Abstract
Copper(I) and copper(II) 1,5-diaza-cis-decalin complexes [(N2)Cu] are effective pre-catalysts for aerobic oxidative coupling of naphthol substrates. Mechanistic studies, however, reveal that these complexes are not the reactive form of the catalyst under steady-state conditions. Rather, the active catalyst forms in a pre-steady-state self-processing step that involves oxygenation of the naphthol substrate. The oxygenated substrate, NapHOX, serves as a cofactor that combines with the (N2)Cu complexes to achieve highly selective, steady-state oxidase reactivity (aerobic oxidative biaryl coupling).
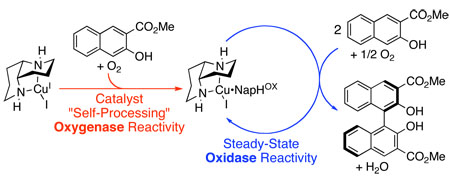
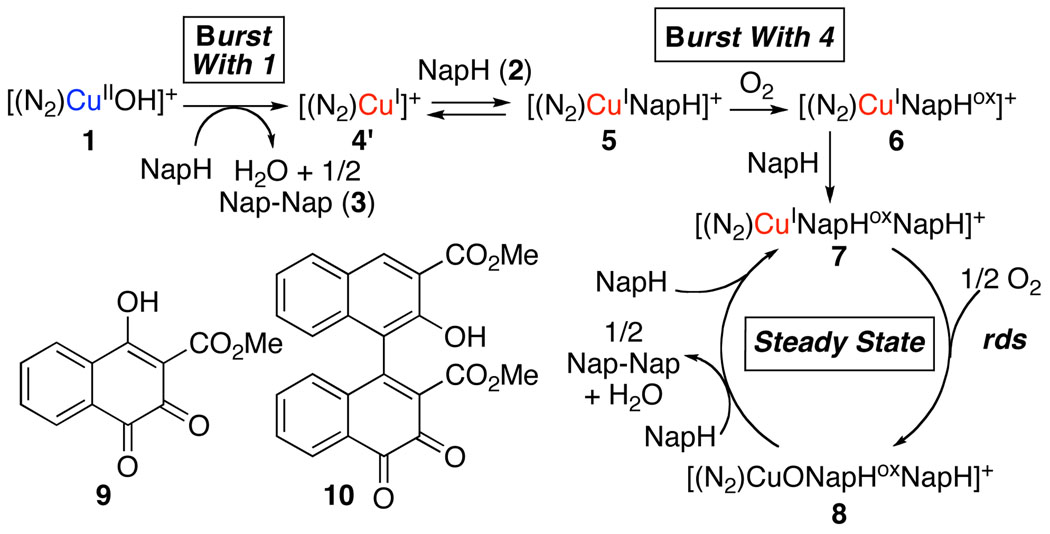
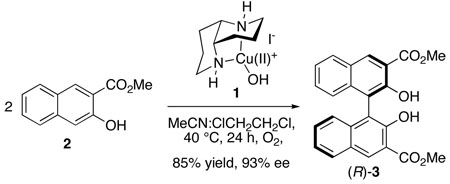
The mechanistic understanding of dioxygen activation and reactivity in biological copper-containing oxidases has grown substantially in recent years.1 Application of these insights to the development of new catalytic oxidation reactions, however, has been much more limited.2,3 We recently reported the development of an effective chemical oxidase system that achieves aerobic oxidative biaryl coupling (OBC) in high yield and enantioselectivity with a 1,5-diaza-cis-decalin copper(II) complex, (N2)CuII(OH)I (1), as the catalyst (eq 1).4,5 This chemistry has enabled the enantioselective synthesis of a variety of chiral 3,3’-disubstituted BINOL derivatives,4b binaphthyl polymers,4c and perylenequinone natural products.4d–f In order to facilitate ongoing efforts to develop new reactions, we have initiated a mechanistic study of this catalytic process. Either CuI or CuII catalyst precursors can be used to initiate the catalytic reaction, but, in both cases, we have observed an unusual kinetic "burst" phase. Mechanistic studies under pre-steady-state and steady-state reaction conditions provide intriguing insights into similarities and differences between this synthetic catalyst system and biological copper oxidases, including the ability to avoid undesired oxygen-atom-transfer ("oxygenase") reactivity under aerobic conditions.
