Abstract
It is well established that aberrant gene regulation by epigenetic mechanisms can develop as a result of pathological processes such as cancer. Methylation of CpG islands is an important component of the epigenetic code and a number of genes become abnormally methylated during tumorigenesis. Some bioactive food components have been shown to have cancer inhibition activities by reducing DNA hypermethylation of key cancer-causing genes through their DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibition properties. The dietary polyphenols, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) from green tea, genistein from soybean and possibly isothiocyanates from plant foods, are some examples of these bioactive food components modulated by epigenetic factors. The activity of cancer inhibition generated from dietary polyphenols is associated with gene reactivation through demethylation in the promoters of methylation-silenced genes such as p16INK4a and retinoic acid receptor β. The effects of dietary polyphenols such as EGCG on DNMTs appear to have their direct inhibition by interaction with the catalytic site of the DNMT1 molecule, and may also influence methylation status indirectly through metabolic effects associated with energy metabolism. Therefore, reversal of hypermethylation-induced inactivation of key tumor suppression genes by dietary DNMT inhibitors could be an effective approach to cancer prevention and therapy. In this analysis, we focus on advances in understanding the effects of dietary polyphenols on DNA methylation modulation during the process of cancer development, which will offer exciting new opportunities to explore the role of diet in influencing the biology of cancer and to understand the susceptibility of the human epigenome to dietary effects.
Keywords: Diet, Cancer prevention, DNMT, DNA methylation, EGCG, Genistein
Introduction
There has been considerable interest in the use of botanicals for various cancer prevention and therapy approaches. Some bioactive food components with DNA methyltransferase (DNMTs) inhibition properties may influence DNA methylation processes and apply their cancer inhibition activities through reactivating key tumor suppressor genes. These dietary compounds including (−)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG) and genistein are widely found in green tea, soybean products and some fruits. This review will introduce current advances for the use of these compounds in cancer chemoprevention including modulating epigenetic mechanisms as applied to in vitro cell cultures as well as in vivo animal and human studies.
DNA methylation and cancer
Epigenetic processes, which literally mean outside conventional genetics and do not involve mutations of DNA itself, have been described to influence patterns of gene expression that are established during development or somatic cell proliferation and transmitted through mitosis by at least two main mechanisms: DNA methylation and histone modification [1]. It is well established that the epigenetic signals act through remodeling of chromatin architecture [2]. Histone modification, which occurs by acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation and ubiquitination of lysine, arginine and serine residues in the amino-terminal tails of the core histone proteins, is an evolutionarily ancient code and is found universally in all eukaryotes [2, 3].
Patterns of DNA methylation are tissue and cell specific and are generated during development involving de novo methylation and demethylation events. DNA methylation is an enzymatic processes mediated by DNA methyltransferases. The process of demethylation is believed to involve an enzymatic reaction. Cervoni et al. found a processive demethylase enzyme, which may contribute to global hypomethylation [4]. However, the accurate catalytic processes and the enzymes responsible for demethylation still remain unsolved. DNA methylation, occurring primarily at cytosine-guanine (CpG) dinucleotides, is a heritable, tissue- and species-specific modification of mammalian DNA [5, 6]. CpG dinucleotides are frequently clustered into CpG islands, regions that are rich in CpG sites. These islands extend about 0.5–3 Kb, occur on average every 100 Kb in the genome and are found in approximately half of all genes in humans [7]. DNA methylation often occurs at the regulatory sites of gene promoter regions and involves an enzymatic process by addition of a methyl group to the 5-position of the cytosine ring of CpG dinucleotides (Fig. 1). It is an important epigenetic determinant in gene expression, maintenance of DNA integrity and stability in many biological processes such as genomic imprinting, normal development and proliferation [8–10]. DNA hypermethylation of CpG islands is usually associated with silencing of the expression of genes in contrast to loss of methylation which often leads to gene reactivation. Abnormal patterns of DNA methylation may ultimately lead to genetic instability and cancer development through epigenetic inactivation of certain critical cancer-related genes by promoter hypermethylation [11] (Fig. 1). These altered genes include tumor suppressor genes, such as the cell cycle checkpoint genes, p21WAF1/CIP1 and p16 INK4a, and growth regulatory genes, such as RAS association domain family 1A (RASSF1A) and retinoic acid receptor β (RARβ). Furthermore, promoter hypomethylation-induced oncogene activation contributes to the processes of tumorigenesis [12]. Aberrant DNA methylation occurs at specific genes in almost all neoplasms, suggesting that this alteration may be a molecular marker in cancer prevention and therapeutic approaches.
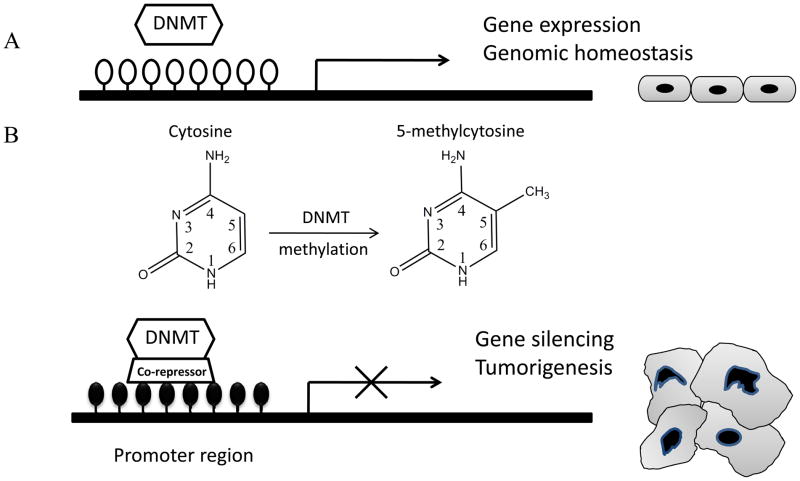
Fig. (1).
DNA methylation in normal and cancer cells. A, DNA methylation in normal cells. A hypomethylated promoter is related to gene expression. B, DNA methylation in cancer cells. Aberrant DNA hypermethylation in the promoter leads to gene silencing and tumorigenesis. The DNA methylation process is catalyzed by the DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) by adding a methyl group (CH3) to the 5-position of the cytosine ring of CpG dinucleotides. White circles, unmethylated CpG sites; black circles, hypermethylated CpG sites.
DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs)
DNA methylation in mammals is an enzymatic process which is primarily mediated by the three known active DNA cytosine methyltransferase (DNMT1, 3a and 3b) [13]. Among them, DNMT1 is the best known and studied member of the DNMT family. It is primarily a maintenance methyltransferase and plays an important role in cell division and development. During cell division, methylation patterns in the parental strand of DNA are maintained in the daughter strand by the action of DNMT1 which catalyses the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), the methyl donor, to the cytosine residues, restoring the symmetrically methylated CpG dinucleotide pair.
DNMT1
The human DNMT1 gene is located at human chromosome 19p13.2 and encodes a 183 kDa protein (Table 1). DNMT1 comprises a large N-terminal domain with regulatory functions and a smaller 500 amino acid C-terminal catalytic domain [14]. The N-terminal regulatory domain harbors different motifs including different start codons, a nuclear localization signal, a PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) interacting domain [15], a replication foci targeting region [16] and a cysteine-rich Zn2+ binding domain comprising six CXXC motifs [17]. These specific domains allow DNMT1 to directly interact with various transcriptional regulators such as DNA methyltransferase 1 associated protein 1 (DMAP1), histone deacetylases (HDACs), suppressor of variegation 3–9 homolog 1 (SUV39H1) and Rb, thereby influencing gene regulation through epigenetic signaling [18].
