Summary
Most of the central circadian clock genes in the mouse exist as paralog pairs (Per1/Per2, Cry1/Cry2, Clock/Npas2) that must both be knocked out to confer arhythmicity [1, 2, 3]. The only exception to this pattern is Bmal1/Mop3, the single knockout of which confers arhythmicity despite the presence of its paralog Bmal2/Mop9 [4]. The knockout of Bmal1 also has significant effects on longevity, metabolism, et al. [5, 6]. These results have led to the conclusion that Bmal1 is a singularly essential clock gene and that Bmal2 has a minimal role in the clock system. In contrast, we find that expression of Bmal2 from a constitutively expressed promoter can rescue the clock and metabolic phenotypes of Bmal1-knockout mice, including rhythmic locomotor activity, rhythmic metabolism, low body weight, and enhanced fat deposition. Combined with the data of Bunger and coworkers who reported that knockout of Bmal1 down-regulates Bmal2 [4], we conclude that Bmal1 and Bmal2 form a circadian paralog pair that is functionally redundant, but that in the mouse, Bmal2 is regulated by Bmal1 such that knockout of Bmal1 alone results in a functionally double Bmal1/Bmal2 knockout. Therefore, the role(s) of Bmal2 may be more important than has been appreciated heretofore.
Keywords: circadian, Bmal1, Bmal2, biological clock
Results and Discussion
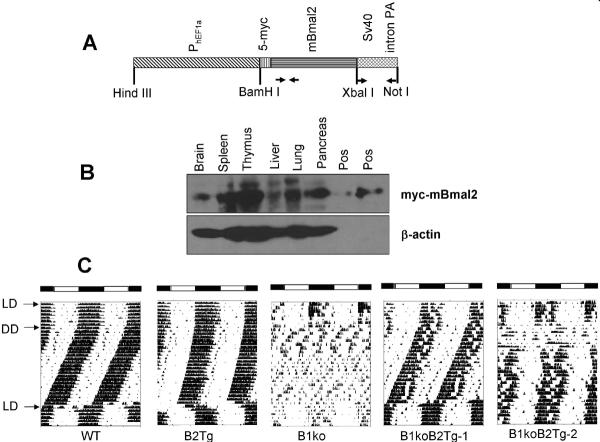
For constitutive expression of Bmal2, we used the promoter region (2.5 kb) for hEF1a that is expressed in many rodent tissues, including the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) of the hypothalamus [7]. The hEF1a promoter was fused to mBmal2 cDNA with five tandem copies of the c-myc tag at the 5' end of the mBmal2 cDNA (Fig. 1A). The construct included the SV40 intron and polyadenylation site at the 3' end. This construct is expressed after transient transfection into mouse 3T3 and human HEK293 cells; it is active in transactivation of E-box-containing promoters with both CLOCK and NPAS2 partners (Fig. S1; 2-fold with CLOCK and 7.4-fold with NPAS2 in 3T3 cells), as we have previously reported for transactivation of E-box-containing promoters with hBMAL2 (aka ARNTL2) in heterodimers with hCLOCK [8, 9]. A transgenic mouse was made with this construct and c-myc-tagged BMAL2 was expressed strongly in spleen, thymus, pancreas and brain as well as weaker but significant expression in liver and lung (Fig. 1B). Expression of c-myc-tagged BMAL2 in mice driven by PhEF1a (B2Tg) lengthens the behavioral locomotor activity by ~0.25 h as compared with wild-type (WT) mice (Figs. 1C, S2). Locomotor activity of Bmal1-knockout mice (B1ko) is arhythmic; however, PhEF1a-driven expression of BMAL2 in B1ko mice rescues the rhythmicity (B1ko/B2Tg; Figs. 1C, S2). In most cases the rescue is apparently complete (as in B1ko/B2Tg-1 in Fig. 1C, n = 4), while in other cases the rescue is clear but not absolutely complete (as in B1ko/B2Tg-2 in Fig. 1C, n = 3). There is less total locomotor activity in the B1ko mouse, but PhEF1a-driven expression of BMAL2 also partially rescues this loss of activity (Fig. S2D and S2E). Some mice tested in the locomotor activity assay harbored the PmPer2∷mPER2∷LUC knockin genetic construct so that their tissues could also be tested for luminescence rhythms in vitro (see below).
