Abstract
Live, attenuated Vibrio cholerae vaccines can induce potent immune responses after only a single oral dose. The strategy of harnessing these strains to present antigens from heterologous pathogens to the mucosal immune system shows great promise. To fully realize this possibility, V. cholerae strains must be created which stably express antigens in vivo in sufficient quantity to generate an immune response. In vivo-induced promoters have been shown to increase stability and immunogenicity of foreign antigens expressed from multicopy plasmids. We report the construction of a series of genetically stabilized plasmids expressing luciferase as a heterologous protein from the following in vivo-induced promoters: V. cholerae PargC, PfhuC, and Pvca1008, and S. Typhi PompC. We demonstrate that several of these expression plasmids meet two critical criteria for V. cholerae live vector vaccine studies. First, the plasmids are highly stable in the V. cholerae vaccine strain CVD103-HgR at low copy number, in the absence of selective pressure. Second, real time bioluminescent imaging (BLI) demonstrates inducible in vivo expression of the promoters in the suckling mouse model of V. cholerae colonization. Moreover, the use of BLI allows for direct quantitative comparison of in vivo expression from four different promoters at various timepoints.
Keywords: Vibrio cholerae, bioluminescent imaging, promoter, vector caccine, in vivo expression
INTRODUCTION
Live attenuated bacterial vaccines offer a promising opportunity to deliver heterologous antigens to the immunological inductive sites involved in a wild type human infection. Several species of enteric bacteria including Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. Typhi) and Shigella flexneri have been used to express antigens from a wide variety of unrelated pathogens. Delivering antigens in this way induces immune responses against both the bacterial host strain and the foreign antigen(s), and has the advantage of oral delivery, increasing safety and compliance.
Vibrio cholerae offers several potential advantages as a live vector vaccine: 1) V. cholerae is non-invasive, but induces excellent mucosal and systemic immune responses often after just one dose of live vaccine; 2) Most attenuated strains of V. cholerae maintain the highly immunogenic B subunit of the primary enterotoxin, cholera toxin, which has been demonstrated to be an excellent adjuvant for heterologous antigens (Holmgren et al., 2005); 3) Attenuated strains of V. cholerae expressing and secreting several antigens can elicit heterologous immunity that is protective in animal models, [reviewed in (Silva et al., 2008)]; and 4) Several live attenuated strains have been demonstrated to be safe and immunogenic in human subjects [reviewed in (Tacket and Sack, 2008; Holmgren and Kaper, 2009)], including one licensed for human use, CVD103-HgR. The safety and immunogenicity of CVD103-HgR has been established in a number of randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials throughout the world, which makes it an ideal vaccine platform for expression and delivery of heterologous antigens (Cryz, Jr. et al., 1990; Cryz, Jr. et al., 1992; Tacket et al., 1992; Kotloff et al., 1992; Cryz, Jr. et al., 1995; Tacket et al., 1999).
A critical balance must be maintained in a live vector vaccine whereby sufficient levels of foreign antigen are expressed to elicit an immune response without over-attenuating the bacterial host strain (Galen and Levine, 2001; Bumann, 2001). Two major factors influencing expression of genes encoding heterologous antigens are plasmid copy number and choice of promoter. Foreign genes expressed from multicopy plasmids may be unstable in vivo. One way to enhance the stability of plasmid-based heterologous expression systems is to use low-copy number plasmids. However, this raises concerns about producing enough heterologous protein in vivo to mount an immune response.
An additional factor in plasmid stability is the choice of promoter for heterologous protein expression. Several promoters have been used previously to express heterologous antigens in V. cholerae vaccine strains, including constitutively active tac, lac and trc promoters. However, constitutive expression of high levels of foreign antigen may be toxic to the live vector. The use of in vivo-inducible (ivi) promoters provides a possible solution to the problem of toxicity or metabolic burden of the heterologous antigen on the host bacterial strain. ivi promoters that exhibit low expression in vitro allow for optimal growth conditions for preparation of inocula, while maximizing expression in vivo. Early examples of V. cholerae promoters used to express foreign antigens include heat-shock-regulated htpG (Butterton et al., 1997; John et al., 2000), iron-regulated irgA (John et al., 2000), anaerobically induced nirB (Chen et al., 1998; Fontana et al., 2000) and the cholera toxin promoter (Fontana et al., 2000; Liang et al., 2003). Several of these strains elicited immune responses against the heterologous antigen, but plasmid instability in vivo was suspected to reduce immunity.
Several genomic-level screens have identified new genes that are activated in vivo after V. cholerae infection of animals and humans (Chiang and Mekalanos, 1998; Lee et al., 2001; Merrell et al., 2002a; Merrell et al., 2002b; Hang et al., 2003; Osorio et al., 2005; Larocque et al., 2005; Larocque et al., 2008). One recent in vivo expression technology (IVET) study conducted in humans led to the identification of several previously unreported and highly inducible ivi promoters with great potential for use in a foreign antigen expression system (Lombardo et al., 2007). Here we exploit several of these novel ivi promoters for expression of bioluminescence using genetically stabilized expression plasmids, originally developed for use in attenuated S. Typhi and S. flexneri live vectors (Galen et al., 1997; Galen et al., 1999; Altboum et al., 2001; Altboum et al., 2003; Stokes et al., 2007). Bioluminescent imaging (BLI) is a highly sensitive technique used previously in mice to follow colonization dynamics non-invasively, leading to the identification of previously unknown sites of pathogen colonization (Hardy et al., 2004; Wiles et al., 2006). Here we use this powerful imaging technique to quantitatively compare the in vivo induction of several V. cholerae ivi promoters previously identified by IVET to be induced in human volunteers.
METHODS
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
CVD103-HgR (O1, Classical biotype) was used for all expression studies. N16961 (O1, El Tor biotype) was used as a template for PCR amplification of promoter sequences. Cells were grown in 1× M9 salts plus 20% glucose as a carbon source, LB, MOPS or EZ-Rich (Teknova). Kanamycin was used at a concentration of 50 μg mL−1 to maintain plasmids in vitro, except where noted.
Construction of luciferase expression plasmids
Construction of pOMP15lux, pOMP5lux, and pOMP60lux
All plasmids are listed in Table 1. Because our intention was to insert several different promoters upstream of the lux operon, our first goal was to create an easily replaceable cassette to move promoters into and out of this plasmid. To this end, pGEN-luxCDABE (a generous gift from M. Lane and H. Mobley) was digested with EcoRI and SnaBI to remove the EM7 promoter, which was replaced by PompC from pSEC84. To accomplish this, PompC was removed from pSEC84 by digestion with SpeI, end-filled with T4 DNA polymerase and subsequent digestion with EcoRI. This PompC fragment was then ligated into pGEN-luxCDABE to create pOMP15lux. We then subcloned the entire PompC-lux fragment from pOMP15lux as a ~6500bp EcoRI -NheI cassette into appropriately digested pSEC10 (ori101) and pSEC84 (oriE1) to create pOMP5lux and pOMP60lux, respectively.
