Full text
PDF

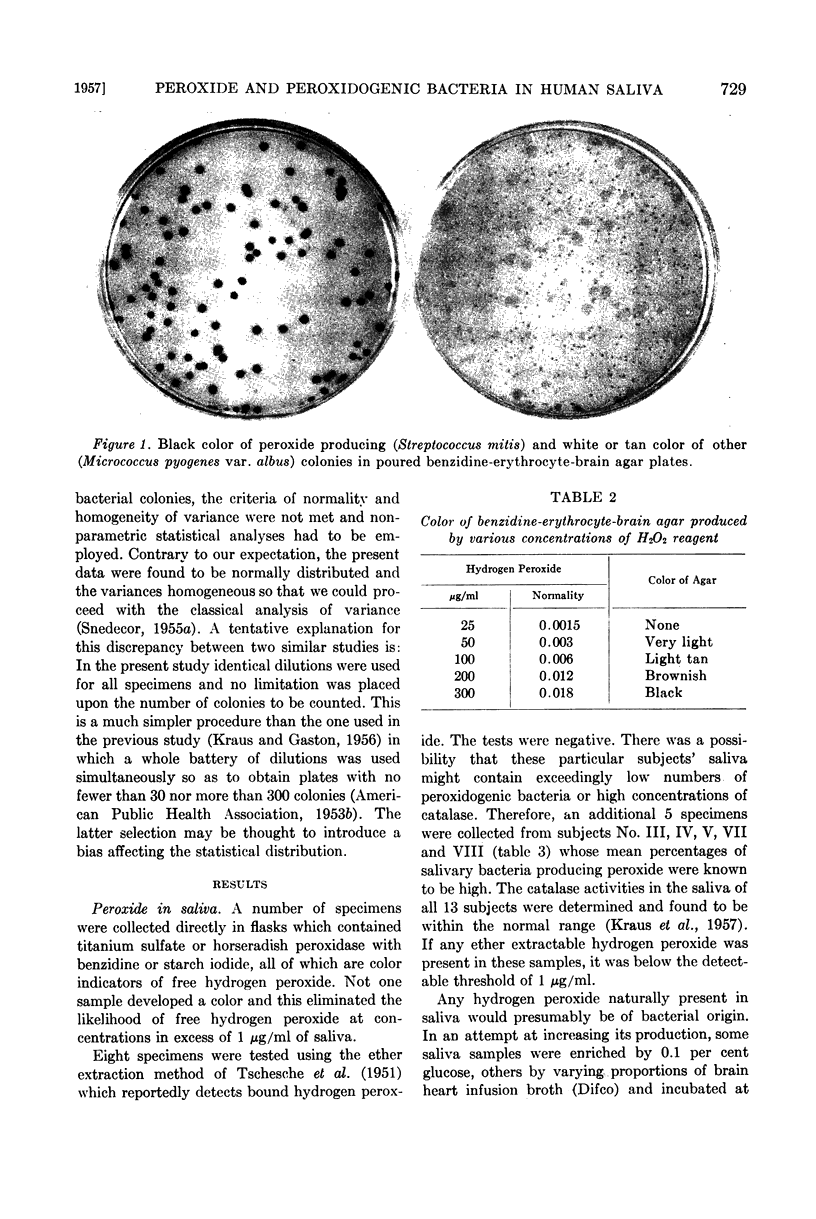

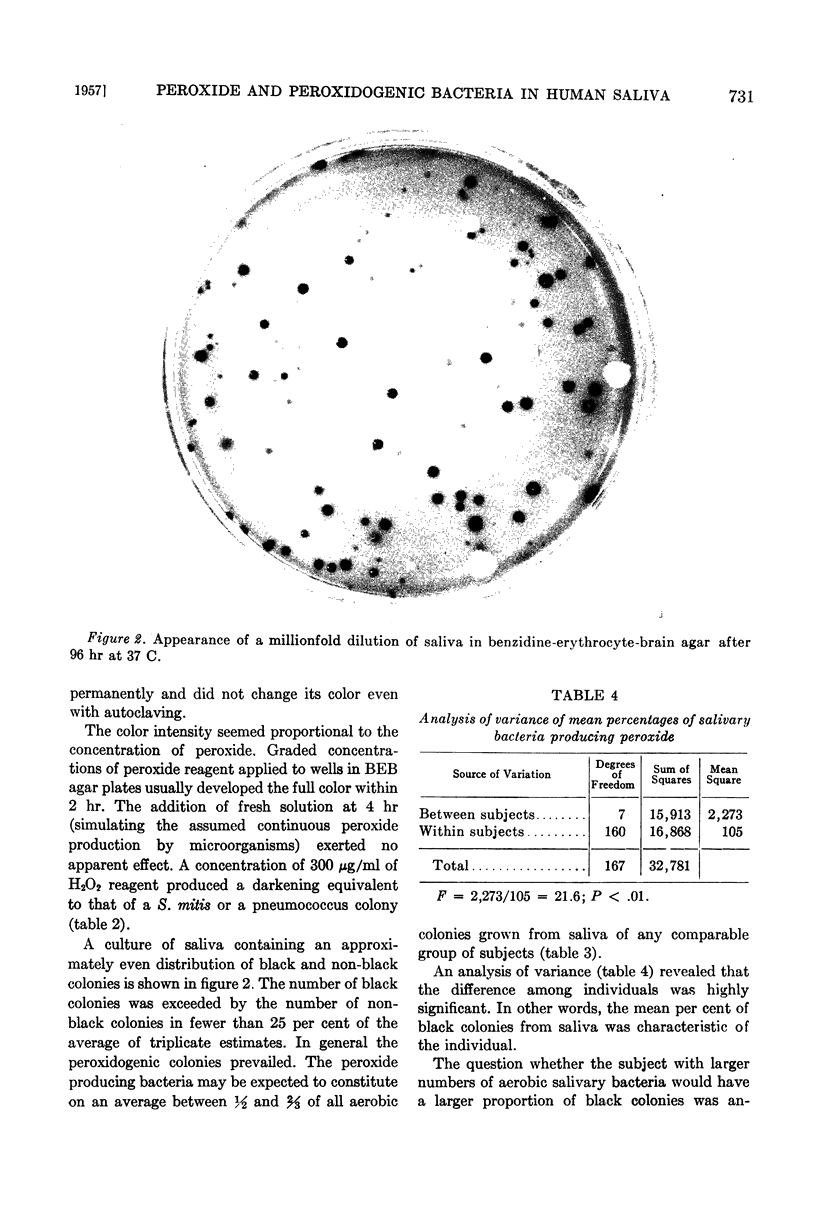
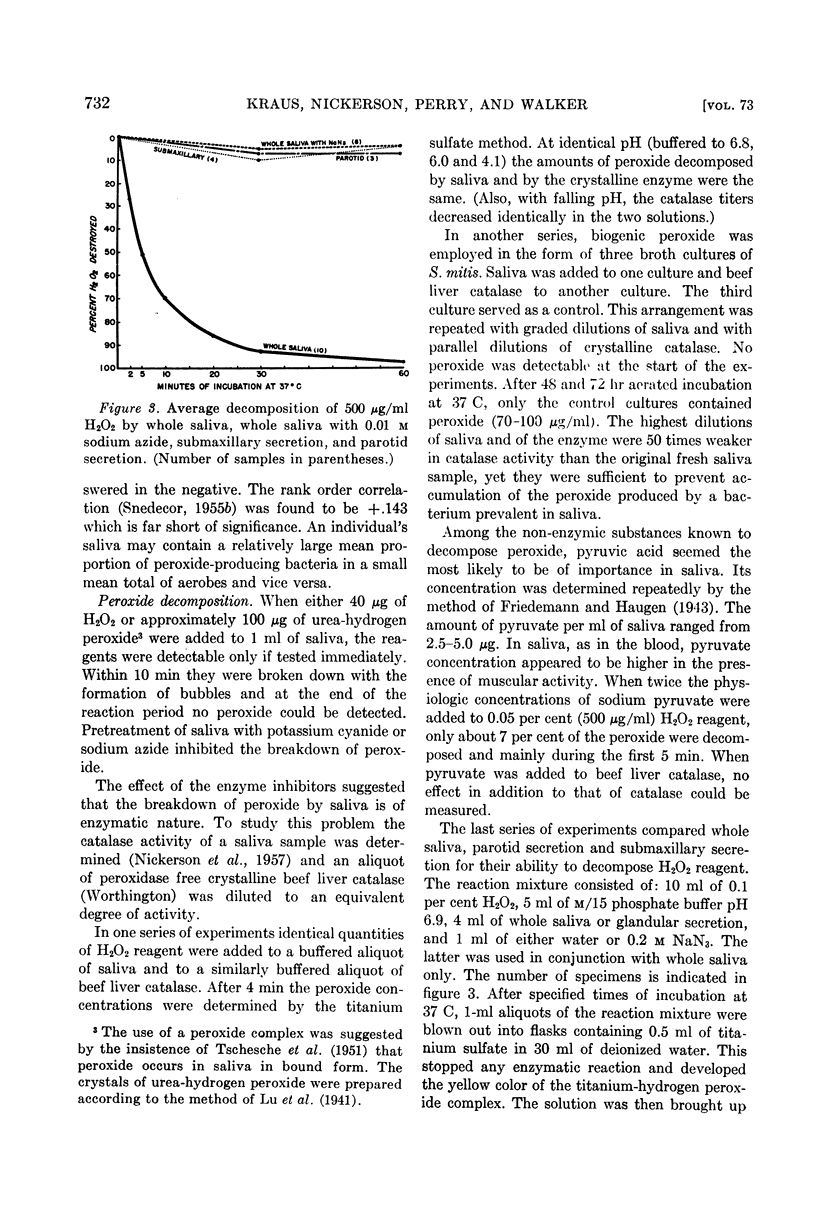



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNEAR D. I., DORMAN D. C. Hydrogen peroxide accumulation during growth of the pneumococcus. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1952 Apr;30(2):191–195. doi: 10.1038/icb.1952.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANNEAR D. I. Mixed bacterial growth. III. Studies on the mixed growths of a viridans streptococcus, a diphtheroid and Staphylococcus albus. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1951 Mar;29(2):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER U. Uber Hydroperoxydproduktion bei gramnegativen Bakterien; zugleich ein Beitrag zur Diagnostik H2O2-bildender Mikroorganismen. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1952;134(2):162–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER U. Uber die Züchtung antibiotischer Keime aus der Luft. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1951;133(2):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt L. F. Oxidation-reduction potentials of pneumococcus cultures: Effect of catalase. Biochem J. 1931;25(1):169–176. doi: 10.1042/bj0250169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUS F. W., GASTON C. Individual constancy of numbers among the oral flora. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jun;71(6):703–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.6.703-707.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilin D., Hartree E. F. Properties of catalase. Catalysis of coupled oxidation of alcohols. Biochem J. 1945;39(4):293–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. W., Gordon J. Production of Hydrogen Peroxide by Bacteria. Biochem J. 1922;16(4):499–506. doi: 10.1042/bj0160499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN R., BIRD L. H. Suppression of catalase activity by peroxidase and its substrates. Biochem J. 1951 Aug;49(3):335–338. doi: 10.1042/bj0490335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON R., JOHNSON A. The inhibitory action of saliva on the diphtheria bacillus: hydrogen peroxide, the inhibitory agent produced by salivary streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1951 Jan-Feb;88(1):81–85. doi: 10.1093/infdis/88.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]