Abstract
Triglyceride synthesis in most mammalian tissues involves the sequential addition of fatty acids to a glycerol backbone, with unique enzymes required to catalyze each acylation step. Acylation at the sn-2 position requires 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase (AGPAT) activity. To date, seven Agpat genes have been identified based on activity and/or sequence similarity, but their physiological functions have not been well established. We have generated a mouse model deficient in AGPAT6, which is normally expressed at high levels in brown adipose tissue (BAT), white adipose tissue (WAT), and liver. Agpat6-deficient mice exhibit a 25% reduction in body weight and resistance to both diet-induced and genetically induced obesity. The reduced body weight is associated with increased energy expenditure, reduced triglyceride accumulation in BAT and WAT, reduced white adipocyte size, and lack of adipose tissue in the subdermal region. In addition, the fatty acid composition of triacylglycerol, diacylglycerol, and phospholipid is altered, with proportionally greater polyunsaturated fatty acids at the expense of monounsaturated fatty acids. Thus, Agpat6 plays a unique role in determining triglyceride content and composition in adipose tissue and liver that cannot be compensated by other members of the Agpat family.
Supplementary key words: acyltransferase, gene-trap, adipose tissue, energy expenditure, 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase
Triglycerides are the primary form of energy storage in mammals, and alterations in triglyceride biosynthesis and metabolism can lead to metabolic diseases such as hyperlipidemia, obesity, and lipodystrophy. In eukaryotes, two major pathways exist for triglyceride synthesis: the glycerol phosphate pathway and the monoacylglycerol pathway. The monoacylglycerol pathway functions predominantly in small intestine to generate triglycerides from monoacylglycerol in dietary fat. The glycerol phosphate pathway, in contrast, is considered the main pathway for triglyceride synthesis and occurs in most cells types. In particular, it is responsible for triglyceride synthesis in adipose tissue. Acylation of glycerol phosphate occurs through a step-wise addition of acyl groups, each addition being catalyzed by a distinct enzyme (1, 2). In recent years, the cloning and identification of several of these enzymes has facilitated their molecular characterization, but many questions remain about the physiological functions of these enzymes.
To date, only a few mouse models with genetic deficiency in the triglyceride biosynthetic pathway have been reported. Mice lacking the mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT), which catalyzes the addition of the first acyl group to glycerol-3-phosphate, showed reduced levels of triglycerides in plasma and liver (3). They also had reduced body weight and adipose tissue mass. Deficiency in acyl-coenzyme A:diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 (DGAT1), responsible for the final step in triglyceride synthesis, leads to reduced adiposity and resistance to diet-induced obesity (4). Dgat1-deficient (Dgat1−/−) mice also showed increased energy expenditure, attributable in part to increased locomotor activity and increased levels of uncoupling protein-1, insulin, and leptin (4–6). Interestingly, Dgat1−/− mice had dry fur and hair loss, which were associated with atrophic sebaceous glands and abnormal lipid composition in the fur (7). Mice deficient in DGAT2 had a marked reduction in triglyceride synthesis and died at birth (8). These studies demonstrated that DGAT2 is essential for viability and that DGAT1 is unable to compensate for a deficiency in DGAT2.
Although GPATs and DGATS catalyze the initial and final acylation steps in triglyceride synthesis from glycerol phosphate, the 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase (AGPAT) enzymes act at an intermediate step. The product of the GPAT reaction, lysophosphatidic acid, is again acylated, this time by an AGPAT, to form phosphatidic acid (1, 2). Several AGPAT proteins have been reported and designated AGPAT1 through AGPAT7. An eighth related sequence was identified recently and designated AGPAT8 (accession number NP_766303; (9)). AGPAT1 and AGPAT2 are well characterized, and their enzymatic activity has been documented (10, 11), whereas the other AGPAT family members were identified based upon sequence homology (12–14) or very modest activity levels (15). Mutations in Agpat2 have been reported in patients with congenital generalized lipodystrophy (16, 17), but no genetically modified animal model of any member of the AGPAT family has been generated. To investigate the importance of AGPAT enzymes in triglyceride biosynthesis and metabolism, we created and characterized a mouse model deficient in one of the most recently described family members, AGPAT6 (previously designated LPAAT-ζ) (13). We identified the mouse Agpat6 gene from sequence tags within the BayGenomics database. We used Agpat6 knockout embryonic stem cells to produce Agpat6−/− mice and then characterized the physiological role of this enzyme in adipose tissue and lipid metabolism.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Generation of Agpat6−/− mice
Mouse embryonic stem cells containing a gene-trap insertion in the Agpat6 gene (cell line number DTM030) were obtained from the BayGenomics gene-trap consortium (baygenomics.ucsf.edu) (18). The insertion of the gene-trap into the Agpat6 gene was verified by direct sequencing of an ES cell cDNA obtained by 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends. Chimeric mice were generated by blastocyst injection and bred to C57BL/6J mice to establish lines carrying the insertional mutation in Agapt6. Offspring were genotyped by PCR with primers specific for the wild-type Agpat6 allele (Agpat6-F, ggattcaagcactcggcagtc; Agpat6-R, gctctacgagaggcaagagg) and for lacZ in the gene-trap allele (LacZ-F, actggcagatgcacggttacg; LacZ-R, cgtagtgtgacgcgatcggca). The combination of the two primer sets made it possible to distinguish mice homozygous for the wild-type allele, heterozygous mice, and mice homozygous for the mutant allele. All blood and tissue samples were obtained after an overnight (16 h) fast. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane gas. Plasma was stored with EDTA at −80°C. Tissues were dissected, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C.
Body weight studies
To minimize the number of mice used, weight curves were generated from male mice fed a standard laboratory chow diet (Purina 5001) and from female mice fed a high-fat/high-carbohydrate (HF/HC) diet (Diet F3282; Bioserve, Frenchtown, NJ). A limited number of female mice were also studied on the chow diet and showed similar results as males (data not shown). To generate Agpat6−/− mice on an obese genetic background, Agpat6+/− mice were crossed with Lep+/ob (C57BL/6J background; obtained from Jackson Laboratory), and Agpat6+/− Lep+/ob offspring were intercrossed to produce Agpat6−/− Lepob/ob animals. Because of the generation of greater numbers of female animals, analysis was restricted to females.
