Abstract
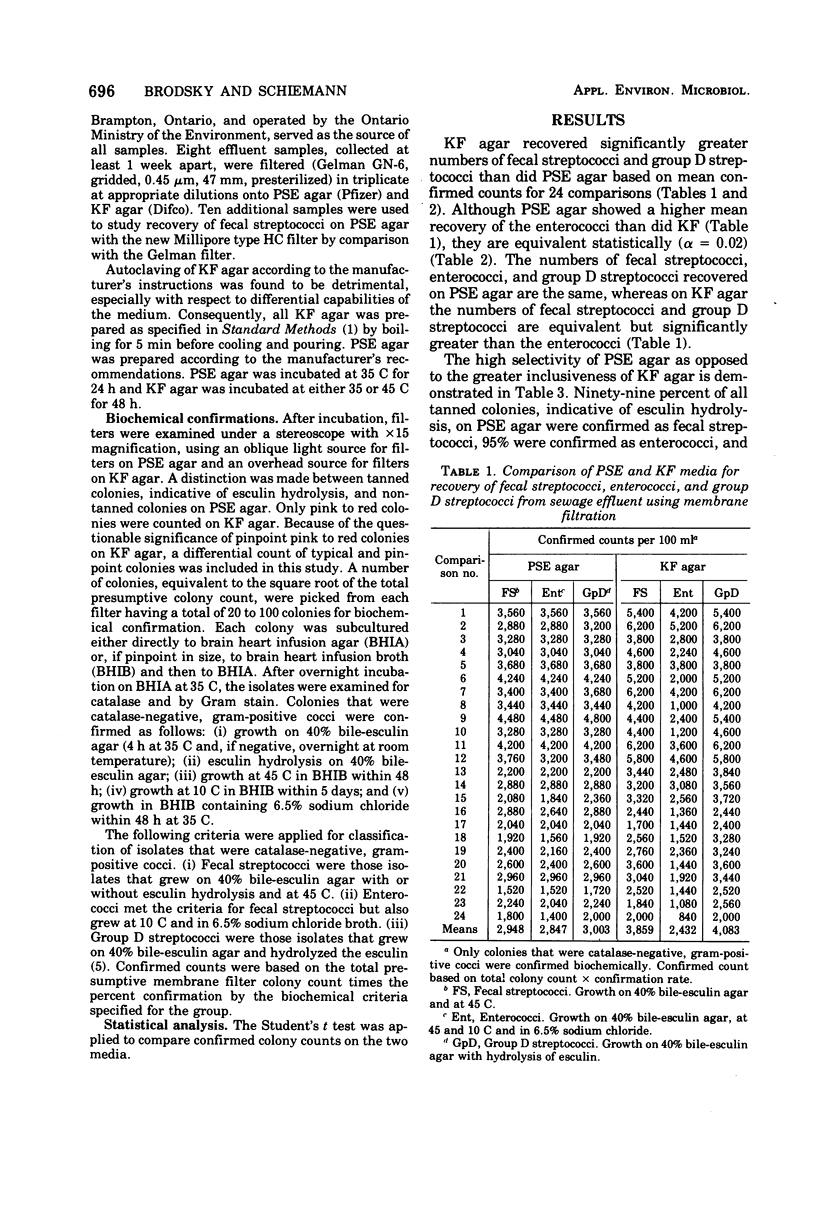
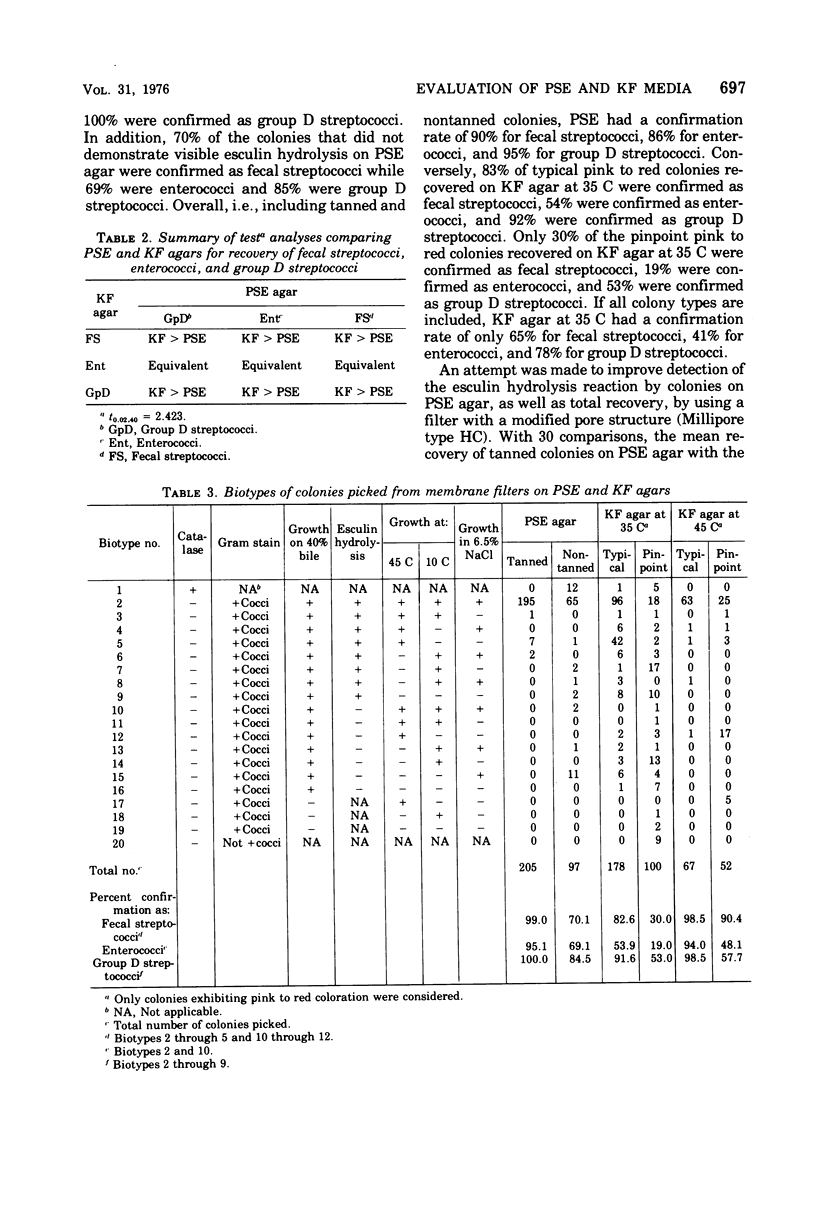
Pfizer selective enterococcus (PSE) and KF agars were compared for their recovery of fecal streptococci from sewage effluent on membrane filters. The results showed that PSE agar is highly selective for the enterococci. The tan color resulting from esculin hydrolysis, which was not always visible on the surfaces of the colonies, is not considered a necessary differential characteristic on PSE agar since more than 90% of all colonies recovered on membrane filters were confirmed as fecal streptococci and 86% were confirmed as enterococci. The detection of esculin hydrolysis on membrane filters was not improved by using the new Millipore type HC filter. KF agar recovered significantly greater numbers of organisms but was not as selective, with 83% of the typical colonies being confirmed as fecal streptococci and 54% as enterococci. An attempt to improve the selectivity of KF agar while retaining its inclusiveness by incubation at 45 C was not successful.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daoust R. A., Litsky W. Pfizer selective enterococcus agar overlay method for the enumeration of fecal streptococci by membrane filtration. Appl Microbiol. 1975 May;29(5):584–589. doi: 10.1128/am.29.5.584-589.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Comparison of several laboratory media for presumptive identification of enterococci and group D streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Aug;26(2):138–145. doi: 10.1128/am.26.2.138-145.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Moody M. D. Presumptive identification of group D streptococci: the bile-esculin test. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):245–250. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.245-250.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Recognition of group D streptococcal species of human origin by biochemical and physiological tests. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1131–1139. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1131-1139.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldreich E. E., Kenner B. A. Concepts of fecal streptococci in stream pollution. