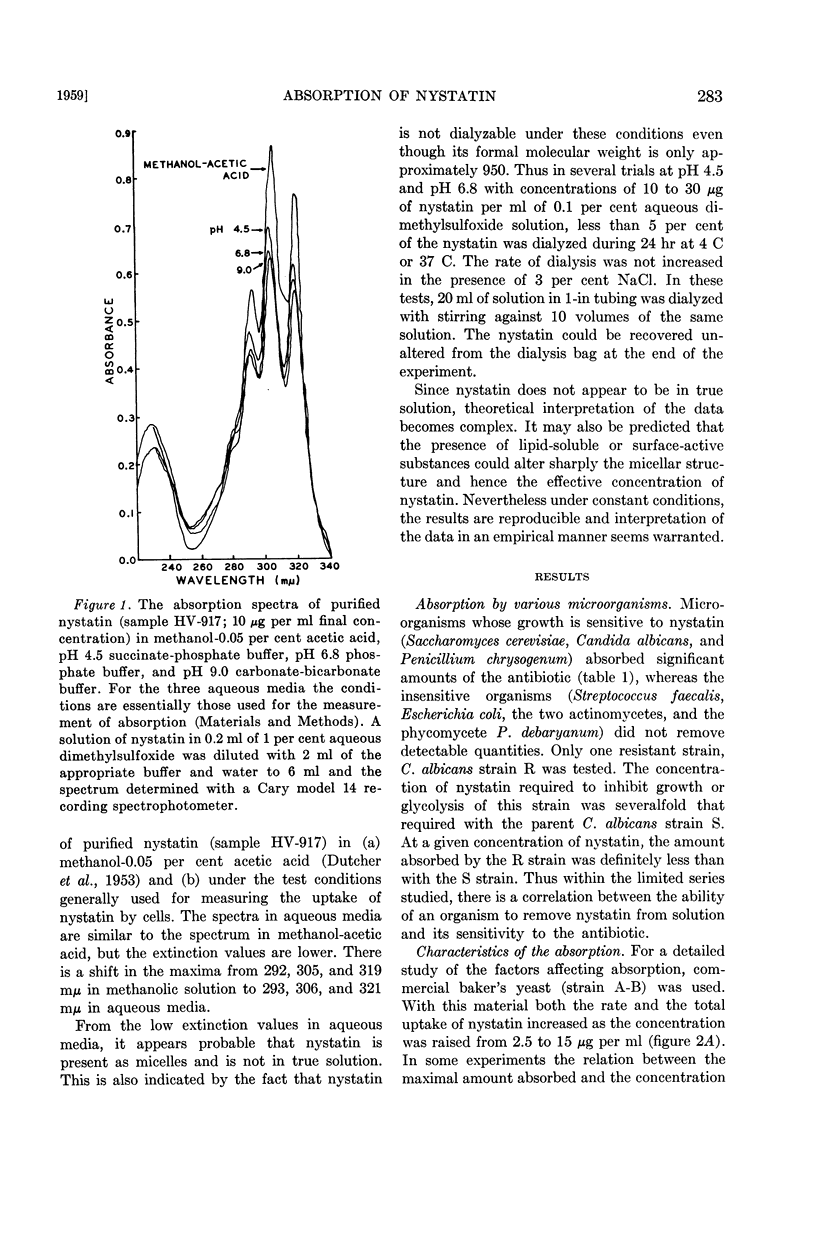
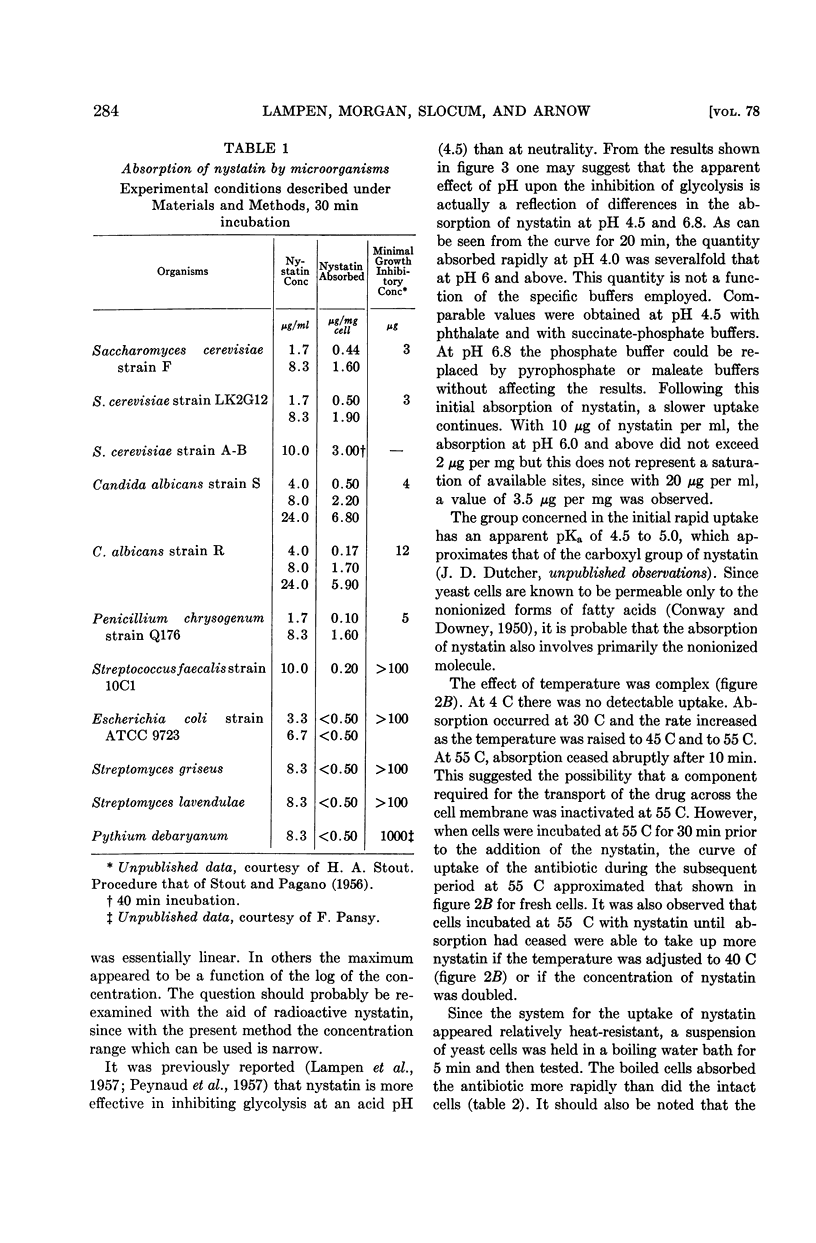
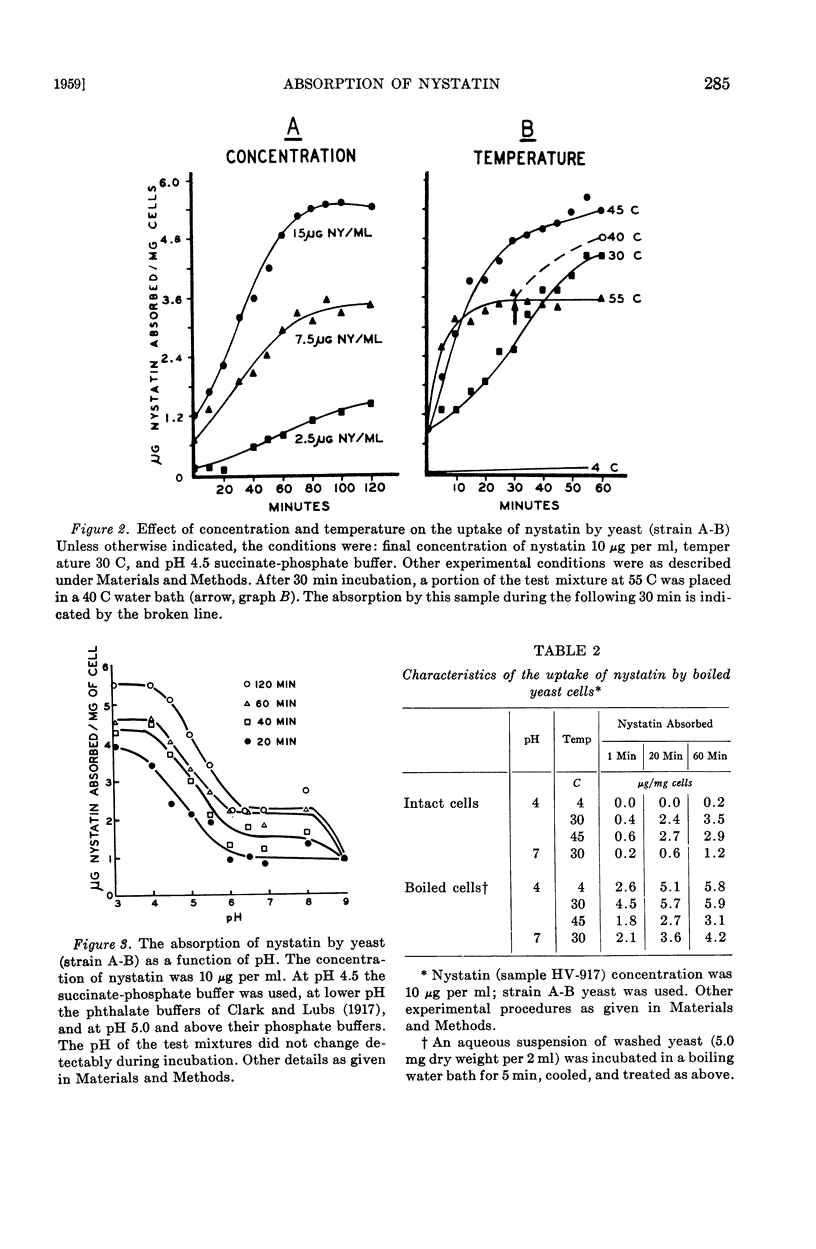
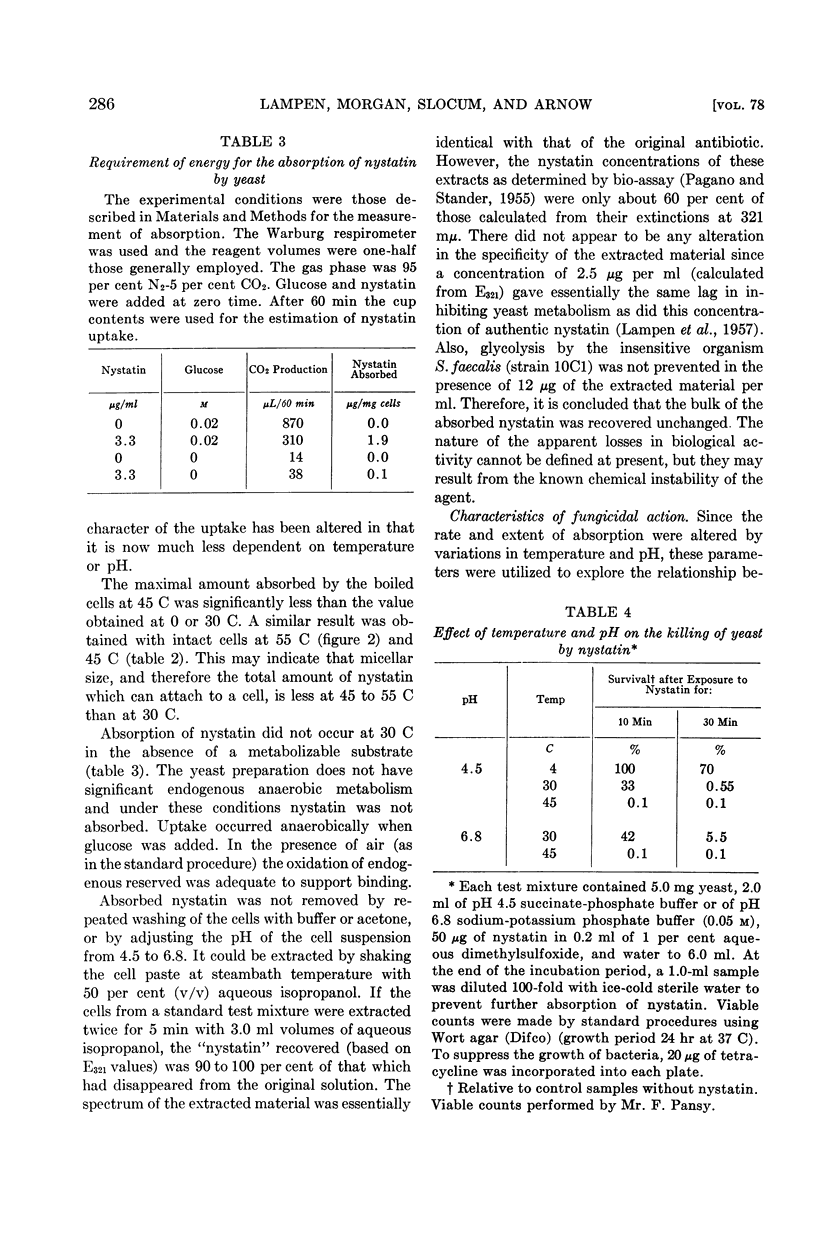
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADLEY S. G. Interactions between phosphate and nystatin in Candida stellatoidea. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):786–789. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN R., HAZEN E. L. Present knowledge of nystatin, an antifungal antibiotic. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Mar;19(5):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY E. J., DOWNEY M. An outer metabolic region of the yeast cell. Biochem J. 1950 Sep;47(3):347–355. doi: 10.1042/bj0470347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. Site of action of radiopenicillin. