Abstract
We present label-free functional photoacoustic imaging of the ocular microvasculature in living animals. The anterior segment of an adult mouse was imaged with a laser exposure level well within the American National Standards Institute safety standards. Individual red blood cells traveling along the iris capillaries were clearly resolved, and the hemoglobin oxygen saturation in the iris microvasculature was imaged spectrally. We believe that photoacoustic imaging has the potential to advance the diagnosis and treatment of ocular diseases in humans.
Visual impairment is highly prevalent worldwide. Ten percent of the U.S. adult population has experienced vision problems [1], many of which are manifest in the ocular circulation [2]. Fluorescence angiography is very successful in the diagnosis of ocular vascular diseases and has been well accepted as the gold standard for ocular circulation imaging. However, an inherent limitation of fluorescence angiography is the required injection of contrast agents (fluorescein or indocyanine green) that can cause pain and complications such as emesis, anaphylactic reactions, or even death [3]. Moreover, the angiographic agents may fail to perfuse if there is conspicuous vascular leakage. Thus, the development of label-free imaging techniques to avoid these problems is warranted.
Our previous work on photoacoustic tomography, an emerging hybrid technique capable of detecting optical absorption ultrasonically, has demonstrated its unique advantage of utilizing endogenous hemoglobin contrast for subcutaneous and cortical vascular imaging in living animals as well as in humans [4, 5]. With recent advances in optical illumination and ultrasonic detection mechanisms [6], we have successfully extended the application of this technique to ophthalmology. Here, we report optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM) for in vivo label-free functional imaging of the ocular microcirculation.
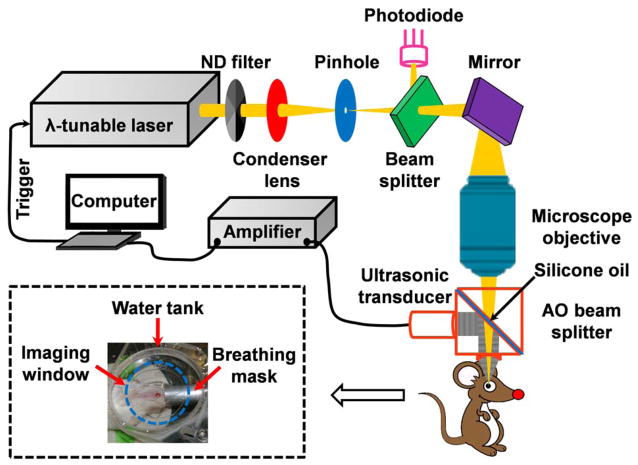
To achieve spectroscopic measurements, our OR-PAM system (Fig. 1) employs a wavelength-tunable laser system consisting of a Nd:YLF pump laser (INNOSLAB, Edgewave) and a dye laser (CBR-D, Sirah). The laser beam is attenuated by a neutral density filter (NDC-100C-2, Thorlabs) before being spatially filtered through a 25-μm pinhole (P25C, Thorlabs), and then is focused by a microscope objective (RMS4X, Thorlabs) to achieve micrometer lateral resolution. An optical beam splitter, in combination with a photodiode (SM05PD1A, Thorlabs), is inserted between the pinhole and the microscope objective to monitor laser intensity fluctuation. A homemade acoustic-optical beam splitter, consisting of two right-angle prisms (NT32-545, Edmund Optics) and a 100-μm thick layer of silicone oil (1000cSt, Clearco Products), is placed under the objective lens to separate optical illumination and acoustic detection [6]. A 75-MHz ultrasonic transducer (V2022 BC, Olympus NDT) is attached to the vertical side of the bottom prism. An acoustic lens (NA: 0.46; radius of curvature: 5.2 mm) is attached to the bottom of the splitter and immersed in the water tank to collect photoacoustic signals. An imaging window in the bottom of the water tank is sealed with an ultrasonically and optically transparent polyethylene membrane. Typically, before imaging, an adult Swiss Webster mouse (Hsd:ND4, Harlan Co., 25–30 g) was anesthetized and transferred to a homemade stereotaxic imaging stage. Lubricating drops (Butler AHS) were gently administered to both eyes, and then ultrasonic gel was evenly applied between the imaging window and the eye for ultrasound coupling and eye hydration. The water tank had a low-pressure contact with the cornea to avoid possible disturbance to the intrinsic ocular circulation. Anesthesia was maintained throughout the experiments by an isoflurane machine (1.0–1.5% vaporized isoflurane with an airflow rate of 1 L/min). The body temperature of the animal was maintained at 37 °C with a temperature controlled heating pad. At the end of the experiments, the animals were euthanized by an intraperitoneal administration of pentobarbital at a dosage of 100 mg/kg.
