Abstract
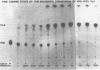
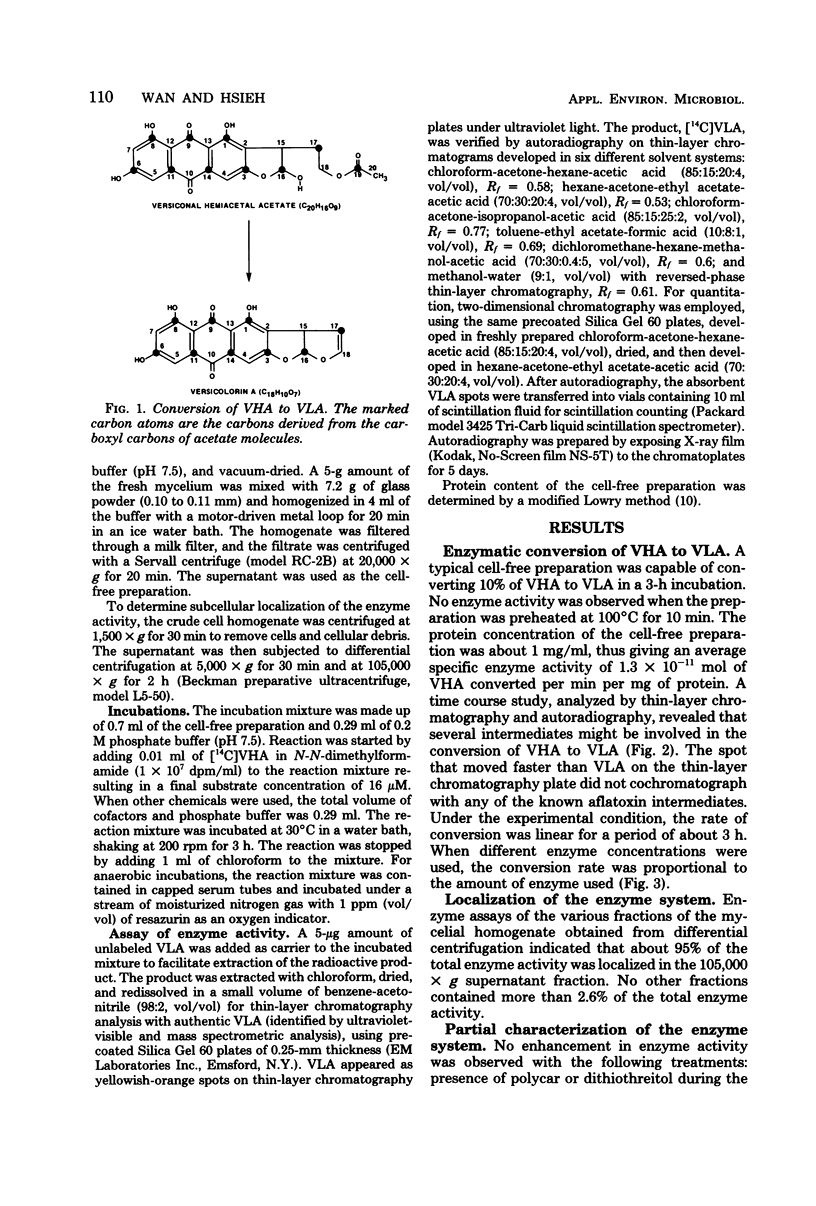
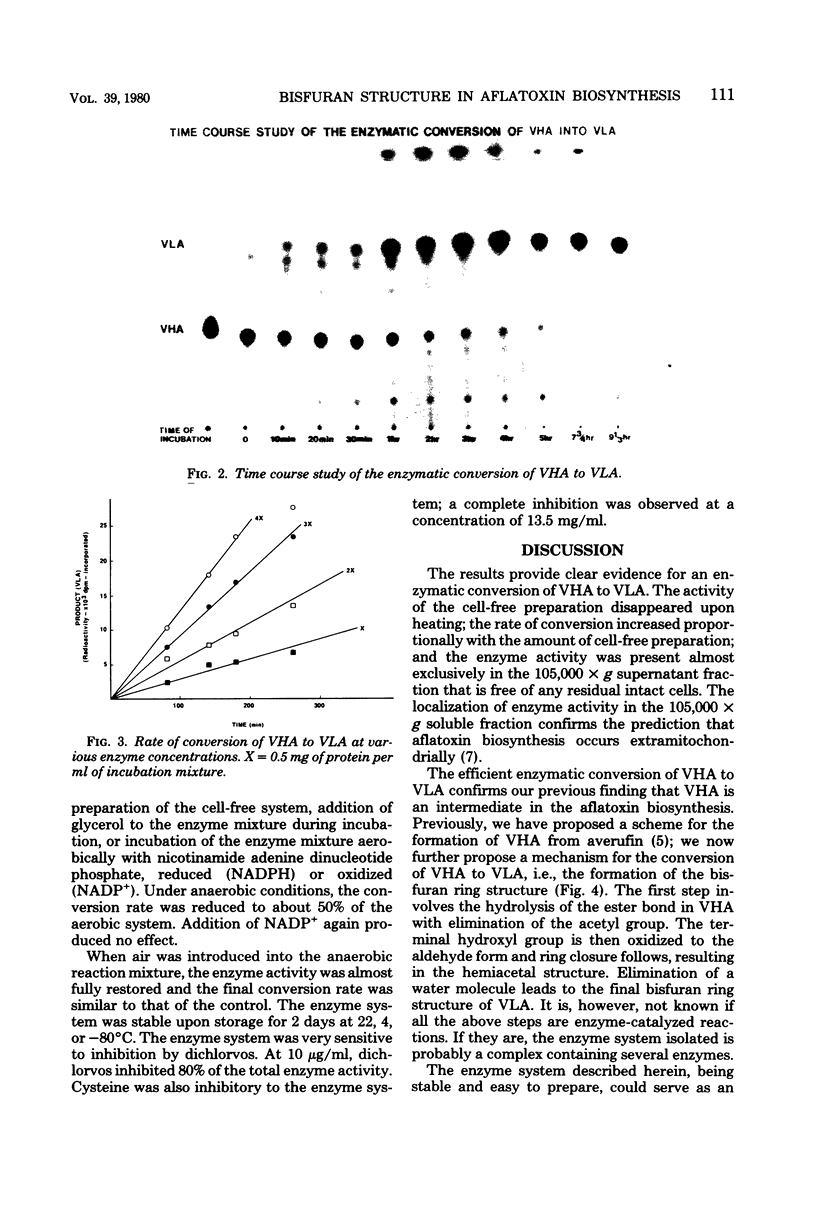
A relatively stable enzyme system that converts versiconal hemiacetal acetate to versicolorin A was isolated from the soluble fraction of the homogenized cells of Aspergillus parasiticus ATCC 15517. The cell-free preparation did not require oxygen or oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate for activity, nor did it require dithiothreitol, polyclar (polyvinyl pyrrolidone), or glycerol for stabilization of activity. It was susceptible to inhibition by dichlorvos and cysteine. Isotope tracer studies revealed involvement of several intermediates in the conversion of versiconal hemiacetal acetate to versicolorin A. These findings confirm the biogenetic relationship of versiconal hemiacetal acetate and versicolorin A, and they confirm that the bisfuran ring structure in aflatoxins and related fungal metabolites is derived from the hemiacetal structure of versiconal hemiacetal acetate.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. S., Dutton M. F. The use of cell free extracts derived from fungal protoplasts in the study of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Experientia. 1979 Jan 15;35(1):21–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01917850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. H., Churchill F., Cole R. J., Dormer J. W. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the structure and biosynthesis of versiconal acetate. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Apr 27;99(9):3159–3161. doi: 10.1021/ja00451a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzell D. L., Singh R., Hsieh D. P., Motell E. L. Nuclear magnetic resonance identification of versiconal hemiacetal acetate as an intermediate in aflatoxin biosynthesis. J Agric Food Chem. 1977 Sep-Oct;25(5):1193–1197. doi: 10.1021/jf60213a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P. Inhibition of aflatoxin biosynthesis of dichlorvos. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 May-Jun;21(3):468–470. doi: 10.1021/jf60187a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Bennett J. W., Cucullu A. F., Stanley J. B. Synthesis of versicolorin A by a mutant strain of Aspergillus parasiticus deficient in aflatoxin production. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 Nov-Dec;23(6):1132–1134. doi: 10.1021/jf60202a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggon K. K., Gupta S. K., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Biosynthesis of aflatoxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):822–855. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.822-855.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj H. G., Viswanathan L., Murthy H. S., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Biosynthesis of aflatoxins by cell-free preparations from Aspergillus flavus. Experientia. 1969 Nov 15;25(11):1141–1142. doi: 10.1007/BF01900235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Hsieh D. P. Aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway: elucidation by using blocked mutants of Aspergillus parasiticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 15;178(1):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Hsieh D. P. Enzymatic conversion of sterigmatocystin into aflatoxin B1 by cell-free extracts of Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 May;31(5):743–745. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.5.743-745.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong J. J., Hsieh D. P. Mutagenicity of aflatoxins related to their metabolism and carcinogenic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2241–2244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong J. J., Singh R., Hsieh D. P. Mutagenicity of fungal metabolites related to aflatoxin biosynthesis. Mutat Res. 1977 Sep;44(3):447–450. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(77)90102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao R. C., Hsieh D. P. Step of dichlorvos inhibition in the pathway of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.52-57.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]