Fig. 1. Constitutive expression of mBmal2 can rescue locomotor activity rhythms of the mBmal1-knockout mouse.
(A) Structure of the Bmal2-transgene vector (“5myc-Bmal2”). The coding region of mBmal2 (cDNA) was fused to an upstream region consisting of 5 tandem repeats of the c-myc sequence (5-myc) and the human EF-1α promoter and to a downstream region composed of the SV40 intron-poly(A) sequence [23]. Primers used for the screening of the transgenic mouse lines are indicated below the construct as arrows.
(B) The expression of 5myc-Bmal2 in the mouse with or without Bmal2 transgene was analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-myc-tag antibody. Lysates from HEK293 cells with 5myc-Bmal2 transfection was used as the positive control, and β-actin was immunoblotted as the loading control.
(C) Locomotor activity records. Representative activity records (actograms) are shown in the double-plotted format. Animals were initially in a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle (LD) for at least 10 d and were then transferred to constant darkness (DD). After at least 20 d in DD, the mice were re-entrained to LD. Arrows indicate transitions between different LD cycles. For the B1ko/B2Tg mice, four mice showed a complete behavioral rescue (B1ko/B2Tg-1 is a representative example), while three mice showed partial rescue (e.g., B1ko/B2Tg-2). White and black bars at the top of the actograms indicate the LD cycle when present. Summary data, including power spectra, period, and activity levels, are depicted in Fig. S2.
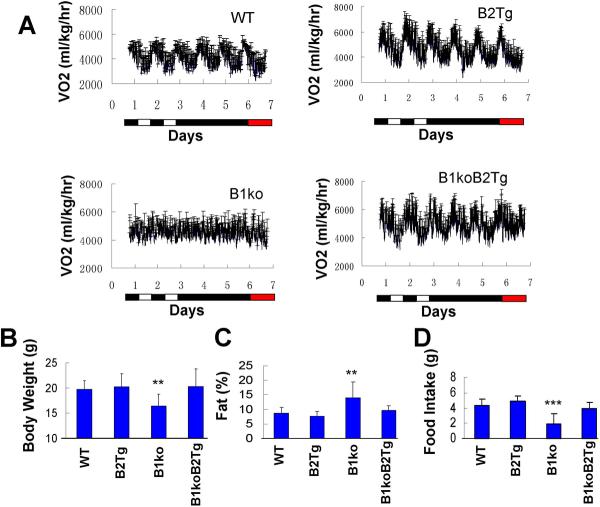
Ectopic expression of Bmal2 also rescues metabolic phenotypes that are associated with the knockout of Bmal1. For example, WT mice exhibit circadian rhythms of oxygen consumption that are disrupted in B1ko mice (Figs. 2A; B1ko mice exhibit either arhythmicity or ultradian rhythms of oxygen consumption, Fig. S3). Constitutive expression of Bmal2 in the WT background (B2Tg) does not significantly affect these metabolic rhythms, but it will rescue robust rhythmicity in the B1ko background (B1ko/B2Tg, Figs. 2A, S3). Other metabolic phenotypes that are associated with the knockout of Bmal1 are significantly (i) reduced body weight (Fig. 2B), (ii) enhanced fat index (Fig. 2C), and (iii) reduced daily food intake (Fig. 2D) in 8-week old mice. All three of these metabolic phenotypes exhibited by B1ko are rescued by the constitutive expression of Bmal2 (B1ko vs. B1ko/B2Tg), but are not affected by Bmal2 expression in the WT background (WT vs. B2Tg, Fig. 2B, 2C, 2D).
Fig. 2. Expression of Bmal2 rescues metabolic phenotypes of Bmal1-knockout mice.
A. Rhythms of oxygen consumption under 2 d of LD 12:12 followed by 3 d of DD, followed by 1 d of red LL. Each bar is the mean±SD (n = 4).
