Abstract
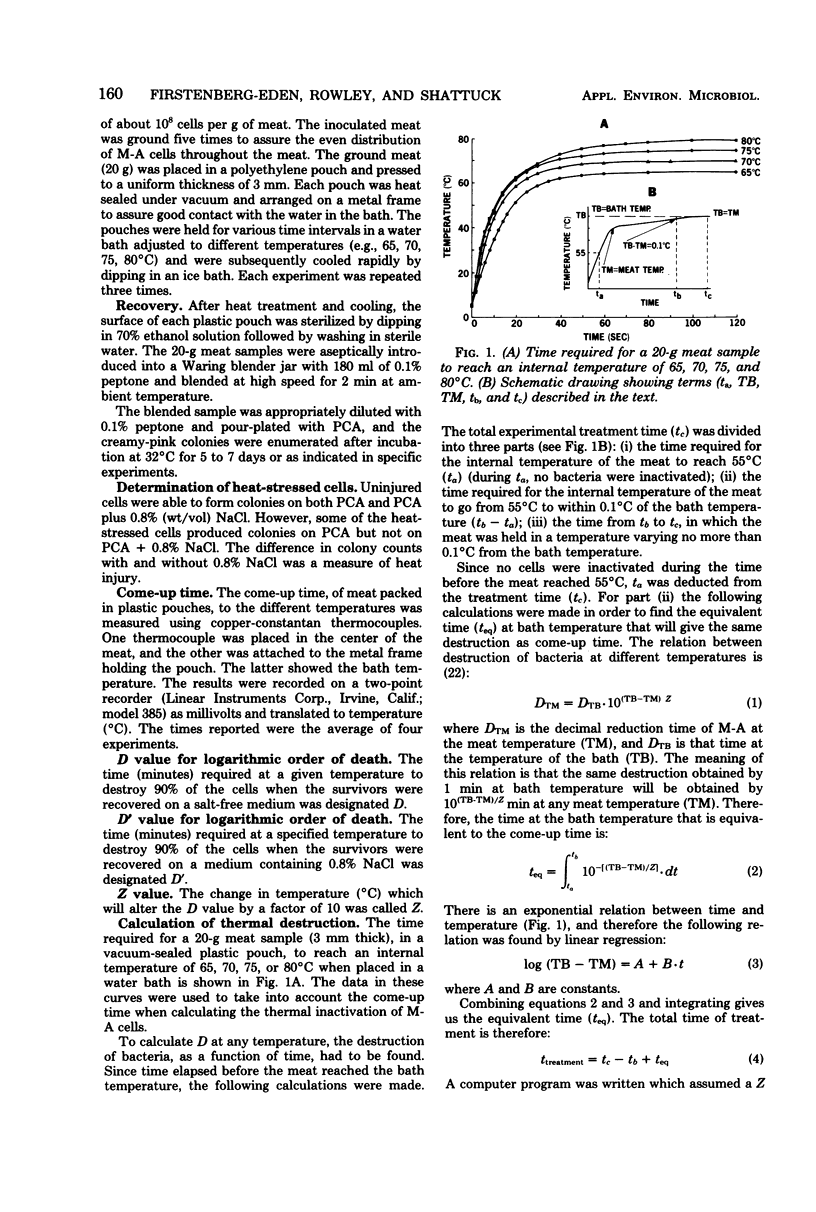
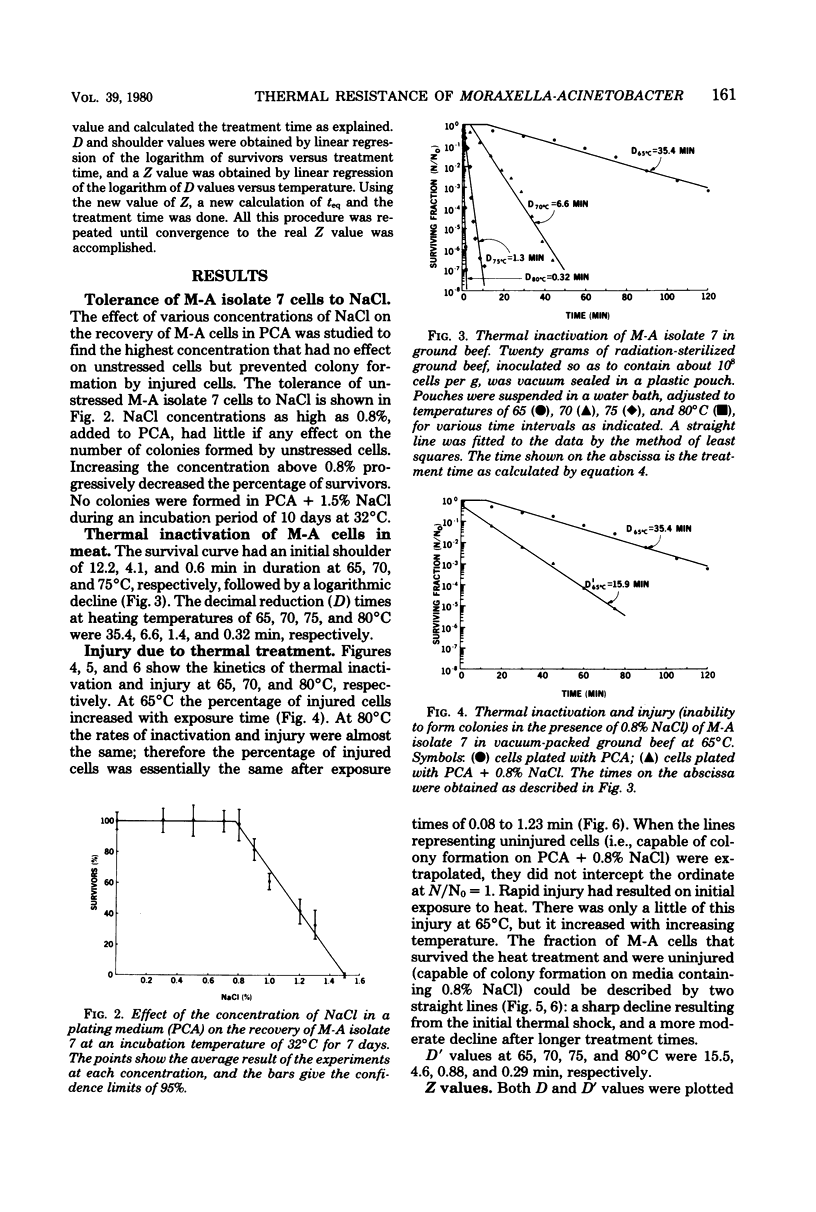
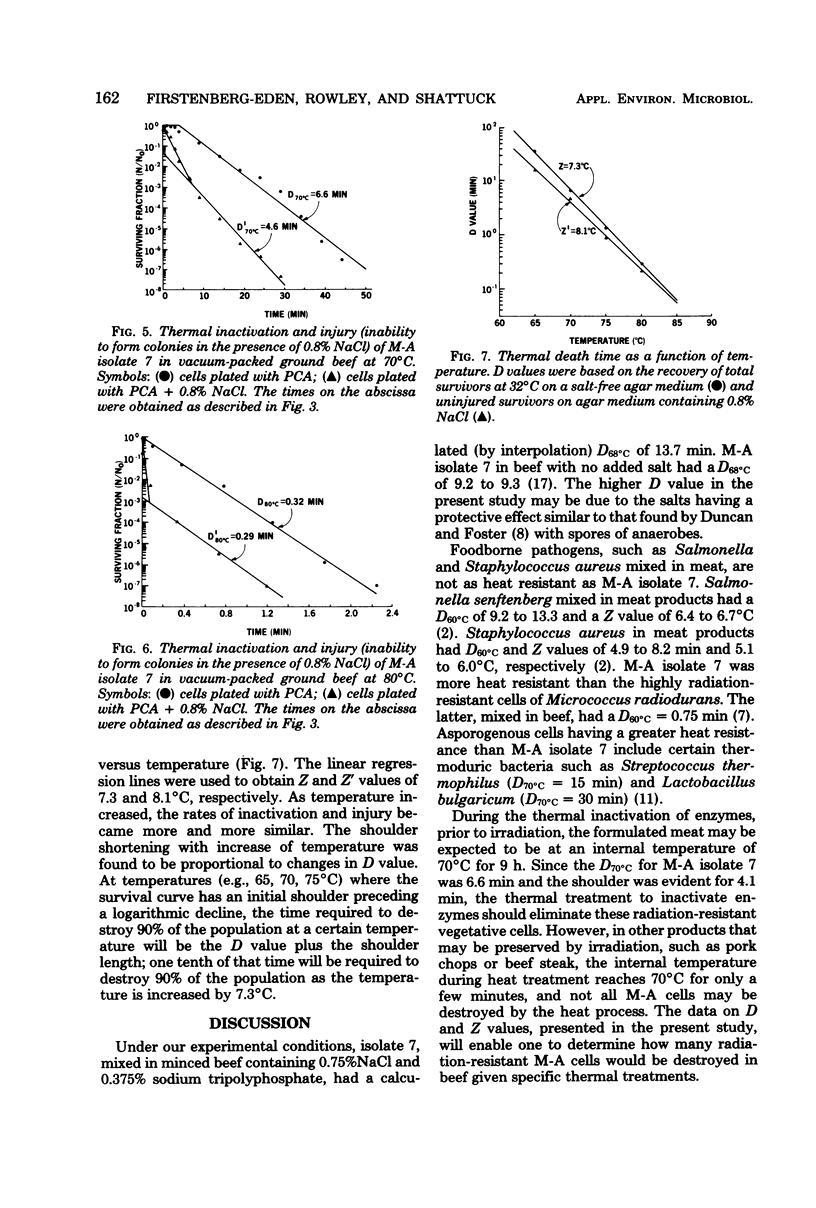
The thermal inactivation and injury (sensitivity to 0.8% NaCl) of a radiation-resistant culture of Moraxella-Acinetobacter mixed in minced beef were determined. Survival curves for Moraxella-Acinetobacter cells in beef had an initial shoulder preceding a logarithmic decline when the cells were heated at 65, 70, and 75 degrees C, but not at 80 degrees C. In all cases, the experimental points not included in the shoulder were linearized by means of a least-squares straight line, and the latter was used to determine D values. Shoulder values of 12.2, 4.1, and 0.6 min at temperatures of 65, 70, and 75 degrees C were added to the respective D values of 35.4, 6.6, and 1.4 min to determine the time required to destroy one log cycle. The Z value was 7.3 degrees C. Moraxella-Acinetobacter cells in meat were more rapidly injured than inactivated, on initial exposure to heat. The number of cells injured by this initial exposure increased as the temperature was increased. At 65 degrees C the percentage of injured cells increased more rapidly with exposure time than did the inactivated cells. As the temperature was increased, the rates of inactivation and injury became more and more similar.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGELOTTI R., FOTER M. J., LEWIS K. H. Time-temperature effects on Salmonellae and Staphylococci in foods. III. Thermal death time studies. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Jul;9:308–315. doi: 10.1128/am.9.4.308-315.