Table 1.
Plasmids used in this study with relevant features noted.
| Plasmid | Approx. copy # | Promoter | Relevant characteristics | Source or reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pGENlux | 15 | Pem7 | ori15A luxCDABE bla hok-sok par parA | Lane et al., 2007 |
| pSEC10 | 5 | PompC | ori101 clyA aph hok-sok par parA | Stokes et al., 2007 |
| pSEC84 | 60 | PompC | oriE1 clyA aph hok-sok par parA | Galen et al., 2004 |
| pOMP5lux | 5 | PompC | ori101 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA | This work |
| pOMP15lux | 15 | PompC | ori15A luxCDABE bla hok-sok par parA | This work |
| pOMP60lux | 60 | PompC | oriE1 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA | This work |
| pCM10 | 5 | Pneg | ori101 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA rrnB | This work |
| pCM11 | 5 | PargC | ori101 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA rrnB | This work |
| pCM13 | 5 | PfhuC | ori101 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA rrnB | This work |
| pCM14 | 5 | Pvca1008 | ori101 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA rrnB | This work |
| pCM17 | 5 | PompC | ori101 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA rrnB | This work |
| pCM18 | 60 | Pneg | oriE1 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA rrnB | This work |
| pCM19 | 60 | PargC | oriE1 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA rrnB | This work |
| pCM22 | 60 | Pvca1008 | oriE1 luxCDABE aph hok-sok par parA rrnB | This work |
Construction of pCM10
To reduce background luminescence resulting from read-through transcription into the lux operon, a copy of the rrnB terminator was PCR amplified from pSE380 (Invitrogen) using primers K5917 and K5918 (Table 2) to construct a cassette flanked at the 5′-terminus by MfeI and at the 3′-terminus with EcoRI and BamHI sites. The resulting PCR product was ligated into pOMP5lux digested with EcoRI and BamHI, creating the 5-copy pCM10 promoterless negative control plasmid, which was confirmed to exhibit extremely low background luminescence.
Table 2.
Primers used in this study. Restriction enzymes sites are underlined.
| Primer # | Template | Cassette created | Direction | Oligonucleotide sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K4125 | N16961 genomic DNA | PargC | forward | caggatcctaagtggtgaaagagagcgaaca |
| K4126 | N16961 genomic DNA | PargC | reverse | tgggaattcgcggccgctatctttgctcctgctattgacagagtg |
| K4245 | N16961 genomic DNA | Pvca1008 | forward | gaattcgcggccgctaatttcgattcctcatcactcaccacggcg |
| K4246 | N16961 genomic DNA | Pvca1008 | reverse | ggatcctattagtttgattgggctttac |
| K5512 | N16961 genomic DNA | PfhuC | forward | gaattcgcggccgcggtgccttaatgaaagtaattg |
| K5513 | N16961 genomic DNA | PfhuC | reverse | ggatccattgcgcatgataaaacctctgc |
| K5917 | pSE380 (Invitrogen) | rrnB-Pneg | forward | caattgataaaacagaatttgcctgg |
| K5918 | pSE380 (Invitrogen) | rrnB-Pneg | reverse | ggatccattcttatgaattcgagtttgtagaaacgcaaaaag |
Construction of 5- and 60-copy expression plasmids
PargC, PfhuC, and Pvca1008 promoters were PCR amplified from wildtype V. cholerae N16961 genomic DNA to create cassettes with 5′-terminal EcoRI-NotI sites and BamHI at the 3′ terminus. Primers used are listed in Table 2. Promoter fragments were inserted as EcoRI - BamHI cassettes into pCM10 digested with the same enzymes, thereby creating 5-copy plasmids with the argC (pCM11), fhuC (pCM13), and vca1008 (pCM14) promoters. The ompC promoter was also removed from pSEC84 as an EcoRI - BamHI cassette and inserted into appropriately digested pCM10 to create the 5-copy pCM17. The terminator-promoter cassette from pCM10, pCM11, and pCM14 was then removed by digestion with XhoI and BamHI and ligated into pOMP60lux digested with the same enzymes to create the 60-copy isogenic plasmids pCM18, pCM19, and pCM22 respectively. The expected nucleotide sequence of all expression plasmids was verified by sequence analysis.
In vitro induction studies
Expression plasmids were introduced into V. cholerae by electroporation as previously described (Marcus et al., 1990). For experiments reported in Figure 1, plasmid-bearing V. cholerae live vectors were subcultured 1:500 from overnight cultures (using 2–3 colonies from freshly streaked plates) into fresh medium and added in triplicate (200 μL per well) to an optical 96-well plate. Absorbance and luminescence of 200 μL cultures grown at 37°C in an optical 96-well plate were measured at 20 min intervals using a Synergy HT luminometer. Triplicate or quadruplicate samples were assayed for each strain and medium condition.
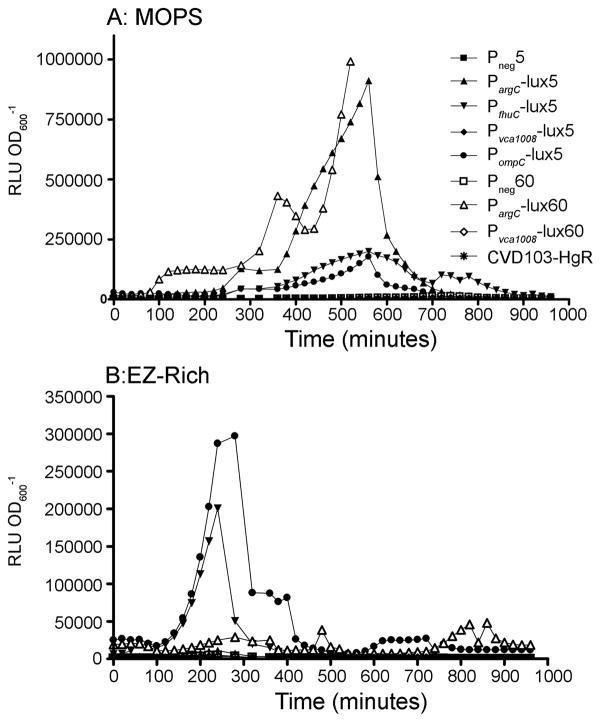
Figure 1.