Table 1.
Summary of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs)
| Gene | Gene location | Molecular weight (kDa) | Expressional distribution | Methylation preference | Activity on DNA | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNMT1 | 19p13.2 | 183 | Ubiquitous expression | Hemimethylated CpG sites | +++ | Primary maintenance methyltransferase in cell division and embryonic development; high expression in tumors |
| DNMT3a | 2p23 | 102 | Ubiquitous expression | CpG dinucleotides | + | De novo methyltransferase; modestly increased in certain tumors |
| DNMT3b | 20q11.2 | 98 | Localized expression in testis, thyroid and bone marrow | CpG dinucleotides | + | De novo methyltransferase; mutated expression leads to ICF syndrome; high expression in tumors |
| DNMT3L | 21q22.3 | 48 | Restricted to gonocytes | No catalytic activity | − | Regulatory factor for de novo DNA methylation and histone modification |
The C-terminal domain of DNMT1 contains all the conserved motifs characteristic of cytosine-C5-methyltransferase and shares a set of 10 conserved amino acid motifs, where the motifs I (DXFXGXG), IV (GFPCQ), and VI (ENV) are most conserved and harbor the active center of the enzyme [19]. The catalysis process involves a conserved mechanism that has been studied best in the bacterial cytosine-C5-methylation (5mC) methyltransferase (MTase), M.HhaI [20–22]. Briefly, this mechanism involves MTase binding to the DNA, eversion of the target nucleotide so that it projects out of the double helix (“base flipping”) into the catalytic pocket of the enzyme, covalent attack of a conserved cysteine nucleophile on cytosine C6, transfer of the methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine to the activated cytosine C5, and the various release steps. The key residue of DNMT1 is cysteine in a PCQ motif conserved in the active site of motif IV, which performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbon-6 of the target cytosine. Moreover, base flipping plays an important role in the enzymatic reaction by providing high accessibility of the target base to the enzyme, thereby allowing for intricate chemical reactions to occur and for accurate recognition of the flipped base. It has been verified in M.HhaI that Gln 237, the amino acid residue of motif ENV (motif VI), is important in stabilizing the flipped cytosine of the DNA protein complex [23].
Homozygosityknockout of DNMT1 is lethal to the embryo in mammals, suggesting a crucial role of DNMT1 in embryonic development. However, studies on DNMT1-overexpression in embryonic stem cells also resulted in lethality of the embryo suggesting accurate expression of DNMT1 is a key factor in maintaining embryonic development [24].
As expected for a maintenance methyltransferase, DNMT1 has a 30- to 40-fold preference for hemimethylated sites [25]. Further investigations proved that DNMT1 activity is required for de novo methylation at non-CpG cytosines [26]. However, increased DNMT1 always occurs in the process of malignant genesis and is associated with hypermethylation of CpG islands leading to silencing expression of tumor suppressor genes [27, 28].
DNMT3
The DNMT3 family includes two major members, DNMT3a and DNMT3b, which play an important role in mediating de novo methylation processes (Table 1) [13, 14]. Both DNMT3a and DNMT3b have a similar C-terminal catalytic domain as DNMT1 has, and a variable region at the N-terminus. Targeted disruption of both Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b in mouse embryonic stem cells blocks de novo methylation, but has no effect on maintenance of an imprinted methylation pattern [29]. However, both DNMT3a and DNMT3b exhibit specialized roles. DNMT3b appears to be critical for the methylation of a particular compartment of the genome. For instance, DNMT3b mutations are linked with a syndrome called ICF (immunodeficiency, centromeric instability, facial abnormalities) [29–31], a rare recessive autosomal disorder characterized by hypomethylation at pericentromeric satellite regions. These phenomena may be due to the different distribution of these two enzymes, whereby DNMT3a is ubiquitously expressed but 3b localizes its activity to the pericentromeric repeats carrying high CG content. DNMT3a cannot replace DNMT3b in this function, possibly because of its distribution mechanism, which is less efficient in methylating highly CG rich DNA. Over-expression of DNMT3b has been shown in various human tumors, while the expression level of DNMT3a is only modestly increased in certain types of tumors [32], indicating that DNMT3b plays a more important role in tumorigenesis than 3a.
Recently, a new member of the DNMT3 family, DNMT3-Like protein (DNMT3L), has been identified as a regulatory factor of DNMT3a and 3b, which has the same Cys-rich 3-Zn-binding domain of the N-terminal as DNMT3a and 3b, but lacks the conserved residues required for DNA MTase activity in the C-terminal domain (Table 1) [13]. It has been shown that DNMT3L regulates DNMT3a and 3b mediated- de novo methylation and histone methylation processes [33]. In addition, DNMT3a and DNMT3L are both required for the methylation of most imprinted loci in germ cells.
The effects of dietary components on DNA methylation
Aberrant patterns and dysregulation of DNA methylation cause stable, heritable transcriptional silencing of the associated gene during tumorigenesis [1, 11]. Epigenetic variability at specific transcription regulation sites appear to be susceptible to modulation by nutritional changes [34]. Therefore dietary components, which can affect the process of DNA methylation, may influence tumorigenesis by regulation of the expression of certain key genes. The development of therapeutic strategies for modifying epigenetic mechanisms, for example, by targeting the activity of DNMTs, provides many opportunities for applying bioactive botanic extracts for alternative cancer chemotherapy and prevention.
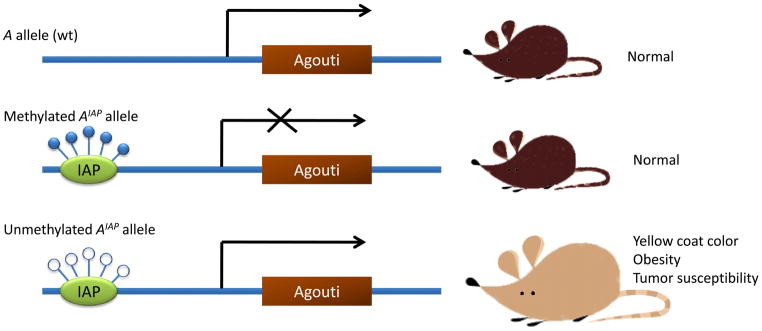
Currently the best evidence to show that nutritional components can modulate epigenetic status of mammal cells comes from studies with mice carrying the agouti viable yellow gene (Fig. 2) [35, 36]. The normal function of the agouti gene is to confer a wild-type coat color but dominant mutations at the agouti locus cause a pleiotropic syndrome which results in excessive amounts of yellow pigment on the coat, together with systemic effects including obesity and a vulnerability to various types of cancer. Various agouti viable yellow alleles (AIAP and Ahvy) have been identified by inserting an intracisternal A particle (IAP), a retroviral element, into the gene. The coat color of mice carrying such an allele varies from yellow to mottle to wild type agouti, which is dependent on the methylation status of IPA in the alleles. When methylated the gene behaves like a wild type allele and is expressed only in the hair follicle. When the unmethylated gene is expressed ubiquitously, the result is the phenotype of the full agouti syndrome, but intermediate levels of methylation cause a mottled appearance. Therefore, the coat color and other aspects of the agouti phenotype provide a direct readout of the methylation status of the allele. The AIAP model system has been successfully used for detecting epigenetic control in mammals through dietary supplementation with methyl donors such as folate, which will be discussed later in this review.
