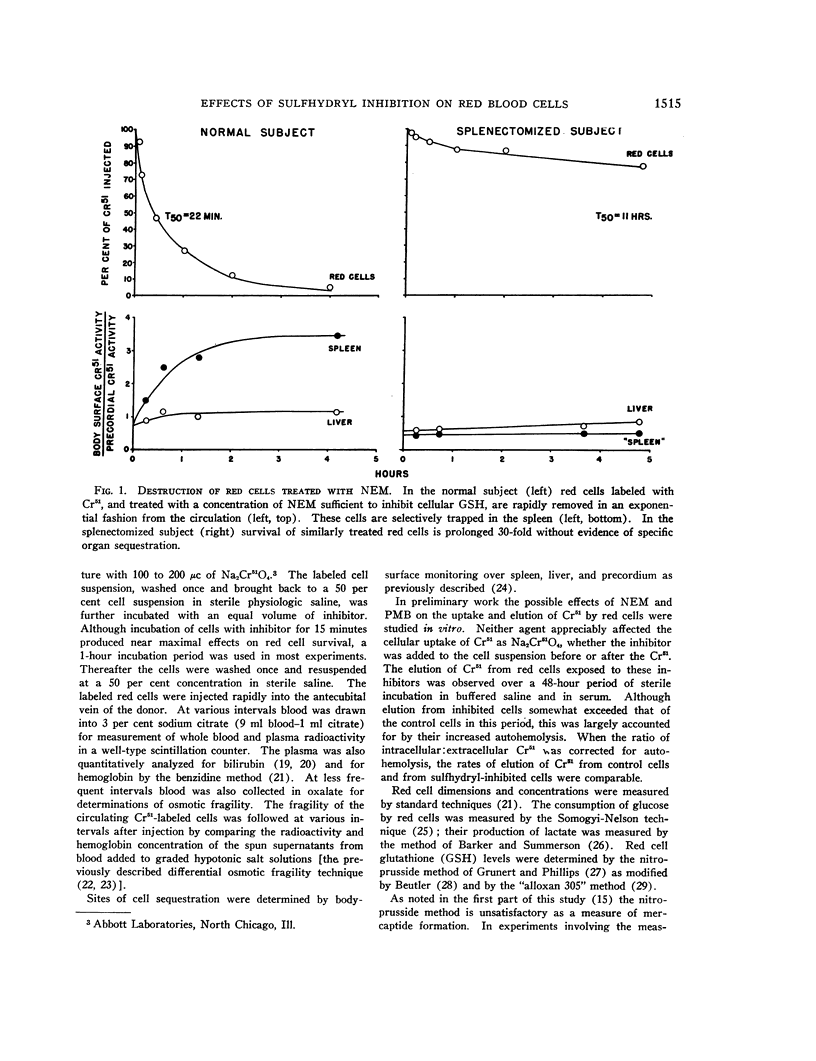
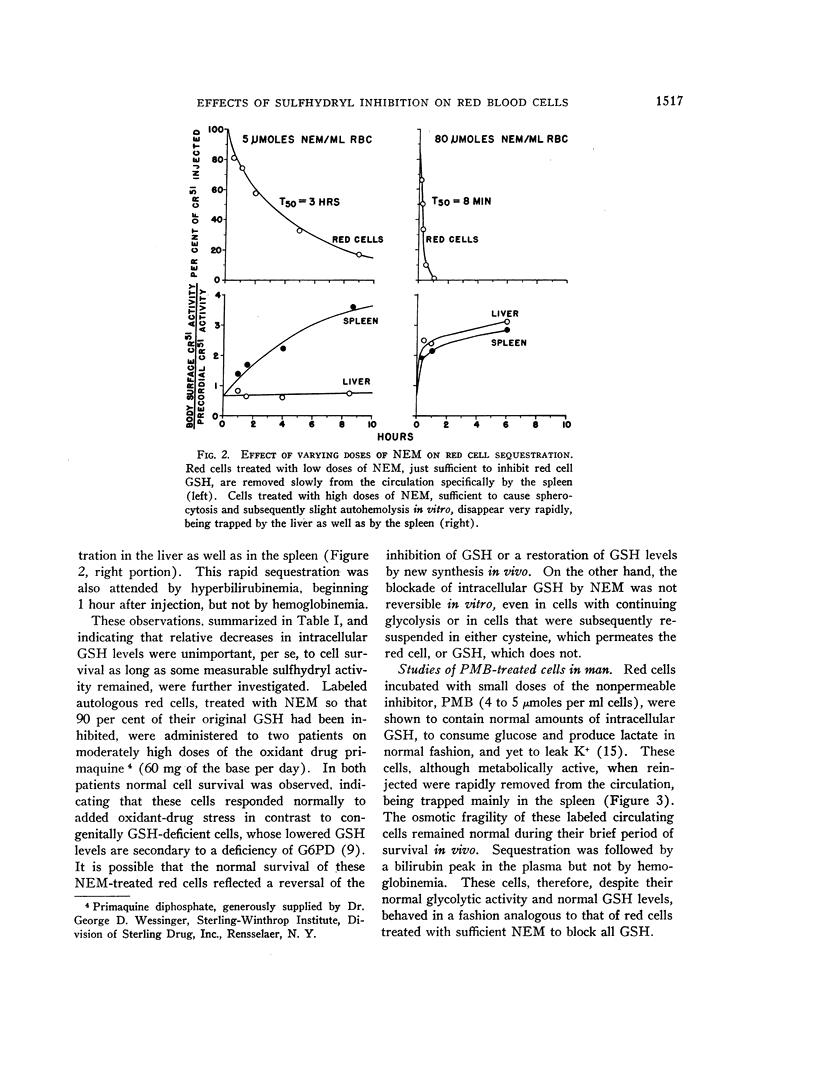
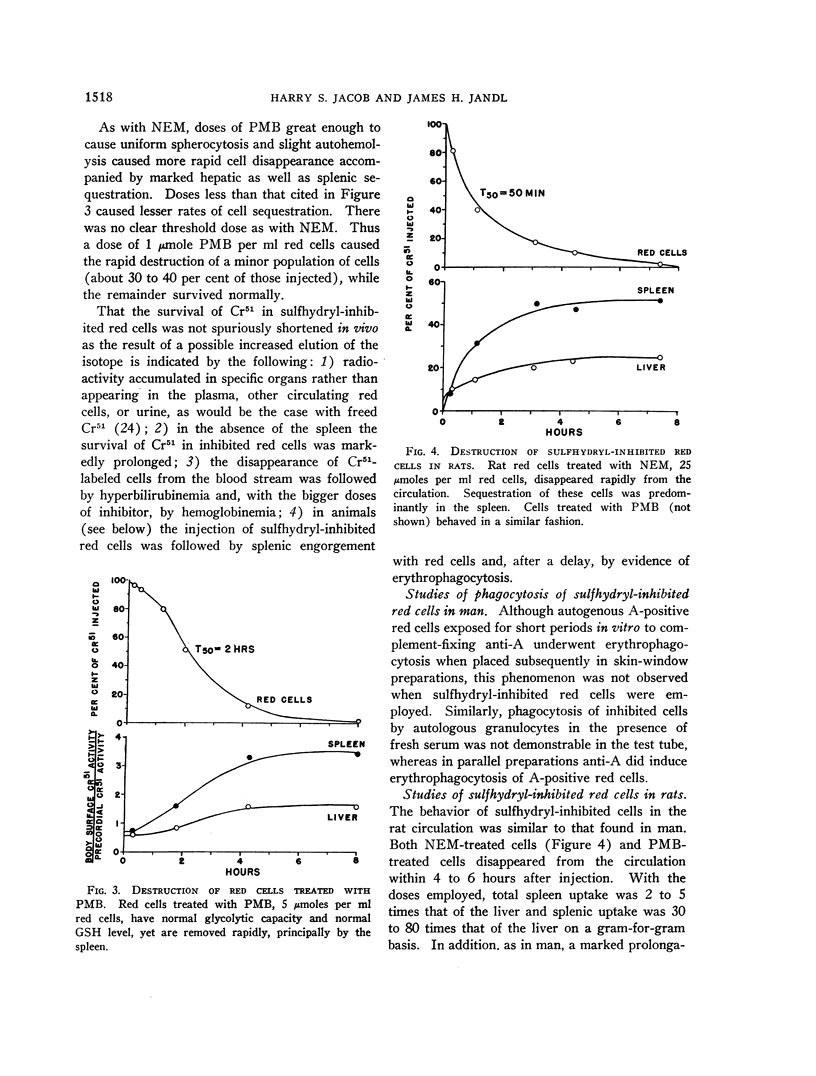
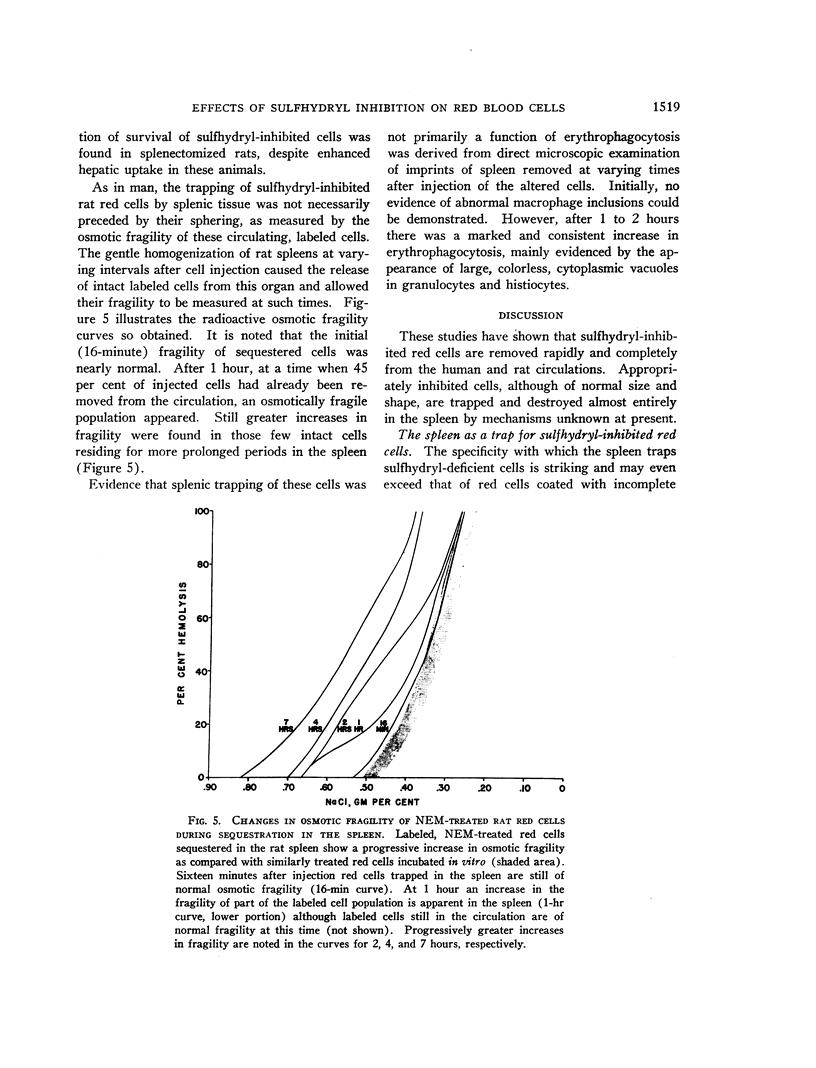
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN D. W., JANDL J. H. Oxidative hemolysis and precipitation of hemoglobin. II. Role of thiols in oxidant drug action. J Clin Invest. 1961 Mar;40:454–475. doi: 10.1172/JCI104273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLISON A. C., BURN G. P. Enzyme activity as a function of age in the human erythrocyte. Br J Haematol. 1955 Jul;1(3):291–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1955.tb05511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALVING A. S., TARLOV A. R., BREWER G., CARSON P. E., KELLER-MEYER R. W., LONG W. K. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: some biological implications. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1960;73:80–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENESCH R. E., BENESCH R. Relation between erythrocyte integrity and sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jan;48(1):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTLER E., DERN R. J., FLANAGAN C. L., ALVING A. S. The hemolytic effect of primaquine. VII. Biochemical studies of drug-sensitive erythrocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Feb;45(2):286–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTLER E. The glutathione instability of drug-sensitive red cells; a new method for the in vitro detection of drug sensitivity. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jan;49(1):84–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTLER E. The hemolytic effect of primaquine and related compounds: a review. Blood. 1959 Feb;14(2):103–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTLE W. B., HAM T. H., SHEN S. C. Observations on the mechanism of hemolytic transfusion reactions occurring without demonstrable hemolysin. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1950;63:161–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOPPIN P. W., PHILIPSON L. The inactivation of enterovirus infectivity by the sulfhydryl reagent p-chloromercuribenzoate. J Exp Med. 1961 Apr 1;113:713–734. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARVIN J. E. Factors affecting the adhesiveness of human leucocytes and platelets in vitro. J Exp Med. 1961 Jul 1;114:51–73. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIGGS R. C., WEISMAN R., Jr, HARRIS J. W. Alterations in osmotic and mechanical fragility related to in vivo erythrocyte aging and splenic sequestration in hereditary spherocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:89–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI104032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNERT R. R., PHILLIPS P. H. A modification of the nitroprusside method of analysis for glutathione. Arch Biochem. 1951 Feb;30(2):217–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARLEY J. D., MAUER A. M. Studies on the formation of Heinz bodies. II. The nature and significance of Heinz bodies. Blood. 1961 Apr;17:418–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS I. M., MCALISTER J. M., PRANKERD T. A. The relationship of abnormal red cells to the normal spleen. Clin Sci. 1957 May;16(2):223–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB H. S., JANDL J. H. Effects of sulfhydryl inhibition on red blood cells. I. Mechanism of hemolysis. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:779–792. doi: 10.1172/JCI104536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., CASTLE W. B. Agglutination of sensitized red cells by large anisometric molecules. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 May;47(5):669–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., ENGLE L. K., ALLEN D. W. Oxidative hemolysis and precipitation of hemoglobin. I. Heinz body anemias as an acceleration of red cell aging. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1818–1836. doi: 10.1172/JCI104206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., GREENBERG M. S., YONEMOTO R. H., CASTLE W. B. Clinical determination of the sites of red cell sequestration in hemolytic anemias. J Clin Invest. 