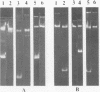
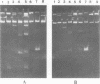
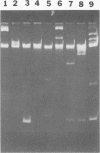
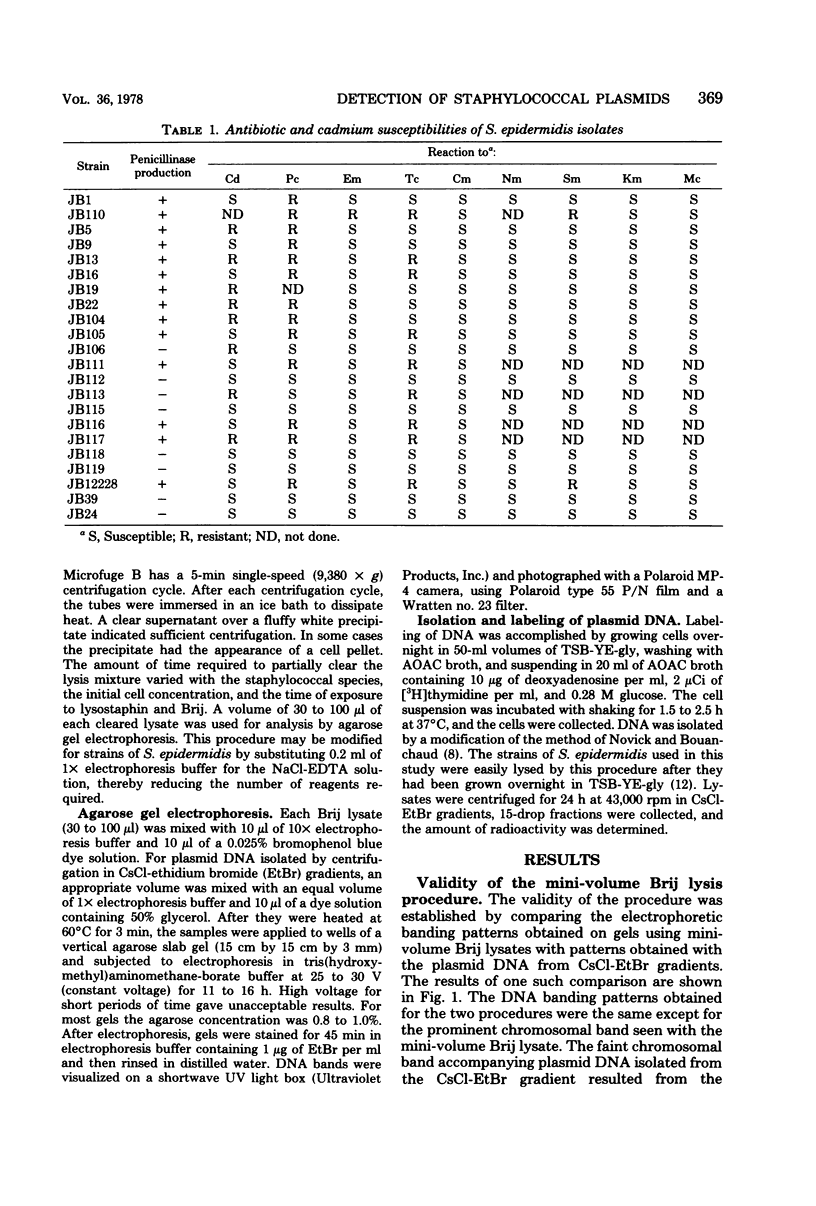
Abstract
A rapid, reproducible, mini-volume assay capable of detecting staphylococcal plasmid DNA in the range of 0.8 to 32 megadaltons has been developed. The assay employs lysostaphin-mediated lysis of cells followed by a short, low-speed centrifugation and does not require treatment with ribonuclease or protease or deproteinization with phenol. A period of only 24 h may be required to detect the presence and size of a plasmid once an organism has been isolated. This method has been used to study the plasmid ecology of Staphylococcus epidermidis and to correlate the presence or absence of plasmids with tetracycline, chloramphenicol, neomycin, penicillin, and cadmium resistances.
