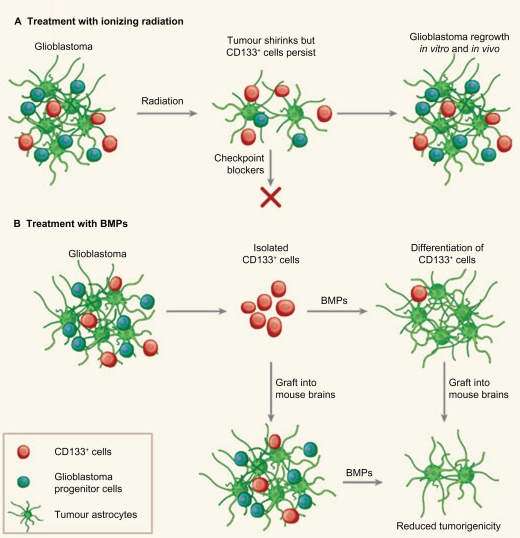
Figure 1.
Glioblastomas are heterogeneous tumors that contain a few tumor-initiating CD133+ stem cells among other, more differentiated, CD133− cells, including glioblastoma progenitor cells. A) Following radiation, the bulk glioblastoma responds and the tumor shrinks. But CD133+ cells activate checkpoint controls for DNA repair more strongly than CD133− cells, resist radiation and prompt the tumor to regrow. These cells could be targeted with DNA-checkpoint blockers to render them radiosensitive. B) BMPs normally cause NSCs to differentiate into astrocytes. When used to treat isolated glioblastoma CD133+ cells, they weaken the cells’ tumorigenicity both in vitro and when engrafted into mice, in vivo. The knowledge that a tumor retains a developmental hierarchy suggests that targeting different cell populations is a promising therapeutic strategy. Copyright © 2006, Nature Publishing Group. Reprinted with permission from Dirks PB. Cancer: stem cells and brain tumours. Nature. 2006;444 (7120):687–688.
Abbreviation: BMPs, bone morphogenic proteins.