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):28–48. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.28-48.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. M., Lubs H. A. The Colorimetric Determination of Hydrogen Ion Concentration and its Applications in Bacteriology : I. J Bacteriol. 1917 Jan;2(1):1–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.2.1.1-34.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL J. W., Jr, JOHNSON M. J. Properties of the penicillin binding component of Micrococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1954 Mar;67(3):321–328. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.3.321-328.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARMAN J. W., MASTERSON J. G. The mechanism of nystatin action. Ir J Med Sci. 1957 Jun;(378):249–253. doi: 10.1007/BF02954476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPEN J. O., MORGAN E. R., SLOCUM A. Effect of nystatin on the utilization of substrates by yeast and other fungi. J Bacteriol. 1957 Sep;74(3):297–302. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.3.297-302.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maass E. A., Johnson M. J. PENICILLIN UPTAKE BY BACTERIAL CELLS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Apr;57(4):415–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.57.4.415-422.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maass E. A., Johnson M. J. THE RELATIONS BETWEEN BOUND PENICILLIN AND GROWTH IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Sep;58(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.3.361-366.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGANO J. F., STOUT H. A. Resistance studies with nystatin. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:704–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D., Cooper P. D., Roberts P. W. The site of action of penicillin. 1. Uptake of penicillin on bacteria. Biochem J. 1950 Feb;46(2):157–161. doi: 10.1042/bj0460157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIDEAU D. Sur le mode d'action des antibiotiques; cas particulier de la spiramycine. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Jun;94(6):709–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


