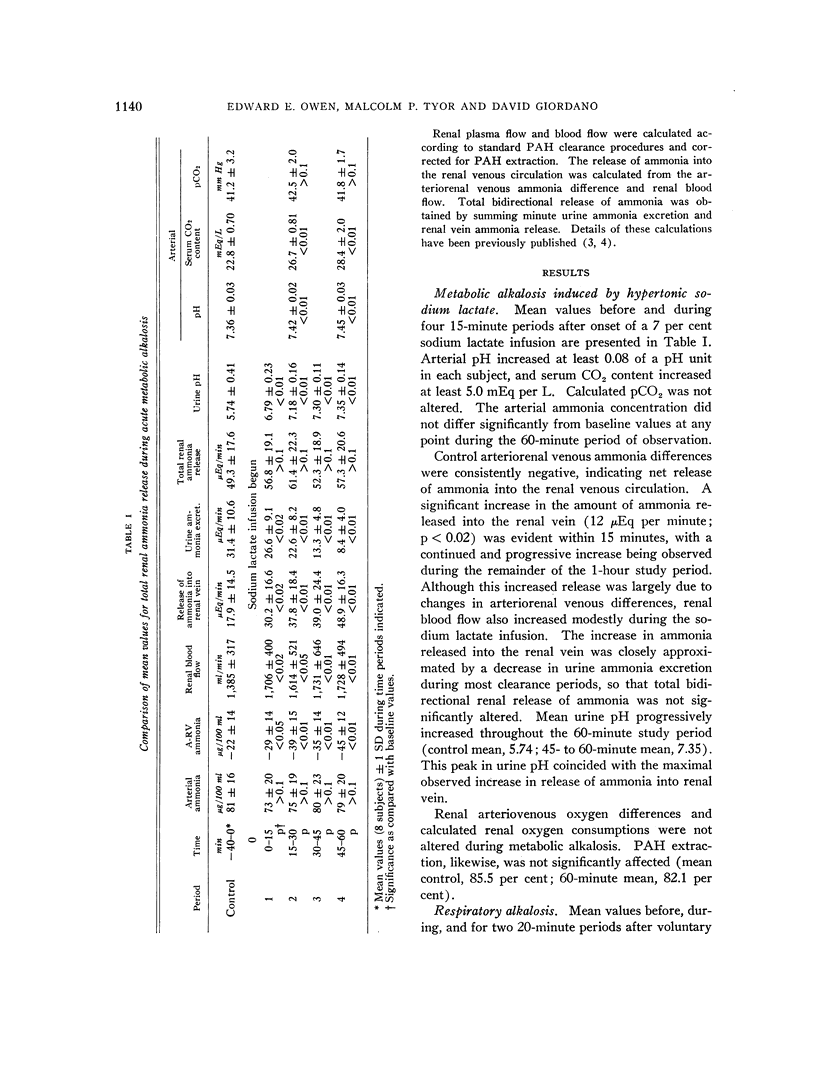
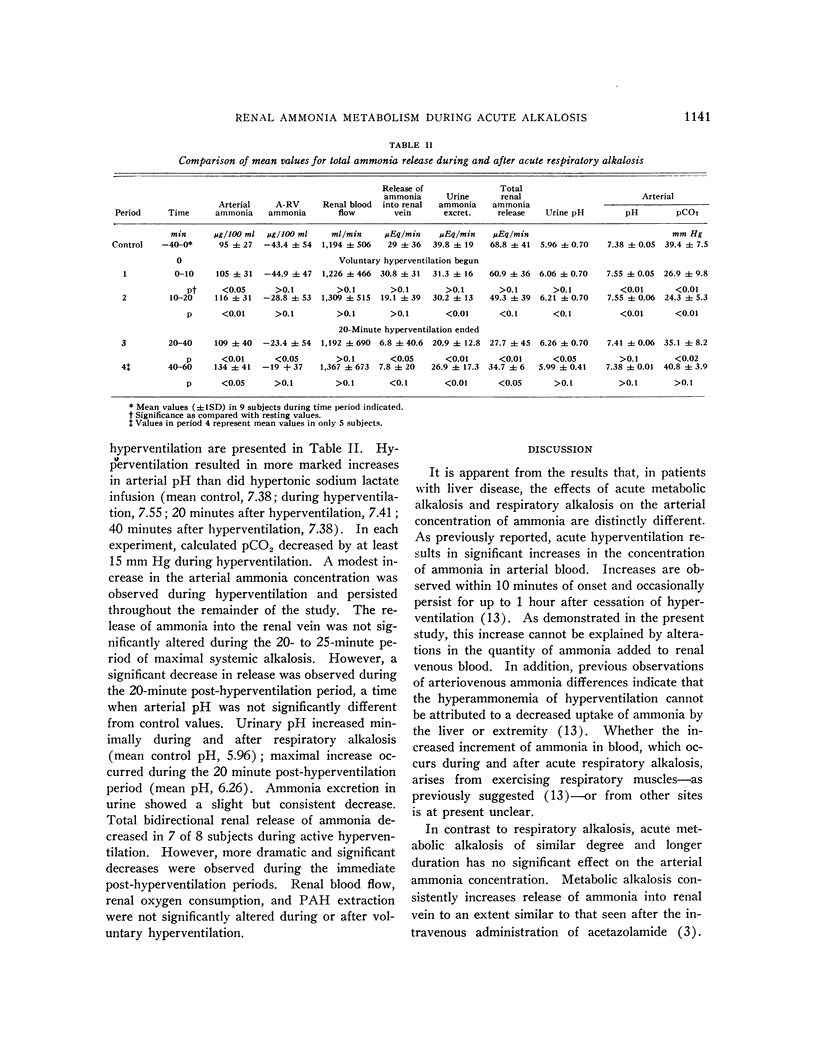
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKER E. S., SINGER R. B., ELKINTON J. R., CLARK J. K. The renal response in man to acute experimental respiratory alkalosis and acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1957 Apr;36(4):515–529. doi: 10.1172/JCI103449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRY J. N., OWEN E. E., FLANAGAN J. F., TYOR M. P. The effect of acute hyperventilation on the blood ammonia concenration of patients with liver disease. The relative role of the kidney, liver, and extremity. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Jun;55:849–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN R. H., DUDA G. D., KORKES S., HANDLER P. A colorimetric micromethod for determination of ammonia; the ammonia content of rat tissues and human plasma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Feb;66(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(57)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARD E., ORLOFF J. Regulation of ammonia excretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jul;182(1):131–138. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.182.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDERMOTT W. V., Jr, ADAMS R. D., RIDDELL A. G. Ammonia metabolism in man. Ann Surg. 1954 Oct;140(4):539–556. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195410000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., BERLINER R. W. The mechanism of the excretion of ammonia in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):223–235. doi: 10.1172/JCI103267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN E. E., FLANAGAN J. F., TYOR M. P. Kidney as a source of blood ammonia: effect of chlorothiazide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct-Dec;102:696–697. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN E. E., JOHNSON J. H., TYOR M. P. The effect of induced hyperammonemia on renal ammonia metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:215–221. doi: 10.1172/JCI104247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN E. E., TYOR M. P., FLANAGAN J. F., BERRY J. N. The kidney as a source of blood ammonia in patients with liver disease: the effect of acetazolamide. J Clin Invest. 1960 Feb;39:288–294. doi: 10.1172/JCI104039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STABENAU J. R., WARREN K. S., RALL D. P. The role of pH gradient in the distribution of ammonia between blood and cerebrospinal fluid, brain and muscle. J Clin Invest. 1959 Feb;38(2):373–383. doi: 10.1172/JCI103811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANBURY S. W., THOMSON A. E. The renal response to respiratory alkalosis. Clin Sci. 1952 Nov;11(4):357–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN J. R., OCHOA S., LYNEN F. Enzymatic synthesis of citric acid. V. Reaction of acetyl coenzyme A. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYOR M. P., OWEN E. E., BERRY J. N., FLANAGAN J. F. The relative role of extremity, liver, and kidney as ammonia receivers and donors in patients with liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1960 Oct;39:420–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. P., PHEAR E. A., SUMMERSKILL W. H., SHERLOCK S. Ammonium tolerance in liver disease: observations based on catheterization of the hepatic veins. J Clin Invest. 1955 Feb;34(2):158–168. doi: 10.1172/JCI103070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


