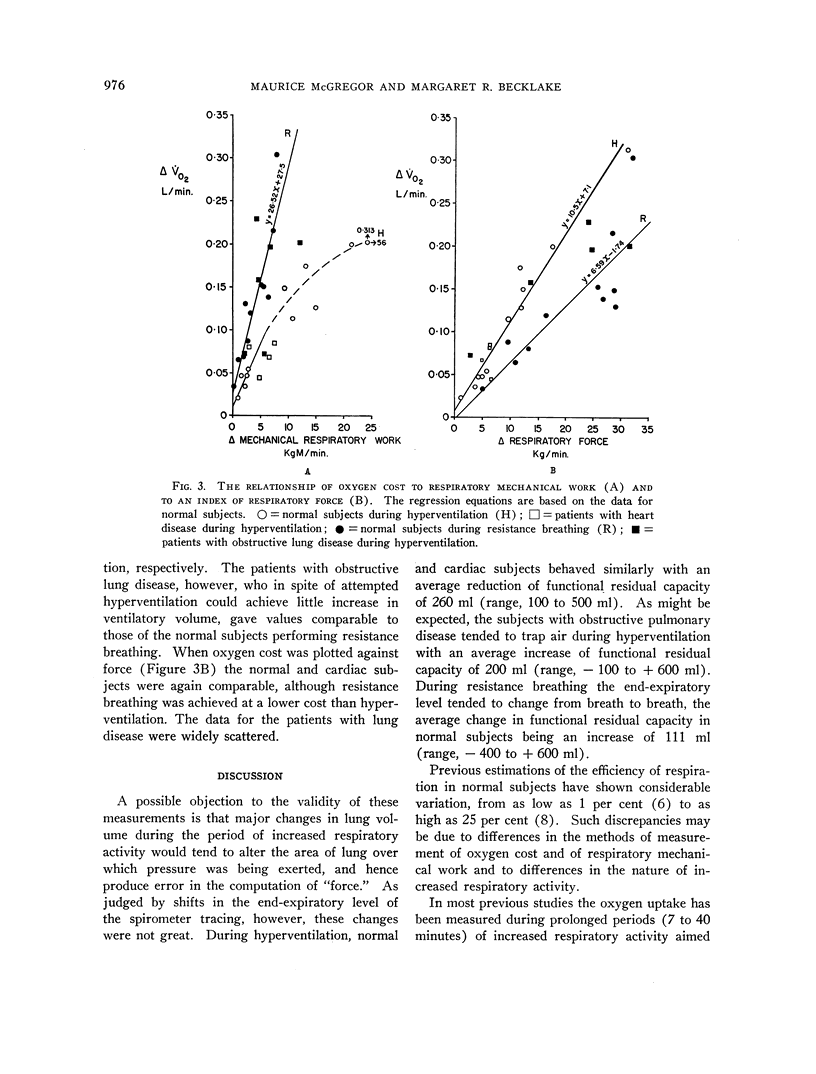
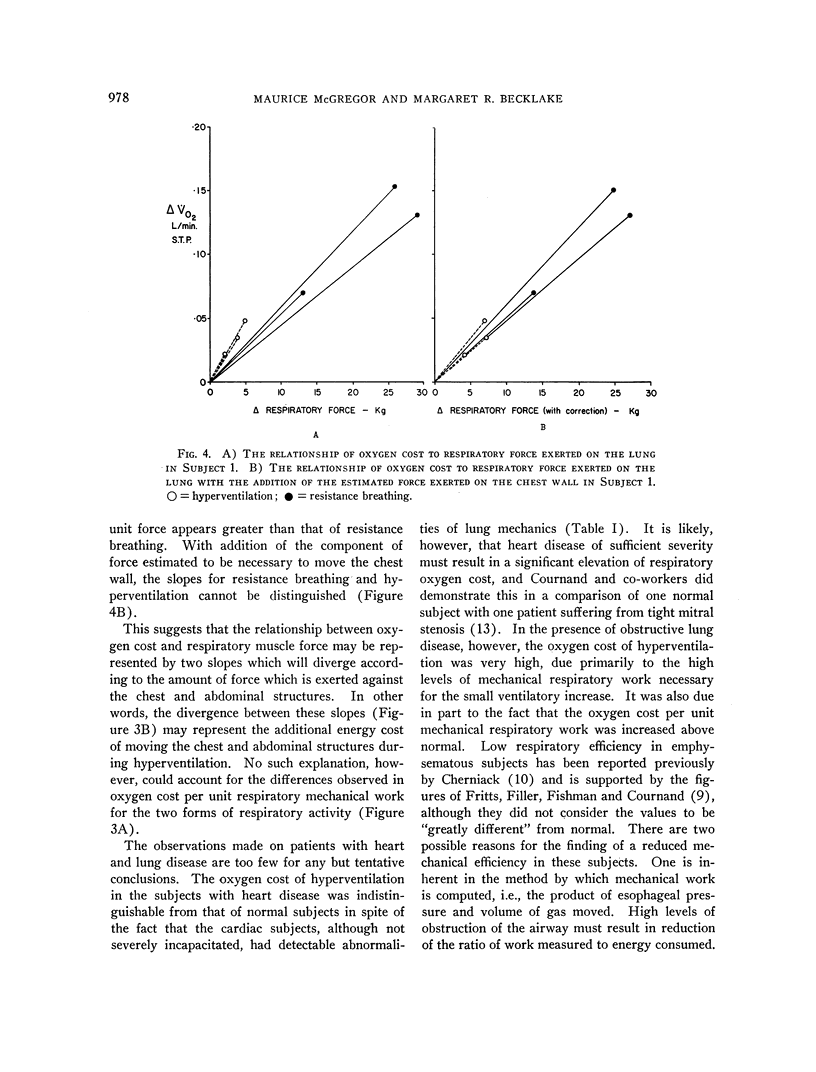
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT R. G., Jr, BRUBACH H. F., SPECHT H. Oxygen cost of breathing. J Appl Physiol. 1958 May;12(3):413–424. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.12.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNIACK R. M. The oxygen consumption and efficiency of the respiratory muscles in health and emphysema. J Clin Invest. 1959 Mar;38(3):494–499. doi: 10.1172/JCI103826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURNAND A., RICHARDS D. W., Jr, BADER R. A., BADER M. E., FISHMAN A. P. The oxygen cost of breathing. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1954;67:162–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRITTS H. W., Jr, FILLER J., FISHMAN A. P., COURNAND A. The efficiency of ventilation during voluntary hyperpnea: studies in normal subjects and in dyspneic patients with either chronic pulmonary emphysema or obesity. J Clin Invest. 1959 Aug;38(8):1339–1348. doi: 10.1172/JCI103909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEUALLEN E. C., FOWLER W. S. Maximal midexpiratory flow. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Dec;72(6):783–800. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.72.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL R., STONE R. W., CHRISTIE R. V. The relationship of dyspnoea to respiratory effort in normal subjects, mitral stenosis and emphysema. Clin Sci. 1954 Nov;13(4):625–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEAD J., GAENSLER E. A. Esophageal and pleural pressures in man, upright and supine. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Jan;14(1):81–83. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILICI-EMILI G., PETIT J. M. Mechanical efficiency of breathing. J Appl Physiol. 1960 May;15:359–362. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY J. F. Oxygen cost of voluntary hyperventilation. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Mar;14(2):187–190. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEREZ C. Progress in understanding and preventing protein malnutrition in Central America. Fed Proc. 1959 Jul;18(2 Pt 2):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARNOFF S. J., BRAUNWALD E., WELCH G. H., Jr, CASE R. B., STAINSBY W. N., MACRUZ R. Hemodynamic determinants of oxygen consumption of the heart with special reference to the tension-time index. Am J Physiol. 1958 Jan;192(1):148–156. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.192.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THERON J. C., ZWI S., McGREGOR M. A low-resistance respiratory valve. Lancet. 1958 Feb 22;1(7017):415–415. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90723-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