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury M. S., Rowley D. B., Anellis A., Levinson H. S. Influence of postirradiation incubation temperature on recovery of radiation-injured Clostridium botulinum 62A spores. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):172–178. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.172-178.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGGAN D. E., ANDERSON A. W., ELLIKER P. R. INACTIVATION OF THE RADIATION-RESISTANT SPOILAGE BACTERIUM MICROCOCCUS RADIODURANS. I. RADIATION INACTIVATION RATES IN THREE MEAT SUBSTRATES AND IN BUFFER. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Sep;11:398–403. doi: 10.1128/am.11.5.398-403.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Foster E. M. Role of curing agents in the preservation of shelf-stable canned meat products. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Feb;16(2):401–405. doi: 10.1128/am.16.2.401-405.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Zawahry Y. A., Rowley D. B. Radiation resistance and injury of Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.50-54.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firstenberg-Eden R., Rosen B., Mannheim C. H. Death and injury of Staphytococcus aureus during thermal treatment of milk. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Aug;23(8):1034–1037. doi: 10.1139/m77-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. A., Bladel B. O., Zingelmann W. J. Radiation injury of Clostridium botulinum spores in cured meat. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Sep;13(5):743–748. doi: 10.1128/am.13.5.743-748.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A. Bacterial injury: a review. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Aug;23(8):935–944. doi: 10.1139/m77-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. D., Jr, Bayne H. G., Alderton G. Nonlogarithmic death rate calculations for Byssochlamys fulva and other microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):596–600. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.596-600.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis N. F. Studies on a radio-resistant coccus isolated from Bombay duck (Harpodon nehereus). J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Apr;66(1):29–35. doi: 10.1099/00221287-66-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. A., Ditchett P. J., Ingram M. The effect of sodium chloride on radiation resistance and recovery of irradiated anaerobic spores. J Appl Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;28(2):336–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1965.tb02162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Fassolitis A. C., Larkin E. P., Read R. B., Jr, Peeler J. T. Inactivation of thirty viruses by gamma radiation. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jul;22(1):61–65. doi: 10.1128/am.22.1.61-65.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch A. B., Maxcy R. B. Characterization of radiation-resistant vegetative bacteria in beef. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):242–250. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.242-250.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