Fig. (2).
Epigenetic effects of the agouti gene on mouse coat color. The agouti viable yellow alleles (AIAP and Ahvy) are formed by inserting an intracisternal A particle (IAP) into the agouti locus. When IAP is methylated, the gene is expressed only in the skin, similar to expression of the wild type allele. Hypomethylation of the IAP gene will generate a ubiquitous expression leading to a yellow coat color, obesity and tumors.
Numerous studies have demonstrated that certain dietary components inhibit cancer proliferation by affecting epigenetic signaling pathways both in vitro and in vivo [37, 38]. The green tea polyphenol, EGCG, is believed to be a key active ingredient for cancer inhibition through epigenetic control. It has been found that EGCG can reverse CpG island hypermethylation of various methylation-silenced genes and reactivate these gene expressions through inhibition of DNMT1 enzymatic activity [39]. Moreover, EGCG has been proposed to regulate gene expression through the mechanism of chromatin remodeling suggesting that EGCG could exert its anticancer ability through both epigenetic mechanisms. Another well-known bioactive dietary compound is the soybean isoflavone, genistein, which has also been found to inhibit tumorigenesis through epigenetic control in several cancer cell lines [40, 41].
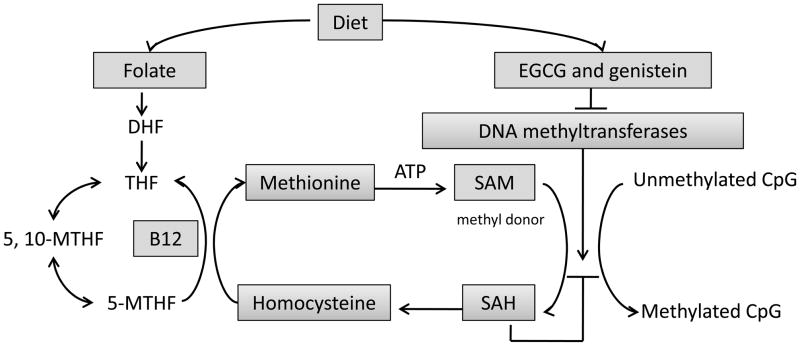
Cellular DNA methylation processes involve a series of catalytic reactions including one-carbon metabolism, creation of the principal methyl donor, S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), and methyl transfer reactions [42] (Fig. 3). As a consequence of methyl group transfer, SAM is converted to S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH), which binds with high affinity to methyltransferases and induces product inhibition. The ratio of SAM: SAH is therefore an important determinant of the methylation capacity. Disturbances in this system may be caused by dietary imbalances by affecting the major regulatory enzymes, thereby altering DNA methylation [43]. Therefore, in a pathological condition such as precancer or even cancer, appropriate intake of a methylation-regulatory bioactive diet may interfere with tumorigenesis leading to cancer prevention and anticancer therapy.
Fig. (3).
A summary of dietary factors affecting DNA methylation processes. Methionine is regenerated by methylation of homocysteine. Folate and vitamin B12 contribute to generating 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF), which provides the methyl group for synthesis of methionine and SAM, the universal methyl donor of biological methylation. EGCG and genistein affect DNA methylation by inhibiting the DNMTs. DHF: dihydrofolate; THF: tetrahydrofolate; 5, 10-MTHF: 5, 10-methylene-tetrahydrofolate.
1. Methyl-donor related diet
A methyl donor diet, refering to a series of dietary components including folate, vitamin B12 and many other compounds, can be used for synthesis of SAM [44]. Folate, a water-soluble B vitamin, which must be obtained from dietary sources or supplements, is of fundamental importance for normal DNA synthesis and repair (Table 2) [45]. 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF), the predominant form of folate in plasma, provides the methyl group for synthesis of methionine and SAM, the universal methyl donor of biological methylation (Fig. 3).
Table 2.
Summary of dietary components for cancer inhibition
| Dietary components | Food source | Classification | Functions in DNA methylation | Roles in cancer prevention | Target gene | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Folate | Many beans and vegetables and some fruits | Water-soluble B vitamin | Providing methyl group for SAM synthesis (Methyl-donor) | Deficiency causes genome-wide DNA hypomethylation and genomic instability | N/A | 44–46 |
| EGCG | Green tea | Botanic polyphenol (Flavonol); tea catechins | Potent DNMT1 inhibitor; SAM/SAH↓ | Reactivation of tumor suppressor genes by promoter hypomethylation | p16INK4a; RAR β; MGMT; hMLH1; GSTP1; WIF-1; RECK | 39, 68, 72–74 |
| Genistein | Soybean | Botanic polyphenol (isoflavone) | DNMT1 inhibitor | Reactivation of tumor suppressor genes by promoter hypomethylation | p16INK4a; RAR β; MGMT; PTEN; CYLD | 40, 92 |
| Selenium | Nuts and animal kidney and liver | Minerals; essential trace element | Inhibiting DNMT1 activity and affecting SAM/SAH | Deficiency causes global hypomethylation and promoter methylation of p53 and p16 genes | p53 and p16 | 96 |
| Isothiocyanates | Cruciferous vegetables | Metabolites of glucosinolates | N/A | Reactivation of GSTP1gene by promoter hypomethylation | GSTP1 | 102 |
Extensive evidence has accumulated suggesting that folate deficiency plays a significant role in developing several tumors, including cancers of the colorectum, lung, pancreas, esophagus, stomach, cervix, and breast, as well as neuroblastoma and leukemia [46]. This may be due to the abnormal process of DNA synthesis and methylation caused by low folate status and numerous studies have explored the relationship between folate status and the human epigenome, both in vitro and in vivo. The AIAP model system, which has been introduced previously, has been successfully used to detect the methylation status in mammals when administrating folate-deficient dietary supplementation [35, 36, 47]. Wolff et al. found that when pregnant female mice were fed a diet supplemented with methyl-donors (folate, methionine, choline and vitamin B12), a large proportion of offspring have a wide-type coat color due to increased IAP methylation as compared with the maternal mice fed with a standard diet [48]. In addition, a methyl group- rich diet has been shown to significantly reduce the proportion of progeny with a kinked tail in AxinFused mice by one-half via increased CpG methylation in the promoter of the AxinFu gene [49]. However, feeding studies in rats with diets deficient in folate showed that significant genome-wide DNA hypomethylation, as well as gene-specific DNA hypermethylation occurs in the liver, suggesting that the effects of folate deficiency on DNA methylation are gene- and site-specific depending on cell type, target organ, and stage of transformation [50, 51].
The most common cause for impairment of folate uptake is chronic ethanol ingestion, which can reduce the intestinal and renal uptake of folate by altering the binding and transport kinetics of folate transport systems [52]. There have been several intervention studies of human populations that investigated the effects of folate deficiency and/or supplementation on DNA methylation status [53, 54]. Generally, folate deficiency was associated with genome-wide DNA hypomethylation. However, the supplementation studies have either no effect or minor effects on DNA methylation [55, 56] suggesting that the timing and duration of folate intervention is important to carcinogenesis. Moreover, a high dose of folate supplementation may promote tumorigenesis if the administration is given after the precancerous lesions have been established [57]. Therefore, an appropriate exposure time of folate supplementation plays an important role in its protective roles on human health.