Gene expression analyses
Total RNA was isolated from mouse tissues by extraction with TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Two micrograms of RNA was reverse-transcribed with oligo(dT) and random primers (Invitrogen). Five percent of the resulting cDNA was used for each RT-PCR or real-time PCR. Real-time PCR was performed in triplicate with Quantitect SYBR Green PCR mix (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) in an iCycler Realtime Detection System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) as described (19). Standard curves were constructed with four serial dilution points of control cDNA (100 ng–100 pg). Data presented were derived from starting quantity (SQ) values of each sample normalized by the square root of the product of values obtained for the housekeeping genes Hprt (for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase) and Tbp (for TATA box binding protein) (20). Primer sequences used in these studies have either been described previously (21, 22) or are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Primer sequences used in real-time PCR experiments
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Agpat1 | cacccaggatgtgagagtctg | ctgacaacgtccaggcgagg |
| Agpat2 | gcaacgacaatggggacctg | acagcatccagcacttgtacc |
| Agpat3 | ctttaccacggcagtccagtg | tgcttgtacatctcttgcaggg |
| Agpat4 | ccagcctcaaacaccacctg | gagcacttgtcctcatcctcc |
| Agpat5 | agctgcagagctatgtgaacg | tcaaaagcaacgtgagtggcc |
| Agpat6 | ggcagaggagctggagtc | tgttgtggtacgtaatgatgg |
| Agpat7 | gacagtggctggtgccttcag | ctttgtacagcagccggtcag |
|
Agpat8 (GenBank accession number NM_172715) |
gtacatgcctcccatgactag | gatccgttgcccacgatcatc |
| Peroxisome proliferators- activated receptor γ coactivator-1α |
ctgcgggatgatggagacag | cgttcgacctgcgtaaagt |
Agpat, 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase.
Histology
Fresh tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and then dehydrated, cleared, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 4 µm, and stained with hematoxylin/eosin. For β-galactosidase staining, tissues were fixed and stained as described previously (23). For adipose size measurement, randomly selected sections from three wild-type mice and three Agpat6−/− mice were used. Sections were digitized, and cell surface area was quantified with NIH Image 1.62 (Wayne Rasband, National Institutes of Health). Cells from each treatment (n = 200) were analyzed to obtain a mean ± SD in arbitrary units.
Plasma glucose, leptin, and insulin
Glucose levels were determined with a One Touch Ultra Blood Glucose Monitor (Lifescan, Milpitas, CA). Insulin levels were determined with an ultrasensitive murine enzyme immunoassay (ALPCO Diagnostics, Windham, NH). Leptin levels were measured by immunoassay (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). Measurements were made in duplicate samples according to the manufacturers’ protocols.
Indirect calorimetry and core body temperature
Activity and oxygen consumption were determined with an Oxymax single cage system and recorded with Oxymax version 3.2 software (Columbus Instruments, Columbus, OH). Horizontal and vertical activity were determined with light beams positioned at 2 and 5 cm from the bottom of the cage to record distance walked by the mouse (cm/h) and rearing on hind legs (counts/h). Oxygen consumption and CO2 production were recorded every 6 min throughout a 24 h period. Values were averaged over light (7 AM–6 PM) and dark (6 PM–7 AM) periods. Core body temperature was measured in all mice with a Ret-3 mouse rectal probe attached to a BAT-10 multipurpose digital thermometer (Physitemp Instruments, Clifton, NJ).
Lipid analysis
For tissue lipid analysis, samples were homogenized in 0.25 M sucrose, 20 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.5, 5 mM EDTA, and 1 mM PMSF with a mechanical ultra-turrax (Janke & Kunkel, Cincinnati, OH). Total proteins were quantified for normalization between samples (BCA kit; Pierce, Rockford, IL), and triglycerides were measured with L-Type TG H reagents (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Richmond, VA) in homogenates or after Folch lipid extraction (24). Thin-layer chromatography was also performed on Folch lipid extracts. Briefly, tissue homogenates were extracted with chloroform-methanol (2:1, v/v). After vortexing and centrifugation, the organic phase was dried under N2, lipids were resuspended in chloroform, and chromatography was performed on silica gel plates with a hexane-ethyl ether-acetic acid (80:20:1) solvent system. Lipids were visualized with iodine vapor and identified based on comigration with lipid standards. For quantitative analysis of the lipid metabolome, plasma and tissues (n = 3 for each group) in chow-fed mice were processed as described previously (25). Data are expressed as fold difference compared with the wild-type mice or percentage of the lipid class, as indicated in the text.
RESULTS
Expression patterns of eight Agpat genes
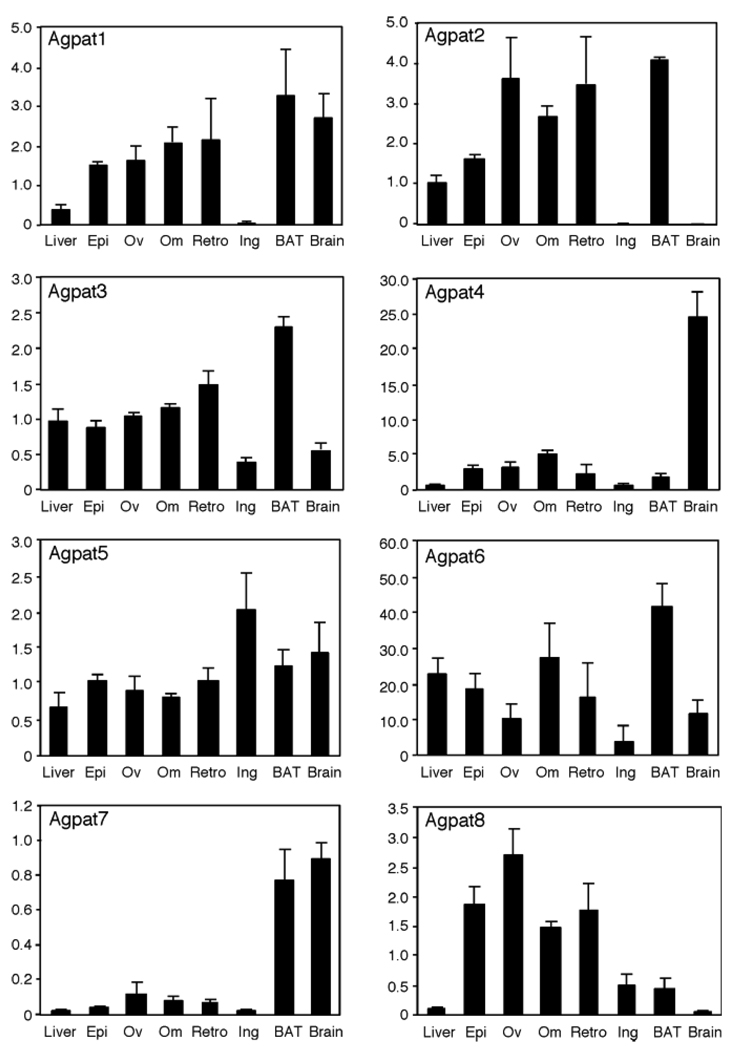
The Agpat6 cDNA was initially cloned from human (known as LPAAT-ζ), and examination in a limited set of tissues showed highest expression in skeletal muscle (13). A reassessment of the tissue distribution of Agpat6 mRNA in a larger set of mouse tissues by Northern blot revealed prominent expression in adipose tissue (brown adipose > white adipose) and liver, as well as in testis, with low expression in skeletal muscle (9). To further characterize the mRNA expression distribution of Agpat6 and other family members, we performed real-time RT-PCR in several fat depots, liver, and brain from C57BL/6J mice. Figure 1 shows that among adipose tissue depots, Agpat6 mRNA is expressed at highest levels in intrascapular brown adipose tissue (BAT), with high levels also detected in visceral white adipose tissue (WAT) depots (omental, epididymal, and retroperitoneal fat pads), and much lower levels were seen in subcutaneous (inguinal) fat tissue. Expression in liver was similar to that in visceral WAT, suggesting a function for AGPAT6 in tissues with important roles in triglyceride metabolism, including fat and liver. A similar expression analysis of the other putative Agpat genes revealed that BAT is also a major site of expression for Agpat1, Agpat2, Agpat3, and Agpat7. All of the genes except Agpat4 and Agpat7 exhibited substantial expression in WAT, with visceral depots being the major site for WAT expression for all genes except Agpat5, which showed highest expression in inguinal WAT. Agpat4 had a distinct pattern, with expression mainly in brain, whereas the closest homolog of Agpat6, Agpat8, was restricted primarily to WAT, with no expression in brain or liver. These results show that the Agpat gene family members have distinct, but overlapping, gene expression patterns.