1956 Aug;35(8):842–867. doi: 10.1172/JCI103338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., JONES A. R., CASTLE W. B. The destruction of red cells by antibodies in man. I. Observations of the sequestration and lysis of red cells altered by immune mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1428–1459. doi: 10.1172/JCI103542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., KAPLAN M. E. The destruction of red cells by antibodies in man. III. Quantitative factors influencing the patterns of hemolysis in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1145–1156. doi: 10.1172/JCI104129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H. The agglutination and sequestration of immature red cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 May;55:663–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOHR G. W., WALLER H. D., KARGES O., SCHLEGEL B., MULLER A. A. Zur Biochemie der Alterung menschlicher Erythrocyten. Klin Wochenschr. 1958 Nov 1;36(21):1008–1013. doi: 10.1007/BF01487970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONDON I. M. Metabolism of the mammalian erythrocyte. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1960 Feb;36:79–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS P. A., JOHNSON A. B., HIRSCHBERG E., BANKS J. Studies on the mechanism of aging of human red blood cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):95–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLISON P. L., CUTBUSH M. Use of isotope-labelled red cells to demonstrate incompatibility in vivo. Lancet. 1955 Jun 25;268(6878):1290–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)92057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAO M., NAKAO T., YAMAZOE S. Adenosine triphosphate and maintenance of shape of the human red cells. Nature. 1960 Sep 10;187:945–946. doi: 10.1038/187945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PACKER J. T., GREENDYKE R. M., SWISHER S. N. The inhibition of erythrophagocytosis in vitro by corticosteroids. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1960;73:93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON J. W., LAZAROW A. Determination of glutathione. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:259–278. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPSON L., CHOPPIN P. W. On the role of virus sulfhydryl groups in the attachment of enteroviruses to erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Sep 1;112:455–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REBUCK J. W., CROWLEY J. H. A method of studying leukocytic functions in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Mar 24;59(5):757–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb45983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. L. Some Points of the Mechanism of Filtration by the Spleen. Am J Pathol. 1928 Jul;4(4):309–320.3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANSONE G., SEGNI G. L'instabilità del glutatione ematico nel favismo; utilizzazione di un test selettivo, introduzione al problema genetico. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1957 Jul;33(7):1057–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEUCH D., RAPOPORT S. M. [Glutathione and triosephosphate dehydrogenase activity in the erythrocytes of rabbits]. Klin Wochenschr. 1960 Aug 1;38:757–758. doi: 10.1007/BF01487277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSEN C. C., COLLIER H. B. The relationship between the glutathione content of rat erythrocytes and their hemolysis by various agents in vitro. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1960 Sep;38:981–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE W. N., TANAKA K. R., MIWA S. A specific erythrocyte glycolytic enzyme defect (pyruvate kinase) in three subjects with congenital non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1961;74:100–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIEVE L., HILL E., HANSON M., FALCONE A. B., WATSON C. J. Normal and abnormal variations and clinical significance of the one-minute and total serum bilirubin determinations. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Sep;38(3):446–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