Luciferase kinetics and stability. The symbols shown in A are used for both panels. The symbols for 5-copy plasmids are solid and those for 60-copy plasmids are open. A) and B) show strains grown in 96-well plates in minimal and rich media respectively. Each value is the mean of triplicate cultures and is representative of at least 3 experiments. The values of 60-copy PargC strain are cut-off at 500 minutes; this strain goes on to achieve a peak level of 3.94 × 106 at 780 minutes and then rapidly declines like the other strains.
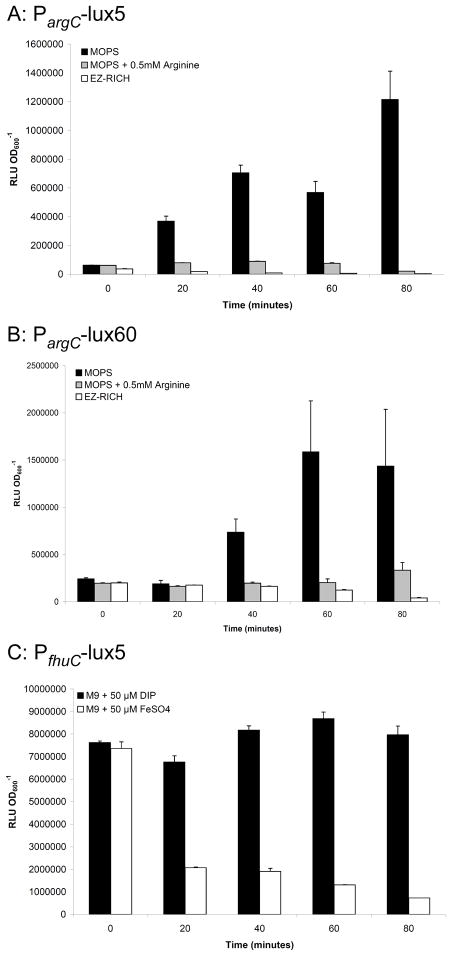
For experiments reported in Figure 2, overnight cultures grown from 2–3 freshly isolated colonies were diluted 1:100 into fresh LB and grown to mid-log phase (OD600 ~0.4). Several 1 mL portions of each culture were pelleted and resuspended in an equal volume of minimal medium supplemented either with 0.5 mM arginine, 50 μM DIP, or 50 μM FeSO4 and added in triplicate (200 μL per well) to an optical 96-well plate. Bioluminescence and absorbance were again measured every 20 min using a Synergy HT luminometer.
Figure 2.
In vitro regulation of promoters. Strains were grown in LB to mid-log phase and then resuspended in permissive or non-permissive medium. A and B) show the relief of repression of the argC promoter by the removal of exogenous arginine in the 5- (A) or 60-copy (B) plasmids. C) shows repression of the fhuC promoter by the addition of FeSO4. Each value is the mean of triplicate cultures, error bars show standard deviation. Each graph is representative of at least three experiments.
In vitro stability studies
In vitro stability experiments were performed essentially as described by Fang et al. (Fang et al., 2008). Briefly, 2–3 freshly isolated colonies were used to establish starter cultures grown at 37°C in LB without selection. 24 hours later the cultures were diluted and plated onto non-selective medium (Day 0) and re-inoculated into fresh LB at a1:100 dilution. This process was repeated each day for up to 5 days. Plate images were acquired using an IVIS 200 imaging system at small binning for 10–30 sec to determine the percentage of luminescent colonies.
In vivo BLI
Freshly isolated colonies were resuspended in 10 mL of PBS and adjusted to an OD600 of 0.2 (~1×108 CFU mL−1). Evans blue dye (40 μL) was then added to 1 mL of each culture. 4–5 day old CD-1 mice were isolated one hour prior to inoculations. Mice were individually anesthetized using 3% isoflurane, intragastrically inoculated with 50 μL of culture through flexible silicon tubing, and imaged immediately for 1 min with medium binning in an IVIS 200 imaging system. Luminescence within the mice was calculated by generating an identically-sized Region of Interest (ROI) circle for all mice using Living Image 3.0 software. Total photon flux (photons sec−1) was used for all calculations. At various time points, the mice were again anesthetized and imaged individually with the same parameters. At the final time point, mice were euthanized immediately after imaging by cervical dislocation and their intestines dissected and submerged in 2 mL PBS + 10% glycerol. After homogenization, the intestinal samples were diluted and plated to determine colony forming units (CFU). Colony plates were imaged as described above to confirm in vivo stability of plasmids. This animal protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care & Use Committee at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Construction of plasmids expressing luciferase under ivi promoter control
To assess the expression of ivi promoters in vivo, we elected to use lux-mediated bioluminescence as a reporter. Bioluminescence is a useful and quantitative tool for studying gene expression of pathogens in vivo in animal models of infection [reviewed in (Contag, 2008)]. Foreign antigens delivered by live vectors are usually expressed using multicopy plasmids such that high levels of antigen are presented to the immune system. However, such plasmids are often unstable and we therefore elected to express the lux operon from genetically stabilized expression plasmids. These plasmids encode a maintenance system comprising the Hok-Sok post-segregational killing function and two plasmid partitioning loci to enhance plasmid inheritance (Galen et al., 1999; Lane et al., 2007). The plasmid pGEN-luxCDABE (Pem7,~15 copies/cell, (Lane et al., 2007)) was re-engineered for this study to create a removable promoter cassette and a copy of the rrnB terminator was inserted upstream of the promoter cassette to eliminate background luminescence observed in the absence of the terminator (data not shown). This re-engineered terminator-EcoRI-Pneg-BamHI-lux operon cassette was then introduced into low copy (~5-copies/cell) and high copy (~60-copies/cell) genetically stabilized plasmids creating promoterless negative controls (Pneg5 and Pneg60).
We then replaced Pneg with one of three ivi promoters identified by IVET in human volunteers (Lombardo et al., 2007). Two of the promoters, PargC and Pvca1008, had also been previously identified in a suckling mouse IVET study (Osorio et al., 2005; Lombardo et al., 2007). These two promoters are induced in the suckling mouse model at levels of 700- and 770-fold, respectively, compared to growth in vitro in rich broth medium. We chose a third promoter from the human IVET study, PfhuC, because a strain with a mutation in this gene was shown in follow-up experiments to display a colonization defect in the suckling mouse intestine. A fourth promoter, PompC, from E. coli was also included in our studies. OmpC is a porin that is present in many gram-negative bacteria, but not in V. cholerae. In E. coli, ompC expression is induced by high osmolarity and it encodes one of the most highly expressed outer membrane proteins. PompC has been used successfully in both attenuated S. Typhi and Shigella strains to express heterologous antigens and has been shown to induce immune responses in animal models (Altboum et al., 2001; Altboum et al., 2003; Galen et al., 2004; Stokes et al., 2007).