Fig. 1.
mRNA levels of 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase (AGPAT)-related enzymes in different tissues. Data were obtained by real-time PCR from three individual C57BL/6J mice. Values shown represent means ± SD in arbitrary units, normalized as described in Materials and Methods. Epi, epididymal fat; Ov, ovarian fat; Om, omental fat; Retro, retroperitoneal fat; Ing, inguinal fat; BAT, brown adipose tissue.
Generation of Agpat6−/− mice by gene-trap
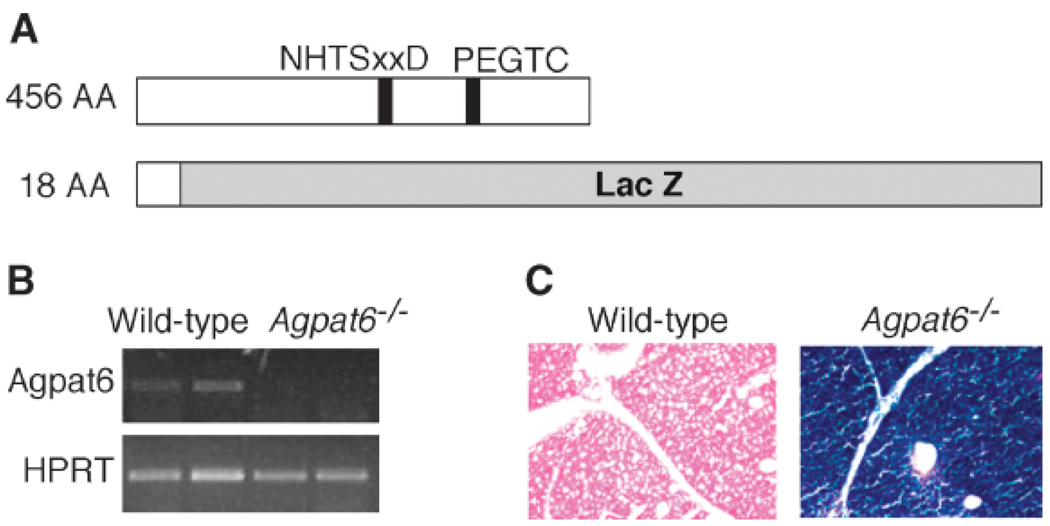
To produce Agpat6−/− mice, we used an embryonic stem cell line carrying an insertional mutation in Agpat6 (BayGenomics cell line DTM030). The insertion is located in intron 2 of Agpat6 (which contains 13 exons and 12 introns) and results in the production of a fusion transcript containing the first two Agpat6 exons joined in-frame to a βgeo reporter gene. The resulting fusion protein is expected to contain only the first 55 amino acids of AGPAT6, which would be reduced to 18 amino acids upon cleavage of the signal peptide (Fig. 2A). This deletion, therefore, eliminates most of the protein, including the conserved motifs implicated in catalysis (NHTSxxD) and glycerol-3-phosphate binding (PEGTC) (9, 26).
Fig. 2.
Generation of Agpat6-deficient (Agpat6−/−) mice. A: Scheme representing the wild-type protein and the AGPAT6−/− fusion protein generated from the gene-trap allele. The size of the AGPAT6 protein portion in amino acids (AA) is noted at left. NHTxxD and PEGTC indicate the putative catalytic and glycerol-3-phosphate binding domains, respectively. B: RT-PCR showing the absence of normal AGPAT6 mRNA in Agpat6−/− mice. Primers used to amplify AGPAT6 cDNA were localized downstream of the gene-trap vector insertion site. HPRT, hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. C: β-Galactosidase staining of a BAT section. The AGPAT6-βgeo fusion protein shows strong staining throughout the BAT. Magnification, 20×.
ES cells carrying the Agpat6 mutation were injected into mouse blastocysts, and chimeric offspring were bred to produce heterozygous Agpat6 knockout mice. Homozygous mutant mice were obtained at the predicted Mendelian frequency, indicating that the AGPAT6 protein is not required for survival. The absence of Agpat6 mRNA in homozygous mice was confirmed by RT-PCR using primers in the 3′ portion of the transcript (Fig. 2B). Staining of BAT from Agpat6−/− mice for lacZ expression revealed a strong blue stain in BAT (Fig. 2C), in agreement with the gene expression data. To determine whether the expression of other members of the Agpat gene family was upregulated in response to AGPAT6 deficiency, we measured mRNA expression of Agpat1–Agpat8 in BAT of the mutant mice. No significant differences in expression levels were observed between wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice (data not shown).
