Abstract
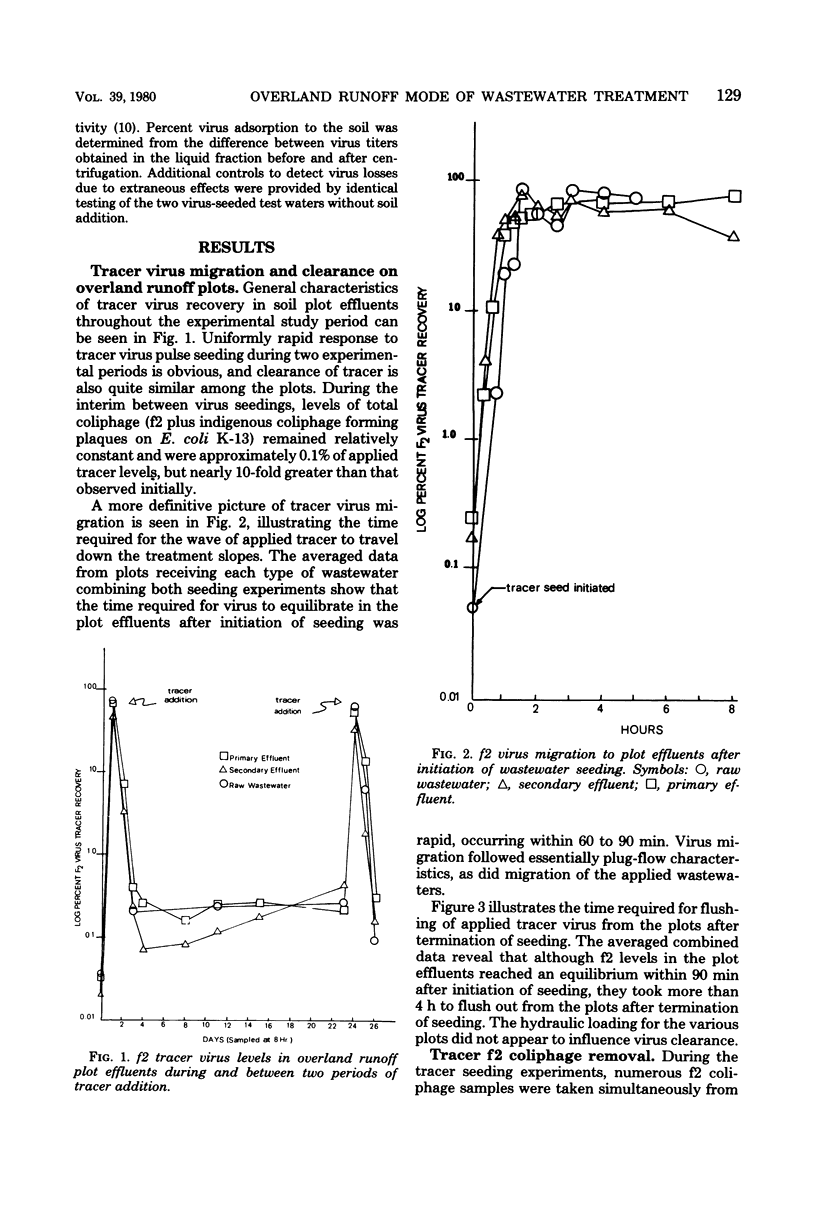
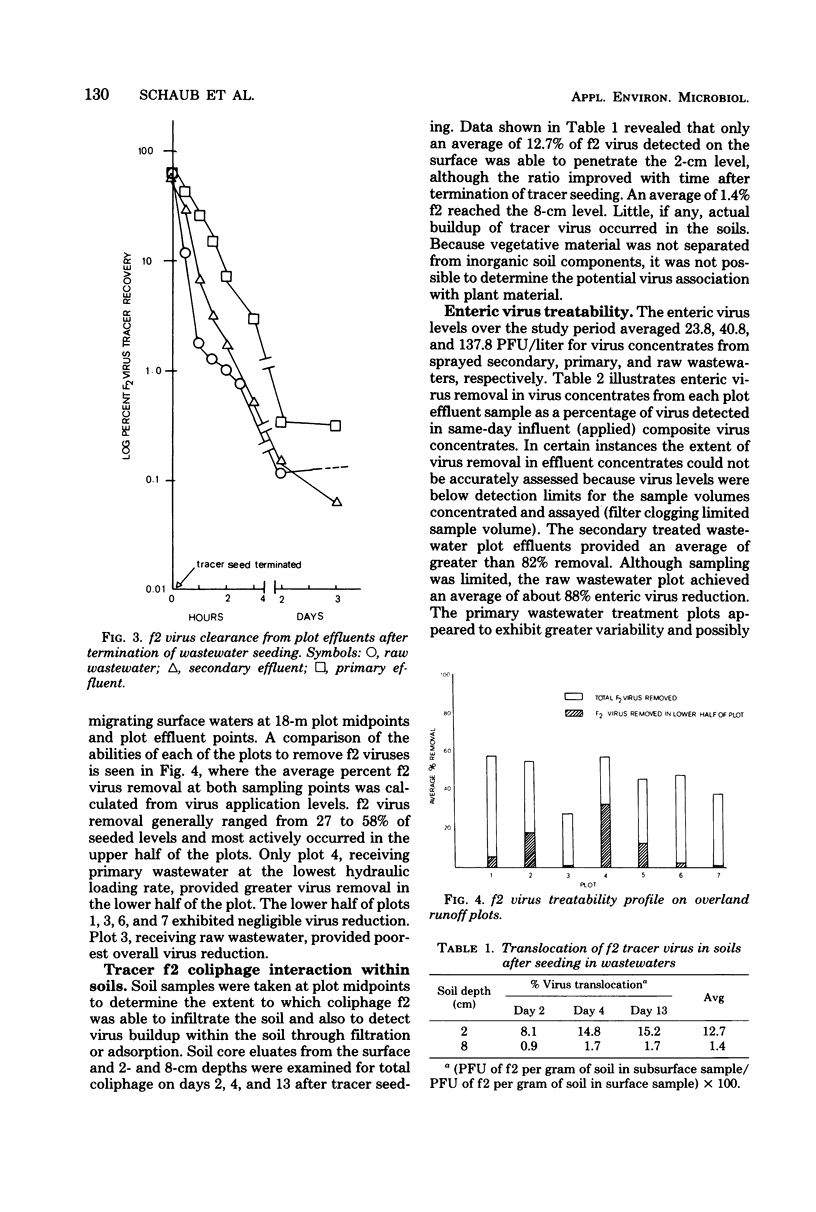
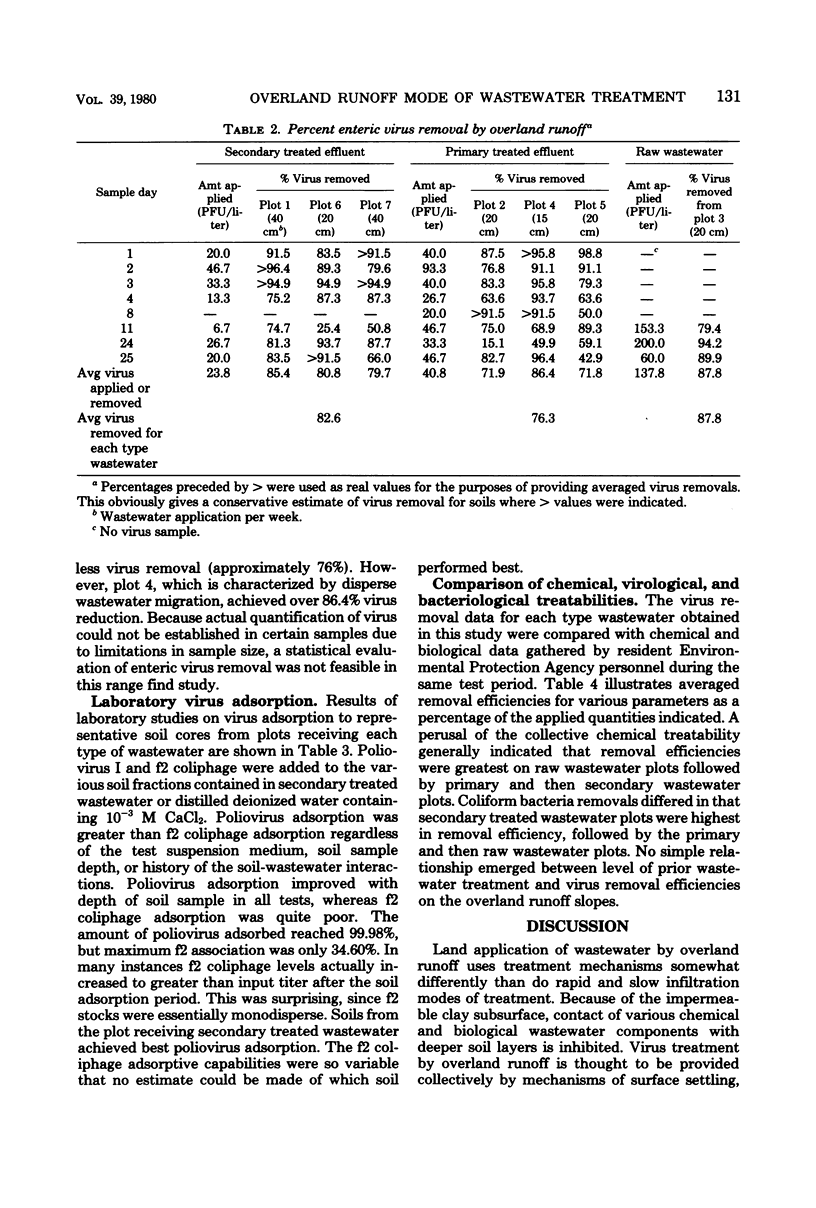
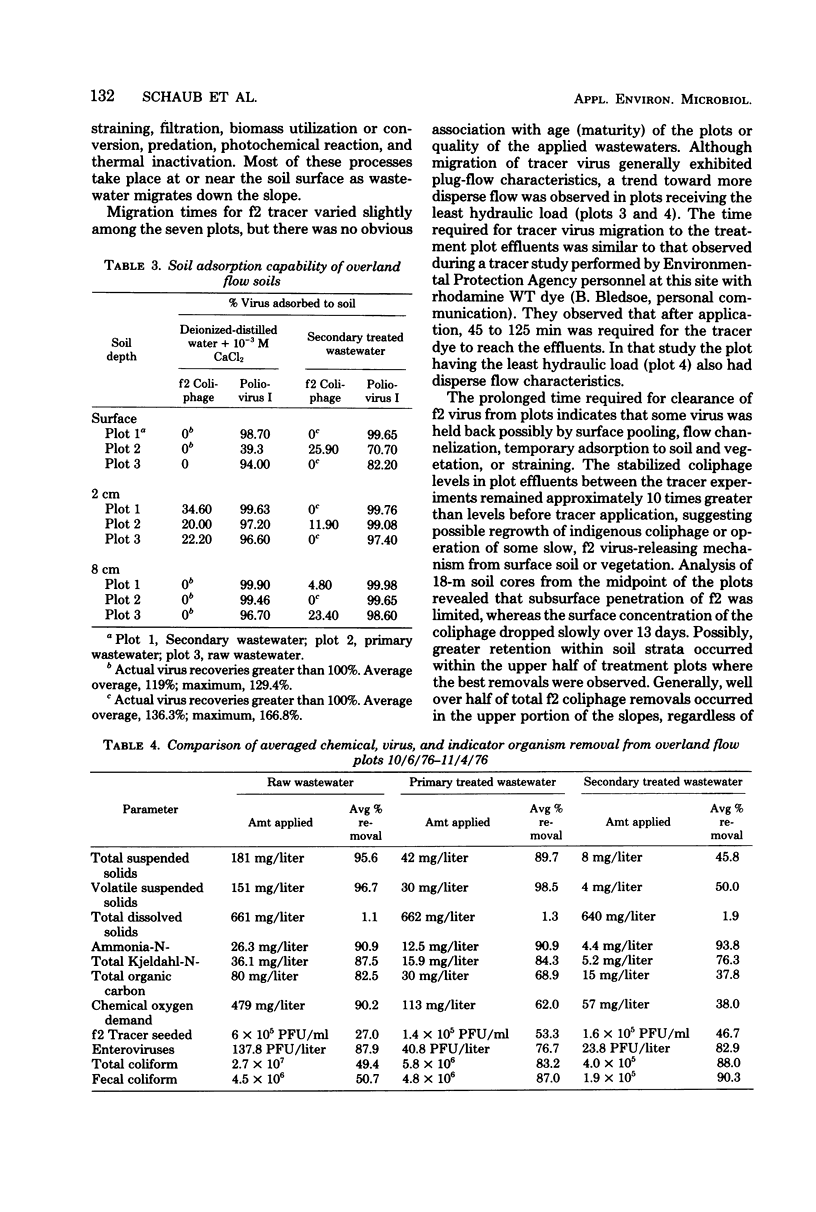
The removal of enteric and tracer viruses by the overland runoff mode of domestic wastewater treatment was evaluated. Raw and primary and secondary treated wastewaters were sprayed onto grass-covered, 36-m soil plots of fine, sandy loam overlying an impermeable clay subsoil. Tracer bacteriophage f2 was seeded into the applied wastewaters, which were subsequently sampled at several points along the length of the plots. Assay of effluent samples revealed modest tracer virus removals of 30 to 60%. Data from timed experiments indicated that advancement of tracer virus to the bottom of the slopes proceeded at the same rate as wastewater, reaching the plot effluents within 50 to 90 min after application. Indigenous enteric virus levels were reduced by approximately 68 to 85% during migration down the treatment slopes. Soil sampling revealed that, although some f2 virus was found associated with the wastewater-saturated topsoil, little penetration of virus into the soil profile occurred. Laboratory soil adsorption studies revealed that poliovirus I was adsorbed much more readily than f2 virus. Comparison of virus removal characteristics during overland runoff with chemical removal characteristics of wastewater did not reveal any obvious correlations that could be used to predict virus removal.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gerba C. P., Lance J. C. Poliovirus removal from primary and secondary sewage effluent by soil filtration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):247–251. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.247-251.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEB T., ZINDER N. D. A bacteriophage containing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar 15;47:282–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson R. J., Merritt C. A. Land application of liquid municipal wastewater sludges. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1975 Jan;47(1):20–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub S. A., Sagik B. P. Association of enteroviruses with natural and artificially introduced colloidal solids in water and infectivity of solids-associated virions. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):212–222. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.212-222.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub S. A., Sorber C. A. Virus and bacteria removal from wastewater by rapid infiltration through soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):609–619. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.609-619.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