2. Dietary polyphenols
Phenolic compounds are among the largest and most ubiquitous groups of plant metabolites. Recently, intensive interest has been focused on the effects of dietary polyphenolic compounds on their anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic activities [58–60]. All plant phenolic compounds arise from the common intermediate, phenylalanine, or its close precursor, shikimic acid. They can be divided into at least ten different classes based on their general chemical structures, such as phenolic acids and derivatives, flavonoids, stilbenes, lignans and others [60]. In this review, we have chosen a select group of polyphenols with the properties of DNMT inhibition to further understand the bioavailabilities of dietary polyphenolic compounds on cancer prevention.
2.1 Tea polyphenols
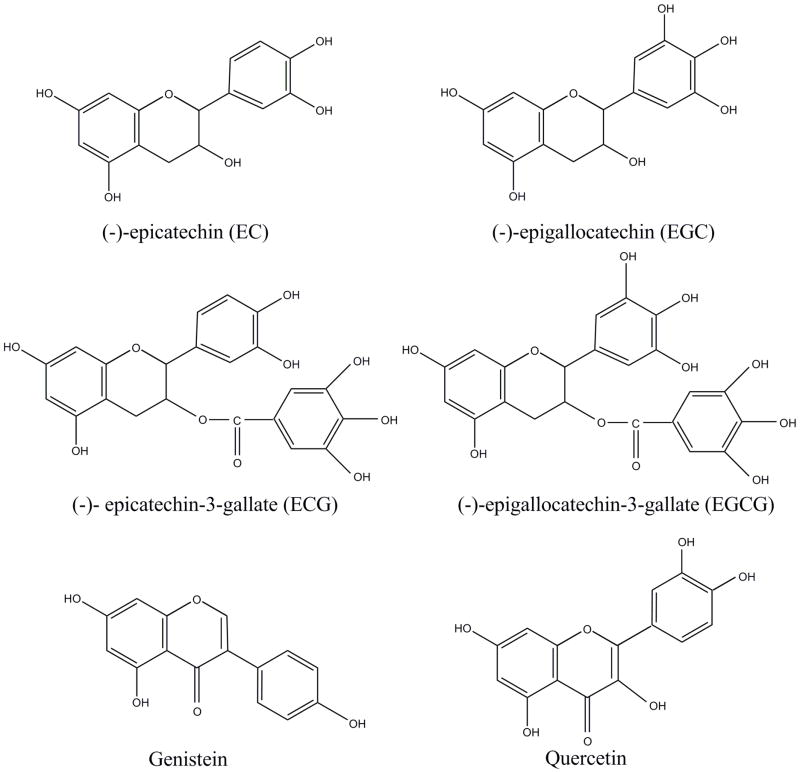
Green tea, a popular beverage consumed worldwide, has been extensively demonstrated to improve human health by prevention of cancer, heart disease, and cataracts. The most abundant chemical compound in green tea beverages is catechins, which include (−)-epicatechin (EC), (−)-epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG), (−)-epigallocatechin (EGC) and (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) (Fig. 4) [61]. Many studies in recent years have demonstrated the chemopreventive and anticancer potential of green tea polyphenols. These investigations have suggested a positive association between green tea and a lower incidence of gastric, esophageal, breast, ovarian, pancreatic, colorectal and skin cancers [60, 62, 63]. Many authors have considered EGCG to be the key active ingredient of green tea because this compound is the most abundant catechin, and the cancer inhibitory activity of EGCG has been extensively demonstrated (Table 2). Moreover, various studies have shown that EGCG can effectively inhibit carcinogenesis in various animal organs [64–66]. Possible mechanisms for the anticancer property of EGCG include: inhibition of cellular oxidative stress, reduction in cancer cell proliferation, inhibition of angiogenesis, and regulation of signal transduction [67].
Fig. (4).
Representative structures of selected dietary polyphenols: EC, EGC, ECG, EGCG, genistein and quercetin.
Recently, several studies have suggested that EGCG can inhibit DNMT activity through a direct interaction with the enzymes, thereby leading to demethylation and reactivation of methylation-silenced genes (Fig. 3) [37, 39, 68–69]. Treatment of human esophageal cells with EGCG has been shown to lower DNMT1 activity leading to hypomethylation and re-expression of genes including the tumor suppressor p16INK4a, RAR β, MGMT, and the DNA mismatch repair gene, hMLH1 [39]. Similar effects were observed in prostate, colon, lung and breast cancer cell lines [37, 69–74]. Our previous studies also show that EGCG treatment can down-regulate expression of a tumor promoting gene, hTERT (human telomerase reverse transcriptase), which leads to inhibition of telomerase activity through decreasing methylation of the hTERT promoter [37]. Although hypermethylation of gene promoters is generally associated with gene silencing, the hTERT promoter, paradoxically, is highly methylated in most tumor cell types, rendering hTERT active [75]. Our studies indicated that EGCG can also inhibit oncogene expression through influencing DNA methylation status of these genes. Moreover, Mittal et al. found that EGCG treatment results in significant inhibition of UVB-induced global DNA hypomethylation patterns in the SKH-1 hairless mouse model [38]. In a study investigating past lifestyle factors in gastric cancer patients, a decreased intake of green tea was found to correlate with methylation of the CDX2 gene [76]. Taken together, these findings provide solid evidence that EGCG can exert its anticancer effects through modulation of DNA methylation. Currently, green tea extracts have been applied in clinical trials including oral cancer prevention indicating tea polyphenols could be used in multiple human cancer preventive and therapeutic purposes due to their bioactivities such as regulating epigenetic factors [77].
Various findings indicate that EGCG is the most potent DNMT inhibitor in tea catechins through direct and indirect mechanisms. In normal metabolic processes, EGCG is methylated by catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) through the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to form MeEGCG and DiMeEGCG both in vitro and in vivo [78, 79]. Given the evidence that EGCG is also a potent inhibitor of COMT, it is thought that EGCG may act as an inhibitor of the DNMTs because both COMT and DNMT belong to the same superfamily of SAM-dependent methyltransferases and share a common core structure at the catalytic site [19, 39].