All plasmids were electroporated into a spontaneous streptomycin-resistant derivative of the attenuated V. cholerae strain CVD103-HgR. The safety and immunogenicity of CVD103-HgR has been tested in thousands of individuals, including children and persons with HIV, making it an ideal V. cholerae vector vaccine [Reviewed in ((Tacket and Sack, 2008)].
Evaluating in vitro expression
A major goal in live vector vaccine construction is to limit expression of the heterologous antigen in vitro to minimize selective pressure for plasmid loss, while maintaining high levels of expression in vivo to induce an immune response. The three V. cholerae ivi promoters were previously shown to have low levels of expression in vitro on rich medium, but expression was detected from a single chromosomal copy, using a very different indirect reporter assay (Osorio et al., 2005; Lombardo et al., 2007). Thus, luciferase expression from the plasmid constructs was first assessed in vitro. Expression from all bioluminescent reporter plasmids was initially monitored using a defined minimal medium (MOPS) versus a rich medium (EZ-Rich). Light output was measured and normalized to optical density in a 16-hour kinetic study. As expected, the promoterless 5- and 60-copy plasmids (Pneg5 and Pneg60) showed low background luminescence in both media (Figure 1A and B). Strains expressing luciferase under the control of PompC displayed constitutively high expression compared to the promoterless negative control in all media tested (Figure 1A and B). All strains showed a dramatic decrease in expression upon entering stationary phase. This phenomenon, observed by several groups, is termed Abrupt Decline of Luciferase Activity (ADLA) (Koga et al., 2005; Galluzzi and Karp, 2007). The cause of ADLA seems to be a decrease in the availability of reduced flavin mononucleotide (FMNH2), which is the direct electron donor for the bacterial luciferase reaction.
The arginine biosynthesis pathway is well characterized in E. coli [Reviewed in (Cunin et al., 1986; Charlier and Glansdorff, 2004)]. The argCBH operon, encoding proteins involved in arginine biosynthesis is negatively regulated by the ArgR repressor, which binds to ARG boxes within the promoter sequence. Additionally, like many other amino acid biosynthesis genes, the arginine regulon is positively regulated by the stringent response, a multifaceted physiological response in the face of starvation [Reviewed in (Cunin et al., 1986; Cashel et al., 2009)]. Thus the full gamut of arginine regulation in V. cholerae can be predicted as follows: full expression in the absence of arginine and under starvation conditions, intermediate expression in the presence of arginine and under starvation conditions, and complete repression in the presence of arginine in rich medium. Consistent with this model, in our kinetics experiments we saw the highest luciferase activity in both PargC-lux5 and PargC-lux60 in minimal medium (Figure 1A). In additional experiments, cultures were initially grown in rich medium, pelleted and resuspended in various media. For the 5-copy plasmid, repression is very quickly alleviated by growth in minimal medium, but is maintained with as little as 0.5 mM arginine in minimal media (Figure 2A), whereas for the 60-copy plasmid, addition of the same amount of arginine only partially repressed bioluminescence (Figure 2B). Increasing the amount of arginine to 5 mM did not increase the repression (data not shown). However, full repression of the 60-copy plasmid was achieved in rich medium (Figure 2B). These data confirm previous findings that V. cholerae PargC exhibits low expression in vitro.
The fhuCDB operon is involved in ferrichrome iron utilization and is part of the Fur regulon (Rogers et al., 2000). At high concentrations in the bacterium, iron binds to Fur, which then binds to Fur boxes in the promoter regions of iron-regulated genes and prevents transcription. The consensus sequence of the Fur box in V. cholerae is similar to that of E. coli (Mey et al., 2005). In our experiments, the PfhuC promoter was only examined using the 5-copy replicons, and showed relatively constant expression in vitro in minimal and rich media that was higher than the promoterless negative control strain (Figure 1A and B). Kinetic experiments in other media showed high expression in minimal medium containing 50 μM 2,2-dipyridyl, which limits iron availability, and low expression in minimal medium containing 50 μM FeSO4 (data not shown). Additionally, in induction experiments, despite high basal level expression in rich LB medium, PfhuC was repressed by the addition of 50 μM FeSO4 to minimal medium (Figure 2C). The design of the IVET study allowed for the inclusion of promoters with low activity in vitro, with higher expression in vivo (Lombardo et al., 2007). Because we are studying the promoter in a multicopy plasmid instead of the single chromosomal copy identified in IVET, we are more likely to see increased activity in vitro.
VCA1008 is a putative outer membrane protein that is necessary for infection of suckling mice (Osorio et al., 2004). The precise regulation of VCA1008 is unknown. Previous studies showed that vca1008 is not induced in vitro in either minimal M9 or rich LB medium, but was induced in vivo in suckling mice using IVET techniques (Osorio et al., 2004). Our initial kinetic studies confirm these findings. Regardless of plasmid copy number or growth conditions, in vitro expression of bioluminescence from Pvca1008 was not detectable above promoterless control levels (Figure 1A and B). Expression could not be demonstrated in any other media tested, including M9 minimal medium, LB, DMEM tissue culture medium (low and high glucose), nor under ToxR-permissive conditions (LB pH 6.5 at 30°C) (data not shown). Additionally, expression could not be seen after infection of T84 intestinal cells (data not shown).
In vitro plasmid stability
Expression of heterologous proteins at high levels can decrease plasmid stability (Londono et al., 1996). Luciferase-expressing plasmids have had limited use in vivo until recently because of issues with stability. The pGEN-luxCDABE plasmid was shown by Lane et al. to be relatively stable in UPEC in vitro for up to 3 days with ~13% plasmid loss (Lane et al., 2007). We examined the in vitro stability of our plasmids in CVD103-HgR, expressing the lux operon from pGEN-luxCDABE under the transcriptional control of PargC, PfhuC, Pvca1008, and PompC from high or low copy plasmids. For live vectors passaged in liquid medium in the absence of antibiotic selection, the 5-copy expression plasmids all maintained 100% stability over a 5 day period, whereas the 60-copy plasmids were quickly lost after 2 days (Figure 3). Plasmid loss did not appear to correlate with high luciferase expression because all three 60-copy plasmids (no promoter, PargC, and Pvca1008) express minimal levels of luciferase, while some of the 5-copy plasmids exhibit high levels of expression in rich media, including PfhuC and PompC (Figure 1B). We therefore attribute plasmid loss to high copy-number, which has previously been suggested to decrease the fitness of the bacterial vector strain due to the greater amount of energy required to maintain the DNA within the host cell (Glick, 1995).