 |
(1) |
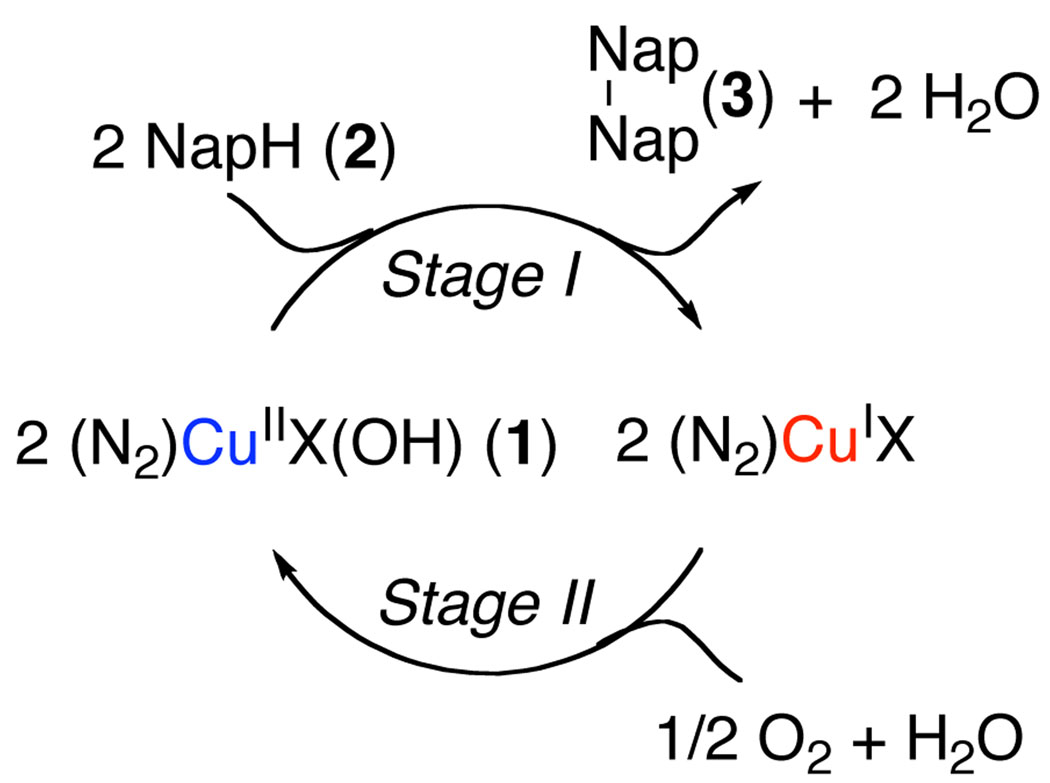
Many biological oxidase reactions proceed by a two-stage “ping-pong” mechanism consisting of two separate half-reactions: (1) substrate oxidation by the oxidized catalyst and (2) dioxygen-coupled oxidation of the reduced catalyst. Our initial studies supported such a mechanism for the OBC reaction (Scheme 1). Copper(II)-hydroxide complex 1 has been characterized crystallographically and exists as a trimer in the solid state.6 This complex is an effective copper source for catalytic OBC (eq 1) and promotes stoichiometric substrate oxidation under anaerobic conditions. Product 3 forms in a 1:2 ratio with respect to the copper concentration, indicating that 1 serves as a one-electron oxidant. The enantioselectivity of the stoichiometric reaction (91% ee) is virtually identical to that observed under catalytic conditions.
Scheme 1.
Hypothetical “Ping-Pong” Mechanism for Copper-Catalyzed Aerobic Oxidative Biaryl Coupling.
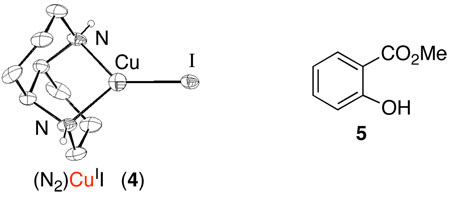
In order to probe the catalyst reoxidation step, the corresponding diaza-cis-decalin copper(I) complex, (N2)CuII, 4, was prepared. This crystallographically characterized complex is an effective copper source for the aerobic OBC reaction providing the identical enantioselectivity (93% ee) as 1. Furthermore, treatment with molecular oxygen converts 4 into 1. In the absence of the naphthol substrate 2, O2-uptake measurements reveal a 4:O2 stoichiometry of 4:1 with or without unreactive substrate analog 5. Although details of the copper(I)-dioxygen reaction pathway remain to be elucidated, these observations, together with the substrate oxidation reaction, support the proposed oxidase pathway in Scheme 1.