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1969 Aug;41(8 Suppl):R336+–R336+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Goldberg D., Sampson J. Laboratory studies with a selective Enterococcus medium. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):433–436. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.433-436.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNER B. A., CLARK H. F., KABLER P. W. Fecal Streptococci. I. Cultivation and enumeration of Streptococci in surface waters. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Jan;9:15–20. doi: 10.1128/am.9.1.15-20.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. A., Fischer J. R., Cabelli V. J. Membrane filter technique for enumeration of enterococci in marine waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jul;30(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/am.30.1.66-71.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova M. T., Brezenski F. T., Litsky W. Evaluation of various media for isolation, enumeration and identification of fecal streptococci from natural sources. Health Lab Sci. 1972 Oct;9(4):289–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLANETZ L. W., BARTLEY C. H. DETECTION AND SANITARY SIGNIFICANCE OF FECAL STREPTOCOCCI IN WATER. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1964 Apr;54:609–614. doi: 10.2105/ajph.54.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbaj J., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Comparison of selective media for isolation of presumptive group D streptococci from human feces. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):1008–1011. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.1008-1011.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek K. J., Suslavich R. V., Sohn B. I., Dawson F. W. Optimum membrane structures for growth of coliform and fecal coliform organisms. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):685–691. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.685-691.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. E., Evans J. B. Evaluation of selective media for enumeration of group D streptococci in bovine feces. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):1086–1087. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.1086-1087.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