B. Body weight of 8-week-old mice. Each bar represents the mean±SD (n = 8; 4 males and 4 females).
C. Percentage body fat composition measured by NMR. Data are presented as mean±SD (n=8 for each group).
D. Daily food intake. Each bar is the mean±SD of eight mice (4 male and 4 female). For panels B, C, & D: **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. One-way ANOVA, post hoc LSD test.
Therefore, PhEF1a-driven expression of BMAL2 can rescue circadian and metabolic phenotypes associated with the knockout of Bmal1 in intact mice. Is this rescue also true for isolated tissues that can express circadian rhythms in vitro, as can be assayed by light emission of tissues from mice with transgenic reporters [10]? Isolated SCN, lung, and liver slices exhibit circadian rhythms of luminescence in vitro from WT and B2Tg animals (Fig. 3; note that the period is significantly longer in lung of B2Tg mice). In contrast, isolated tissues–including the SCN–of neither B1ko nor B1ko/B2Tg mice exhibit circadian rhythms in vitro. To be confident that B1ko/B2Tg mice in which locomotor activity was rescued corresponded exactly with animals whose SCN activity rhythms in vitro were not rescued, we tested four separate B1ko/B2Tg mice (with the PmPer2∷mPER2∷LUC knockin construct) for locomotor activity and then sacrificed them for SCN luminescence activity. Figure S4 shows that all four mice exhibited a rescue of the locomotor activity rhythm, but their SCN luminescence activity in vitro was not rhythmic. Glucocorticoids have been reported to synchronize peripheral clocks both in vitro and in vivo [11, 12, 13]. After treating liver explants with dexamethasone (DEX, a synthetic glucocorticoid), we observed persistent circadian rhythms of PER2∷LUC luminescence in B1ko/B2Tg slices as compared with highly damped oscillations from in B1ko slices (Fig. 3). Therefore, even though expression of Bmal2 is able to rescue behavioral rhythmicity and metabolic phenotypes of intact B1ko mice (Figs. 1 & 2), it appears to be less effective in rescuing B1ko phenotypes in isolated tissues (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
Expression of Bmal2 does not rescue the rhythmicity of B1ko SCN or lung tissues in vitro, but can rescue liver rhythmicity after dexamethasone (DEX) stimulation. Panels A, C, E show the raw data of luminescence from tissues of PmPer2∷mPer2-Luc knockin mice monitored in vitro. Tissue explants were dissected on Day 0 and recorded with a LumiCycle apparatus. Dark blue: WT; Magenta: Bmal2 Tg; Black: Bmal1ko; Light blue: Bmal1ko/Bmal2Tg. Panels B, D, F show the period analyses of those data (AR = arhythmic), plotted as means ± SD (N≥3, * p<0.05 by two-tailed T test).
A/B. suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) slices.
C/D. lung slices.
E/F. liver slices; + DEX (100 nM) on Day 8. In panel F, blue histograms represent the recording interval prior to DEX treatment (for WT vs. B2Tg, p = 0.11), and red histograms represent the interval during the DEX treatment.
Since the endogenous Bmal2 gene is intact in Bmal1-knockout mice, why does it not sustain rhythmicity in B1ko mice in the same way that it does in the B1ko/B2Tg mice? A clue to an explanation is found in the original Bmal1-knockout data [4]; when Bmal1 is knocked out, Bmal2 mRNA levels are knocked down to basal levels. We repeated these findings (Fig. 4A, 4B). Therefore, it is possible that Bmal2 expression in WT mice is regulated by BMAL1 so that knockout of Bmal1 leads to a condition that is essentially a double Bmal1/Bmal2 knock-out/down. Indeed, examination of the upstream promoter/enhancer region of Bmal2 indicates the presence of 8 E-boxes (2 canonical E-boxes {CACGTG} and 6 non-canonical E-boxes {CA-GC/TG-TG}) that could be regulated by BMAL1/CLOCK and BMAL1/NPAS2 heterodimers [14, 15, 16]. To test this hypothesis, we made a reporter construct with the putative promoter/enhancer region of mBmal2 fused to luciferase (PBmal2∷luc). In transient transfection assays that introduced this reporter into either mouse 3T3 cells or human HEK293 cells, we found that BMAL1/NPAS2 or BMAL2/NPAS2 heterodimers could activate Bmal2 expression in both cell types and the BMAL1/NPAS2 transactivation of PBmal2 could be inhibited by expression of mCRY2 in HEK293 cells (Figs. 4C and S1E)[14–17]. Additionally, in mouse 3T3 cells, BMAL1/CLOCK and BMAL2/CLOCK heterodimers could also activate the Bmal2 promoter/enhancer (Fig. 4C).
