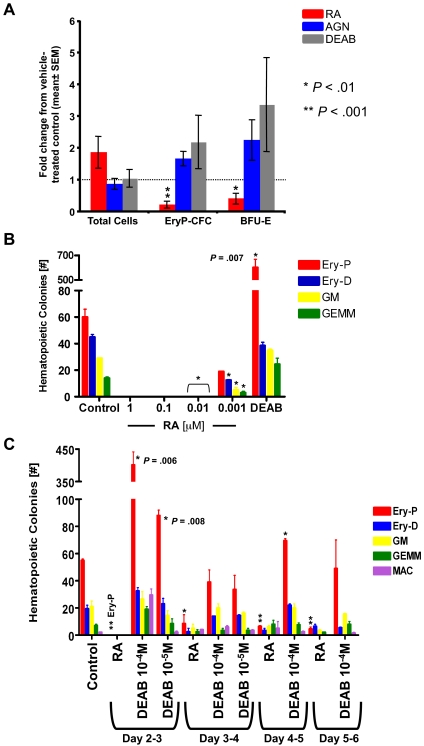
Figure 6.
Primitive erythroid progenitors in murine yolk sac cultures and murine ESC cultures are inhibited after treatment with RA and are increased by DEAB. All statistical analyses used 1-way Student t tests to calculate P values comparing treated groups with the normalized control; *P < .01, **P < .001. (A) Pooled, stage-matched yolk sac explants were cultured in vehicle control, 10−5M AGN193109, 10−5M DEAB, or 10−6M RA, and plated in methylcellulose for colony-forming assays. The data are depicted as mean fold change in comparison to the vehicle control cultures ± SEM. After DEAB treatment, P = .1 for Ery-CFC and P = .08 for BFU-E colonies. For AGN193109 treatment, P = .06 for EryP-CFC and P = .08 for BFU-E colonies. There was no statistical difference in the total number of cells for each treatment. (B) EBs from ESC cultures were incubated in the presence of various concentrations of RA, 10−4M DEAB, or DMSO control, then plated for colony-forming assays as described in “Methods.” (C) 10−6M RA, DEAB, or DMSO was added to EB shaking cultures at various time points between days 2 and 6 of ESC differentiation and washed out after 24 hours of incubation. After the sixth day of ESC differentiation, cells were counted and plated for colony assays.