Agpat6−/− mice have reduced body weight and fat mass and are resistant to obesity
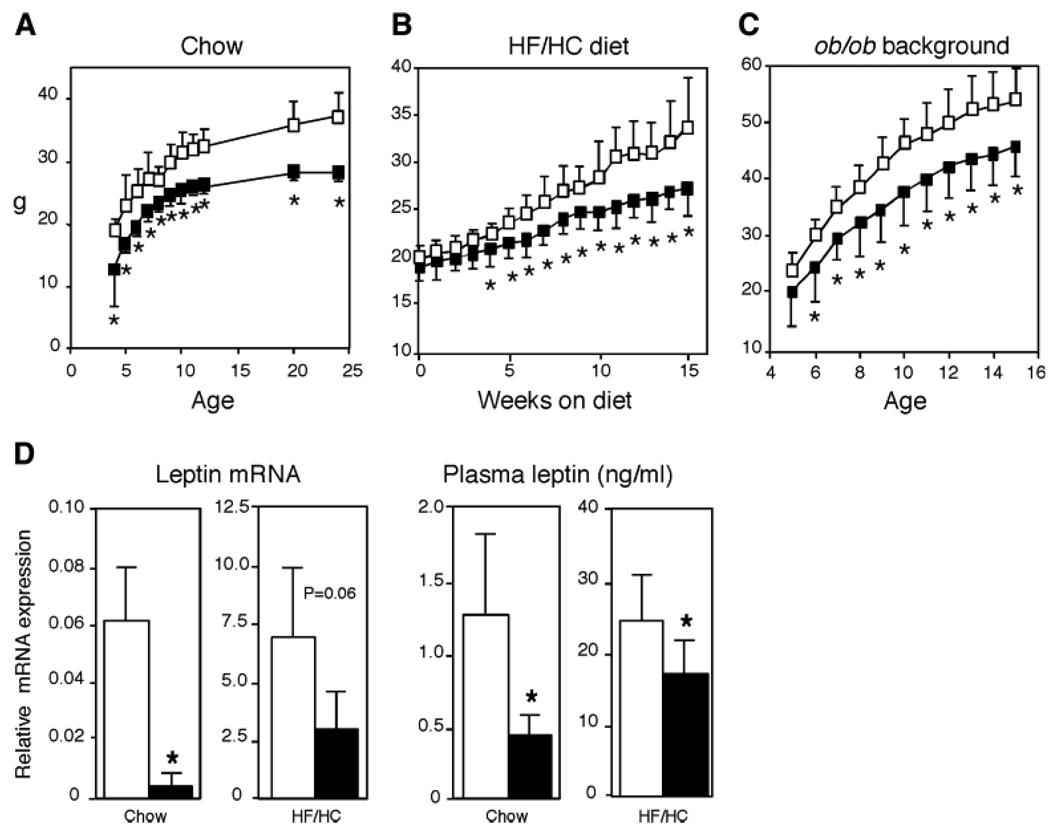
Based on its prominent expression in adipose tissue and its predicted role in triglyceride biosynthesis, we hypothesized that Agpat6 deficiency might affect adipose tissue mass and body weight. Analysis of body weight in Agpat6−/− mice from weaning through 6 months of age revealed substantially lower body weight than in wild-type or Agpat6+/− mice (Fig. 3A). At 6 months of age, the Agpat6−/− mice showed a reduction of 10 g (~25%) in body weight. Analysis of the total carcasses of mice from which WAT and BAT depots had been removed showed a tendency toward a lower percentage of carcass fat in Agpat6−/− mice (12.0 ± 4.5% vs. 6.1 ± 2.7%), although this difference did not reach significance (P = 0.065, n = 4 in each group). To determine whether Agpat6 deficiency confers resistance to obesity, wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice were fed a HF/HC diet for 15 weeks or crossed onto the genetically obese leptin-deficient ob/ob background. On both the HF/HC diet and the ob/ob background, Agpat6−/− mice maintained significantly lower body weight and did not become obese (Fig. 3B, C). Thus, Agpat6 deficiency protects against both diet-induced obesity and genetically induced obesity.
Fig. 3.
Body weight curves and leptin levels in wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice. A: Male mice fed a chow diet from birth to 25 weeks of age. Chow-fed female mice were not analyzed at all time points but exhibited a similar significant difference in body weight compared with wild-type mice at 6 months of age (data not shown). B: Female mice fed a high-fat/high-carbohydrate (HF/HC) diet for 15 weeks beginning at 8 weeks of age. Male mice were not analyzed. C: Female mice on an ob/ob background from 5 to 15 weeks of age. Male mice were not analyzed. For A–C, open and closed squares represent wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice, respectively (n = 8 in each group). D: The left panels represent leptin mRNA levels in gonadal fat tissue determined by real-time PCR (n = 4 for each group). The right panels show plasma leptin levels obtained by ELISA. Open and closed bars represent wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice, respectively. Chow-fed values were from the male mice shown in A and used epididymal fat tissue; HF/HC values were from female mice shown in B and used periuterine fat tissue. * P < 0.05.
To determine whether the reduced body weight in Agpat6−/− mice was attributable to decreased adipose tissue mass, we isolated gonadal and inguinal WAT and interscapular BAT fat pads. There was a significant decrease in the proportion of body weight composed of gonadal fat on both chow (1.7 ± 0.26% vs. 1.2 ± 0.14%; P < 0.05) and HF/HC (6.7 ± 2.1% vs. 4.6 ± 1.4%; P < 0.05) diets. These differences in fat mass were reflected in reduced leptin mRNA in adipose tissue and circulating leptin levels on both chow and high-fat diets (Fig. 3D). Although body weight was clearly reduced by Agpat6 deficiency, no significant differences in percentage of fat mass were observed in wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice on the ob/ob background. Agpat6−/− mice exhibited no difference from wild-type mice in proportional liver weight on either chow or HF/HC diet or on the obese genetic background.
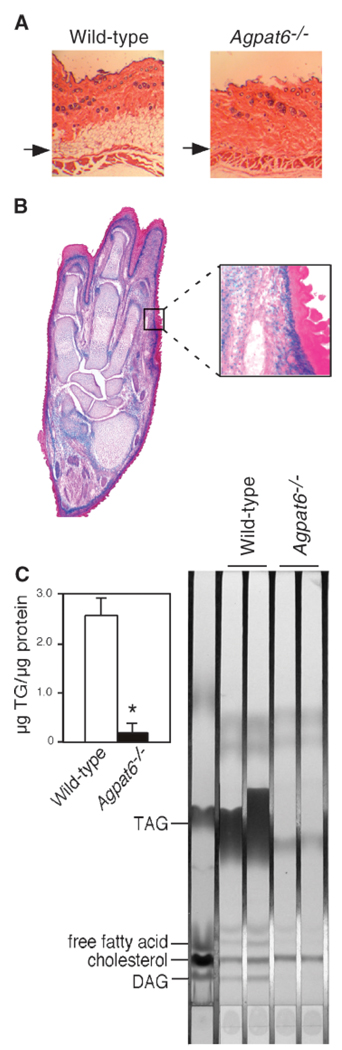
Subdermal lipodystrophy in Agpat6−/− mice
Histological examination of adipose tissue depots revealed major differences between wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice. First, we observed an absence of subdermal fat in the skin of Agpat6−/− mice that were older than 4 months of age (Fig. 4A). Staining for β-galactosidase expression in Agpat6−/− skin sections revealed substantial Agpat6 expression in the subdermal layer (Fig. 4B). We did not observe changes in the thickness of the epidermis, in the number of fat cells surrounding the sebaceous glands, or in the cellular infiltration of the dermis in Agpat6−/− mice. However, lipid extraction of skin biopsies revealed a striking reduction in triglyceride content in Agpat6−/− mice (Fig. 4C). Analysis of neutral lipid species in skin by thin-layer chromatography confirmed a striking depletion of triglycerides, diacylglycerols (DAGs), and free fatty acids in Agpat6−/− lipid extracts, whereas cholesterol levels appeared normal (Fig. 4C). To determine whether lipid depletion in the skin affected the integrity and function of the fur coat, we assessed water repulsion with a swimming test (7). No differences were observed between wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice (data not shown). Thus, Agpat6 deficiency leads to a subdermal lipodystrophy but does not appear to alter permeability functions of the fur.
Fig. 4.
Subdermal adipose tissue deficiency in the Agpat6−/− mouse. A: Skin cross-sections with hematoxylin/eosin. Arrows indicate the presence of the fat cell layer in wild-type mice but not in Agpat6−/− mice. Magnification, 160×. B: Left, β-galactosidase staining of a paw cross-section from an Agpat6−/− mouse showing AGPAT expression in the subdermal layer. Magnification, 40×. Right, close-up of the boxed region at left. Magnification, 100×. C: Triglyceride (TG) levels (left) and neutral lipid species determined by thin-layer chromatography (right) from skin lipid extracts of chow-fed mice. DAG, diacylglycerol; TAG, triacylglycerol. * P < 0.001.