Figure 1.
Schematic of the photoacoustic ophthalmic angiography system. The inset photograph shows the animal positioning. λ: wavelength; AO: acoustic-optical; ND: neutral density.
Compared with conventional fluorescence angiography, OR-PAM has multiple advantages. First, hemoglobin absorption provides endogenous and functional imaging contrast. In OR-PAM, a nanosecond-pulsed laser beam is absorbed by hemoglobin molecules circulating in the ocular microvasculature. The resulting transient thermoelastic expansion induces wideband ultrasonic waves, which are detected by a high-frequency ultrasonic transducer to form a projection or volumetric angiogram (Fig. 2a and Media 1). Since hemoglobin is the predominant light absorber in the intrinsic microcirculation, blood vessels detected by OR-PAM must contain red blood cells (RBC), the carrier of hemoglobin. This characteristic guarantees that OR-PAM images only RBC-perfused capillaries, the functional subset of capillaries responsible for supplying oxygen to the eye.
Figure 2.
Label-free photoacoustic ophthalmic angiography of the iris microvasculature of a living adult Swiss Webster mouse. (a) The maximum amplitude projection image acquired at 570 nm (volumetric visualization is available online as Media 1). (b) A close-up of the boxed area in panel a. The yellow arrows indicate individual red blood cells (RBC) in iris capillaries. (c) The profile of an RBC crossed by the red dashed line in panel b. LIC: lesser iris circle. PA: photoacoustic signal.
A second advantage is that tight optical focusing and the high nonradiative quantum yield of hemoglobin enable single-RBC resolution and sensitivity. The 5-μm resolution in our current design matches the average size of single RBCs. Moreover, hemoglobin is a non-fluorescent molecule, and thus almost all the absorbed photon energy is converted to heating, which elicits photoacoustic emission. OR-PAM’s micrometer spatial resolution enables visualizing individual RBCs traveling along iris capillaries (Fig. 2b). The Gaussian fit of the cross-sectional photoacoustic signal profile (Fig. 2c) of a chosen particle observed by OR-PAM (crossed by the red dashed line in Fig. 2b) has a full-width-at-half-maximum of ~6 μm. The size and high contrast-to-noise ratio (~20 dB) suggest that these particles (the yellow arrows in Fig. 2b) are single RBC disks imaged sideways. The high detection sensitivity also permits the use of a laser exposure level well within the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) safety standards (expanded upon later).
Third, endogenous contrast combined with low-level exposure enables repetitive imaging or chronic monitoring, which is highly desirable for treatment evaluation and drug development. As a simple demonstration, we re-imaged the same region of interest shown in Fig. 2a. With the focal plane lowered towards the posterior segment, the peripheral vascular structures—the ciliary process (CP), the recurrent choroidal branch (RCB), and the major iris circle (MIC), which bifurcates into multiple radial iris arteries (RIA)—are better visualized in Fig. 3, though the lesser iris circles (LIC) are slightly blurred. Compared with Fig. 2a, Fig. 3 shows essentially no change in the general microvascular morphology.
Figure 3.