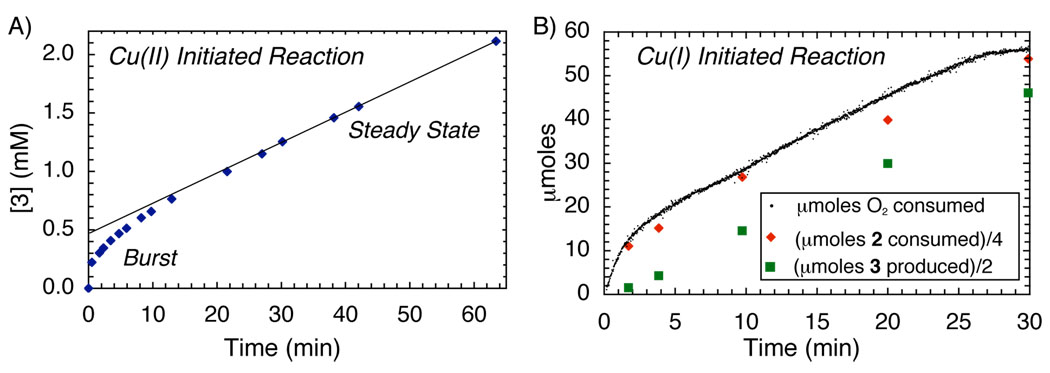
The kinetics of the catalytic reactions were analyzed by HPLC measurement of substrate and product concentrations and by continuous gas manometry. When the reaction was initiated with CuII complex 1, the timecourse (Figure 1A) revealed an initial burst of product formation followed by slower steady-state turnover. The burst reflects stoichiometric oxidation of the substrate by 1, resulting in formation of approximately 0.5 equiv of product. The slower steady-state rate suggests that the chemistry of OBC (Stage I, Scheme 1) is not rate determining and points to reoxidation of the catalyst by O2 (Stage II, Scheme 1) as the rate-determining step.
Figure 1.
A) Kinetic time-course for product (3) formation in the OBC with catalyst 1 from HPLC. Conditions: [2] = 94 mM, [4-biphenyl phenyl ether] = 23 mM, [1] = 2 mM, atmospheric O2, MeCN, 40 °C. B) Kinetic time-course for the OBC with catalyst 4. (●) actual O2 uptake; ( ) µmols [2] consumed divided by 4; (
) µmols [2] consumed divided by 4; ( ) µmols [3] formed divided by 2. Conditions: [2] = 151 mM, [4] = 10 mM, pO2 = 840 Torr, [4-Biphenyl phenyl ether] = 42 mM, 6 mL MeCN, 40 °C. Concentrations of 2 and 3 determined by GC.
) µmols [3] formed divided by 2. Conditions: [2] = 151 mM, [4] = 10 mM, pO2 = 840 Torr, [4-Biphenyl phenyl ether] = 42 mM, 6 mL MeCN, 40 °C. Concentrations of 2 and 3 determined by GC.
