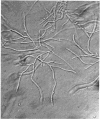
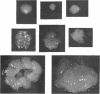
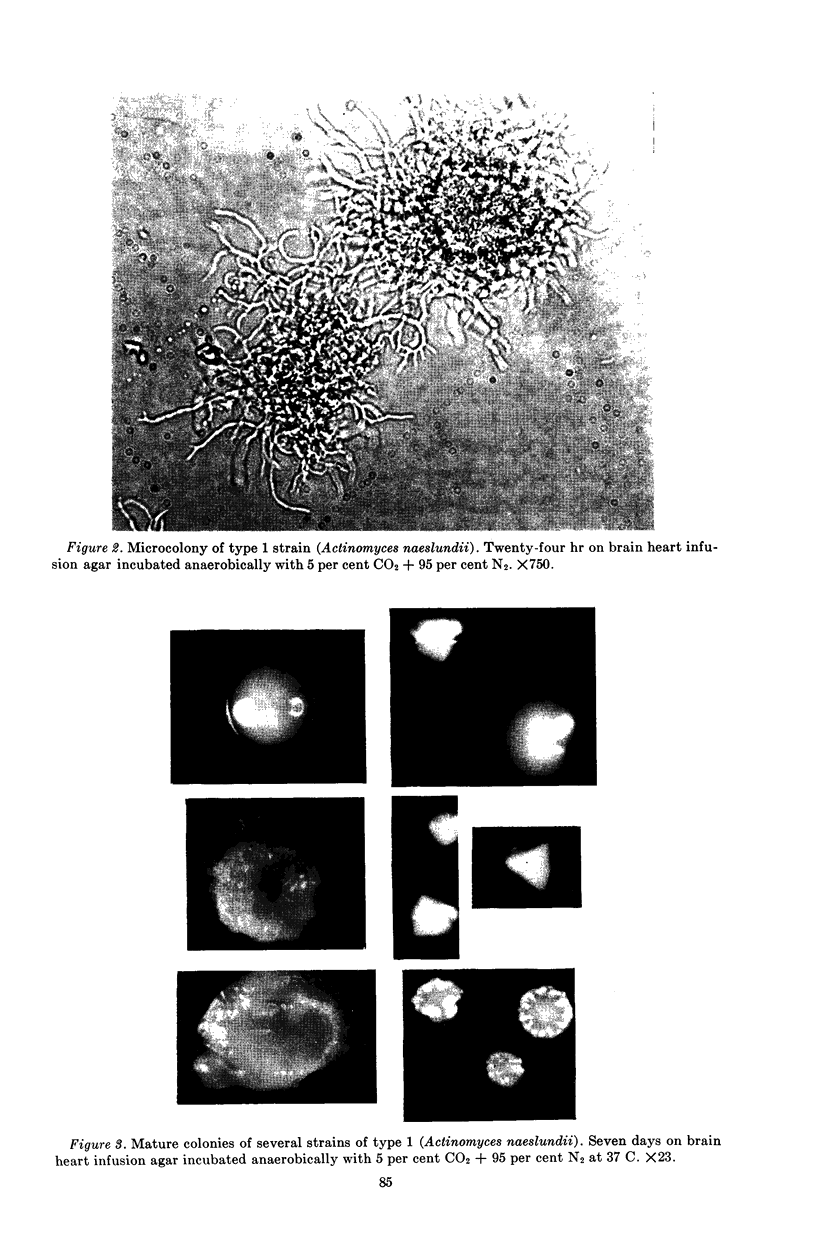
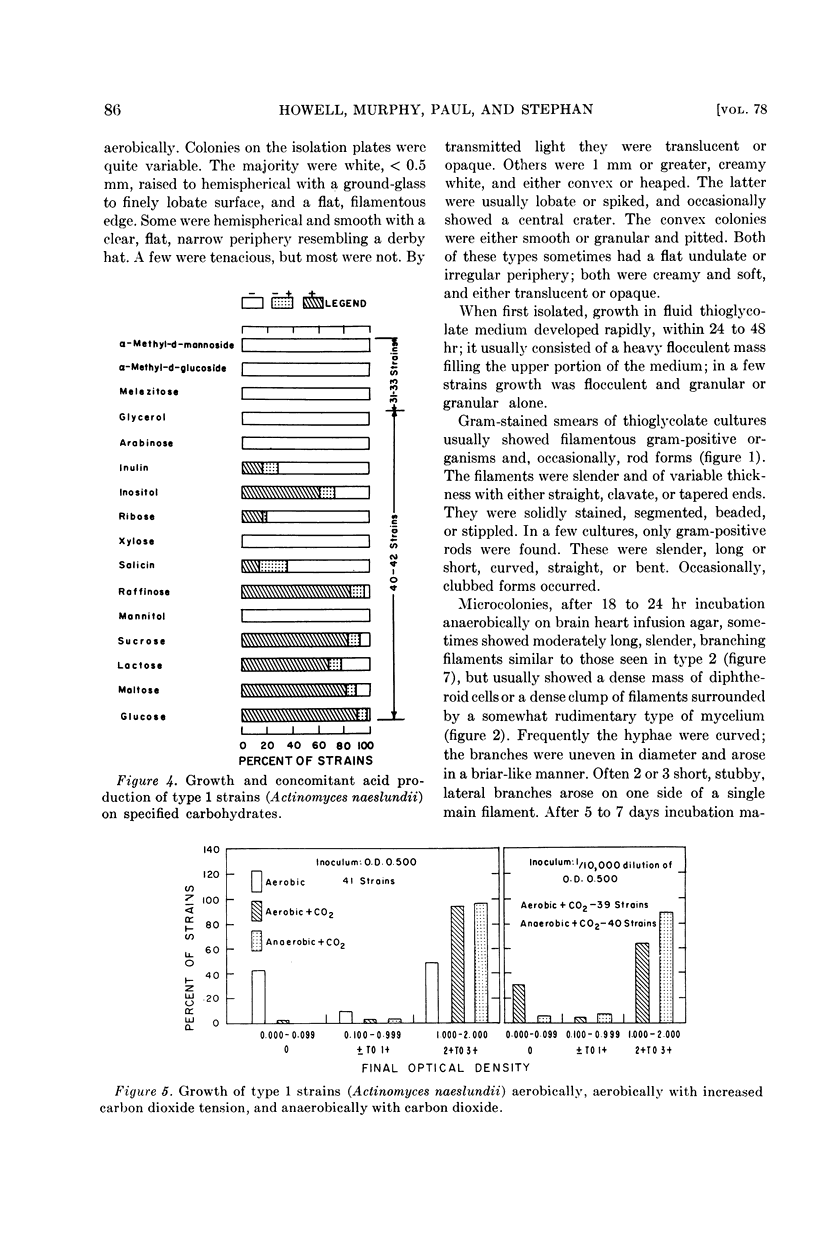
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ENNEVER J. J., WARNER B. W. Phosphatase and the oral Actinomyces. J Dent Res. 1952 Feb;31(1):25–26. doi: 10.1177/00220345520310011601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNEVER J., ROBINSON H. B. G., KITCHIN P. C. Actinomyces and the dentobacterial plaque. J Dent Res. 1951 Feb;30(1):88–96. doi: 10.1177/00220345510300011801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P. Actinomycosis of the lung; aetiology, diagnosis and chemotherapy. Tubercle. 1952 Sep;33(9):258–266. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(52)80124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P. The sensitivity of actinomyces israeli to antibiotics. Br Med J. 1952 Jun 14;1(4771):1263–1264. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4771.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEISTER R. S., MEYER E. The effect of aureomycin and penicillin on experimental actinomycosis infections in mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jul;38(1):101–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAZEN E. L., LITTLE G. N. Actinomyces bovis and anaerobic diphtheroids pathogenicity for hamsters and some other differentiating characteristics. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Jun;51(6):968–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAZEN E. L., LITTLE G. N., RESNICK H. The hamster as a vehicle for the demonstration of pathogenicity of Actinomyces bovis. J Lab Clin Med. 1952 Dec;40(6):914–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, FITZGERALD R. J. The production of acid phosphatase by certain species of Actinomyces. J Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(4):437–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.4.437-442.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, PINE L. Comparison of physiological and biochemical characters of Actinomyces spp. with those of Lactobacillus bifidus. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Dec;15(3):428–445. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-3-428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, PINE L. Studies on the growth of species of Actinomyces. I. Cultivation in a synthetic medium with starch. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jan;71(1):47–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.1.47-53.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER E., VERGES P. Mouse pathogenicity as a diagnostic aid in the identification of actinomyces bovis. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Oct;36(4):667–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER N. G., DRAKE C. H. Experimental actinomycosis. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1951 Oct 30;6(1):28–37. doi: 10.1007/BF02115731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. The Source of Infection in Actinomycosis. J Bacteriol. 1942 Feb;43(2):193–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.2.193-209.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON L. Isolation and comparison of Actinomyces from human and bovine infections. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1950 Feb 15;25(4):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON L., LOVESTEDT S. A. An Actinomyces-like organism obtained from the human mouth. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1951 May 9;26(10):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]