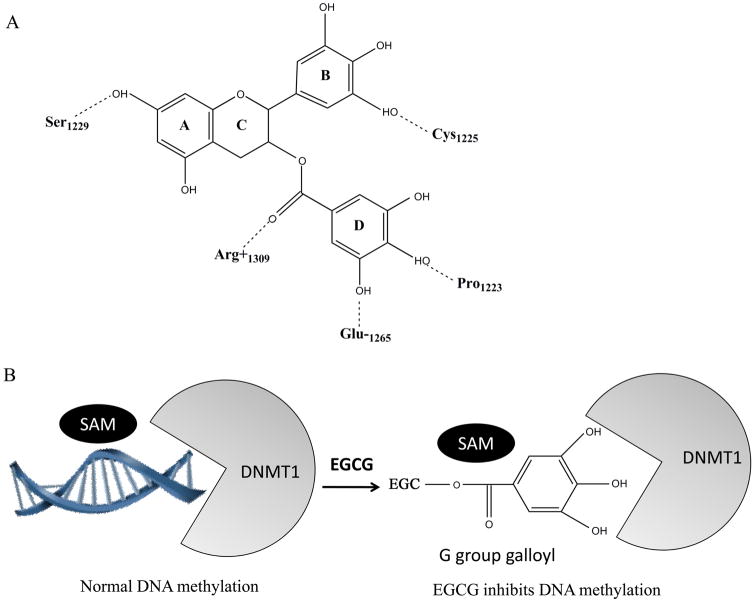
In 2003, Fang et al. found that EGCG is a competitive inhibitor of DNMT in a dose-dependent manner [39]. They also investigated the inhibitory activities of structural analogues of EGCG including ECG, EGC, EC, and methylated EGCG and found a rank order of potency: EGCG > ECG, MeEGCG > EGC, and DiMeEGCG > EC. Molecular modeling of the interaction between EGCG and DNMT1 indicated that docking of EGCG (D ring) into the putative cytosine pocket formed potential hydrogen bonds with two catalytically important residues, Glu1265 and Pro1223, which were the same residues that appear to stabilize the flipped cytosine through hydrogen bonding [19, 23]. In addition, possible hydrogen bond formation between the hydroxyl groups of the EGCG A and B rings with Ser1229 and Cys1225, respectively, also may have contributed to the high-affinity DNMT1 binding. Therefore, EGCG is well accommodated in a hydrophilic pocket of DNMT1 by effectively forming at least four hydrogen bonds within the DNMT1 catalytic binding center, thus blocking entry of the key nucleotide cytosine into its active site and preventing methylation process (Fig. 5). Lee et al. also pointed out that Mg2+ is probably coordinated to Glu1265 at the catalyticcore site and may play an important role in direct inhibition of DNA methylation by EGCG [80].
Fig. (5).
Molecular mechanisms of EGCG on DNMT1 inhibition. A, Molecular structure of hydrogen-binding network of interaction between EGCG and DNMT1 [36]. Hydrogen bonds that form between EGCG and DNMT1 are represented with dotted lines. The numbers of amino acid residues of DNMT1 contacting with the atoms of EGCG are indicated. B, Schematic drawing of EGCG affecting DNA methylation through inhibiting DNMT1. EGCG shows competitive inhibition of DNMT1 by effectively forming at least four hydrogen bonds within the DNMT1 catalytic binding center, thus blocking entry of the DNA nucleotide cytosine into its active site and preventing methylation process. The gallic acid moiety (D ring) of EGCG plays a crucial role in its high-affinity interaction with the catalytic site of DNMT1.
However, the direct inhibition of DNMT activity by EGCG is much stronger than the effect of other tea catechins. It was also reported that consumption of polyphenols could lead to a decrease in available SAM and an increase in SAH and homocysteine levels, and hence an inhibition of DNA methylation reactions in humans [81] suggesting indirect inhibitory effects on DNA methylation by EGCG. This conjecture is supported by animal studies demonstrating that EGCG consumption can moderately decrease the level of SAM (without increasing the level of SAH) in the intestine through drinking fluid [68]. Furthermore, acute intragastric (i.g.) treatment with high doses of EGCG significantly elevated plasma levels of homocysteine, decreased the levels of plasma methionine, and decreased the levels of intestinal SAM and SAH. However, this high administration through i.g. is equivalent to the consumption of 4200 mg of EGCG or 20–35 cups of green tea by an individual, and it may produce toxicity.
The potential inhibition of DNMT3a and DNMT3b by tea polyphenols has also been determined by using the prokaryotic SssI DNA methyltransferase, which is functionally similar to the human DNMT3a and DNMT3b and methylates both unmethylated and hemimethylated DNA substrates with almost equal efficiency [80, 82]. It was found that EGCG shows a more potent direct inhibition on SssI DNA methyltransferase than the other tea polyphenols suggesting an overall inhibition of DNMT1, DNMT3a and DNMT3b by EGCG.
2.2 Soy isoflavone genistein
The soybean product, genistein, belongs to flavonoids, the largest class of phenolic compounds (Fig. 4) [60]. Genistein has been shown to be associated with a lower incidence and mortality rate of breast cancer in Asian women who consume soybean products as their daily diet [83, 84]. Genistein is believed to be a chemopreventive agent against various types of cancer cells, including cancers of prostate, esophageal and colon [85]. It is becoming clear that genistein exerts multiple effects on cancer cell growth. Possible mechanismsfor the antiproliferative property of genistein include: preventionof DNA mutation, reduction in cancer cell proliferation, inhibition of angiogenesis, and induction of differentiation [86–88]. One potential mechanism that has recently received considerable attention is that genistein may be involved in regulation of gene transcription activity by modulating epigenetic events such as DNA methylation and/or chromatin modification (Table 2 and Fig. 3) [40, 41, 89].
It has been shown that genistein supplementation of maternal mice during gestation could shift the coat color of heterozygous viable yellow agouti (Avy/a) offspring, indicating that genistein acts during early embryonic development [90]. Day et al. also reported that consumption of a genistein diet altered the prostate DNA methylation pattern of specific genes in C57BL/6J mice indicating that genistein may be involved in preventing the development of certain cancers by maintaining a protective DNA methylation profile [91]. Genistein was shown to inhibit DNMT activity and in esophageal and prostate cancer cells reversed aberrant DNA methylation, leading to reactivation of gene expression including p16INK4a, RAR β, MGMT, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and CYLD and the effect was synergistically enhanced in combination with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine[40, 92]. However, the anti-cancer properties of genistein in breast cancer have raised concerns because its estrogen-like effect may be contraindicated for women at high risk of breast cancer or breast cancer patients with estrogen-sensitive tumors. Studies both in epidemiology and animals have confirmed that exposure to soy diet in women in early life greatly impacts breast cancer risk suggesting exposure time is essential for genistein to exert its effects on breast cancer prevention [93]. We also found that treatment of genistein results in transcription suppression of hTERT leading to telomerase activity inhibition by affecting DNMT expression in human breast cancer cells [41]. However, Fang et al. found that the inhibition of genistein on DNMT is weaker than that of EGCG, yet it is more active in demethylating activity leading to reactivation of methylation-silenced genes. One potential reason may be due to a greater stability of genistein in the cell culture medium that can reach to higher intracellular concentrations than does EGCG [68].
2.3 Other Polyphenols
In addition to the aforementioned EGCG and genistein, the inhibition of DNMT activity of other common dietary phenolic compounds, which are abundant in many fruits, vegetables, and beverages, was also determined [68, 80]. These compounds include myricetin and quercetin (flavanols), hesperetin and naringenin (flavanols), apigenin and luteolin (flavanols), garcinol, curcumin, and hydroxycinnamic acid. All these compounds are weaker direct inhibitors of the DNMTs compared with EGCG because these polyphenols, lacking a gallic/pyrogallic acid moiety, cannot form a similarly strong coordination with the DNMT catalytic center, which, in turn, interferes with the activities of DNMTs inhibition. However, polyphenols with catechol structures could still exert a considerably strong indirect inhibition of DNA methylation through converting SAM: SAH ratio during their metabolic methylation by COMT.
3. Selenium
Selenium is an essential trace element with both anti-oxidant and pro-apoptotic properties (Table 2) [94, 95]. Interventional trials provide the strongest evidence for protective effects of selenium against various cancers. Davis et al. have demonstrated that in the colon and liver, selenium deficiency causes global hypomethylation and in addition, promoter methylation of p53 and p16 genes, suggesting that impacting DNA methylation may be a crucial mechanism of selenium for cancer prevention [96]. Selenium has been shown to inhibit DNMT through direct interaction and indirect action by influencing plasma homocysteine concentrations and the SAM: SAH ratio [97, 98].
