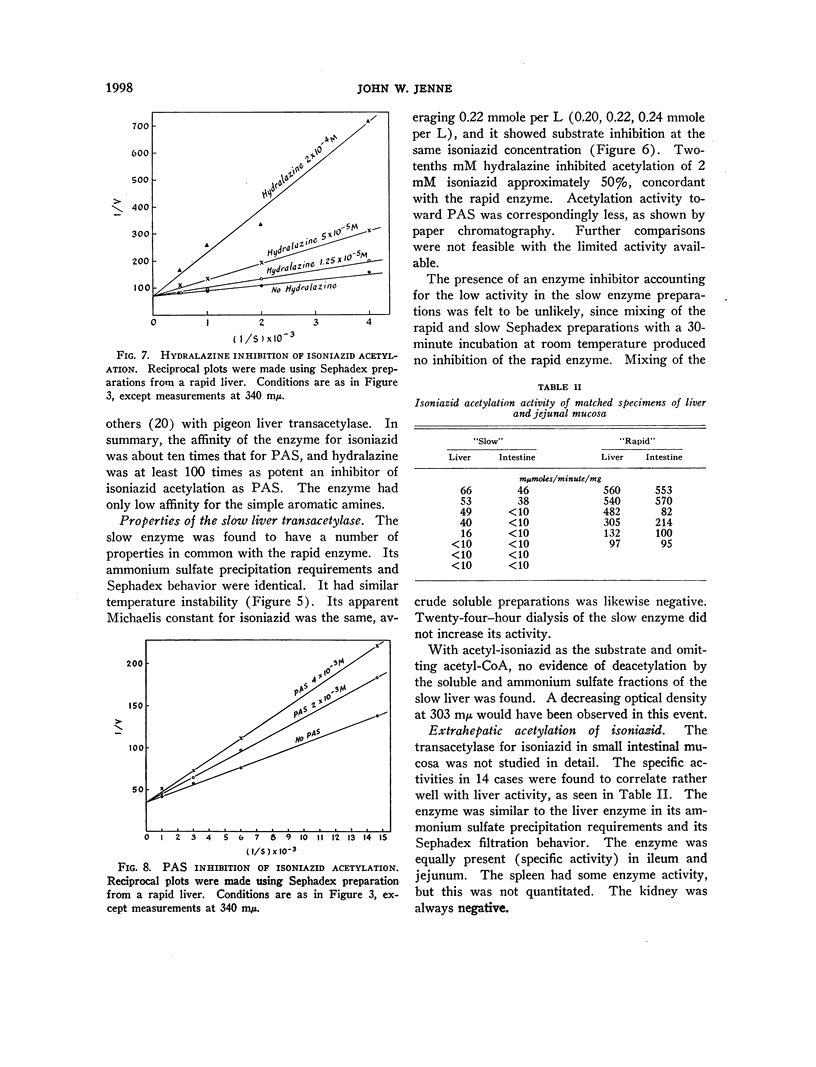
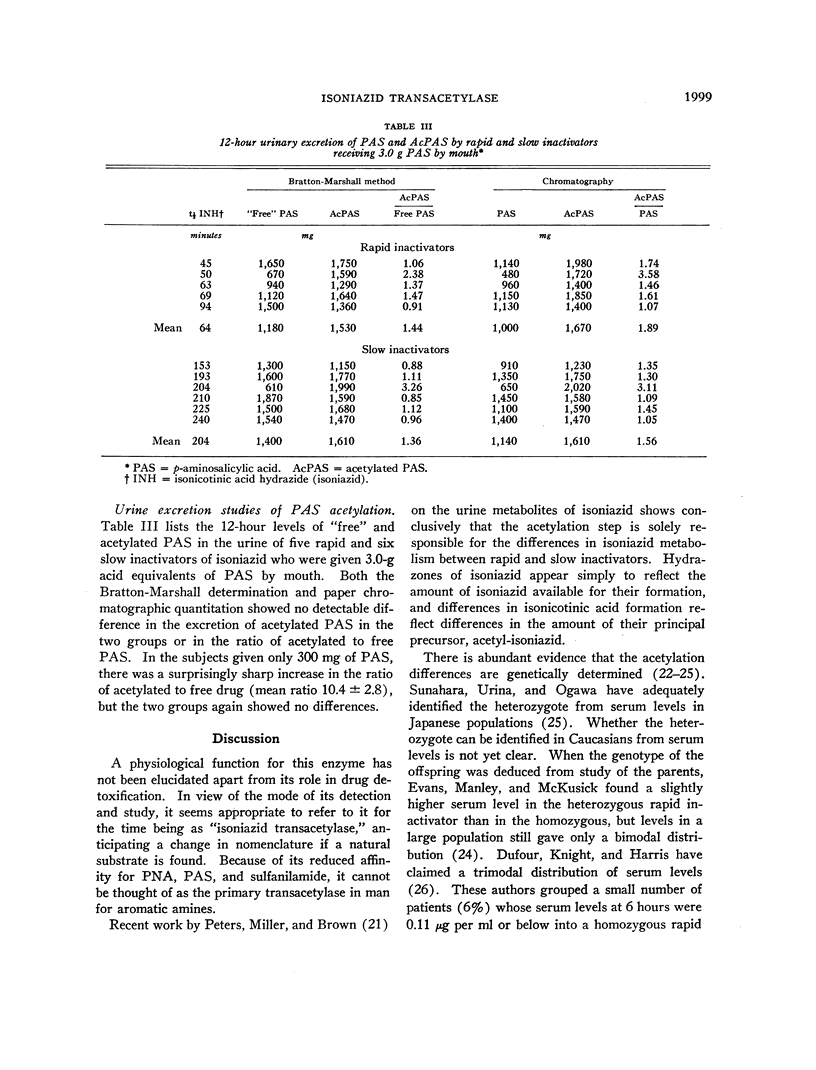
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A. The affinity of isonicotinic hydrazide for metals. Experientia. 1953 Oct 15;9(10):370–370. doi: 10.1007/BF02167635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTMANN K., MASSMANN W. [The blood level of INH in adults and children]. Beitr Klin Tuberk Spezif Tuberkuloseforsch. 1960;122:239–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUFOUR A. P., KNIGHT R. A., HARRIS H. W. GENETICS OF ISONIAZID METABOLISM IN CAUCASIAN, NEGRO, AND JAPANESE POPULATIONS. Science. 1964 Jul 24;145(3630):391–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A. ENZYMES AND DRUG SENSITIVITY. ACETYLATION POLYMORPHISMS. Proc R Soc Med. 1964 Jun;57:508–511. doi: 10.1177/003591576405700627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A., MANLEY K. A., McKUSICK V. A. Genetic control of isoniazid metabolism in man. Br Med J. 1960 Aug 13;2(5197):485–491. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5197.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A., WHITE T. A. HUMAN ACETYLATION POLYMORPHISM. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Mar;63:394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRYMOYER J. W., JACOX R. F. INVESTIGATION OF THE GENETIC CONTROL OF SULFADIAZINE AND ISONIAZID METABOLISM IN THE RABBIT. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Dec;62:891–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRYMOYER J. W., JACOX R. F. STUDIES OF GENETICALLY CONTROLLED SULFADIAZINE ACETYLATION IN RABBIT LIVERS: POSSIBLE IDENTIFICATION OF THE HETEROZYGOUS TRAIT. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Dec;62:905–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNE J. W., MACDONALD F. M., MENDOZA E. A study of the renal clearances, metabolic inactivation rates, and serum fall-off interaction of isoniazid and paraminosalicylic acid in man. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Sep;84:371–378. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.3.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNE J. W. PHARMACOKINETICS AND THE DOSE OF ISONIAZID AND P-AMINOSALICYLIC ACID IN THE TREATMENT OF TUBERCULOSIS. Antibiot Chemother. 1964;12:407–432. doi: 10.1159/000386751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNE J. W. Studies of human patterns of isoniazid metabolism using an intravenous fall-off technique with a chemical method. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Jan;81:1–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.81.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON W. J. The inhibition of sulphanilamide acetylation by aromatic and heterocyclic carboxamides and carboxhydrazides. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1955 Mar;33(2):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUENER H., FAVEZ G. The inhibition of isoniazid inactivation by means of PAS and benzoyl-PAS in man. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Jul;80(1 Pt 1):26–37. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.1P1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. Kinetic considerations in pharmacogenetic studies of drug metabolism. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(9):949–953. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY H. M., Jr A method of quantitating 1-hydrazinophthalazine in body fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):566–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS J. H., GORDON G. R., BROWN P. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE CAPACITIES OF HUMAN SUBJECTS TO ACETYLATE ISONIAZID, SULFANILAMIDE AND SULFAMETHAZINE. Life Sci. 1965 Jan;4:99–107. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS J. H. Studies on the metabolism of isoniazid. 2. The influence of para-aminosalicylic acid on the metabolism of isoniazid by man. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Aug;82:153–163. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.82.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULERT A. R. Physiological disposition of hydralazine (1-hydrazinophthalazine) and a method for its determination in biological fluids. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1961 Jun 1;132:1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNAHARA S., URANOM, OGAWAM Genetical and geographic studies on isoniazid inactivation. Science. 1961 Nov 10;134(3489):1530–1531. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3489.1530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABOR H., MEHLER A. H., STADTMAN E. R. The enzymatic acetylation of amines. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):127–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YARD A. S., MCKENNIS H., Jr ASPECTS OF THE METABOLISM OF ISONIAZID AND ACETYLISONIAZID IN THE HUMAN AND THE DOG. J Med Pharm Chem. 1962 Jan;5:196–203. doi: 10.1021/jm01236a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



