Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRICKER N. S., KIME S. W., Jr, MORRIN P. A., ORLOWSKI T. The influence of glomerular filtration rate, solute excretion and hydration on the concentrating mechanism of the experimentally diseased kidney in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jun;39:864–875. doi: 10.1172/JCI104107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRICKER N. S., MORRIN P. A., KIME S. W., Jr The pathologic physiology of chronic Bright's disease. An exposition of the "intact nephron hypothesis". Am J Med. 1960 Jan;28:77–98. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRICKER N. S., STOKES J. M., LUBOWITZ H., DEWEY R. R., BERNARD H. R., HARTROFT P. M. Experimentally induced permanent unilateral renal disease in dogs. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Oct;52(4):571–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRICKER N. S., STRAFFON R. A., MAHONEY E. P., MERRILL J. P. The functional capacity of the kidney denervated by autotransplantation in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1958 Feb;37(2):185–193. doi: 10.1172/JCI103597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIGGS A. P., WAUGH W. H., HARMS W. S., FINDLEY T. Pathogenesis of uremic acidosis as indicated by urinary acidification on a controlled diet. Metabolism. 1961 Oct;10:749–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESAUTELS R. E. Hemisection of the bladder for the collection of separate urine samples. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1957 Dec;105(6):767–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., LASSITER W. E., MYLLE M. Localization of urine acidification in the mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1960 Mar;198:581–585. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
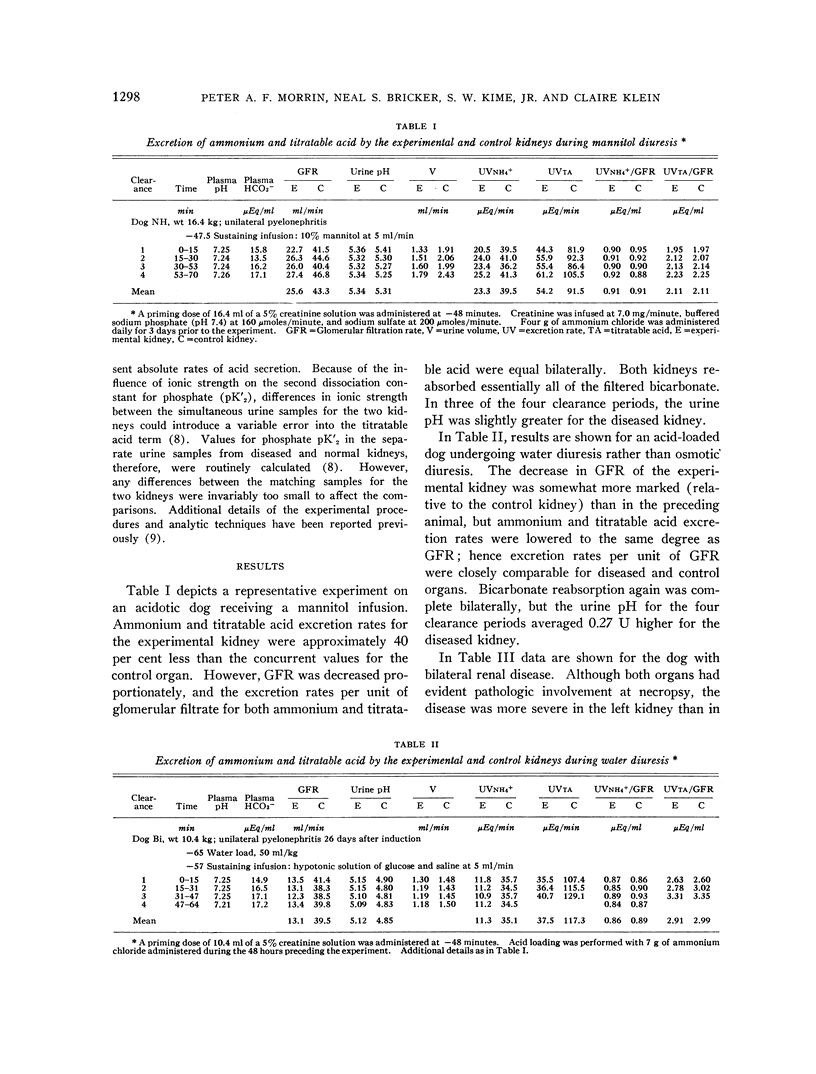
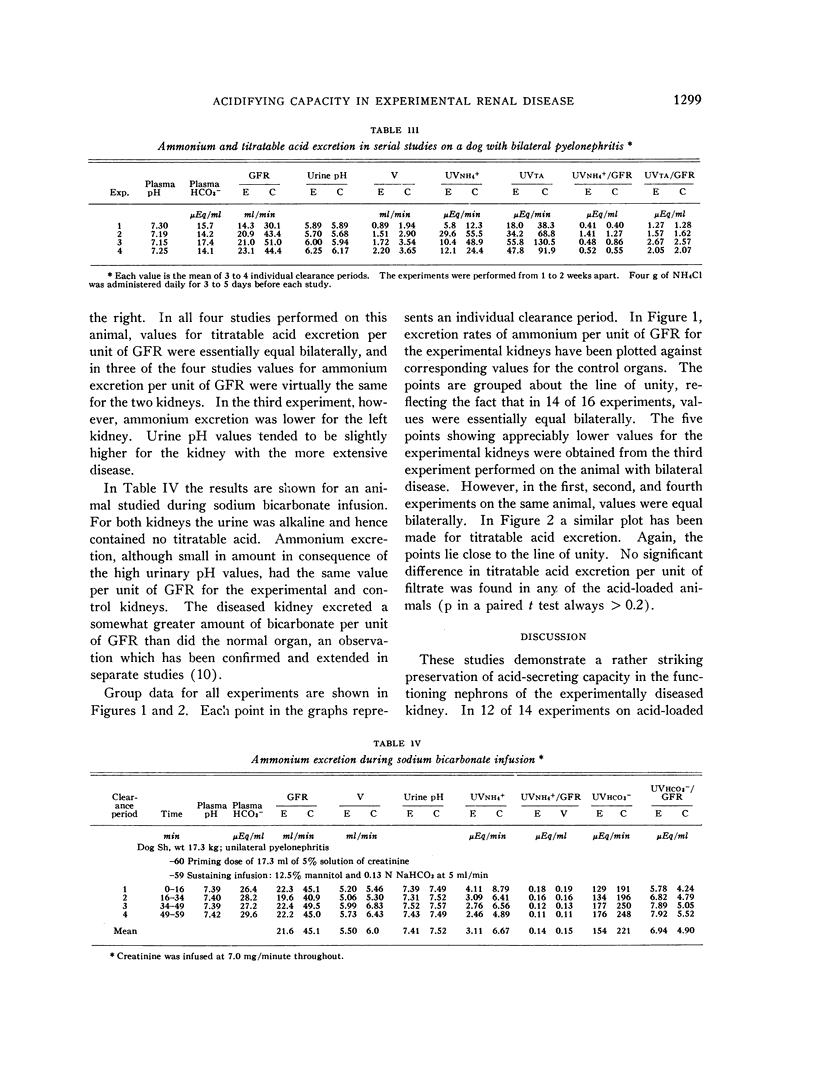
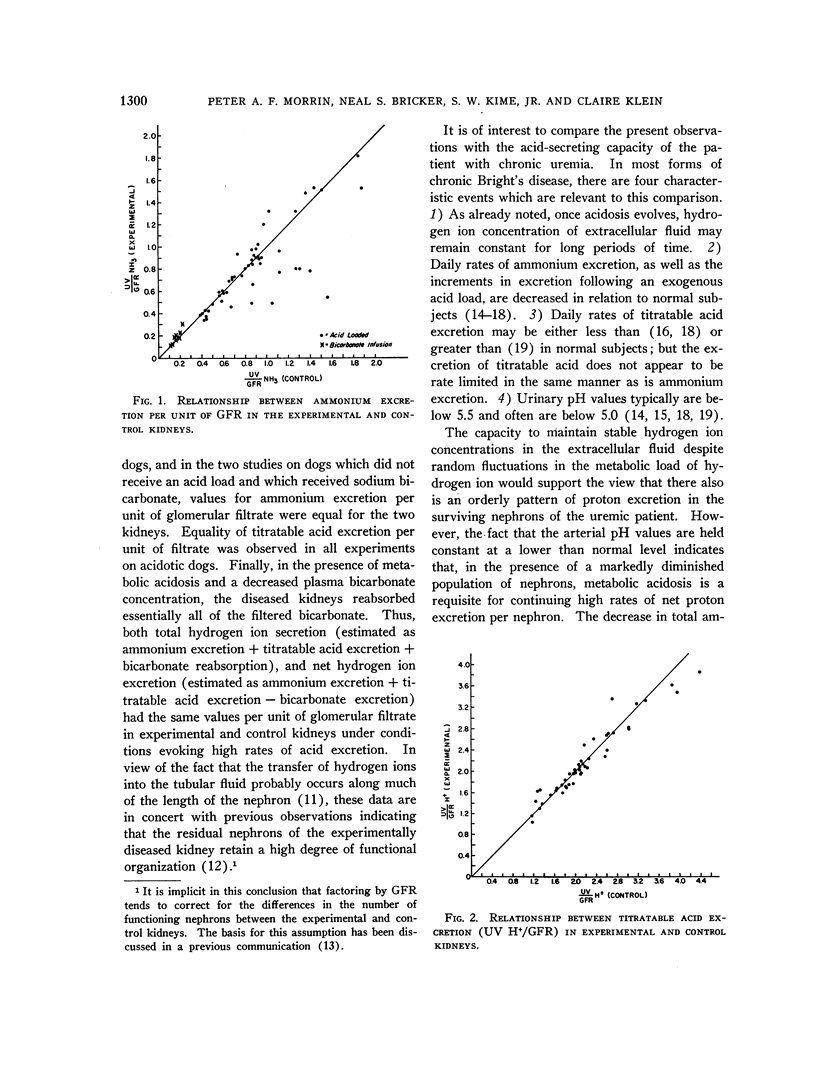
- MORRIN P. A., GEDNEY W. B., NEWMARK L. N., BRICKER N. S. Bicarbonate reabsorption in the dog with experimental renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jun;41:1303–1311. doi: 10.1172/JCI104593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHAN D. G., RODKEY F. L. A colorimetric procedure for the determination of blood ammonia. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 May;49(5):779–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., BANK N., CUTLER R. W. The influence of urinary ionic strength on phosphate pK2' and the determination of titratable acid. J Clin Invest. 1959 Feb;38(2):347–356. doi: 10.1172/JCI103808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., HALL P. W., 3rd, HAYS R. M., RELMAN A. S. On the mechanism of acidosis in chronic renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):39–52. doi: 10.1172/JCI103794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorius O. W., Roemmelt J. C., Pitts R. F., Calhoon D., Miner P. THE RENAL REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE IN MAN. IV. THE NATURE OF THE RENAL COMPENSATIONS IN AMMONIUM CHLORIDE ACIDOSIS. J Clin Invest. 1949 May;28(3):423–439. doi: 10.1172/JCI102087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Slyke D. D., Linder G. C., Hiller A., Leiter L., McIntosh J. F. THE EXCRETION OF AMMONIA AND TITRATABLE ACID IN NEPHRITIS. J Clin Invest. 1926 Feb;2(3):255–288. doi: 10.1172/JCI100045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRONG O., DAVIES H. E. The excretion of acid in renal disease. Q J Med. 1959 Apr;28(110):259–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



