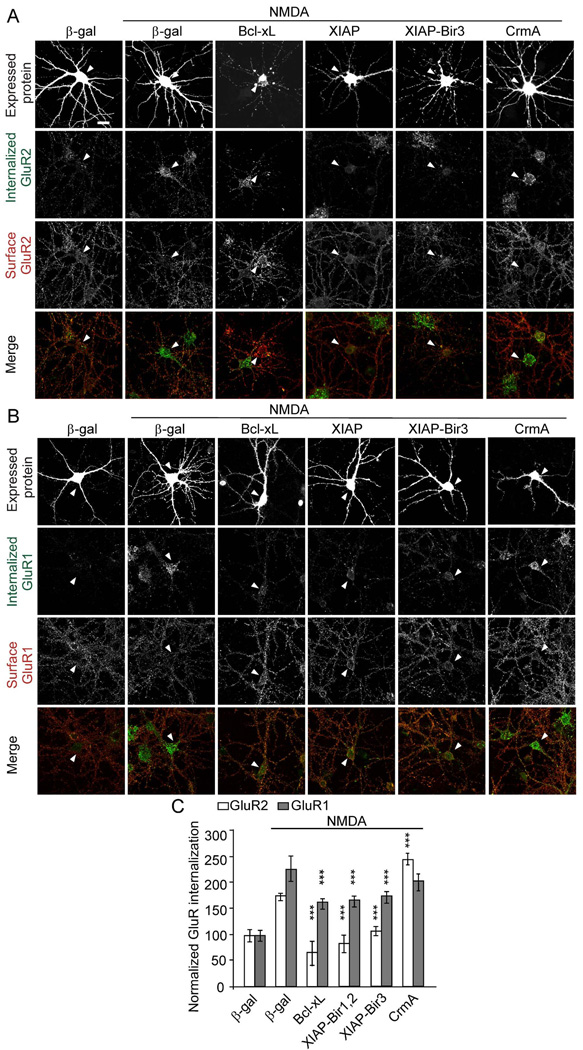
Figure 5.
Anti-apoptotic proteins inhibit AMPA receptor internalization. Cultured hippocampal neurons (DIV14) were transfected with Bcl-xL, XIAP-Bir1,2, XIAP-Bir3 or CrmA, or control β-gal. At 2–4 days after transfection, neurons were treated with NMDA as indicated, and GluR2 (A) and GluR1 internalization (B) was measured by the antibody-feeding internalization assay, as in Figure 4. A and B show immunostaining for the transfected protein (upper row), internalized GluR (second row), surface-remaining GluR (third row), and merge of internalized and surface GluR (bottom row). All individual channels of this triple labeling experiment are shown in grayscale. Arrowheads mark the cell body of transfected cells. Note that the cell body of a Bcl-xL transfected neuron in (A) lies adjacent to an untransfected neuron. Histograms show internalization index for GluR normalized to unstimulated control-transfected neurons (C). n=15–30 neurons for each group. ***p<0.001 (compared to NMDA stimulated β-gal control). The graph shows mean ± SEM. Scale bar, 20 µm. See also Figure S4.