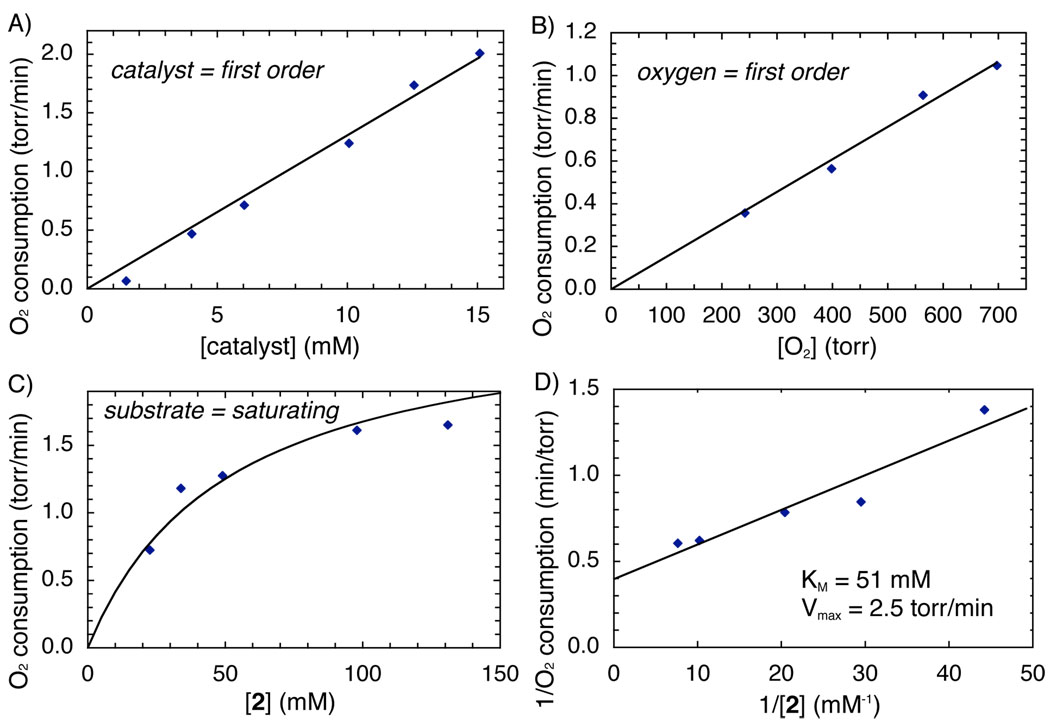
Reactions with CuI complex 4 were examined with the expectation of a linear product-formation profile associated with the steady-state rate in Figure 1A. However, another burst phase was observed, this time corresponding to the rapid consumption of one-quarter equivalent of molecular oxygen (Figure 1B). Formation of product 3 was not observed until after the oxygen-uptake burst. The steady-state catalytic turnover rate is identical for both catalyst precursors, and kinetic analysis reveals that this rate exhibits a first-order dependence on [4] and [O2] (Figures 2A and 2B). Taken together, these data indicate that aerobic oxidation of the catalyst is indeed the turnover-limiting step of the reaction (Stage II, Scheme 1). The gas-uptake burst observed with 4 as the catalyst precursor, however, indicates that 4 itself cannot be the catalyst resting state.
Figure 2.
Dependencies of steady-state rate in MeCN at 40 °C. A) Dependence on catalyst 4 concentration: [2] = 120 mM, pO2 normalized to 849 Torr. B) Dependence on initial O2 pressure: [2] = 190 mM, [4] = 10 mM. C) Dependence on substrate 2 concentration: [4] = 13 mM, pO2 normalized to 849 Torr. D) Lineweaver-Burk plot of Figure 2C.
The burst behavior with CuI complex 4 provides a clue into the identity of the actual catalyst. Figure 1B reveals that substrate 2 is consumed in the burst; however, this material is not transformed into product 3, but instead yields a substrate oxygenation product, designated NapHOX. This oxygenase reactivity is not observed after the burst phase is complete. During steady-state turnover, substrate 2 is converted exclusively into product 3 (Figure 1B). These results suggest selective oxidase reactivity arises from enlistment of a cofactor, NapHOX, formed in a catalyst "self-processing" event analogous to that characterized in biological catalysts, such as amine oxidases.7 We speculate that the combination of NapHOX with the (N2)Cu complex forms the kinetically competent catalyst (e.g., 6, Scheme 2) that effects the highly selective oxidase activity observed in the OBC reaction (Scheme 2). NapHOX is likely a quinone as supported by the isolation of ortho-quinones 9 and 10 from reaction mixtures that were halted within the first turnover (5 min).
Scheme 2.
“Sequential” Mechanism for Copper-Catalyzed Aerobic OBC Consistent with the Kinetic Data.
Oxidation of a substrate/Cu-cofactor complex, such as 7, is proposed to be the rate-determining step under steady-state conditions. The “sequential” mechanism in Scheme 2 differs from the “ping pong” mechanism often encountered in biological oxidase catalysis; however, this proposal accounts for the first order dependencies of catalyst precursor [4] and [O2], and the saturation dependence on the substrate [2] (Figure 2).