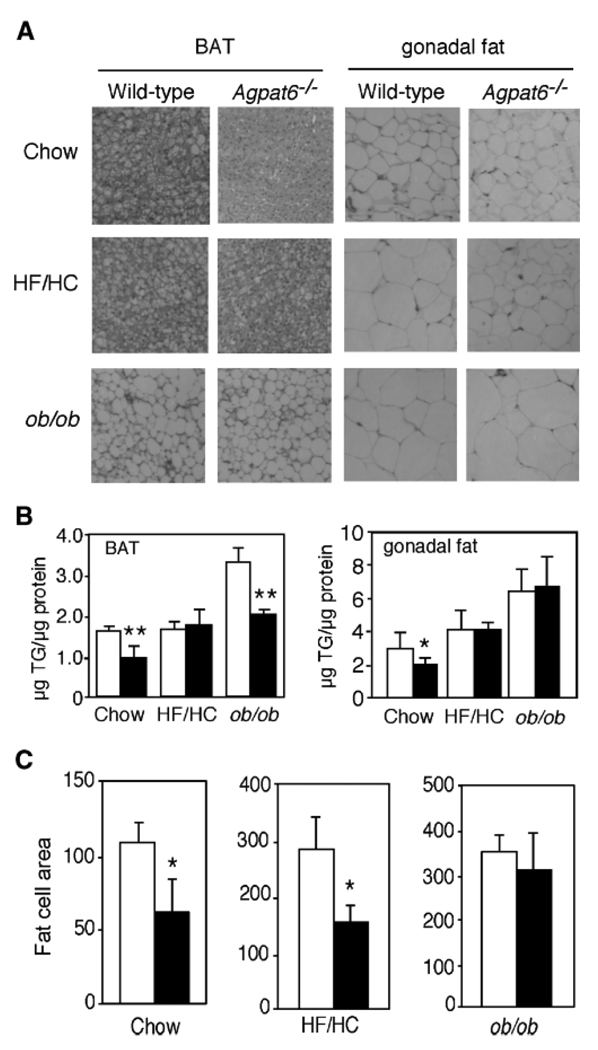
The BAT and gonadal WAT depots in chow-fed Agpat6−/− mice also exhibited decreased triglyceride content (Fig. 5A, B). The difference in triglyceride content in BAT and WAT was not observed on the high-fat diet (Fig. 5B), suggesting the existence of a compensatory mechanism involving dietary lipids. On the ob/ob background, Agpat6−/− mice had reduced triglyceride levels in BAT but not in gonadal WAT (Fig. 5B). The average size of adipocytes in the gonadal fat was reduced in Agpat6−/− mice on both the chow and HF/HC diets (Fig. 5C).
Fig. 5.
Altered fat cell size and triglyceride content in Agpat6−/− tissues. A: Hematoxylin/eosin-stained BAT and gonadal fat pad sections from mice fed chow, fed a HF/HC diet, or on the ob/ob background, as indicated. Magnification, 320×. B: Triglyceride (TG) levels in BAT and gonadal fat tissue isolated from mice under the conditions shown in A. C: Quantitation of fat cell area in gonadal fat pad sections from female mice under the conditions indicated. Randomly chosen sections from three wild-type mice and three Agpat6−/− mice were used, and a total of 200 cells from each were measured with NIH Image software. Values are expressed as means ± SD in arbitrary units. Open and closed bars represent wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice, respectively. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.
Reduced fat mass and smaller adipocyte size are typically associated with insulin sensitivity. Although there were no significant differences in glucose levels in Agpat6−/− versus wild-type mice, a trend toward reduced insulin levels was observed in Agpat6−/− mice on the ob/ob background (Table 2). On the chow diet, Agpat6−/− mice had lower plasma triglyceride levels, but this decrease was not observed on the HF/HC diet or on the ob/ob background. Interestingly, the triglyceride content of the livers of Agpat6−/− mice on the ob/ob background was increased (1.3 ± 0.6 vs. 2.6 ± 0.5 µg/mg protein; P < 0.05), suggesting partial reallocation of dietary fat storage from adipose tissue to liver.
TABLE 2.
Plasma levels of glucose, insulin, and triglycerides
| Sex | Genotype | Condition | Glucose | Insulin | Triglycerides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/dl | µg/dl | mg/dl | |||
| Male | Wild type | Chow diet | 89 ± 16 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 40 ± 19 |
| Male | Agpat6−/− | Chow diet | 83 ± 18 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 19 ± 9a |
| Female | Wild type | HF/HC diet | 80 ± 17 | 0.38 ± 027 | 38 ± 20 |
| Female | Agpat6−/− | HF/HC diet | 68 ± 15 | 0.34 ± 0.24 | 27 ± 9 |
| Female | Wild type | ob/ob background | 121 ± 46 | 7.40 ± 3.79 | 42 ± 22 |
| Female | Agpat6−/− | ob/ob background | 170 ± 114 | 4.02 ± 0.82 | 44 ± 30 |
HF/HC, high-fat/high-carbohydrate.
P < 0.05 versus the wild type.
Altered fatty acid composition in lipids from BAT and liver of Agpat6−/− mice
A quantitative assessment of lipid composition and fatty acid distribution in plasma, BAT, and liver was generated with a combination of thin-layer and gas chromatography. Table 3 presents the concentrations of triacylglycerols (TAGs), DAGs, phospholipids, and the constituent fatty acids in each species. The data are expressed as relative levels in Agpat6−/− compared with wild-type mice. Fatty acid compositions of each lipid class expressed as mol% are reported in supplementary Table I and summarized below. No statistically significant differences were noted in the concentrations of lipid classes in the plasma. In BAT, there was a trend toward decreased TAG (311,003 ± 92,183 vs. 246,995 ± 25,011 nmol/g) and DAG (3,494 ± 751 vs. 2,232 ± 302 nmol/g) levels, although the differences did not achieve statistical significance, perhaps because of the small numbers of samples (n = 3 for each genotype). There were, however, significant alterations in MUFA versus PUFA composition in several lipid classes in the Agpat6−/− BAT. TAG had reduced MUFA (48.3% vs. 40.8%; P < 0.05); DAG showed a similar decrease in MUFA (38.0% vs. 33.8%) and a concomitant increase in PUFA (21.6% vs. 27.0%; P < 0.05). The phosphatidylcholine fraction also contained less MUFA and more PUFA, and the proportion of PUFA in free fatty acids was also increased (17.3% vs. 25.9%; P < 0.05), whereas saturated fatty acids (48.6% vs. 42.1%; P < 0.05) were reduced (see supplementary Table I).
TABLE 3.