Fig. 4.
The Bmal2 promoter/enhancer is activated by BMAL1/CLOCK and BMAL1/NPAS2 heterodimers. Levels of Bmal1(A) and Bmal2 (B) mRNA levels in liver. Transcripts of Bmal1 and Bmal2 were quantified by real-time PCR and normalized with reference to Hprt mRNA levels as a control. The data were normalized by setting the maximum value of Bmal1 or Bmal2 mRNA levels to 1.0. Blue triangles show data from WT mice, while red squares show data from B1ko mice; lines connect the averages at each time point (n = 3 or 4 except for WT at 56 h, where n = 2). (C) Effect of CLOCK/NPAS2 and BMAL1/BMAL2 on expression of the mBmal2 promoter in 3T3 cells. The total amount of plasmid DNA that was transfected was kept constant among by addition of the empty vector DNA when appropriate. Data are mean±SD (n≥4) of firefly luciferase activity (PmBmal2∷Fluc) normalized by the Renilla luciferase control (PCMV∷Rluc). The activity in samples transfected with the reporter construct (i.e., “PmB2-Fluc” without plasmids expressing other proteins) was set as 1.0. Significant differences in pairwise comparisons at the p < 0.05 level are indicated by letters. (D) Control of circadian gene expression by Bmal1 and Bmal2. Left panel: in wild-type mice, E-box clock-controlled genes (CCGs) are activated by both BMAL1 and BMAL2 proteins in combination with CLOCK and NPAS2. Expression of the Bmal2 gene is regulated by BMAL1/CLOCK and/or BMAL1/NPAS2 heterodimers. Right panel: in the Bmal1ko/Bmal2Tg mouse, expression of BMAL2 from the transgene (and possibly from the endogenous Bmal2 gene that is also activated by BMAL2 from the transgene) regulates the expression of the CCGs, thereby rescuing clock and metabolic phenotypes that result from Bmal1/Bmal2 knock-out/down in the Bmal1ko mouse.
We conclude that BMAL1 is not absolutely necessary for circadian rhythms of locomotor activity or metabolic phenotypes, but that it may functionally replaced by expression of its paralog BMAL2 from a constitutively expressed promoter. Combined with the data of Bunger and coworkers who reported that knockout of Bmal1 down-regulated Bmal2 [4], we conclude that Bmal1 and Bmal2 form a circadian paralog pair that is functionally redundant, but that in the mouse, Bmal2 is regulated by Bmal1 such that knockout of Bmal1 alone results in a functionally double Bmal1/Bmal2 knockout. This conclusion is consistent with our observation that the promoter of mBmal2 is regulated by BMAL1/NPAS2 and BMAL1/CLOCK transactivation. Some siRNA analyses have led to the conclusion that Bmal2 knockdown has no effect on the circadian rhythmicity of human osteosarcoma (U2OS) cell cultures [18]. On the other hand, other siRNA studies in 3T3 fibroblasts have supported the opposite conclusion, namely that knocking Bmal2 mRNA levels down disrupts the circadian system in cell cultures [19], which is more consistent with the implications of our study, and perhaps indicates that there are tissue/species specific variations in the role of Bmal2 in the clock mechanism.