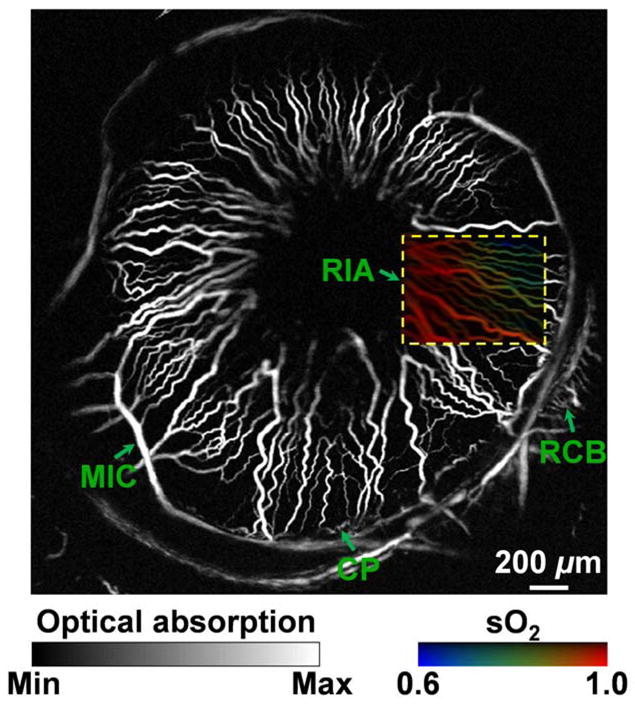
Label-free photoacoustic ophthalmic angiography of hemoglobin oxygen saturation (sO2) in the iris microvasculature of a living adult Swiss Webster mouse. The imaged region is the same as that shown in Fig. 2a, but with a focal plane closer to the posterior segment to better visualize the peripheral vascular structures. A dual-wavelength (570 and 578 nm) sO2 measurement was performed on the boxed region of interest. A vessel-by-vessel sO2 mapping was generated and overlaid on the maximum amplitude projection image acquired at 570 nm. CP: ciliary process; MIC: major iris circle; RCB: recurrent choroidal branch; RIA: radial iris artery.
As a fourth advantage, spectroscopic measurements offer functional characterization of blood oxygenation. Capitalizing on the distinct difference in the absorption spectra of oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) and deoxyhemoglobin (HbR), we used two excitation wavelengths (570 and 578 nm) to estimate the concentrations of HbO2 and HbR, thereby mapping the hemoglobin oxygenation saturation (sO2) on a single-vessel basis (the dashed-line box in Fig. 3). Blood oxygenation levels are pseudocolored from blue to red in an ascending order. From the sO2 mapping, we can clearly identify the RIAs, and we can also observe the transition in blood oxygenation from arteries to veins.
For potential clinical applications, the maximum permissible exposure (MPE) that OR-PAM can apply is subject to the ANSI safety standards for the eye [7]. Since the pulse repetition frequency (PRF) of our OR-PAM laser is less than the critical frequency (55 kHz for wavelengths between 0.4 to 1.05 μm), three ANSI rules need to be tested. The experimental parameters used for the following calculation are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Experimental parameters.
λ: wavelength; PRF: pulse repetition frequency; t: duration of a single pulse; TBscan: exposure duration of each B-scan; Tmax: duration of a complete exposure; α: angular subtense.
Because 570 and 578 nm are close to each other and show minimal differences in terms of the safety limits, we use 570 nm throughout the calculation.
In the experiments shown in Figs. 2a and 3, the imaged region of interest is 4 mm by 4 mm, with a scanning step size of 2.5 μm. Unidirectional cross-sectional scanning (B-scan) is utilized to avoid the effect due to the backlash of the mechanical scanner. Each forward B-scan takes ~2.7 s, and the scanner reposition takes another ~1.8 s. The total image acquisition time is ~2 hr (7200 s), which is limited by the mechanical scanning speed.
The angular subtense is estimated by the numerical aperture of the microscope objective, which is 0.1 in our current system.