Figure 3.
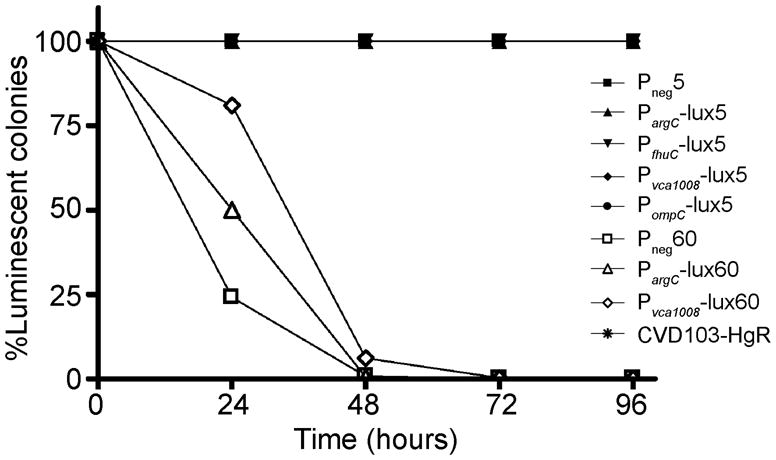
Plasmid maintenance in the absence of selective pressure in vitro. Strains were serially passaged at 1:100 dilutions over 5 days in rich medium without antibiotics. The first time point (0 hours) is the first plating after 24 hours of growth in liquid medium without selection. The symbols for 5-copy plasmids are solid and those for 60-copy plasmids are open.
Evaluating in vivo promoter induction
Suckling mice provide a model for colonization with V. cholerae strains, but their immune systems are too immature to examine the immunogenicity of vaccine strains [Reviewed in (Klose, 2000)]. Several groups have utilized various adult mouse models to study the immunogenicity of V. cholerae live vector vaccines with inconsistent results (Butterton et al., 1996; Chen et al., 1998). In this study we focused only on quantifying in vivo induction of ivi promoters controlling luciferase expression in suckling mice. Because the suckling mice are removed from their mothers, colonization studies are limited to 24 hours. We compared expression of the promoters at an early (4-hour) and late (24-hour) timepoint.
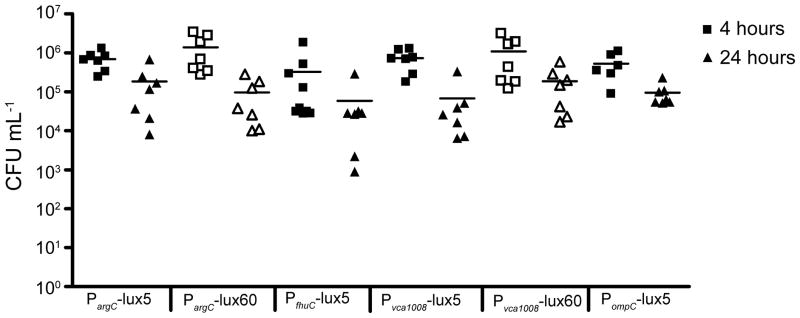
To study the induction of PargC, PfhuC, Pvca1008 and PompC in vivo, we inoculated 5-day old CD-1 mice with ~1×107 CFU of each strain and imaged the mice at 0, 4, and 24 hours post inoculation using an IVIS 200 imaging system. Mice were anesthetized and imaged individually for the best results. Representative images from each time point of a single mouse in each group inoculated with 5-copy plasmids are shown in Figure 4. Because the amount of bacteria per mouse was different at each time point, the total flux (photons sec−1) was normalized to CFU mL−1 of either the initial inoculum (0-hour) or intestinal homogenates (4- and 24-hour). All strains tested colonized mice at similar levels (Figure 5).
Figure 4.
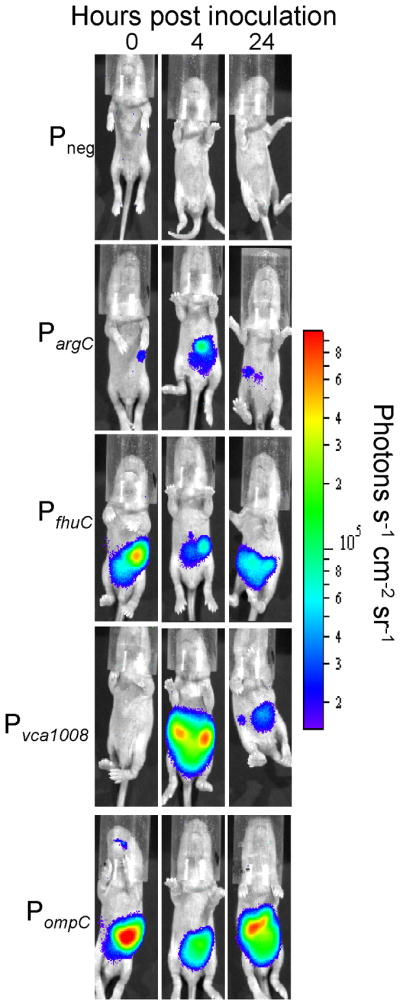
Representative images demonstrating in vivo promoter induction from 5-copy plasmids. 5-day old CD-1 mice were inoculated with CVD103-HgR carrying luciferase-expressing plasmids (dose ~107). 1-minute images were acquired immediately after inoculation (0 hour) and at 4- and 24-hours p.i. Note that the images represent raw luciferase activity that is not normalized to CFU mL−1 as in Figure 6.
Figure 5.
Colonization levels in suckling mice. 5-day old CD-1 mice were inoculated with CVD103-HgR carrying luciferase-expressing plasmids (dose ~107). Groups were split into two for enumerating bacteria in the intestine at 4- or 24-hour. Each symbol represents a single mouse and the bar represents the mean. The 4-hour time point is represented by squares and 24-hours by triangles. Closed symbols are used for 5-copy replicons and open symbols for 60-copy replicons.
