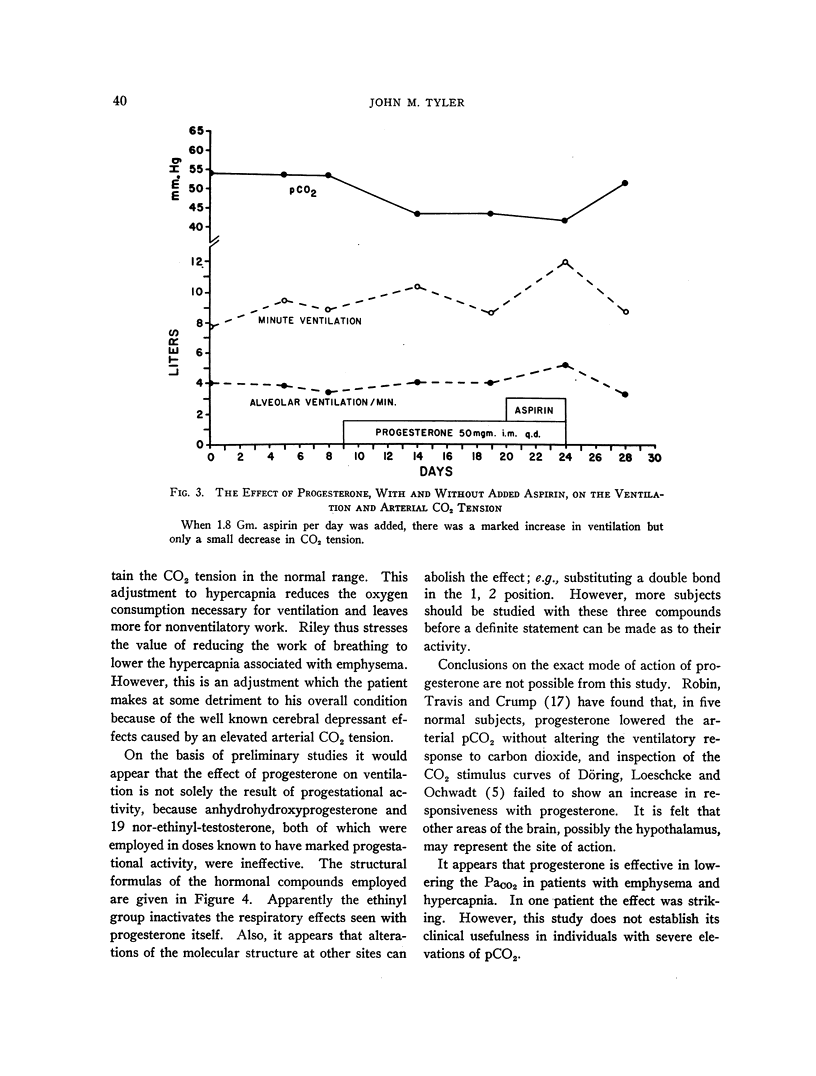
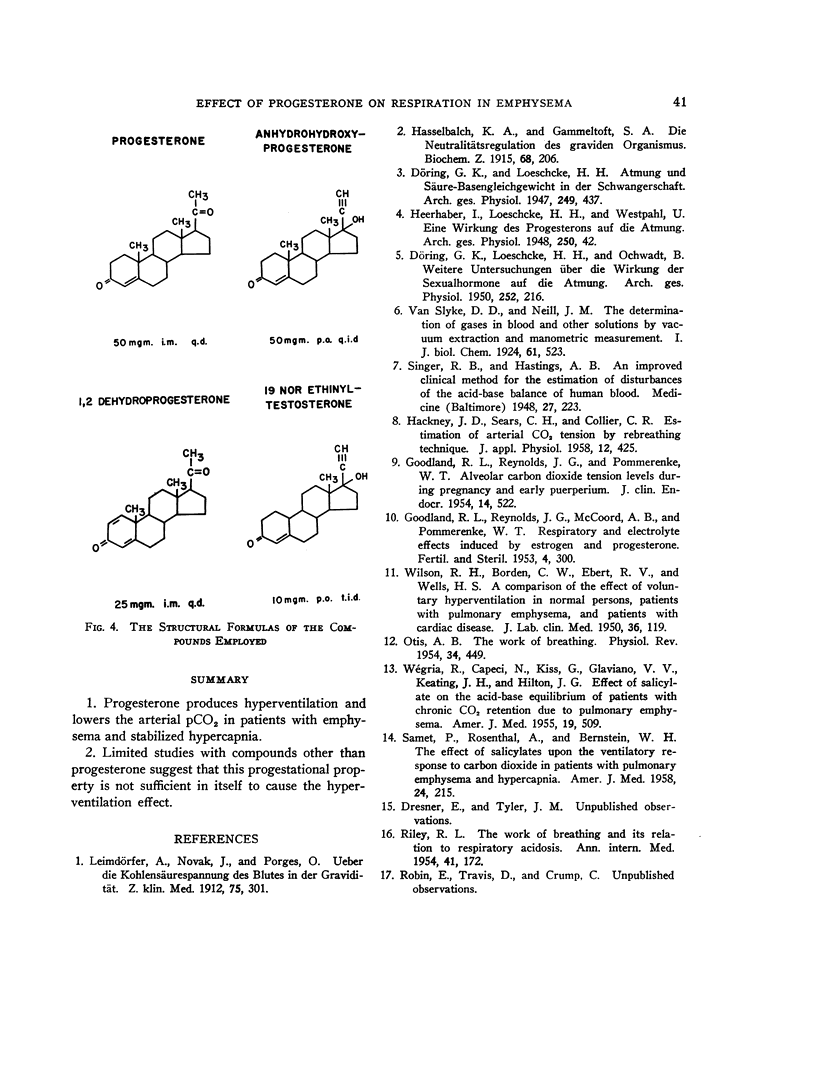
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GOODLAND R. L., REYNOLDS J. G., MCCOORD A. B., POMMERENKE W. T. Respiratory and electrolyte effects induced by estrogen and progesterone. Fertil Steril. 1953 Jul-Aug;4(4):300–317. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)31327-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODLAND R. L., REYNOLDS J. G., POMMERENKE W. T. Alveolar carbon dioxide tension levels during pregnancy and early puerperium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1954 May;14(5):522–530. doi: 10.1210/jcem-14-5-522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HACKNEY J. D., SEARS C. H., COLLIER C. R. Estimation of arterial CO2 tension by rebreathing technique. J Appl Physiol. 1958 May;12(3):425–430. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.12.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTIS A. B. The work of breathing. Physiol Rev. 1954 Jul;34(3):449–458. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1954.34.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMET P., ROSENTHAL A., BERNSTEIN W. H. The effect of salicylates upon the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide in patients with pulmonary emphysema and hypercapnia. Am J Med. 1958 Feb;24(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEGRIA R., CAPECI N., KISS G., GLAVIANO V. V., KEATING J. H., HILTON J. G. Effect of salicylate on the acid-base equilibrium of patients with chronic CO2 retention due to pulmonary emphysema. Am J Med. 1955 Oct;19(4):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(55)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON R. H., BORDEN C. W., EBERT R. V., WELLS H. S. A comparison of the effect of voluntary hyperventilation in normal persons, patients with pulmonary emphysema, and patients with cardiac disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Jul;36(1):119–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



