Abstract
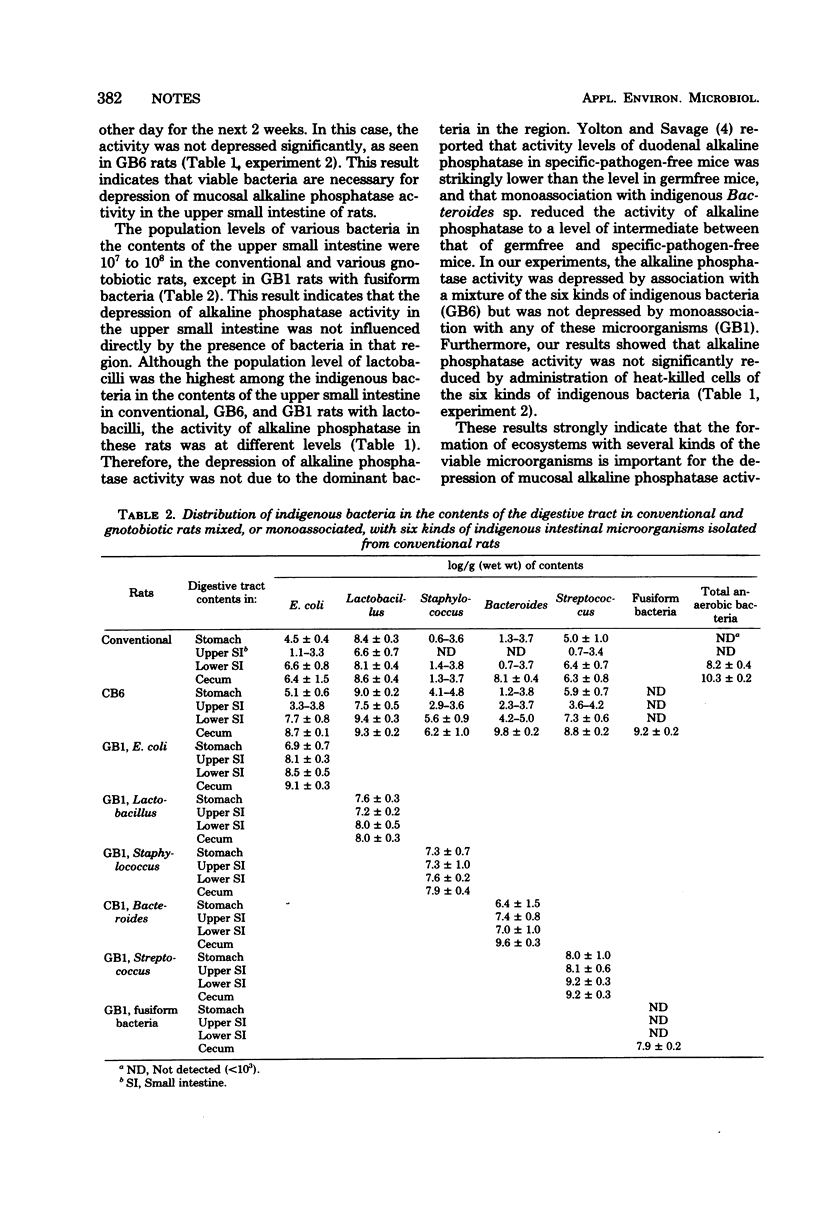
Depression of intestinal alkaline phosphatase activity can be caused by the formation of the microbial ecosystem with several kinds of viable microorganisms in rats.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kawai Y., Morotomi M. Intestinal enzyme activities in germfree, conventional, and gnotobiotic rats associated with indigenous microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):771–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.771-778.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morotomi M., Watanabe T., Suegara N., Kawai Y., Mutai M. Distribution of indigenous bacteria in the digestive tract of conventional and gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):962–968. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.962-968.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suegara N., Morotomi M., Watanabe T., Kawal Y., Mutai M. Behavior of microflora in the rat stomach: adhesion of lactobacilli to the keratinized epithelial cells of the rat stomach in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):173–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.173-179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolton D. P., Savage D. C. Influence of certain indigenous gastrointestinal microorganisms on duodenal alkaline phosphatase in mice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):880–888. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.880-888.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