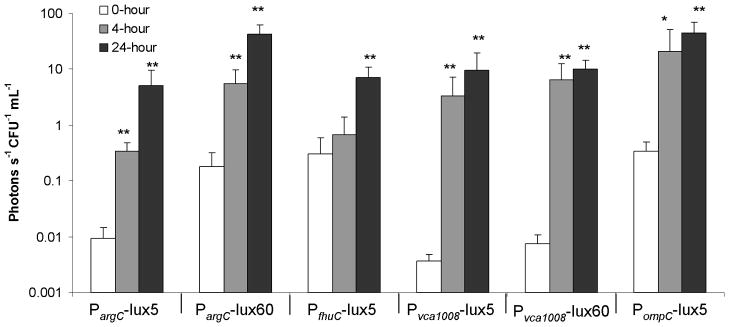
Since the argCBGH operon was identified as being in vivo-induced by IVET studies in both suckling mice and human studies, displaying a 700-fold induction level in the suckling mouse intestine (Osorio et al., 2005), it appeared to be an excellent candidate for in vivo bioluminescence studies. In the suckling mouse intestine, PargC in the 5-copy plasmid showed very low expression at the 0-hour timepoint and was induced 36-fold above that of the inocula at 4 hours and a further 544-fold above the inocula at 24-hours (Figure 6). The 60-copy plasmid had a higher background bioluminescence at the 0-hour time point but achieved one of the highest total expression levels of all constructs, reaching 42.3 vs. 5.1 photons−1 sec−1 CFU−1 mL−1 for the 5-copy plasmid at 24-hours (Figure 6). Despite high levels of expression in the mouse intestine, the lack of stability in vitro in the absence of selective pressure (Figure 3) may ultimately detract from using PargC with 60-copy plasmids for antigen expression in V. cholerae live vectors. The 5-copy plasmid, however, shows great promise for use in V. cholerae live vector strains because of its tight regulation and stability in vitro and high induction in the mouse intestine.
Figure 6.
Quantified in vivo bioluminescence. ROIs were calculated for each mouse using Living Image 3.0 software, giving a unit of photons sec−1. The relative bioluminescence per bacteria was calculated for each promoter construct by normalizing the total flux to CFU mL−1 from either the calculated inocula (0-hour) or intestinal homogenates (4- and 24-hour). N=7–10 mice. Significant differences in luminescence between the 0-hour and 4- or 24-hour were determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test. *, P<0.05. **, P<0.005.
The fhuACDB operon was also identified as being in vivo-induced by IVET studies in both suckling mice and human studies, displaying induction late in the infection of suckling mice (Schild et al., 2007). By measuring bioluminescence, we demonstrated that there was substantial induction of PfhuC in the suckling mouse intestine, with a 24-fold increase in expression above the inocula, but the induction was only statistically significant at the 24-hour time point (Figure 6), confirming the previous findings of Schild et al. Although expression of the fhuC promoter can be repressed in vitro by adding FeSO4 to the medium, the basal level of expression is still quite high compared to PargC and Pvca1008 (see below), and therefore may not be useful for the expression of possibly toxic antigens in V. cholerae live vectors.
As with PargC and PfhuC, the vca1008 promoter was shown by IVET to be inducible in vivo in both suckling mice and human studies, exhibiting the highest induction of all promoters studied in the suckling mouse model (Osorio et al., 2005). Although we were unable to detect expression of luciferase from the vca1008 promoter in vitro, consistent with previous findings (Osorio et al., 2004), we observed excellent induction in vivo. This promoter is strongly induced in suckling mice using both the 5- and 60-copy replicons. Activation of the vca1008 promoter occurred by 4-hours post infection and remained elevated at 24-hours (Figures 4 and 6). In additional experiments, expression from Pvca1008 was shown to occur as early as one hour post-inoculation, the earliest time point tested (data not shown). Interestingly, the maximum amount of bioluminescence was equivalent for both the 5- and 60-copy plasmids. We conclude that regulation of this promoter is exquisitely sensitive to the in vivo environment, as it exhibits virtually no leakiness of expression in vitro even when present in high-copy number, but shows excellent induction in vivo. Pvca1008 represents an intriguing candidate for achieving tightly regulated expression of heterologous antigens in V. cholerae live vector vaccines. In the case of expression of antigens that are toxic to the host strain, maximal repression could be attained in vitro during preparation of the strain for immunizations, possibly ensuring better immunogenicity due to improved fitness of the live vector.
As discussed above, since the E. coli OmpC protein does not have an orthologue in V. cholerae, we were uncertain as to whether PompC would be induced in vivo in V. cholerae. Surprisingly, we observed a 100-fold induction of PompC in the sucking mouse intestine. Indeed, PompC showed the highest total expression of bioluminescence for the 5-copy replicons, with an average of 44.8 photons−1 sec−1 CFU−1 mL−1, a level equivalent to expression levels from PargC carried by 60-copy plasmids (Figure 6). As with PargC, use of PompC with 5-copy replicons shows great promise for use in V. cholerae live vector strains because of its in vitro stability and high induction in the mouse intestine.
Concluding remarks
In summary, this study has identified three excellent candidate promoters, PargC Pvca1008, and PompC, for use in regulated expression of heterologous antigens in attenuated V. cholerae live vector vaccine strains. Since the promoters were originally identified in an El Tor strain and then studied here using bioluminescence in a Classical strain it is likely that they will function well in both biotypes. The rational identification and direct demonstration of in vivo expression of these promoters has identified useful tools for advancing the development V. cholerae multivalent live vector vaccines.
Our series of luciferase-expressing stabilized plasmids could also be useful for the study of other enteric pathogens. For bacteria with more robust mouse colonization models, strains expressing luxCDABE from the ompC promoter could be very useful for studying colonization dynamics, without having to create chromosomal lux fusions. Our plasmids can be transformed into other bacterial strains, including S. Typhi. After transforming 5-copy replicons expressing PompC- controlled luciferase into S. Typhi and inoculating mice intranasally, we were able to track both colonization and tissue distribution over a 5-day period (data not shown). These plasmids could also be used to examine in vivo induction of other predicted in vivo-induced promoters in V. cholerae or other bacteria. More detailed studies of induction kinetics or in situ induction studies could be performed with enteric bacteria since the gastrointestinal tract can be removed from colonized mice and quantitatively imaged. Additionally, bacteria expressing luciferase have been used to target tumor cells and non-invasively follow tumor growth and metastasis over time without the need for exogenous luciferin injections, as is necessary when imaging tumor cells that have been engineered to express the firefly luc gene. Min et al. have recently used E. coli expressing luciferase from a plasmid stabilized using the asd balanced-lethal host-vector system to image a variety of tumors in living mice (Min et al., 2008a; Min et al., 2008b). Our system could easily be adapted for such use.
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the advice and gift of plasmid constructs from J. Galen. Thanks to L. Plemons for excellent technical assistance. A.-M. Hansen, N. Morin, and M.-J. Lombardo are also thanked for advice and editorial assistance. We are grateful to M. Lane and H. Mobley for the gift of pGENluxCDABE. This work was supported by R0I AI19716 (J.B.K.). C.E.M. was supported by a predoctoral fellowship on T32 DK067872, “Research Training in Gastroenterology” (J.P. Raufman, PI).