Despite the rescue of behavioral/metabolic phenotypes by expression of Bmal2 from the hEF1a promoter, constitutive expression of Bmal2 does not rescue robust and/or sustained rhythmicity of isolated SCN, liver, or lung tissue in vitro. Because the SCN is thought to be the central pacemaker underlying the behavioral locomotor rhythm, it is perplexing that the B1ko/B2Tg mice in which the behavioral rhythm is rescued does not have a concomitant rescue of the in vitro rhythm of the SCN. This result is not without precedent, however. For example, another study using Per1−/− mice found robust circadian rhythms of locomotion but the luminescence activity of SCN slices in vitro was essentially arhythmic [20]. That report concluded that either (i) a small population of rhythmic neurons in the Per1−/− SCN is sufficient to drive locomotor rhythms, or (ii) in vivo physiological factors can compensate for the atypical activity of Per1−/− SCN. Our results with B1ko/B2Tg mice may be another example of this phenomenon. In summary, our data support a key role for Bmal2/Arntl2 in the clock system that has been overlooked by previous studies. Bmal2/Arntl2 may be responsible for many of the important clock and non-clock functions that have been attributed to Bmal1 in the mouse. This is noteworthy because polymorphisms of Arntl2 in humans may have important consequences such as susceptibility to diabetes [21]. Therefore, as we extend our understanding of mammalian circadian rhythms from the mouse model to humans, it will be important to appreciate the potential significance of Arntl2.
Experimental Procedures
Complete Experimental Procedures are described in Supplemental Data.
Generation of Bmal2 transgenic mice (B2Tg)
To generate a transgenic mouse strain expressing mBmal2 constitutively, we selected a promoter for elongation factor-1α (PhEF1α) that can drive constitutive expression in many rodent tissues, including the SCN [7]. PhEF1α was ligated to five tandem repeats of the c-myc tag (“5myc”), followed by the mBmal2 ORF ([22], Fig. 1A). Then, the SV40 small-T intron and the SV40 early gene transcriptional termination/polyadenylation signal sequence [23] was fused to the 5' end of the construct. The final construct is called “PEF1α-Myc-mB2-SV40intronPA.” The transgenic mouse was made by the Vanderbilt Transgenic Mouse/Embryonic Stem Cell Resource and founder mice were screened by PCR for Bmal2 and for the SV40 poly(A) signal. We obtained three founders of PEF1α-mBmal2 transgenic mice (B2Tg) and all of them were fertile. Two lines of the B2Tg mice (designated #1 and #3) showed free-running periods significantly longer than those of wild-type mice in DD. The other line (#2) showed no significant difference in the free-running period. In this study, we used line #3 to analyze molecular and physiological circadian rhythms. All the B2Tg mice used in this study were heterozygous for the PEF1α-Myc-mB2-SV40intronPA transgene.
Promoter/enhancer assays
Mouse 3T3 and human HEK293 cells were transfected using Lipofectamine™ 2000 (Invitrogen) with luminescence reporter constructs: PK2.8-Luc (reporter for the PK promoter [24]) or pGL4-PmB2 (reporter for mBmal2 promoter activity), and the pCMV-Rluc as a transfection control. To make pGL4-PmB2, a fragment extending from the mouse Bmal2 upstream region (−4706 from transcription start site) to the first intron (+339 from transcription start site) was amplified by PCR from mouse genomic DNA (C57BL/6 strain) and inserted into XhoI and BglII sites of the pGL4.11 luciferase vector (Promega).
Locomotor behavior assay
Animal care and use procedures were approved by Vanderbilt University institutional guidelines. Mice were singly housed in cages equipped with running wheels on a LD 12:12 cycle for at least 10 d before being released into constant darkness. ClockLab software (Actimetrics, Evanston, IL) was used to collect data and produce double-plotted actograms as well as the periodogram and activity analyses. χ2 periodogram analyses were performed to obtain periods using the first 20 days of data in DD. To measure circadian phase angle at the termination of the LD cycle, linear regressions were fit through the activity onsets for the 7 days before and 6–20 days after release into DD (the first 5 days in DD were excluded to avoid “transients” [25]).
Oxygen consumption, body weight/fat composition, and food intake assays
Sex and age matched mice were used for all metabolic experiments. The mice were singly housed in indirect calorimetry cages (“OxyMax,” Columbus Instruments). Mice were monitored for 2 d in LD, 3 d in DD, and followed by 1–2 d in dim red light (red light intensity inside mouse cages was ~1 μmol/m2s), during which time oxygen consumption (VO2) was measured every 15 min. Energy expenditure was calculated as described previously [26]. LumiCycle software (Actimetrics Inc., Evanston, IL) was used to subtract the 24-h moving average from the raw oxygen consumption (VO2) results for the 3 d in DD and to smooth the data by 2-h adjacent averaging. The period of the VO2 rhythm in DD was determined by periodogram analyses of the smoothed data. Body fat composition was determined with an mq10 nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer (Bruker Optics). For food intake assessment, mice were placed in individual cages and the amount of food that was consumed in 24 h was measured.