Rule 1. Single Pulse Limit. The MPE for a single laser pulse is
| (1) |
where CE= α2/(αmaxαmin) = 267 is the extended source correction factor. Here, αmax = 100 mrad is the apparent angle subtended by a source above which the thermal hazard is proportional to the radiance of the source, and αmin = 1.5 mrad is the apparent angle subtended by a source above which extended source MPEs apply.
Rule 2. Average Power Limit. First, consider one cross-sectional scan (B-scan). During each B-scan, the OR-PAM laser sends a pulse train containing 1600 pulses with a PRF of 600 Hz. Since the B-scan exposure time (~2.7 s) is longer than 0.7 s and the wavelength is between 400 and 600 nm, dual limits due to both photochemical and thermal effects apply here. For photochemical effects, the MPE for the B-scan pulse train is
| (2) |
where CB = 100.02(λ−450)= 251 is the wavelength correction factor, and α = 200 mrad is the angular subtense. For thermal effects, the MPE for the B-scan pulse train is
| (3) |
where TBscan = 2.7 s is the exposure duration of each B-scan as listed in Table 1. Thus, the MPE/pulse for the B-scan pulse train is
| (4) |
where nBscan = 1600 is the number of pulses in each B-scan. Second, consider the total 2-hour laser exposure. For photochemical effects, the MPE for the total exposure duration is the same as that for each B-scan, as calculated in Eq. (2). For thermal effects, the MPE for the total exposure duration is
| (5) |
where T2 = 100 s is the exposure duration beyond which the thermal MPE for an extended source is constant in terms of irradiance, and Tmax = 7200 s is the duration of a complete exposure. Thus, the MPE/pulse for the total 2-hour laser exposure is
| (6) |
where nTotal = 2.56×106 is the number of pulses in the total 2-hour exposure.
Rule 3. Repetitive Pulse Limit. The MPE is
| (7) |
Rule 3 is the most conservative of the three. Therefore, the overall MPE for each pulse is 3.3×10−6 J/cm2. If the pupil diameter D is 7 mm [7], the maximum permissible single laser pulse energy in our OR-PAM system is
| (8) |
which is ~30 times greater than our experimentally used laser pulse energy of ~40 nJ.
Thus, we conclude that OR-PAM eliminates the need for injected contrast agents, offers significant promise for diagnosis and monitoring of ocular diseases, and poses essentially no radiation hazards. For clinical applicability, the next step is to improve the imaging speed of the system, through methods such as optical scanning [8].
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate Prof. James Ballard’s close reading of the manuscript. This work was sponsored by National Institutes of Health Grants R01 EB000712, R01 NS46214, R01 EB008085, and U54 CA136398. L.V.W. has a financial interest in Microphotoacoustics, Inc. and Endra, Inc., which, however, did not support this work.
Footnotes
OCIS codes: 170.3880, 170.5120, 330.7327, 140.3360.
References
- 1.Summary Health Statistics for U.S. Adults: National Health Interview Survey. 2007 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Aiello LP, Avery RL, Arrigg PG, Keyt BA, Jampel HD, Shah ST, Pasquale LR, Thieme H, Iwamoto MA, Park JE, Nguyen HV, Aiello LM, Ferrara N, King GL. New Engl J Med. 1994;331:1480. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199412013312203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hurley BR, Regillo CD. Fluorescein Angiography: General Principles and Interpretation. In: Fernando Arevalo J, editor. Retinal Angiography and Optical Coherence Tomography. Springer; 2009. pp. 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wang X, Pang Y, Ku G, Xie X, Stoica G, Wang LV. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:803. doi: 10.1038/nbt839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang HF, Maslov K, Stoica G, Wang LV. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:848. doi: 10.1038/nbt1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Maslov K, Zhang HF, Hu S, Wang LV. Opt Lett. 2008;33:929. doi: 10.1364/ol.33.000929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.ANSI Z136.1–2007, American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers. American National Standards Institute Inc; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xie Z, Jiao S, Zhang HF, Puliafito CA. Opt Lett. 2009;34:1771. doi: 10.1364/ol.34.001771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]