Reference List
- 1.Altboum Z, Barry EM, Losonsky G, Galen JE, Levine MM. Attenuated Shigella flexneri 2a Delta guaBA strain CVD 1204 expressing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) CS2 and CS3 fimbriae as a live mucosal vaccine against Shigella and ETEC infection. Infect Immun. 2001;69:3150–3158. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.5.3150-3158.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Altboum Z, Levine MM, Galen JE, Barry EM. Genetic characterization and immunogenicity of coli surface antigen 4 from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli when it is expressed in a Shigella live-vector strain. Infect Immun. 2003;71:1352–1360. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1352-1360.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bumann D. Regulated antigen expression in live recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strongly affects colonization capabilities and specific CD4(+)-T-cell responses. Infect Immun. 2001;69:7493–7500. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7493-7500.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Butterton JR, Ryan ET, Acheson DW, Calderwood SB. Coexpression of the B subunit of Shiga toxin 1 and EaeA from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in Vibrio cholerae vaccine strains. Infect Immun. 1997;65:2127–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.6.2127-2135.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Butterton JR, Ryan ET, Shahin RA, Calderwood SB. Development of a germfree mouse model of Vibrio cholerae infection. Infect Immun. 1996;64:4373–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.10.4373-4377.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cashel M, Gentry D, Hernandez V, Vinella D. EcoSal —Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. Washington, D.C: ASM Press; 2009. The Stringent Response. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Charlier D, Glansdorff N. EcoSal-Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. Washington, D.C: ASM Press; 2004. Biosynthesis of Arginine and Polyamines. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen I, Finn TM, Yanqing L, Guoming Q, Rappuoli R, Pizza M. A recombinant live attenuated strain of Vibrio cholerae induces immunity against tetanus toxin and Bordetella pertussis tracheal colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1998;66:1648–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.4.1648-1653.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chiang SL, Mekalanos JJ. Use of signature-tagged transposon mutagenesis to identify Vibrio cholerae genes critical for colonization. Mol Microbiol. 1998;27:797–805. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Contag PR. Bioluminescence imaging to evaluate infections and host response in vivo. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;415:101–118. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-570-1_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cryz SJ, Jr, Kaper J, Tacket C, Nataro J, Levine MM. Vibrio cholerae CVD103-HgR live oral attenuated vaccine: construction, safety, immunogenicity, excretion and non-target effects. Dev Biol Stand. 1995;84:237–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cryz SJ, Jr, Levine MM, Kaper JB, Furer E, Althaus B. Randomized double-blind placebo controlled trial to evaluate the safety and immunogenicity of the live oral cholera vaccine strain CVD 103-HgR in Swiss adults. Vaccine. 1990;8:577–80. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90012-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cryz SJ, Jr, Levine MM, Losonsky G, Kaper JB, Althaus B. Safety and immunogenicity of a booster dose of Vibrio cholerae CVD 103-HgR live oral cholera vaccine in Swiss adults. Infect Immun. 1992;60:3916–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3916-3917.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cunin R, Glansdorff N, Pierard A, Stalon V. Biosynthesis and metabolism of arginine in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1986;50:314–352. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.3.314-352.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fang CM, Wang JY, Chinchilla M, Levine MM, Blackwelder WC, Galen JE. Use of mchI encoding immunity to the antimicrobial peptide microcin H47 as a plasmid selection marker in attenuated bacterial live vectors. Infect Immun. 2008;76:4422–4430. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00487-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fontana MR, Monaci E, Yanqing L, Guoming Q, Duan G, Rappuoli R, Pizza M. IEM101, a naturally attenuated Vibrio cholerae strain as carrier for genetically detoxified derivatives of cholera toxin. Vaccine. 2000;19:75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Galen JE, Gomez-Duarte OG, Losonsky GA, Halpern JL, Lauderbaugh CS, Kaintuck S, Reymann MK, Levine MM. A murine model of intranasal immunization to assess the immunogenicity of attenuated Salmonella typhi live vector vaccines in stimulating serum antibody responses to expressed foreign antigens. Vaccine. 1997;15:700–8. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(96)00227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Galen JE, Levine MM. Can a ‘flawless’ live vector vaccine strain be engineered? Trends Microbiol. 2001;9:372–6. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(01)02096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Galen JE, Nair J, Wang JY, Wasserman SS, Tanner MK, Sztein MB, Levine MM. Optimization of plasmid maintenance in the attenuated live vector vaccine strain Salmonella typhi CVD 908-htrA. Infect Immun. 1999;67:6424–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.12.6424-6433.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Galen JE, Zhao L, Chinchilla M, Wang JY, Pasetti MF, Green J, Levine MM. Adaptation of the endogenous Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi clyA-encoded hemolysin for antigen export enhances the immunogenicity of anthrax protective antigen domain 4 expressed by the attenuated live-vector vaccine strain CVD 908-htrA. Infect Immun. 2004;72:7096–106. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7096-7106.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Galluzzi L, Karp M. Intracellular redox equilibrium and growth phase affect the performance of luciferase-based biosensors. J Biotechnol. 2007;127:188–198. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Glick BR. Metabolic load and heterologous gene expression. Biotechnol Adv. 1995;13:247–261. doi: 10.1016/0734-9750(95)00004-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hang L, John M, Asaduzzaman M, Bridges EA, Vanderspurt C, Kirn TJ, Taylor RK, Hillman JD, Progulske-Fox A, Handfield M, Ryan ET, Calderwood SB. Use of in vivo-induced antigen technology (IVIAT) to identify genes uniquely expressed during human infection with Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:8508–8513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1431769100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hardy J, Francis KP, DeBoer M, Chu P, Gibbs K, Contag CH. Extracellular replication of Listeria monocytogenes in the murine gall bladder. Science. 2004;303:851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1092712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Holmgren J, Adamsson J, Anjuere F, Clemens J, Czerkinsky C, Eriksson K, Flach CF, George-Chandy A, Harandi AM, Lebens M, Lehner T, Lindblad M, Nygren E, Raghavan S, Sanchez J, Stanford M, Sun JB, Svennerholm AM, Tengvall S. Mucosal adjuvants and anti-infection and anti-immunopathology vaccines based on cholera toxin, cholera toxin B subunit and CpG DNA. Immunol Lett. 2005;97:181–8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Holmgren J, Kaper J. Oral cholera vaccines. In: Levine M, editor. New Generation Vaccines. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 27.John M, Crean TI, Calderwood SB, Ryan ET. In vitro and in vivo analyses of constitutive and in vivo-induced promoters in attenuated vaccine and vector strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 2000;68:1171–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.68.3.1171-1175.