Full text
PDF

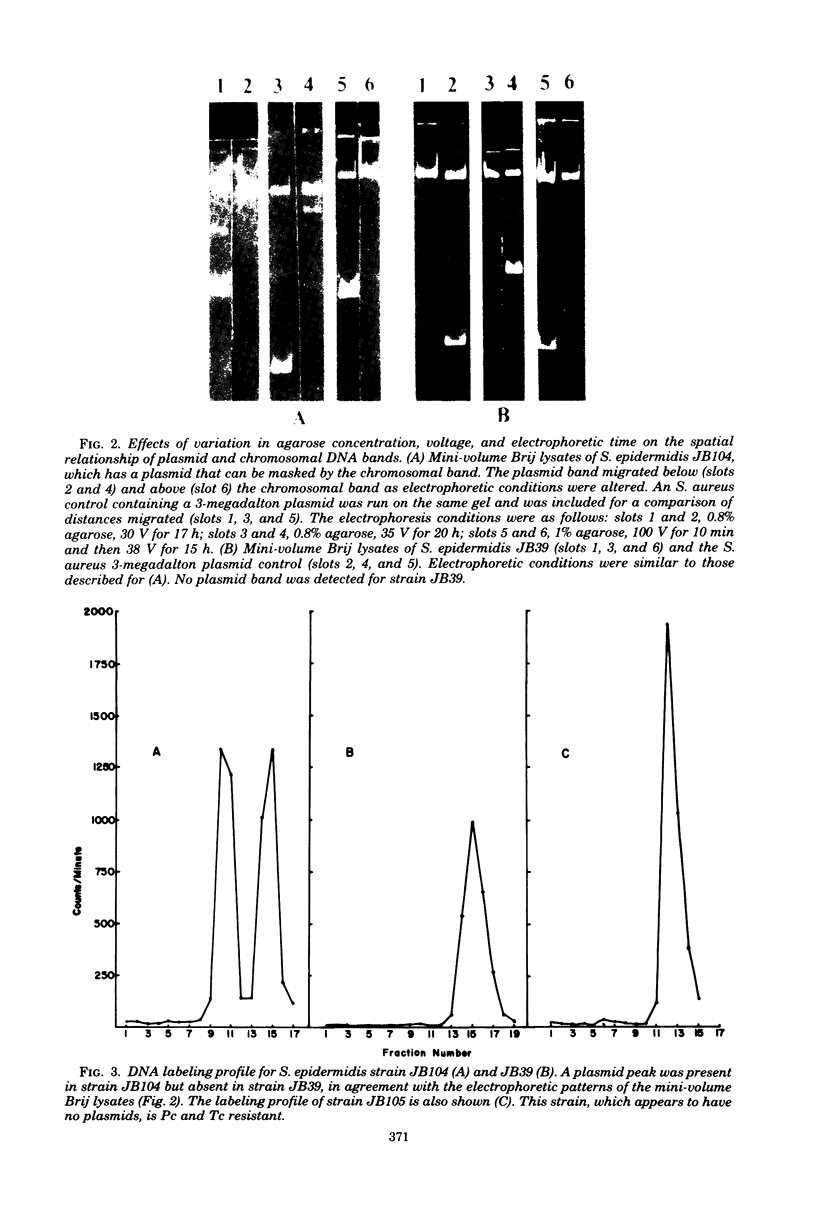



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. N., Strickland R. H., Cox M. F. Some properties of the beta-lactamase genes in Staphylococcus epidermidis. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Oct;18(4):628–630. doi: 10.1128/am.18.4.628-630.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. Plasmid detection and sizing in single colony lysates. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):393–394. doi: 10.1126/science.318764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W. Antibiotic resistance plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus and their clinical importance. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.1-32.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshew B. H., Rosenblum E. D. Plasmid for tetracycline resistance in Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):568–574. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar K., Heczko P. B. Transduction of penicillin resistance together with ability to ferment mannitol and ribose in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):449–452. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Bouanchaud D. The problems of drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. Extrachromosomal nature of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:279–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poston S. M., Palmer T. J. Transduction of penicillinase production and other antibiotic-resistance markers in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):235–242. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendorf L. L., Kayser F. H. Transduction and plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid analysis in a multiply antibiotic-resistant strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):679–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.679-686.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S. Polyfunctional penicillinase plasmid in Staphylococcus epidermidis: bacteriophage restriction and modification mutants. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):697–706. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.697-706.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kloos W. E. A simple test system for the separation of staphylococci from micrococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):337–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.337-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiffler P. W., Sweeney H. M., Cohen S. Co-transduction of plasmids mediating resistance to tetracycline and chloramphenicol in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):934–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.934-944.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford J., Boseley P., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Novel screening procedure for recombinant plasmids. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):391–393. doi: 10.1126/science.318763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieckiewicz J. A. Relationship between resistance to metallic ions and production of beta-lactamase in strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1976;21(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]