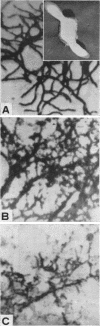
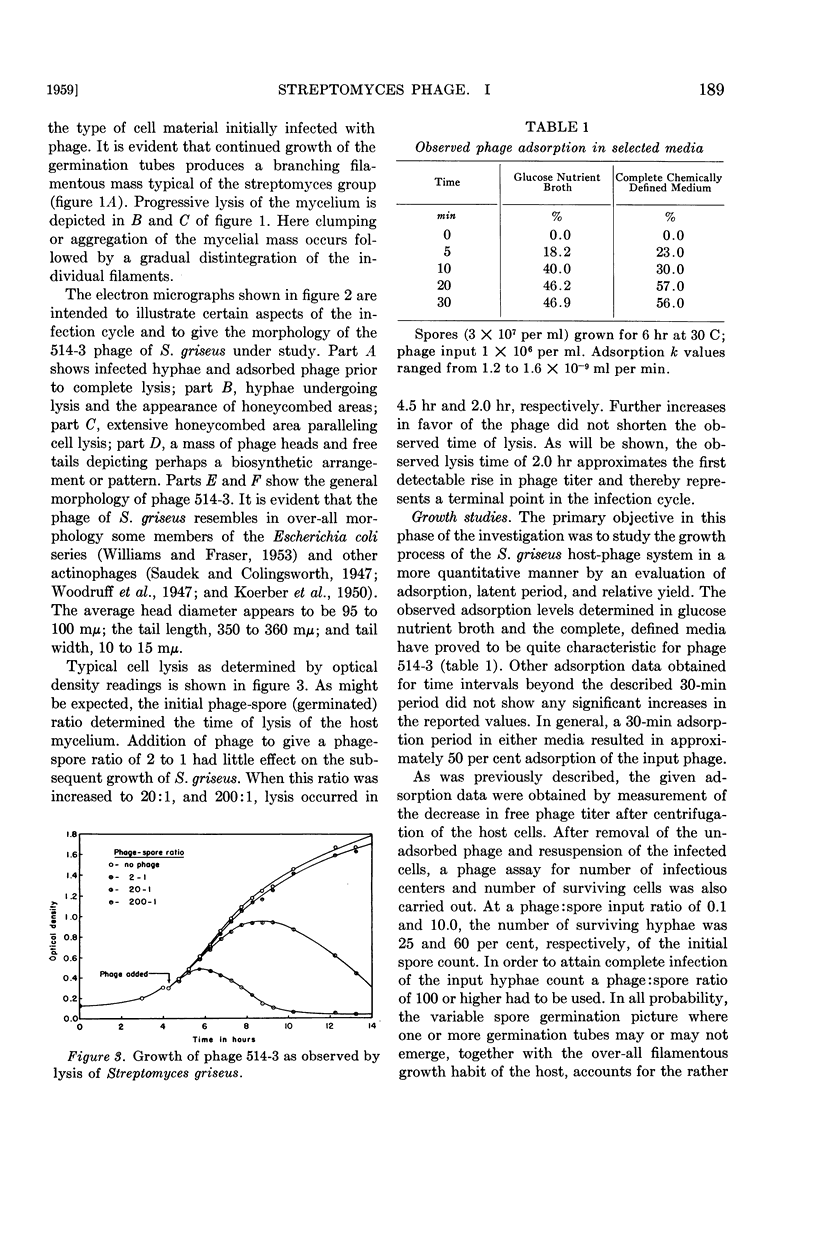
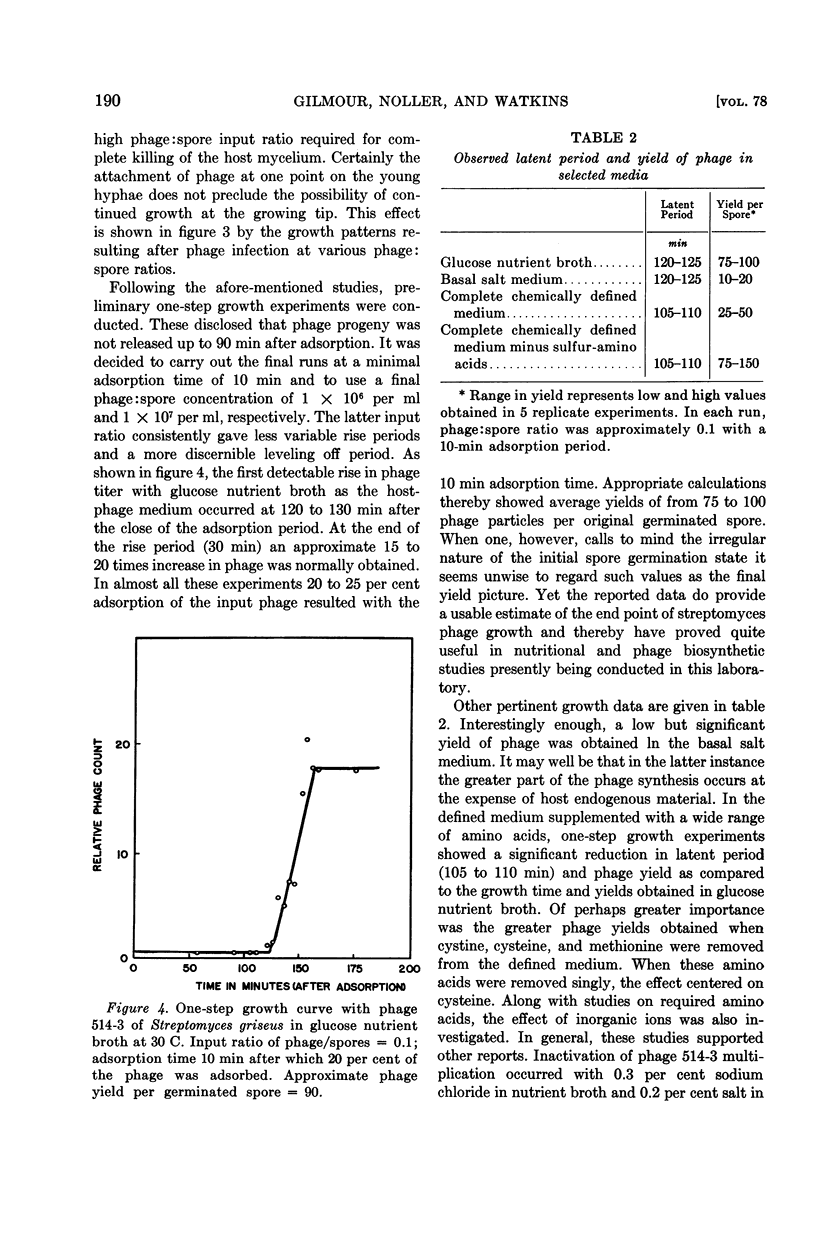
Full text
PDF
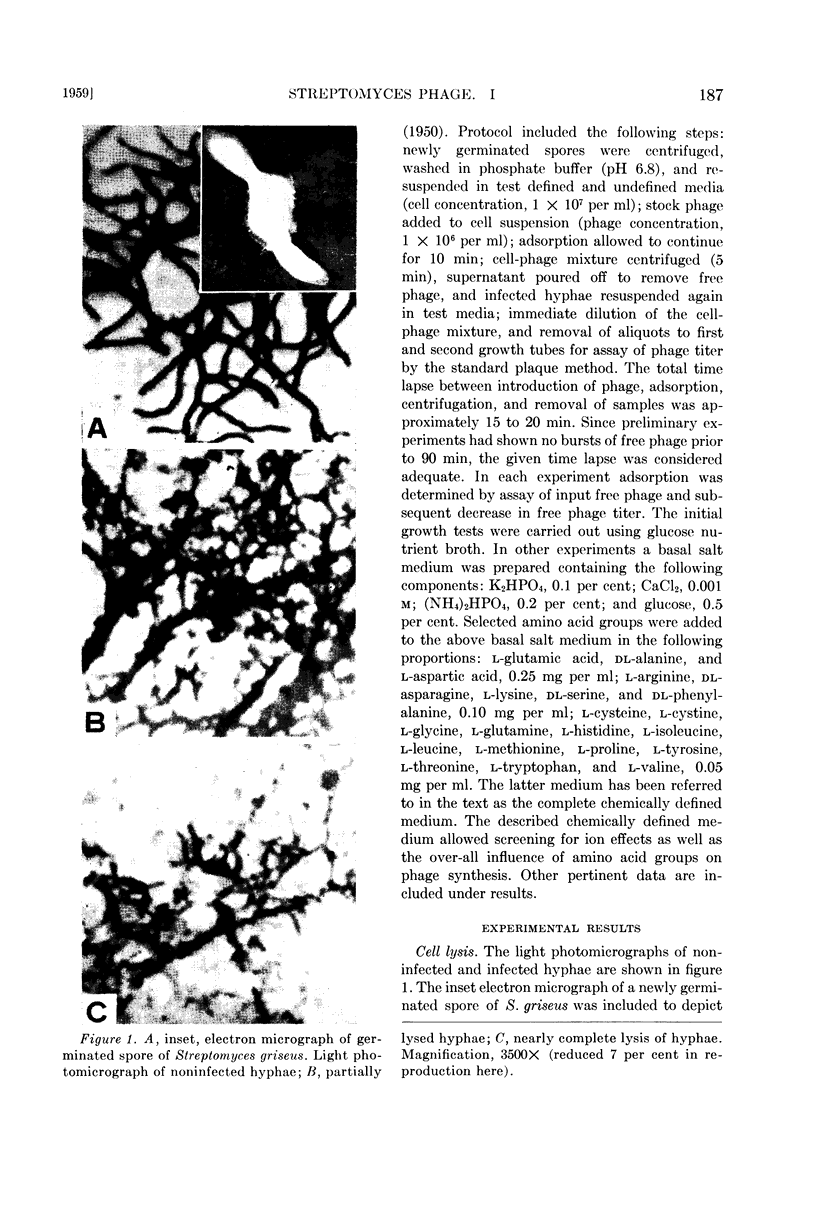
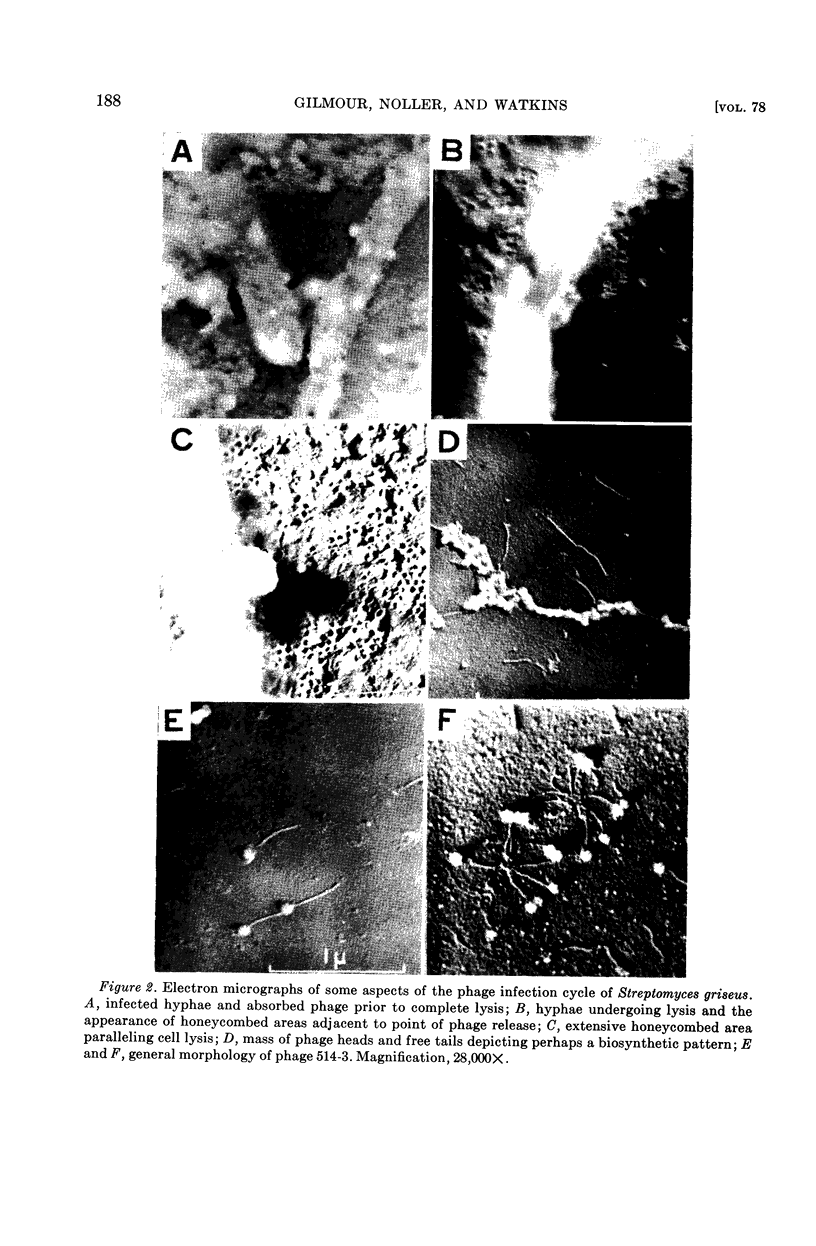


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER R. R., MCCOY E. Characterization of Streptomyces griseus bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1956 Sep;72(3):378–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.3.378-386.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The effect of phage infection on the metabolic activity of the host cell. Br J Exp Pathol. 1952 Aug;33(4):368–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOERBER W. L., GREENSPAN G., LANGLYKKE A. F. Observations on the multiplication of phages affecting Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):29–37. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.29-37.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMAN D., LANGLYKKE A. F., ROTHBERG H. D., Jr Observations on the chemical inhibition of Streptomyces griseus bacteriophage multiplication. J Bacteriol. 1951 Feb;61(2):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.2.135-143.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly H. C., Harris D. A., Waksman S. A. An Actinophage for Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1947 Oct;54(4):451–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.4.451-466.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., FRASER D. Morphology of the seven T-bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(4):458–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.4.458-464.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff H. B., Nunheimer T. D., Lee S. B. A Bacterial Virus for Actinomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1947 Oct;54(4):535–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.4.535-541.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]