Effect of Agpat6 deficiency on lipid composition in plasma, BAT, and liver
| Tissue | Lipid class | Class | SFA | MUFA | PUFA | n3 | n6 | n7 | n9 | Plasmalogen lipids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | DAG | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.72 | 0.95 | 0.69 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.71 |
| Plasma | TAG | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.61 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.67 |
| Plasma | FFA | 1.20 | 1.24 | 1.16 | 1.21 | 1.11 | 1.22 | 1.49 | 1.07 | 1.70 |
| Plasma | LysoPC | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 1.20 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.87 | 1.10 |
| Plasma | PC | 1.09 | 1.08 | 0.94 | 1.15 | 1.32 | 1.12 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 1.21 |
| Plasma | PE | 1.23 | 1.27 | 1.14 | 1.23 | 1.19 | 1.24 | 1.96 | 0.99 | 1.05 |
| BAT | DAG | 0.64a | 0.63 | 0.57b | 0.80 | 0.31b | 0.91 | 0.48a | 0.60b | 0.34b |
| BAT | TAG | 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.97 | 0.63 | 1.00 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.59 |
| BAT | FFA | 0.79 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 1.15 | 0.62 | 1.23 | 0.55 | 0.78 | N.D. |
| BAT | PC | 1.07 | 1.07 | 0.76 | 0.19 | 1.07 | 1.23 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.88 |
| Liver | DAG | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.61 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.57 |
| Liver | TAG | 0.55b | 0.56b | 0.49b | 0.59b | 0.61b | 0.59b | 0.47b | 0.50 | 0.04 |
| Liver | FFA | 1.17 | 1.47b | 0.76a | 1.18 | 1.32 | 1.16 | 0.79 | 0.75 | 4.65 |
| Liver | LysoPC | 1.50b | 1.57b | 1.49 | 1.38b | 1.14 | 1.47a | 0.68a | 1.70 | 0.56 |
| Liver | PC | 1.12 | 1.13 | 0.94 | 1.17b | 1.37b | 1.11a | 1.09 | 0.91 | 1.16 |
| Liver | PE | 1.05 | 1.07 | 0.99 | 1.05 | 1.20 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.97 | 1.28b |
| Liver | PS | 1.35 | 1.39 | 1.26 | 1.31 | 1.34 | 1.29 | 1.26 | 1.26 | 1.41 |
BAT, brown adipose tissue; DAG, diacylglycerol; N.D., not detectable; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PS, phosphatidylserine; SFA, saturated fatty acid; TAG, triacylglycerol. Values represent the ratio of mean values from Agpat6−/− mice compared with wild-type mice (n = 3 for each) for total lipid class and the fatty acid constituents. Class and ratio of mass for lipid class are indicated; n3, n6, n7, and n9 represent positions of the double bond in the fatty acid chain.
P < 0.08 for Agpat6−/− versus the wild type.
P < 0.05 for Agpat6−/− versus the wild type.
The liver also exhibited a significant reduction in TAG concentration (161,521 ± 11,829 vs. 88,158 ± 7,532 nmol/g; P < 0.05) and an increase in lysophosphatidylcholine (1,110 ± 148 vs. 1,670 ± 245 nmol/g; P < 0.05). The reduction in TAG was characterized by a decrease in all classes of fatty acids (saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated), with a redistribution of MUFA (37.4 ± 0.5% vs. 33.8 ± 1.2%; P < 0.05) to PUFA (37.2 ± 0.5% vs. 40.3 ± 2.7%; P < 0.05). Overall, Agpat6−/− mice had reduced concentrations of TAG in the tissues and altered fatty acid composition, with reduced MUFA and increased PUFA contents.
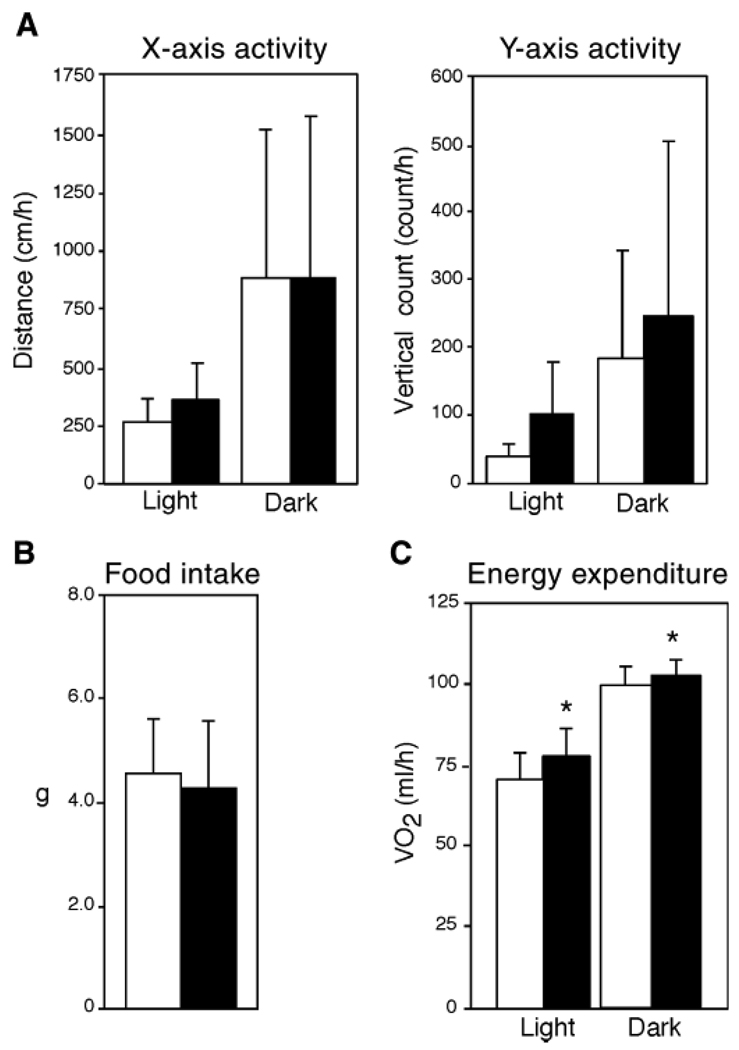
Increased energy expenditure and normal thermogenesis in Agpat6−/− mice
The observed reduction in body weight and resistance to obesity in Agpat6−/− mice suggested altered food intake, activity, or energy metabolism. Food intake and activity were comparable to those of wild-type mice (Fig. 6A, B). However, Agpat6−/− mice showed higher energy expenditure by indirect calorimetry during both light (sleeping) and dark (active) periods of the diurnal cycle (Fig. 6C). No differences were observed in respiratory quotient (data not shown). Despite increased energy expenditure, core body temperature at room temperature was identical in wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice (36.3 ± 0.58C vs. 36.3 ± 0.4°C; n = 9). The maintenance of normal body temperature despite increased energy expenditure raises the possibility that increased energy expenditure is an adaptation to maintain body temperature in the absence of a normal insulating layer of subdermal fat (Fig. 4).
Fig. 6.