4. Isothiocyanates
Isothiocyanates, metabolites of glucosinolates, are found naturally in cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cabbages, and watercress and have been reported to reduce the incidence of prostate cancer (Table 2) [99]. Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC), a hydrolytic product of glucosinolate gluconasturtin, has been proposed to reduce cell growth of prostate cancer both in vivo and in vitro [100, 101]. Current studies have found that PEITC could reactivate the expression of glutathione S-transferase gene (GSTP1), a cellular detoxifying factor, through inducing hyomethylation of the promoter of GSTP1 in prostate cancer cells [102]. A synergistic effect on reactivating GSTP1 was also observed when PEITC was combined with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine. However, the precise mechanism of the effect of the isothiocyanates on DNA methylation is still unknown and requires further investigation.
Future research direction
Dietary supplement approaches have been amply demonstrated in cancer prevention by influencing epigenetic pathways both in vitro and in vivo. Future investigations on dietary intervention that combine these dietary components with epigenetic modulators such as the DNMT inhibitor, 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-aza-dCyd), could be applied in clinical trials. Moreover, future exploration for new drugs using dietary compounds with more biological activity will be beneficial for new cancer therapeutical approaches.
Summary
Interest in the role of bioactive botanic ingredients on epigenetics in human health and disease has expanded rapidly in recent years. In this review, we have discussed some bioactive dietary compounds which could exert their anticancer properties through epigenetic mechanisms. These dietary components including folate, EGCG, genistein, selenium and isothiocyanates can influence DNA methylation processes, thereby leading to altered gene expression profiles and ultimately, cancer inhibition. This study will offer exciting new opportunities to explore the role of diet in influencing the biology of cancer and to understand the susceptibility of the human epigenome to dietary effects. More importantly, better understanding the precise mechanisms of the impact of the human diet on cancer development will certainly facilitate the field of new drug discovery and novel approaches to cancer therapeutic strategies.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the Susan G. Komen for the Cure.
Abbreviations
- COMT
catechol-O-methyltransferase
- DNMT
DNA methyltransferase
- EGCG
(−)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate
- GSTP1
glutathione S-transferase gene
- hMLH1
human mutL homolog 1
- hTERT
human telomerase reverse transcriptase
- IAP
intracisternal A particle
- MGMT
O6-methylguanine methyltransferase
- 5mC MTase
cytosine-C5-methylation methyltransferase
- PEITC
phenethyl isothiocyanate
- RARβ
retinoic acid receptor β
- SAH
S-adenosylhomocysteine
- SAM
S-adenosylmethionine
References
- 1.Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones P. Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature. 2004;429:457–63. doi: 10.1038/nature02625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Narlikar G, Fan H, Kingston R. Cooperation between complexes that regulate chromatin structure and transcription. Cell. 2002;108:475–87. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00654-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jenuwein T, Allis C. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1063127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cervoni N, Bhattacharya S, Szyf M. DNA demethylase is a processive enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8363–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.13.8363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Razin A, Riggs A. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980;210:604–10. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cross S, Bird A. CpG islands and genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995;5:309–14. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Antequera F, Bird A. Number of CpG islands and genes in human and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:11995–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li E, Beard C, Jaenisch R. Role for DNA methylation in genomic imprinting. Nature. 1993;366:362–5. doi: 10.1038/366362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li E, Beard C, Forster A, Bestor T, Jaenisch R. DNA methylation, genomic imprinting, and mammalian development. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:297–305. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chan M, Liang G, Jones P. Relationship between transcription and DNA methylation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;249:75–86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59696-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Baylin S, Ohm J. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer - a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:107–16. doi: 10.1038/nrc1799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gaudet F, Hodgson J, Eden A, Jackson-Grusby L, Dausman J, Gray J, Leonhardt H, Jaenisch R. Induction of tumors in mice by genomic hypomethylation. Science. 2003;300:489–92. doi: 10.1126/science.1083558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bestor T. The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:2395–402. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.16.2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yen R, Vertino P, Nelkin B, Yu J, el-Deiry W, Cumaraswamy A, Lennon G, Trask B, Celano P, Baylin S. Isolation and characterization of the cDNA encoding human DNA methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992;20:2287–91. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.9.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chuang L, Ian H, Koh T, Ng H, Xu G, Li B. Human DNA-(cytosine-5) methyltransferase-PCNA complex as a target for p21WAF1. Science. 1997;277:1996–2000. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5334.1996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Leonhardt H, Page A, Weier H, Bestor T. A targeting sequence directs DNA methyltransferase to sites of DNA replication in mammalian nuclei. Cell. 1992;71:865–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90561-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bestor T. Activation of mammalian DNA methyltransferase by cleavage of a Zn binding regulatory domain. EMBO J. 1992;11:2611–7. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rountree M, Bachman K, Baylin S. DNMT1 binds HDAC2 and a new co-repressor, DMAP1, to form a complex at replication foci. Nat Genet. 2000;25:269–77. doi: 10.1038/77023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cheng X. Structure and function of DNA methyltransferases. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995;24:293–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.24.060195.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wu J, Santi D. Kinetic and catalytic mechanism of HhaI methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:4778–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Klimasauskas S, Kumar S, Roberts R, Cheng X. HhaI methyltransferase flips its target base out of the DNA helix. Cell. 1994;76:357–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90342-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang X, Bruice T. The mechanism of M.HhaI DNA C5 cytosine methyltransferase enzyme: a quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:6148–53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601587103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jeltsch A. Beyond Watson and Crick: DNA methylation and molecular enzymology of DNA methyltransferases. Chembiochem. 2002;3:274–93. doi: 10.1002/1439-7633(20020402)3:4<274::AID-CBIC274>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Biniszkiewicz D, Gribnau J, Ramsahoye B, Gaudet F, Eggan K, Humpherys D, Mastrangelo M, Jun Z, Walter J, Jaenisch R. Dnmt1 overexpression causes genomic hypermethylation, loss of imprinting, and embryonic lethality. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:2124–35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2124-2135.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jeltsch A. On the enzymatic properties of Dnmt1: specificity, processivity, mechanism of linear diffusion and allosteric regulation of the enzyme. Epigenetics. 2002;1:63–6. doi: 10.4161/epi.1.2.2767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Grandjean V, Yaman R, Cuzin F, Rassoulzadegan M. Inheritance of an epigenetic mark: the CpG DNA methyltransferase 1 is required for de novo establishment of a complex pattern of non-CpG methylation. PLoS One. 2007;2:e1136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.De Marzo A, Marchi V, Yang E, Veeraswamy R, Lin X, Nelson W. Abnormal regulation of DNA methyltransferase expression during colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1999;59:3855–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Robert M, Morin S, Beaulieu N, Gauthier F, Chute I, Barsalou A, MacLeod A. DNMT1 is required to maintain CpG methylation and aberrant gene silencing in human cancer cells. Nat Genet. 2003;33:61–65. doi: 10.1038/ng1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Okano M, Bell D, Haber D, Li E. DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell. 1999;99:247–57. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81656-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hansen R, Wijmenga C, Luo P, Stanek A, Canfield T, Weemaes C, Gartler S. The DNMT3B DNA methyltransferase gene is mutated in the ICF immunodeficiency syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:14412–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xu G, Bestor T, Bourc’his D, Hsieh C, Tommerup N, Bugge M, Hulten M, Qu X, Russo J, Viegas-Péquignot E. Chromosome instability and immunodeficiency syndrome caused by mutations in a DNA methyltransferase gene. Nature. 1999;402:187–91. doi: 10.1038/46052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Robertson K, Uzvolgyi E, Liang G, Talmadge C, Sumegi J, Gonzales F, Jones P. The human DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) 1, 3a and 3b: coordinate mRNA expression in normal tissues and overexpression in tumors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:2291–8. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.11.2291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jia D, Jurkowska R, Zhang X, Jeltsch A, Cheng X. Structure of Dnmt3a bound to Dnmt3L suggests a model for de novo DNA methylation. Nature. 2007;449:248–51. doi: 10.1038/nature06146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Waterland R, Jirtle R. Early nutrition, epigenetic changes at transposons and imprinted genes, and enhanced susceptibility to adult chronic diseases. Nutrition. 2004;20:63–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2003.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yen T, Gill A, Frigeri L, Barsh G, Wolff G. Obesity, diabetes, and neoplasia in yellow A(vy)/− mice: ectopic expression of the agouti gene. FASEB J. 1994;8:479–88. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.8.8181666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Michaud E, van Vugt M, Bultman S, Sweet H, Davisson M, Woychik R. Differential expression of a new dominant agouti allele (Aiapy) is correlated with methylation state and is influenced by parental lineage. Genes Dev. 1994;8:1463–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.12.1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Berletch J, Liu C, Love W, Andrews L, Katiyar S, Tollefsbol T. Epigenetic and genetic mechanisms contribute to telomerase inhibition by EGCG. J Cell Biochem. 2008;103:509–19. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mittal A, Piyathilake C, Hara Y, Katiyar S. Exceptionally high protection of photocarcinogenesis by topical application of (--)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in hydrophilic cream in SKH-1 hairless mouse model: relationship to inhibition of UVB-induced global DNA hypomethylation. Neoplasia. 2003;5:555–65. doi: 10.1016/s1476-5586(03)80039-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fang M, Wang Y, Ai N, Hou Z, Sun Y, Lu H, Welsh W, Yang C. Tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits DNA methyltransferase and reactivates methylation-silenced genes in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003;63:7563–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fang M, Chen D, Sun Y, Jin Z, Christman J, Yang C. Reversal of hypermethylation and reactivation of p16INK4a, RARbeta, and MGMT genes by genistein and other isoflavones from soy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:7033–41. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li Y, Liu L, Andrews L, Tollefsbol T. Genistein depletes telomerase activity through cross-talk between genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:289–96. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hoffman D, Cornatzer W, Duerre J. Relationship between tissue levels of S-adenosylmethionine, S-adenylhomocysteine, and transmethylation reactions. Can J Biochem. 1979;57:56–65. doi: 10.1139/o79-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Williams K, Schalinske K. New insights into the regulation of methyl group and homocysteine metabolism. J Nutr. 2007;137:311–4. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shane B, Stokstad E. The interrelationships among folate, vitamin B12, and methionine metabolism. Adv Nutr Res. 1983;5:133–70. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9937-7_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Suh J, Herbig A, Stover P. New perspectives on folate catabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 2001;21:255–82. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kim Y. Folate and carcinogenesis: evidence, mechanisms, and implications. J Nutr Biochem. 1999;10:66–88. doi: 10.1016/s0955-2863(98)00074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kotsopoulos J, Sohn K, Kim Y. Postweaning dietary folate deficiency provided through childhood to puberty permanently increases genomic DNA methylation in adult rat liver. J Nutr. 2008;138:703–9. doi: 10.1093/jn/138.4.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wolff G, Kodell R, Moore S, Cooney C. Maternal epigenetics and methyl supplements affect agouti gene expression in Avy/a mice. FASEB J. 1998;12:949–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Waterland R, Dolinoy D, Lin J, Smith C, Shi X, Tahiliani K. Maternal methyl supplements increase offspring DNA methylation at Axin Fused. Genesis. 2006;44:401–6. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim Y. Nutritional epigenetics: impact of folate deficiency on DNA methylation and colon cancer susceptibility. J Nutr. 2005;135:2703–9. doi: 10.1093/jn/135.11.2703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Stempak J, Sohn K, Chiang E, Shane B, Kim Y. Cell and stage of transformation-specific effects of folate deficiency on methionine cycle intermediates and DNA methylation in an in vitro model. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:981–90. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hamid A, Wani N, Kaur J. New perspectives on folate transport in relation to alcoholism-induced folate malabsorption--association with epigenome stability and cancer development. FEBS J. 2009;276:2175–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Jacob R, Gretz D, Taylor P, James S, Pogribny I, Miller B, Henning S, Swendseid M. Moderate folate depletion increases plasma homocysteine and decreases lymphocyte DNA methylation in postmenopausal women. J Nutr. 1998;128:1204–12. doi: 10.1093/jn/128.7.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kim Y. Folate and DNA methylation: a mechanistic link between folate deficiency and colorectal cancer? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13:511–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fenech M, Aitken C, Rinaldi J. Folate, vitamin B12, homocysteine status and DNA damage in young Australian adults. Carcinogenesis. 1998;19:1163–71. doi: 10.1093/carcin/19.7.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kim Y, Baik H, Fawaz K, Knox T, Lee Y, Norton R, Libby E, Mason J. Effects of folate supplementation on two provisional molecular markers of colon cancer: a prospective, randomized trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:184–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Song J, Medline A, Mason J, Gallinger S, Kim Y. Effects of dietary folate on intestinal tumorigenesis in the apcMin mouse. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5434–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rhodes M, Price K. Identification and analysis of plant phenolic antioxidants. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1997;6:518–21. doi: 10.1097/00008469-199712000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yoon J, Baek S. Molecular targets of dietary polyphenols with anti-inflammatory properties. Yonsei Med J. 2005;46:585–96. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.5.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yang C, Landau J, Huang M, Newmark H. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by dietary polyphenolic compounds. Annu Rev Nutr. 2001;21:381–406. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Graham H. Green tea composition, consumption, and polyphenol chemistry. Prev Med. 1992;21:334–50. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(92)90041-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yang C, Chen L, Lee M, Landau J. Effects of tea on carcinogenesis in animal models and humans. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996;401:51–61. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0399-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Katiyar S, Mukhtar H. Tea consumption and cancer. World Rev Nutr Diet. 1996;79:154–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ju J, Hong J, Zhou J, Pan Z, Bose M, Liao J, Yang G, Liu Y, Hou Z, Lin Y, Ma J, Shih W, Carothers A, Yang C. Inhibition of intestinal tumorigenesis in Apcmin/+ mice by (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, the major catechin in green tea. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10623–31. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Naasani I, Oh-Hashi F, Oh-Hara T, Feng W, Johnston J, Chan K, Tsuruo T. Blocking telomerase by dietary polyphenols is a major mechanism for limiting the growth of human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2003;63:824–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Liao S, Umekita Y, Guo J, Kokontis J, Hiipakka R. Growth inhibition and regression of human prostate and breast tumors in athymic mice by tea epigallocatechin gallate. Cancer Lett. 1995;96:239–43. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(95)03948-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lambert J, Yang C. Cancer chemopreventive activity and bioavailability of tea and tea polyphenols. Mutat Res. 2003;523–4:201–8. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(02)00336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Fang M, Chen D, Yang C. Dietary polyphenols may affect DNA methylation. J Nutr. 2007;137:223S–8S. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.1.223S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lee A, Fraser M, Meng X, Binns C. Protective effects of green tea against prostate cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2006;6:507–13. doi: 10.1586/14737140.6.4.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Johnson I, Belshaw N. Environment, diet and CpG island methylation: epigenetic signals in gastrointestinal neoplasia. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46:1346–59. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.09.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Tachibana H. Molecular basis for cancer chemoprevention by green tea polyphenol EGCG. Forum Nutr. 2009;61:156–69. doi: 10.1159/000212748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Pandey M, Shukla S, Gupta S. Promoter demethylation and chromatin remodeling by green tea polyphenols leads to re-expression of GSTP1 in human prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2009 doi: 10.1002/ijc.24988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Gao Z, Xu Z, Hung M, Lin Y, Wang T, Gong M, Zhi X, Jablon D, You L. Promoter demethylation of WIF-1 by epigallocatechin-3-gallate in lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:2025–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kato K, Long N, Makita H, Toida M, Yamashita T, Hatakeyama D, Hara A, Mori H, Shibata T. Effects of green tea polyphenol on methylation status of RECK gene and cancer cell invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:647–54. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Guilleret I, Yan P, Grange F, Braunschweig R, Bosman F, Benhattar J. Hypermethylation of the human telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT) gene correlates with telomerase activity. Int J Cancer. 2002;101:335–41. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Yuasa Y, Nagasaki H, Akiyama Y, Sakai H, Nakajima T, Ohkura Y, Takizawa T, Koike M, Tani M, Iwai T, Sugihara K, Imai K, Nakachi K. Relationship between CDX2 gene methylation and dietary factors in gastric cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:193–200. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tsao A, Liu D, Martin J, Tang X, Lee J, El-Naggar A, Wistuba I, Culotta K, Mao L, Gillenwater A, Sagesaka Y, Hong W, Papadimitrakopoulou V. Relationship between CDX2 gene methylation and dietary factors in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Prev Res (Phila Pa) 2009;2:931–41. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Meng X, Sang S, Zhu N, Lu H, Sheng S, Lee M, Ho C, Yang C. Identification and characterization of methylated and ring-fission metabolites of tea catechins formed in humans, mice, and rats. Chem Res Toxicol. 2002;15:1042–50. doi: 10.1021/tx010184a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lu H, Meng X, Li C, Sang S, Patten C, Sheng S, Hong J, Bai N, Winnik B, Ho C, Yang C. Glucuronides of tea catechins: enzymology of biosynthesis and biological activities. Drug Metab Dispos. 2003;31:452–61. doi: 10.1124/dmd.31.4.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lee W, Shim J, Zhu B. Mechanisms for the inhibition of DNA methyltransferases by tea catechins and bioflavonoids. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;68:1018–30. doi: 10.1124/mol.104.008367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Olthof M, Hollman P, Zock P, Katan M. Consumption of high doses of chlorogenic acid, present in coffee, or of black tea increases plasma total homocysteine concentrations in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;73:532–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/73.3.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Okano M, Xie S, Li E. Cloning and characterization of a family of novel mammalian DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferases. Nat Genet. 1998;19:219–20. doi: 10.1038/890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Lee H, Gourley L, Duffy S, Estéve J, Lee J, Day N. Dietary effects on breast-cancer risk in Singapore. Lancet. 1991;337:1197–200. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92867-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Fang C, Tseng M, Daly M. Correlates of soy food consumption in women at increased risk for breast cancer. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005;105:1552–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2005.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Barnes S. Effect of genistein on in vitro and in vivo models of cancer. J Nutr. 1995;125:777S–83S. doi: 10.1093/jn/125.3_Suppl.777S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Fotsis T, Pepper M, Adlercreutz H, Fleischmann G, Hase T, Montesano R, Schweigerer L. Genistein, a dietary-derived inhibitor of in vitro angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:2690–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Okura A, Arakawa H, Oka H, Yoshinari T, Monden Y. Effect of genistein on topoisomerase activity and on the growth of [Val 12]Ha-ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;157:183–9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Messina M, McCaskill-Stevens W, Lampe J. Addressing the soy and breast cancer relationship: review, commentary, and workshop proceedings. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:1275–84. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djj356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Majid S, Kikuno N, Nelles J, Noonan E, Tanaka Y, Kawamoto K, Hirata H, Li L, Zhao H, Okino S, Place R, Pookot D, Dahiya R. Genistein induces the p21WAF1/CIP1 and p16INK4a tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer cells by epigenetic mechanisms involving active chromatin modification. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2736–44. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Dolinoy D, Weidman J, Waterland R, Jirtle R. Maternal genistein alters coat color and protects Avy mouse offspring from obesity by modifying the fetal epigenome. Environ Health Perspect. 2006;114:567–72. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Day J, Bauer A, DesBordes C, Zhuang Y, Kim B, Newton L, Nehra V, Forsee K, MacDonald R, Besch-Williford C, Huang T, Lubahn D. Genistein alters methylation patterns in mice. J Nutr. 2002;132:2419S–23S. doi: 10.1093/jn/132.8.2419S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kikuno N, Shiina H, Urakami S, Kawamoto K, Hirata H, Tanaka Y, Majid S, Igawa M, Dahiya R. Genistein mediated histone acetylation and demethylation activates tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:552–60. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Messina M, Wu A. Perspectives on the soy-breast cancer relation. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89:1673S–9S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.26736V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Clark L, Cantor K, Allaway W. Selenium in forage crops and cancer mortality in U.S. counties. Arch Environ Health. 1991;46:37–42. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1991.9937427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Clark L, Combs GJ, Turnbull B, Slate E, Chalker D, Chow J, Davis L, Glover R, Graham G, Gross E, Krongrad A, Lesher JJ, Park H, Sanders BJ, Smith C, Taylor J. Effects of selenium supplementation for cancer prevention in patients with carcinoma of the skin. A randomized controlled trial. Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Study Group. JAMA. 1996;276:1957–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Davis C, Uthus E, Finley J. Dietary selenium and arsenic affect DNA methylation in vitro in Caco-2 cells and in vivo in rat liver and colon. J Nutr. 2000;130:2903–9. doi: 10.1093/jn/130.12.2903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Davis C, Uthus E. Dietary selenite and azadeoxycytidine treatments affect dimethylhydrazine-induced aberrant crypt formation in rat colon and DNA methylation in HT-29 cells. J Nutr. 2002;132:292–7. doi: 10.1093/jn/132.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Uthus E, Ross S. Dietary selenium affects homocysteine metabolism differently in Fisher-344 rats and CD-1 mice. J Nutr. 2007;137:1132–6. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.5.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Chiao J, Wu H, Ramaswamy G, Conaway C, Chung F, Wang L, Liu D. Ingestion of an isothiocyanate metabolite from cruciferous vegetables inhibits growth of human prostate cancer cell xenografts by apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:1403–8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Zhang Y, Talalay P. Anticarcinogenic activities of organic isothiocyanates: chemistry and mechanisms. Cancer Res. 1994;54:1976s–81s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Hecht S. Chemoprevention by isothiocyanates. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1995;22:195–209. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240590825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Wang L, Beklemisheva A, Liu X, Ferrari A, Feng J, Chiao J. Dual action on promoter demethylation and chromatin by an isothiocyanate restored GSTP1 silenced in prostate cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2007;46:24–31. doi: 10.1002/mc.20258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]