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Klose KE. The suckling mouse model of cholera. Trends Microbiol. 2000;8:189–191. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(00)01721-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Koga K, Harada T, Shimizu H, Tanaka K. Bacterial luciferase activity and the intracellular redox pool in Escherichia coli. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005;274:180–188. doi: 10.1007/s00438-005-0008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kotloff KL, Wasserman SS, O’Donnell S, Losonsky GA, Cryz SJ, Levine MM. Safety and immunogenicity in North Americans of a single dose of live oral cholera vaccine CVD 103-HgR: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover trial. Infect Immun. 1992;60:4430–2. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4430-4432.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lane MC, Alteri CJ, Smith SN, Mobley HL. Expression of flagella is coincident with uropathogenic Escherichia coli ascension to the upper urinary tract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:16669–16674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607898104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Larocque RC, Harris JB, Dziejman M, Li X, Khan AI, Faruque AS, Faruque SM, Nair GB, Ryan ET, Qadri F, Mekalanos JJ, Calderwood SB. Transcriptional profiling of Vibrio cholerae recovered directly from patient specimens during early and late stages of human infection. Infect Immun. 2005;73:4488–93. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.8.4488-4493.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Larocque RC, Krastins B, Harris JB, Lebrun LM, Parker KC, Chase M, Ryan ET, Qadri F, Sarracino D, Calderwood SB. Proteomic analysis of Vibrio cholerae in human stool. Infect Immun. 2008;76:4145–4151. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00585-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee SH, Butler SM, Camilli A. Selection for in vivo regulators of bacterial virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:6889–6894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.111581598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liang W, Wang S, Yu F, Zhang L, Qi G, Liu Y, Gao S, Kan B. Construction and evaluation of a safe, live, oral Vibrio cholerae vaccine candidate, IEM108. Infect Immun. 2003;71:5498–5504. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.10.5498-5504.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lombardo MJ, Michalski J, Martinez-Wilson H, Morin C, Hilton T, Osorio CG, Nataro JP, Tacket CO, Camilli A, Kaper JB. An in vivo expression technology screen for Vibrio cholerae genes expressed in human volunteers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:18229–18234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705636104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Londono LP, Chatfield S, Tindle RW, Herd K, Gao XM, Frazer I, Dougan G. Immunisation of mice using Salmonella typhimurium expressing human papillomavirus type 16 E7 epitopes inserted into hepatitis B virus core antigen. Vaccine. 1996;14:545–552. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(95)00216-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Marcus H, Ketley JM, Kaper JB, Holmes RK. Effects of DNase production, plasmid size, and restriction barriers on transformation of Vibrio cholerae by electroporation and osmotic shock. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990;56:149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Merrell DS, Butler SM, Qadri F, Dolganov NA, Alam A, Cohen MB, Calderwood SB, Schoolnik GK, Camilli A. Host-induced epidemic spread of the cholera bacterium. Nature. 2002a;417:642–645. doi: 10.1038/nature00778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Merrell DS, Hava DL, Camilli A. Identification of novel factors involved in colonization and acid tolerance of Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 2002b;43:1471–1491. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mey AR, Wyckoff EE, Kanukurthy V, Fisher CR, Payne SM. Iron and fur regulation in Vibrio cholerae and the role of fur in virulence. Infect Immun. 2005;73:8167–8178. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8167-8178.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Min JJ, Kim HJ, Park JH, Moon S, Jeong JH, Hong YJ, Cho KO, Nam JH, Kim N, Park YK, Bom HS, Rhee JH, Choy HE. Noninvasive real-time imaging of tumors and metastases using tumor-targeting light-emitting Escherichia coli. Mol Imaging Biol. 2008a;10:54–61. doi: 10.1007/s11307-007-0120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Min JJ, Nguyen VH, Kim HJ, Hong Y, Choy HE. Quantitative bioluminescence imaging of tumor-targeting bacteria in living animals. Nat Protoc. 2008b;3:629–636. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Osorio CG, Crawford JA, Michalski J, Martinez-Wilson H, Kaper JB, Camilli A. Second-generation recombination-based in vivo expression technology for large-scale screening for Vibrio cholerae genes induced during infection of the mouse small intestine. Infect Immun. 2005;73:972–80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.2.972-980.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Osorio CG, Martinez-Wilson H, Camilli A. The ompU paralogue vca1008 is required for virulence of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 2004;186:5167–71. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.15.5167-5171.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rogers MB, Sexton JA, DeCastro GJ, Calderwood SB. Identification of an operon required for ferrichrome iron utilization in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 2000;182:2350–2353. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.8.2350-2353.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schild S, Tamayo R, Nelson EJ, Qadri F, Calderwood SB, Camilli A. Genes induced late in infection increase fitness of Vibrio cholerae after release into the environment. Cell Host Microbe. 2007;2:264–277. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2007.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Silva AJ, Eko FO, Benitez JA. Exploiting cholera vaccines as a versatile antigen delivery platform. Biotechnol Lett. 2008;30:571–579. doi: 10.1007/s10529-007-9594-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stokes MG, Titball RW, Neeson BN, Galen JE, Walker NJ, Stagg AJ, Jenner DC, Thwaite JE, Nataro JP, Baillie LW, Atkins HS. Oral administration of a Salmonella enterica-based vaccine expressing Bacillus anthracis protective antigen confers protection against aerosolized B. anthracis. Infect Immun. 2007;75:1827–1834. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01242-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tacket CO, Cohen MB, Wasserman SS, Losonsky G, Livio S, Kotloff K, Edelman R, Kaper JB, Cryz SJ, Giannella RA, Schiff G, Levine MM. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentered trial of the efficacy of a single dose of live oral cholera vaccine CVD 103-HgR in preventing cholera following challenge with Vibrio cholerae O1 El tor inaba three months after vaccination. Infect Immun. 1999;67:6341–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.12.6341-6345.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tacket CO, Losonsky G, Nataro JP, Cryz SJ, Edelman R, Kaper JB, Levine MM. Onset and duration of protective immunity in challenged volunteers after vaccination with live oral cholera vaccine CVD 103-HgR. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:837–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.4.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tacket C, Sack D. Cholerae vaccines. In: Plotkin Stanley A, Orenstein Walter A, Offit Paul A., editors. Vaccines. 2008. pp. 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wiles S, Pickard KM, Peng K, MacDonald TT, Frankel G. In vivo bioluminescence imaging of the murine pathogen Citrobacter rodentium. Infect Immun. 2006;74:5391–5396. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00848-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]