Increased energy expenditure in Agpat6−/− mice. A: Activity measurements in chow-fed mice. The left panel represents the distance covered per hour, and the right panel represents vertical rearing activity. The light period was from 7 AM to 6 PM, and the dark period was from 6 PM to 7 AM (n = 6 mice for each group). B: Average daily food consumption determined on four independent days for each mouse (n = 8 mice for each group). C: Oxygen consumption (VO2, ml/h) determined by indirect calorimetry (n = 8 mice for each group). Open and closed bars represent wild-type and Agpat6−/− mice, respectively. * P < 0.01.
One key mechanism for heat generation and energy dissipation in rodents is thermogenesis in BAT. However, given the prominent expression of Agpat6 in BAT, we wondered whether thermogenesis in this tissue might be impaired in Agpat6−/− mice. To assess thermogenic capacity, mice were housed at 4°C for 4 h. Wild-type mice are able to maintain adequate body temperature under these conditions, largely through nonshivering thermogenesis in BAT. We found that Agpat6−/− mice maintained the same body temperature as wild-type mice during this acute cold exposure, indicating that cold-induced thermogenesis is not compromised (data not shown). In addition, the expression of key thermogenic response genes, including uncoupling protein-1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α, and genes involved in fatty acid oxidation, including acyl-CoA oxidase-1 and carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1b (see supplementary Fig. I), were normal in BAT from Agpat6−/− mice. Thus, despite the reduced stores of triglycerides in the BAT, Agpat6−/− mice have a normal thermogenic response to acute cold exposure.
DISCUSSION
The AGPAT family contains at least eight members, raising the question of redundancy in physiological function. One approach to investigate this question is to produce and characterize mouse strains lacking specific AGPAT proteins. Here, we used a mutant ES cell line from a gene-trap resource to generate a mouse strain lacking AGPAT6. An analysis of this model indicates that, despite its sequence similarity and partially overlapping tissue expression pattern with other family members, AGPAT6 plays a critical physiological role in the accumulation of triglyceride in WAT and BAT depots, particularly in the subdermal region. Furthermore, AGPAT6 is required for triglyceride production in mammary epithelium, rendering Agpat6−/− mice unable to nurse their offspring (9). These studies demonstrate that AGPAT6 has a nonredundant function within the AGPAT family.
The phenotype of Agpat6−/− mice is consistent with a role for this enzyme in triglyceride synthesis in BAT and WAT and exhibits similarities to the phenotype of Dgat1−/− mice. Agpat6−/− mice have reduced triglyceride content in both BAT and WAT and smaller adipocytes in the gonadal fat pad. Particularly striking was the nearly complete absence of subdermal adipose tissue in mature Agpat6−/− mice. This depot-specific lipodystrophy is a unique feature of these mice and suggests a specific role for Agpat6 in the accumulation of triglycerides in subdermal adipocytes. Similar to the Dgat1−/− mouse, Agpat6−/− mice exhibit ~25% lower body weight than wild-type counterparts on both chow and HF/HC diets (27). Deficiency in either Agpat6 or Dgat1 also leads to increased energy expenditure, conferring resistance to diet-induced obesity (4). However, whereas Dgat1+/− mice on a high-fat diet had body weights intermediate between wild-type and knockout mice (27), we observed no phenotype in heterozygous Agpat6+/− mice on either chow or HF/HC diet or on the obese genetic background. Both Agpat6−/− and Dgat1−/− mice are resistant to genetically induced obesity, but the effects of genetic background are distinct. Thus, Agpat6−/− mice are resistant to obesity on the leptin-deficient ob/ob genetic background, whereas Dgat1−/− mice are resistant to obesity on the Agouti yellow background but not on the ob/ob background (5). A possible explanation for the lack of effect of Dgat1 deficiency on the ob/ob background is that leptin deficiency leads to a compensatory increase in Dgat2 expression, leading to normal levels of triglycerides in adipose tissue. There appears to be no such compensation in the setting of Agpat6 deficiency.
The profound defect in subdermal adipose tissue accumulation in Agpat6−/− mice underscores a specific role for AGPAT6 in this fat depot. This aspect of the phenotype was not evident until mice reached ~4 months of age, at which time the subdermal adipose accumulation in wild-type mice was obvious. To investigate whether Agpat6 might have a role in the differentiation of adipocyte precursors to mature adipoctyes, we isolated embryonic fibroblasts from wild-type and Agpat6−/− embryos and differentiated them in culture with the addition of appropriate hormones and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ ligand (19). Agpat6−/− fibroblasts were capable of normal differentiation in culture, as determined by the accumulation of Oil Red O-staining droplets (L. Vergnes, unpublished data), suggesting that the lack of subdermal adipose tissue in the mutant mice is most likely a consequence of impaired triglyceride synthesis in these particular cells. Other mouse models with reduced subdermal adipose tissue include transgenic mice overexpressing human apolipoprotein C-I in the skin (28), fatty acid transport protein-4-deficient mice (29), and Dgat1−/− and Dgat2−/− mice (7, 8). In each of these models, there were abnormalities in skin structure and function in addition to the adipose content, such as dry skin, hair loss, epidermal hyperplasia/hyperkeratosis, and abnormal sebaceous gland function. In contrast, the Agpat6−/− mice had normal-appearing hair and epidermis and did not have impaired water repulsion, suggesting a very specific role for AGPAT6 in lipid accumulation within subdermal adipocytes without affecting other characteristics of the skin.
The resistance to obesity in Agpat6−/− mice is likely related both to a role for AGPAT6 in triglyceride accumulation in adipose tissue and to the increased energy expenditure observed in these mice. The mechanism underlying the increased energy expenditure is unknown, but it does not appear to be caused by increased activity; therefore, it probably has a metabolic basis. It is clear that Agpat6 deficiency does not impair acute cold-induced thermogenesis, suggesting that the reduction in BAT triglyceride content is not sufficient to deplete fuel for thermogenesis. Thus, the increased metabolic rate in Agpat6−/− mice may not be a direct consequence of the absence of AGPAT6 but rather a compensatory response to maintain normal body temperature in the absence of a subdermal adipose tissue layer.
The function of each AGPAT enzyme is not well established. The activities of AGPAT1 and AGPAT2 in converting lysophosphatidic acid to phosphatidic acid are well documented, but the activities of the other members of the family remain unclear. The existence of at least eight enzymes in the AGPAT protein family raises questions about the specific role of each member. Several possibilities exist. If all members do possess AGPAT activity, it is possible that distinct physiological roles arise from their specific tissue distributions or from biochemical differences among the enzymes in transferring acyl groups of different chain lengths. Some support for this latter possibility comes from the observation that the fatty acid composition of glycerolipids and phospholipids was altered in tissues of Agpat6−/− mice. Overall, there was an increase in PUFA at the expense of MUFA in TAGs, DAGs, and phospholipids, suggesting that AGPAT6 has a preference for MUFA substrates. On the other hand, it is also conceivable that AGPAT6 may function at a different step in TAG synthesis, acting as another type of glycerolipid acyltransferase. The ultimate answer to the role that each AGPAT plays awaits both biochemical characterization of purified enzymes and physiological analysis through the derivation and analysis of additional genetic models of AGPAT deficiency.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Robert Chin and Ping Xu for mouse colony management and technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Program for Genomic Applications (Grant U01 HL-66621).
