Abstract
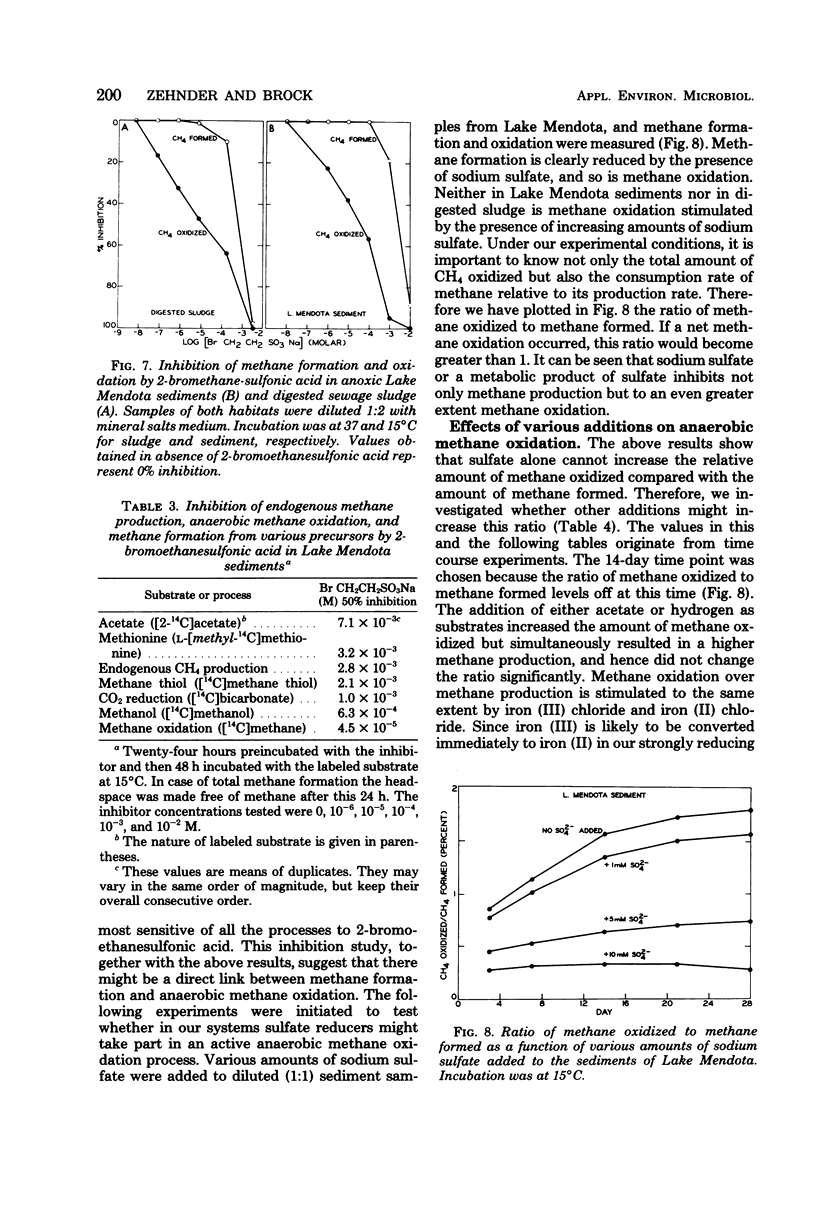
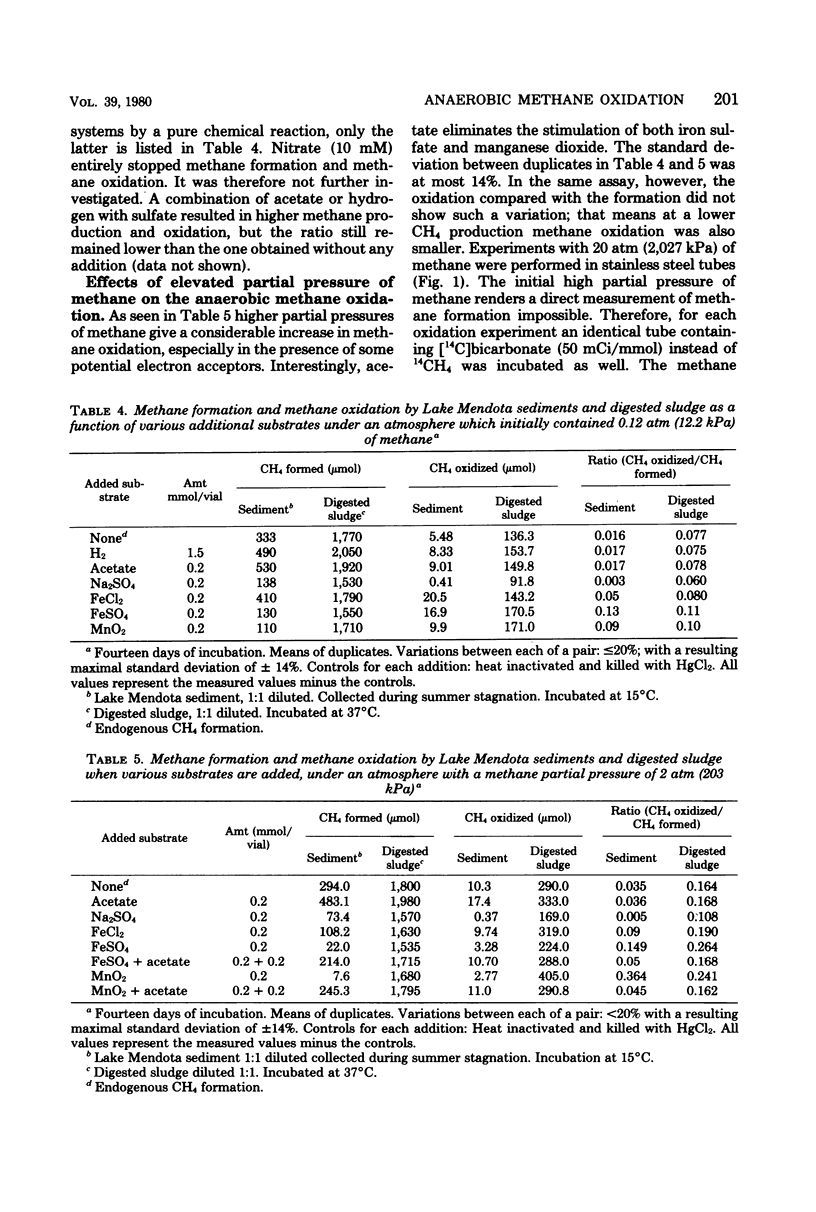
Anoxic sediments and digested sewage sludge anaerobically oxidized methane to carbon dioxide while producing methane. This strictly anaerobic process showed a temperature optimum between 25 and 37°C, indicating an active microbial participation in this reaction. Methane oxidation in these anaerobic habitats was inhibited by oxygen. The rate of the oxidation followed the rate of methane production. The observed anoxic methane oxidation in Lake Mendota and digested sewage sludge was more sensitive to 2-bromoethanesulfonic acid than the simultaneous methane formation. Sulfate diminished methane formation as well as methane oxidation. However, in the presence of iron and sulfate the ratio of methane oxidized to methane formed increased markedly. Manganese dioxide and higher partial pressures of methane also stimulated the oxidation. The rate of methane oxidation in untreated samples was approximately 2% of the CH4 production rate in Lake Mendota sediments and 8% of that in digested sludge. This percentage could be increased up to 90% in sludge in the presence of 10 mM ferrous sulfate and at a partial pressure of methane of 20 atm (2,027 kPa).