Tissue culture and in vitro luminescence recording
PmPer2∷mPER2∷LUC knockin mice (a gift from Dr. Joseph Takahashi) that had been back-crossed with the C57BL/6 strain for more than 10 generations were crossed with Bmal1+/− and Bmal2 transgenic (B2Tg) mice. All B2Tg or PmPer2∷mPER2∷LUC mice used in this study were heterozygous. One to two h before lights-off of LD 12:12, the mouse was sacrificed by cervical dislocation under dim red light, and cultures of SCN, liver, and lung were prepared as previously described [27]. In vitro rhythms were analyzed for period, etc., using the analysis software for the LumiCycle (Actimetrics, version 2.31 [27].
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to many individuals for their assistance and/or supplying of materials for this project. In particular, to Drs. Hajime Tei and K. Hanaoka for their gift of the hEF1a promoter construct, to Dr. Heping Yan for the anti-myc antibody, to Dr. Chris Bradfield for the B1ko mouse, to Dr. Joseph Takahashi for the PER2∷LUC mouse, to Dr. Nicolas Cermakian for the pCS2-mBmal1/2 plasmids, to Dr. Ron Emeson for the SV40 intron, to Dr. Qun-Yong Zhou for the PK2.8-luc reporter, to Dr. David Nelson for the mNpas2 construct, and to Drs. Charles Weitz and Steven Reppert for the plasmids encoding mCry1, mCry2, and mClock. We also thank Dr. Ron Emeson and the Vanderbilt Transgenic Mouse/Embryonic Stem Cell Resource for their unfailingly generous assistance and advice in the construction of the B2Tg mouse. Finally, we thank Dr. Andy Schoenhard for assistance & suggestions and Drs. Yao Xu & Brian Robertson for help with figure preparation. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01-MH43836, R21-NS054991, and K02-MH01179 to CHJ, R01-NS051278 to SY, and U24 DK59637 to the Vanderbilt Mouse Metabolic Phenotyping Center) and a P&F grant from the Vanderbilt Diabetes and Research Training Center (2P60DK020593).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.DeBruyne JP, Weaver DR, Reppert SM. CLOCK and NPAS2 have overlapping roles in the suprachiasmatic circadian clock. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:543–5. doi: 10.1038/nn1884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vitaterna MH, Selby CP, Todo T, Niwa H, Thompson C, Fruechte EM, et al. Differential regulation of mammalian period genes and circadian rhythmicity by cryptochromes 1 and 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:12114–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.21.12114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zheng B, Albrecht U, Kaasik K, Sage M, Lu W, et al. Nonredundant roles of the mPer1 and mPer2 genes in the mammalian circadian clock. Cell. 2001;105:683–694. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bunger MK, Wilsbacher LD, Moran SM, Clendenin C, Radcliffe LA, Hogenesch JB, et al. Mop3 is an essential component of the master circadian pacemaker in mammals. Cell. 2000;103:1009–17. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00205-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rudic RD, McNamara P, Curtis AM, Boston RC, Panda S, Hogenesch JB, et al. BMAL1 and CLOCK, two essential components of the circadian clock, are involved in glucose homeostasis. PLoS Biol. 2004;2:e377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kondratov RV, Kondratova AA, Gorbacheva VY, Vykhovanets OV, Antoch MP. Early aging and age-related pathologies in mice deficient in BMAL1, the core component of the circadian clock. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1868–73. doi: 10.1101/gad.1432206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Numano R, Yamazaki S, Umeda N, Samura T, Sujino M, Takahashi R, et al. Constitutive expression of the Period1 gene impairs behavioral and molecular circadian rhythms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:3716–21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600060103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schoenhard JA, Eren M, Johnson CH, Vaughan DE. Alternative splicing yields novel BMAL2 variants: tissue distribution and functional characterization. Am. J. Physiol. 2002;283:C103–C114. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00541.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schoenhard JA, Smith LH, Painter CA, Eren M, Johnson CH, Vaughan DE. Regulation of the PAI-1 promoter by circadian clock components: differential activation by BMAL1 and BMAL2. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003;35:473–481. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(03)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yoo SH, Yamazaki S, Lowrey PL, Shimomura K, Ko CH, Buhr ED, et al. PERIOD2∷LUCIFERASE real-time reporting of circadian dynamics reveals persistent circadian oscillations in mouse peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:5339–46. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308709101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Balsalobre A, Brown SA, Marcacci L, Tronche F, Kellendonk C, et al. Resetting of circadian time in peripheral tissues by glucocorticoid signaling. Science. 2000;289:2344–7. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5488.2344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Izumo M, Johnson CH, Yamazaki S. Circadian gene expression in mammalian fibroblasts revealed by real-time luminescence reporting: temperature compensation and damping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:16089–94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2536313100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Reddy AB, Maywood ES, Karp NA, King VM, Inoue Y, Gonzalez FJ, et al. Glucocorticoid signaling synchronizes the liver circadian transcriptome. Hepatology. 2007;45:1478–88. doi: 10.1002/hep.21571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gekakis N, Staknis D, Nguyen HB, Davis FC, Wilsbacher LD, King DP, et al. Role of the CLOCK protein in the mammalian circadian mechanism. Science. 1998;280:1564–9. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5369.1564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hogenesch JB, Gu YZ, Jain S, Bradfield CA. The basic-helix-loophelix-PAS orphan MOP3 forms transcriptionally active complexes with circadian and hypoxia factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:5474–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.10.5474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Reick M, Garcia JA, Dudley C, McKnight SL. NPAS2: an analog of clock operative in the mammalian forebrain. Science. 2001;293:506–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1060699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kume K, Zylka MJ, Sriram S, Shearman LP, Weaver DR, Jin X, et al. mCRY1 and mCRY2 are essential components of the negative limb of the circadian feedback loop. Cell. 1999;98:193–205. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baggs JE, Price TS, DiTacchio L, Panda S, Fitzgerald GA, Hogenesch JB. Network features of the mammalian circadian clock. PLoS Biol. 2009;7:e52. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sasaki M, Yoshitane H, Du NH, Okano T, Fukada Y. Preferential inhibition of BMAL2-CLOCK activity by PER2 reemphasizes its negative role and a positive role of BMAL2 in the circadian transcription. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:25149–59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.040758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pendergast JS, Friday RC, Yamazaki S. Endogenous Rhythms in Period1 Mutant SCN In Vitro Do Not Represent Circadian Behavior. J. Neurosci. 2009;29:14681–14686. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3261-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hung MS, Avner P, Rogner UC. Identification of the transcriptional factor ARNTL2 as a candidate gene for the type 1 diabetes locus Idd6. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:2732–42. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dardente H, Fortier EE, Martineau V, Cermakian N. Cryptochromes impair phosphorylation of transcriptional activators in the clock: a general mechanism for circadian repression. Biochem J. 2007;402:525–36. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Choi T, Huang M, Gorman C, Jaenisch R. A generic intron increases gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1991;11:3070–4. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cheng MY, Bullock CM, Li C, Lee AG, Bermak JC, Belluzzi J, et al. Prokineticin 2 transmits the behavioural circadian rhythm of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Nature. 2002;417:405–10. doi: 10.1038/417405a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Debruyne JP, Noton E, Lambert CM, Maywood ES, Weaver DR, Reppert SM. A clock shock: mouse CLOCK is not required for circadian oscillator function. Neuron. 2006;50:465–77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.03.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ayala JE, Bracy DP, Julien BM, Rottman JN, Fueger PT, Wasserman DH. Chronic treatment with sildenafil improves energy balance and insulin action in high fat-fed conscious mice. Diabetes. 2007;56:1025–33. doi: 10.2337/db06-0883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yamazaki S, Takahashi JS. Real-time luminescence reporting of circadian gene expression in mammals. Methods Enzymol. 2005;393:288–301. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)93012-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.