Figure 1.
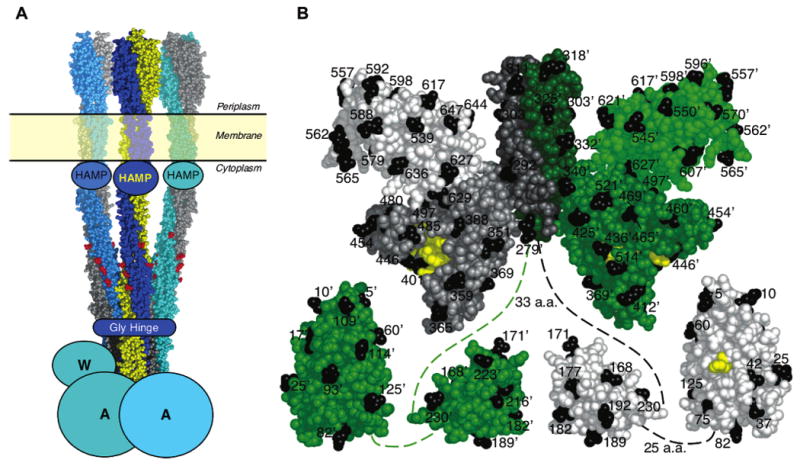
Summary of structural models from previous studies. (A) Model of the core complex consisting of the transmembrane receptor oligomer, CheA kinase, and CheW coupling protein. The receptors are shown as a trimer-of-dimers (49, 50) based on a composite structural model (reviewed in ref 6). HAMP is a conserved domain of unknown structure (51–53), while Gly Hinge is also a conserved element (54). Homodimeric CheA and monomeric CheW are schematic. (B) Structural model of CheA showing one subunit in shades of green and the other in shades of gray. Black identifies the 70 positions of Cys substitutions used in this study. Yellow marks catalytic residues including H48, the site of phosphorylation on the P1 domain, and the ATP binding residues on the P4 domain. The composite CheA structure is assembled from S. typhimurium P1 domain (12), E. coli P2 domain (10), and T. maritima P3+P4+P5 domain fragment (11). Dashed lines indicate extended flexible linkers of undetermined structure that connect the domains.
