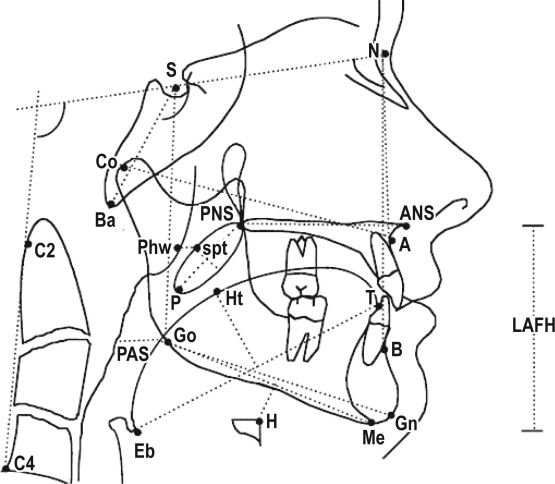
Figure 1.
Definitions of cephalometric landmarks and measurements
Anatomical Landmarks: ANS (Anterior nasal spine)—tip of the median sharp bony process of the palatine bone in the hard palate. A Point—deepest midline point on the maxillary alveolus between ANS and the maxillary alveolar crest. B Point—deepest midline point between the mandibular alveolar crest and the gnathion. Ba (Basion)—most inferior point on the anterior margin of the foramen magnum in the median plane. Go (Gonion)—most lateral external point at the junction of the horizontal and ascending rami of the mandible. Gn (Gnathion)—most antero-inferior point on the bony mandibular symphysis. H (Hyoidale)—most antero-superior point on the body of the hyoid bone. Me (Mentum)—lowest point on the bony outline of the mandibular symphysis. MP (Mandibular plane)—line joining Me and Go. N (Nasion)—most anterior point of the fronto-nasal suture. PNS (Posterior nasal spine)—tip of the posterior spine of the palatine bone of the hard palate. spt (soft palate tangent)—tangent point on a line parallel to the long axis of the soft palate at the maximum width. Phw (Posterior pharyngeal wall)—point on the posterior pharyngeal wall at the same horizontal level as spt. S (Sella)—the center of the sella turcica. Bony Dimensions: SN—anterior cranial base length. LAFH-—lower anterior face height (ANS-Me). AFH—anterior face height (N-Me). PFH—posterior face height (S-Go). Go-Me—mandibular length. ANS-PNS—maxillary length. Co-A—midface length. Overjet—horizontal distance between the upper and lower central incisors measured parallel to the occlusal plane. It is measured from the labioincisal edge of one upper central incisor to the labial surface of the corresponding lower central incisor with the upper and lower teeth in centric occlusion. Overbite—vertical distance between the incisal edge of the upper central incisor and the incisal edge of the lower central incisor. MP-H—perpendicular distance from the MP to H. Soft Tissue Dimensions: RPAS—width of nasopharynx (Phw-spt). PAS—distance between the posterior pharyngeal wall and the dorsal surface of the base of the tongue, measured on the line that intersects Go and B point. PNS-P—posterior nasal spine to the tip of the soft palate. Mx Soft Palate—maximal soft palate thickness. Tongue Length—length of the tongue. Tongue Height—maximal height of the tongue. Angular Measurements: BaSN—cranial base angulation in the mid-sagittal plane. SNA—angle from S to N to A Point. SNB—angle from S to N to B Point. ANB—angle from A Point to N to B Point. Y-Axis—facial axis (GnSN). Gonial Angle—angle formed by the posterior border of the mandible and the mandibular plane. CVT-SN—angulation of the cervical spine (C2-C4) with the cranial base (SN). SN-PP—angulation of the cranial base (SN) with the palatal plane. SN-OP—angulation of the cranial base (SN) with the occlusal plane. SN-MP—angulation of the cranial base (SN) with the mandibular plane. PP-MP—angulation of the palatal plane with the mandibular plane.