In conclusion, several unique features of the catalytic OBC with 1,5-diaza-cis-decalin copper complexes have been identified. Copper complexes 1 and 4 are effective pre-catalysts for the OBC reaction, but they do not comprise the active redox couple under steady-state conditions. Copper(I) complex 4 exhibits pre-steady-state oxygenase activity in the presence of substrate 2 to produce a cofactor that alters the reactivity of the Cu catalyst. The modified catalyst reacts somewhat more slowly with O2 than 4, but it exhibits exclusive oxidase activity, achieving C–C bond formation with enantioselectivities nearly identical to those obtained in the stoichiometric oxidative coupling reaction promoted by CuII complex 1. Further studies are needed to elucidate the precise identity of the cofactor NapHOX and the steady-state catalyst 7, but the present results highlight important opportunities to achieve selective modulation of oxidase vs. oxygenase activity in aerobic oxidation reactions.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgment
Financial support was provided by the NSF (MCK: CHE-0616885), the NIH (MCK: CA109164), and the DOE (SSS: DE-FG02-05ER15690). The invaluable assistance of Dr. Patrick Carroll in obtaining the X-ray structure is gratefully acknowledged. We thank B.A. Steinhoff for helpful discussions and assistance with gas-uptake kinetics experiments.
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available: Experimental procedures and kinetic data. This material is available free of charge via the internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.For selected reviews, see: Mirica LM, Ottenwaelder X, Stack TDP. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:1013. doi: 10.1021/cr020632z. Lewis EA, Tolman WB. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:1047. doi: 10.1021/cr020633r. Hatcher LQ, Karlin KD. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2004;9:669. doi: 10.1007/s00775-004-0578-4. Solomon EI, Chen P, Metz M, Le S, Palmer AE. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001;40:4570. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20011217)40:24<4570::aid-anie4570>3.0.co;2-4.
- 2.Noteworthy success has been achieved in aerobic alcohol oxidation. For leading references, see: Wang YD, DuBois JL, Hedman B, Hodgson KO, Stack TDP. Science. 1998;279:537. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5350.537. Chaudhuri P, Hess M, Muller J, Hildenbrand K, Bill E, Weyhermuller T, Wieghardt K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:9599. Marko IE, Gautier A, Dumeunier RL, Doda K, Philippart F, Brown SM, Urch CJ. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004;43:1588. doi: 10.1002/anie.200353458. Gamez P, Arends I, Sheldon RA, Reedijk J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004;346:805.
- 3.For a survey of "bio-inspired" copper-catalyzed oxidation reactions, including industrial examples see: Gamez P, Aubel PG, Driessen WL, Reedijk J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2001;30:376–385. Punniyamurthy T, Rout L. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2008;252:134. Thomas F. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007:2379. van der Vlugt JI, Meyer F. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2007;22:191–240.
- 4.(a) Li X, Yang J, Kozlowski MC. Org. Lett. 2001;3:1137. doi: 10.1021/ol015595x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Li X, Hewgley JB, Mulrooney CA, Yang JM, Kozlowski MC. J. Org. Chem. 2003;68:5500. doi: 10.1021/jo0340206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Xie X, Phuan PW, Kozlowski MC. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2003;42:2168. doi: 10.1002/anie.200250325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Mulrooney CA, Li X, DiVirgilio ES, Kozlowski MC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:6856. doi: 10.1021/ja027745k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) DiVirgilio ES, Dugan EC, Mulrooney CA, Kozlowski MC. Org. Lett. 2007;9:385–388. doi: 10.1021/ol062468y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) O’Brien EM, Morgan; BJ, Kozlowski MC. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Early View. [Google Scholar]
- 5.For related work, see: Smrcina M, Polakova J, Vyskocil S, Kocovsky P. J. Org. Chem. 1993;58:4534. Nakajima M, Kanayama K, Miyoshi I, Hashimoto S. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995;36:9519. Nakajima M, Miyoshi I, Kanayama K, Hashimoto S-I. J. Org. Chem. 1999;64:2264. Kim KH, Lee DW, Lee YS, Ko DH, Ha DC. Tetrahedron. 2004;60:9037. Roithova J, Schroder D. Chem. Eur. J. 2008;14:2180. doi: 10.1002/chem.200701277.
- 6.Kozlowski MC, Li XL, Carroll PJ, Xu ZR. Organometallics. 2002;21:4513. [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Klinman JP. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2001;98:14766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.011602498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Mure M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004;37:131. doi: 10.1021/ar9703342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Brazeau BJ, Johnson BJ, Wilmot CM. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004;428:22. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.03.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Du-Bois JL, Klinman JP. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005;433:255. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.08.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.