Full text
PDF

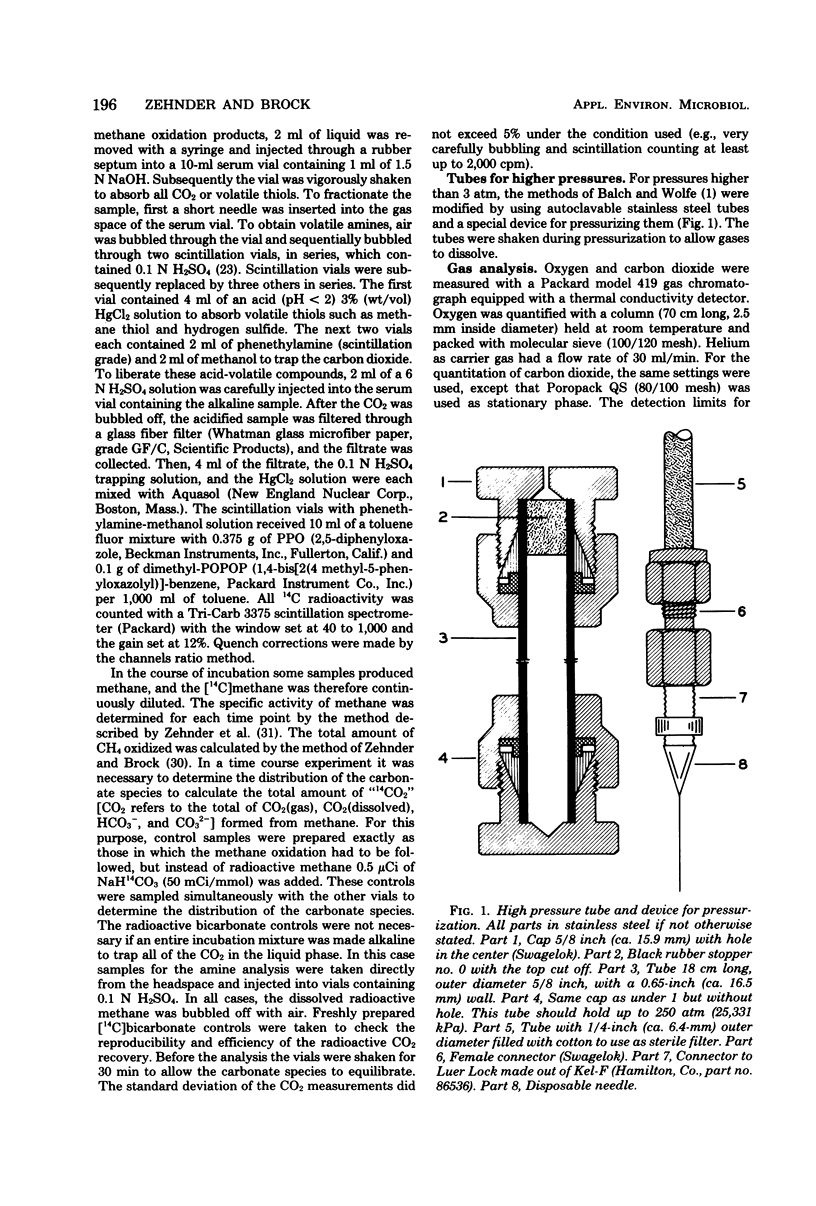
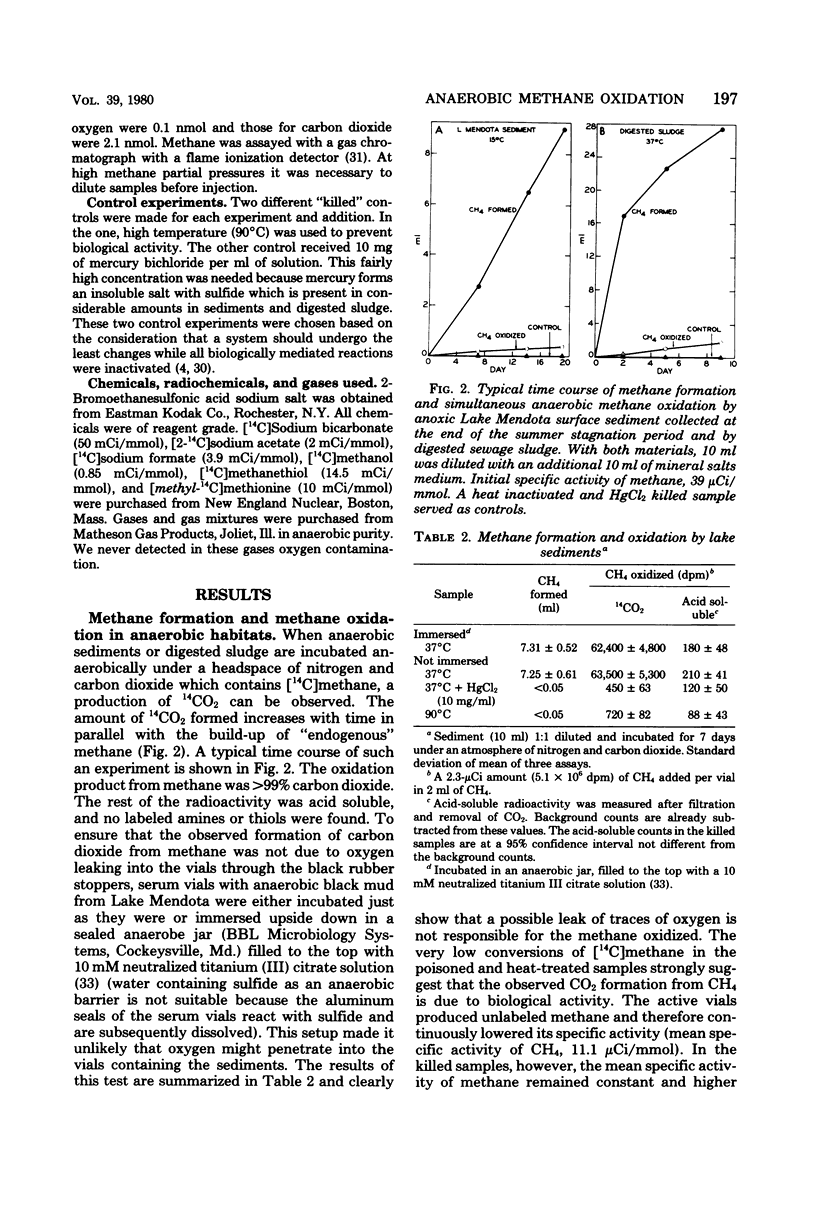
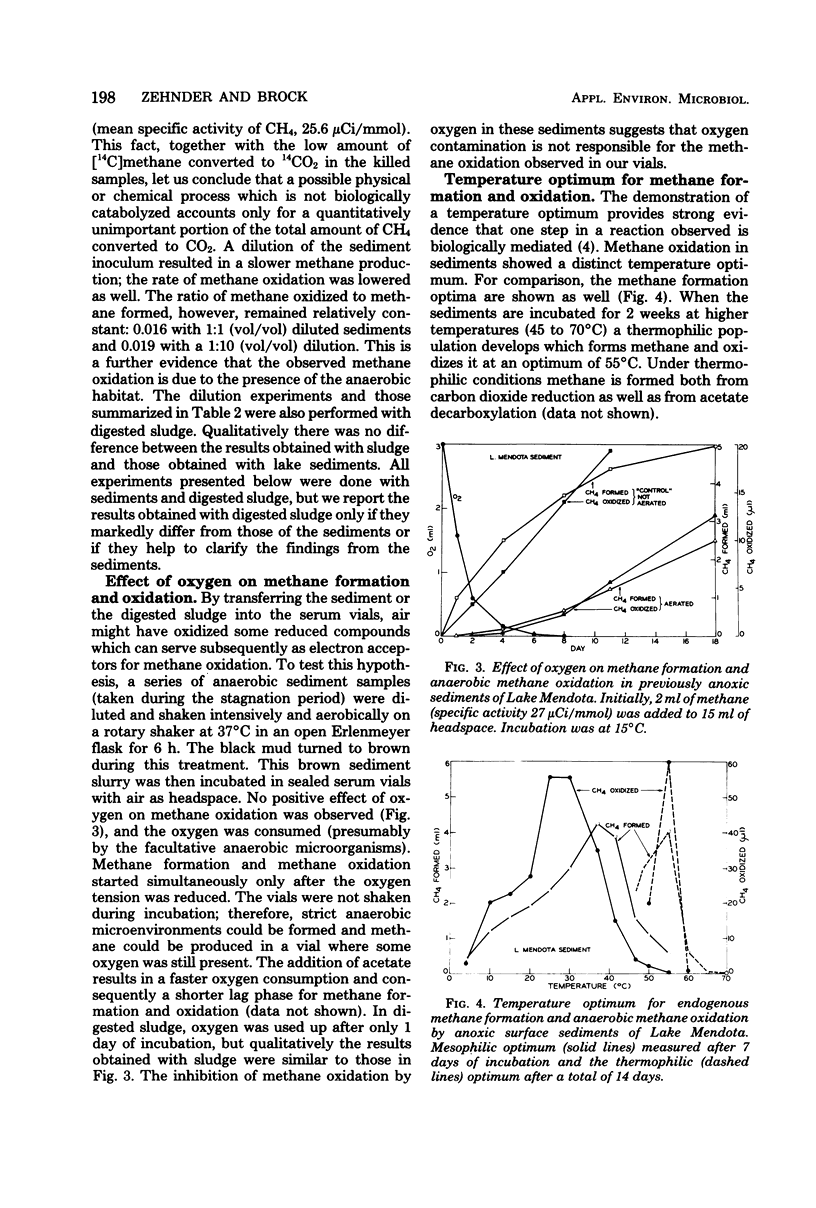
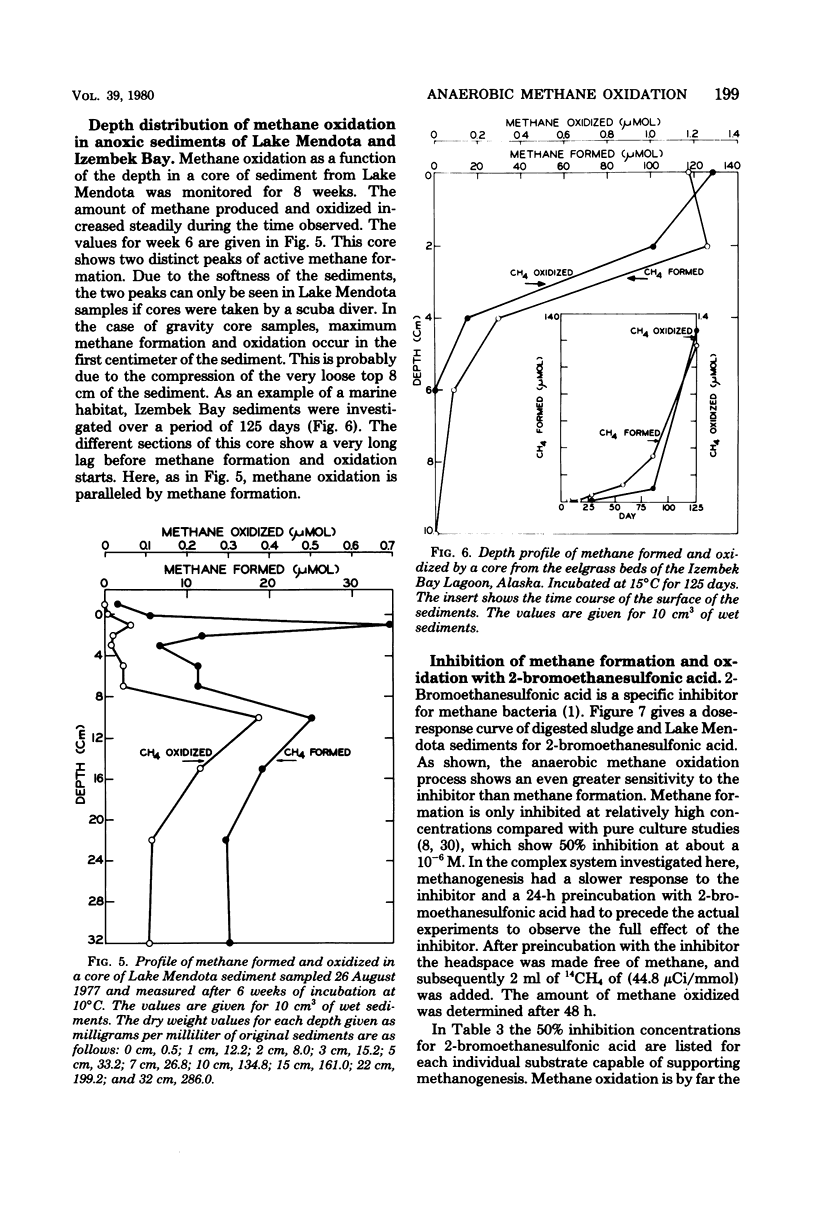



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Od'ea K. Amorphous ferrous sulfide as a reducing agent for culture of anaerobes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):254–256. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.254-256.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappenberg T. E., Prins R. A. Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. 3. Experiments with 14C-labeled substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(3):457–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00399358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins I. J., Quayle J. R. Oxygenation of methane by methane-grown Pseudomonas methanica and Methanomonas methanooxidans. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(2):201–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1180201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar H. F., Wuhrmann K. Kinetic parameters and relative turnovers of some important catabolic reactions in digesting sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.1-7.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oremland R. S., Taylor B. F. Inhibition of methanogenesis in marine sediments by acetylene and ethylene: validity of the acetylene reduction assay for anaerobic microcosms. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):707–709. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.707-709.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patt T. E., Cole G. C., Bland J., Hanson R. S. Isolation and characterization of bacteria that grow on methane and organic compounds as sole sources of carbon and energy. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):955–964. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.955-964.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Fliermans C. B., Brock T. D. Technique for measuring 14 CO 2 uptake by soil microorganisms in situ. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):595–600. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.595-600.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. H., Mah R. A. Kinetics of acetate metabolism during sludge digestion. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):368–371. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.368-371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertlieb D., Vishniac W. Methane utilization by a strain of Rhodopseudomonas gelatinosa. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1722–1724. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1722-1724.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Nelson D. R., Klevickis S. C., Zeikus J. G. Association of hydrogen metabolism with methanogenesis in Lake Mendota sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):312–318. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.312-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Effect of sulfate on carbon and electron flow during microbial methanogenesis in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.275-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Brock T. D. Methane formation and methane oxidation by methanogenic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):420–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.420-432.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Huser B., Brock T. D. Measuring radioactive methane with the liquid scintillation counter. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):897–899. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.897-899.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Wuhrmann K. Titanium (III) citrate as a nontoxic oxidation-reduction buffering system for the culture of obligate anaerobes. Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1165–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.793008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Winfrey M. R. Temperature limitation of methanogenesis in aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jan;31(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.1.99-107.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