Abbreviations
- AGPAT
1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase
- BAT
brown adipose tissue
- DAG
Diacylglycerol
- DGAT1
acyl-coenzyme A:diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1
- GPAT
glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase
- HF/HC
high-fat/high-carbohydrate
- TAG
Triacylglycerol
- WAT
white adipose tissue
Footnotes
The online version of this article (available at http://www.jlr.org) contains additional table and figure.
Supplemental Material can be found at: http://www.jlr.org/cgi/content/full/M500553-JLR200/DC1
REFERENCES
- 1.Agarwal AK, Garg A. Congenital generalized lipodystrophy: significance of triglyceride biosynthetic pathways. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003;14:214–221. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(03)00078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Coleman RA, Lee DP. Enzymes of triacylglycerol synthesis and their regulation. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004;43:134–176. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7827(03)00051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hammond LE, Gallagher PA, Wang S, Hiller S, Kluckman KD, Posey-Marcos EL, Maeda N, Coleman RA. Mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase-deficient mice have reduced weight and liver triacylglycerol content and altered glycerolipid fatty acid composition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002;22:8204–8214. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.23.8204-8214.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Smith SJ, Cases S, Jensen DR, Chen HC, Sande E, Tow B, Sanan DA, Raber J, Eckel RH, Farese RV., Jr Obesity resistance and multiple mechanisms of triglyceride synthesis in mice lacking Dgat. Nature. 2000;25:87–90. doi: 10.1038/75651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen HC, Smith SJ, Ladha Z, RJensen D, Ferreira LD, Pulawa LK, McGuire JG, Pitas RE, Eckel RH, Farese RV., Jr Increased insulin and leptin sensitivity in mice lacking acyl CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1. J. Clin. Invest. 2002;109:1049–1055. doi: 10.1172/JCI14672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chen HC, Ladha Z, Smith SJ, Farese RV., Jr Analysis of energy expenditure at different ambient temperatures in mice lacking DGAT1. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003;284:E213–E218. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00248.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen HC, Smith SJ, Tow B, Elias PM, Farese RV., Jr Leptin modulates the effects of acyl CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase deficiency on murine fur and sebaceous glands. J. Clin. Invest. 2002;109:175–181. doi: 10.1172/JCI13880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stone SJ, Myers H, Brown BE, Watkins SM, Feingold KR, Elias PM, Farese RV., Jr Lipopenia and skin barrier abnormalities in DGAT2-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:11767–11776. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311000200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Beigneux AP, Vergnes L, Qiao X, Quatela S, Davis R, Watkins SM, Coleman RA, Walzem RL, Philips M, Reue K, Young S. Agpat6—a novel lipid biosynthetic gene required for triacylglycerol production in mammary epithelium. J. Lipid Res. 2006;47:734–744. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M500556-JLR200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aguado B, Campbell RD. Characterization of a human lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase that is encoded by a gene located in the class III region of the human major histocompatibility complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:4096–4105. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.7.4096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Eberhardt C, Gray PW, Tjoelker LW. Human lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase. cDNA cloning, expression, and localization to chromosome 9q34.3. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:20299–20305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.32.20299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kawaji H, Schonbach C, Matsuo Y, Kawai J, Okazaki Y, Hayashizaki Y, Matsuda H. Exploration of novel motifs derived from mouse cDNA sequences. Genome Res. 2002;12:367–378. doi: 10.1101/gr.193702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li D, Yu L, Wu H, Shan Y, Guo J, Dang Y, Wei Y, Zhao S. Cloning and identification of the human LPAAT-zeta gene, a novel member of the lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase family. J. Hum. Genet. 2003;48:438–442. doi: 10.1007/s10038-003-0045-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ye GM, Chen C, Huang S, Han DD, Guo JH, Wan B, Yu L. Cloning and characterization a novel human 1-acyl-snglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase gene AGPAT7. DNA Seq. 2005;16:386–390. doi: 10.1080/10425170500213712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lu B, Jiang YJ, Zhou Y, Xu FY, Hatch GM, Choy PC. Cloning and characterization of murine 1-acyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferases and their regulation by PPARalpha in murine heart. Biochem. J. 2005;385:469–477. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Agarwal AK, Arioglu E, De Almeida S, Akkoc N, Taylor SI, Bowcock AM, Barnes RI, Garg A. AGPAT2 is mutated in congenital generalized lipodystrophy linked to chromosome 9q34. Nat. Genet. 2002;31:21–23. doi: 10.1038/ng880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Magre J, Delepine M, Van Maldergem L, Robert JJ, Maassen JA, Meier M, Panz VR, Kim CA, Tubiana-Rufi N, Czernichow P, et al. Prevalence of mutations in AGPAT2 among human lipodystrophies. Diabetes. 2003;52:1573–1578. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.6.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stryke D, Kawamoto M, Huang CC, Johns SJ, King LA, Harper CA, Meng EC, Lee RE, Yee A, L’Italien L, et al. BayGenomics: a resource of insertional mutations in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:278–281. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Phan J, Peterfy M, Reue K. Lipin expression preceding peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is critical for adipogenesis in vivo and in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:29558–29564. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403506200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F. Accurate normalization of realtime quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002;3:0034.1–0034.11. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Phan J, Reue K. Lipin, a lipodystrophy and obesity gene. Cell Metab. 2005;1:73–83. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2004.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Peterfy M, Phan J, Reue K. Alternatively spliced lipin isoforms exhibit distinct expression pattern, subcellular localization, and role in adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:32883–32889. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503885200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Beigneux AP, Kosinski C, Gavino B, Horton JD, Skarnes WC, Young SG. ATP-citrate lyase deficiency in the mouse. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:9557–9564. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310512200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957;226:497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Watkins SM, Lin TY, Davis RM, Ching JR, DePeters EJ, Halpern GM, Walzem RL, German JB. Unique phospholipid metabolism in mouse heart in response to dietary docosahexaenoic or alpha-linolenic acids. Lipids. 2001;36:247–254. doi: 10.1007/s11745-001-0714-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Leung DW. The structure and functions of human lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferases. Front. Biosci. 2001;6:D944–D953. doi: 10.2741/leung. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen HC, Farese RV., Jr Inhibition of triglyceride synthesis as a treatment strategy for obesity: lessons from DGAT1-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005;25:482–486. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000151874.81059.ad. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jong MC, Gijbels MJJ, Dahlmans VEH, van Gorp PJJ, Koopman S-J, Ponec M, Hofker MH, Havekes LM. Hyperlipidemia and cutaneous abnormalities in transgenic mice over-expressing human apolipoprotein C1. J. Clin. Invest. 1998;101:145–152. doi: 10.1172/JCI791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Herrmann T, van der Hoeven F, Grone H-J, Stewart AF, Langbein L, Kaiser I, Liebisch G, Gosch I, Buchkremer F, Drobnik W, et al. Mice with targeted disruption of the fatty acid transport protein 4 (Fatp4, Slc274a) gene show features of lethal restrictive dermopathy. J. Cell Biol. 2003;161:1105–1115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200207080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.