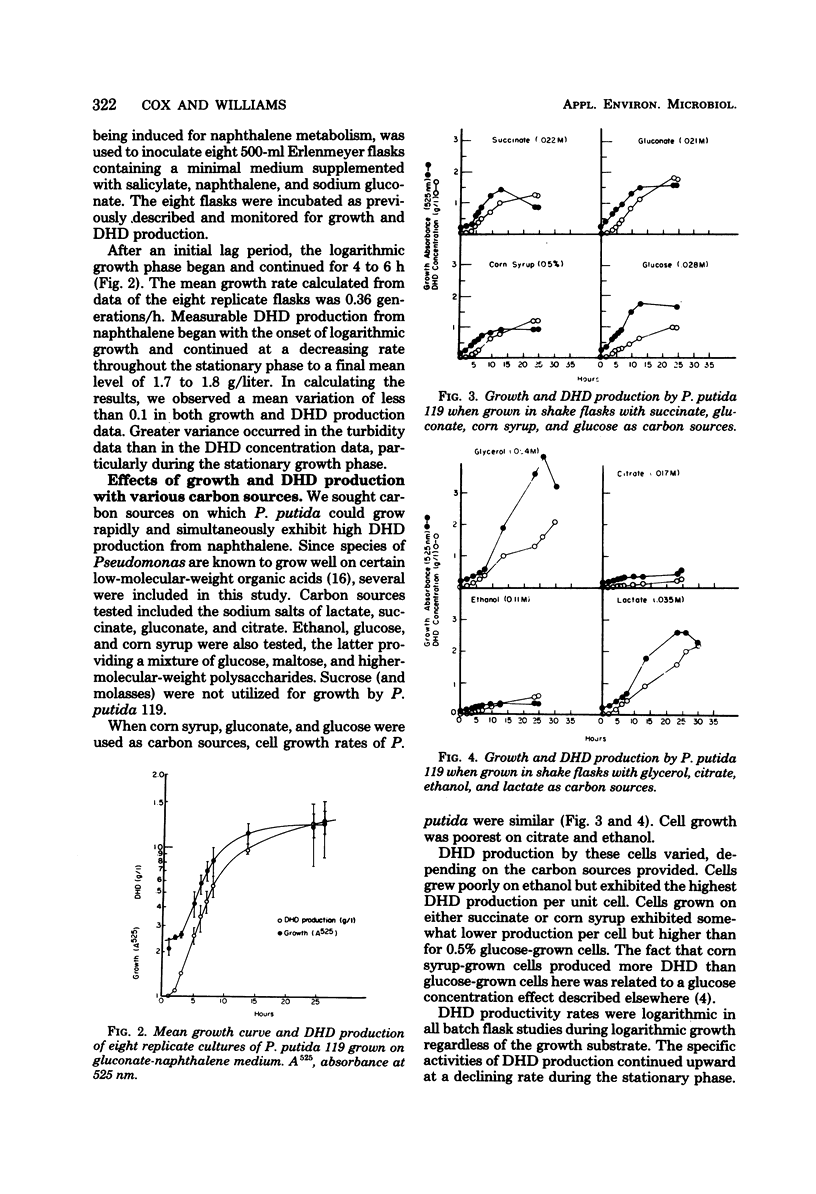
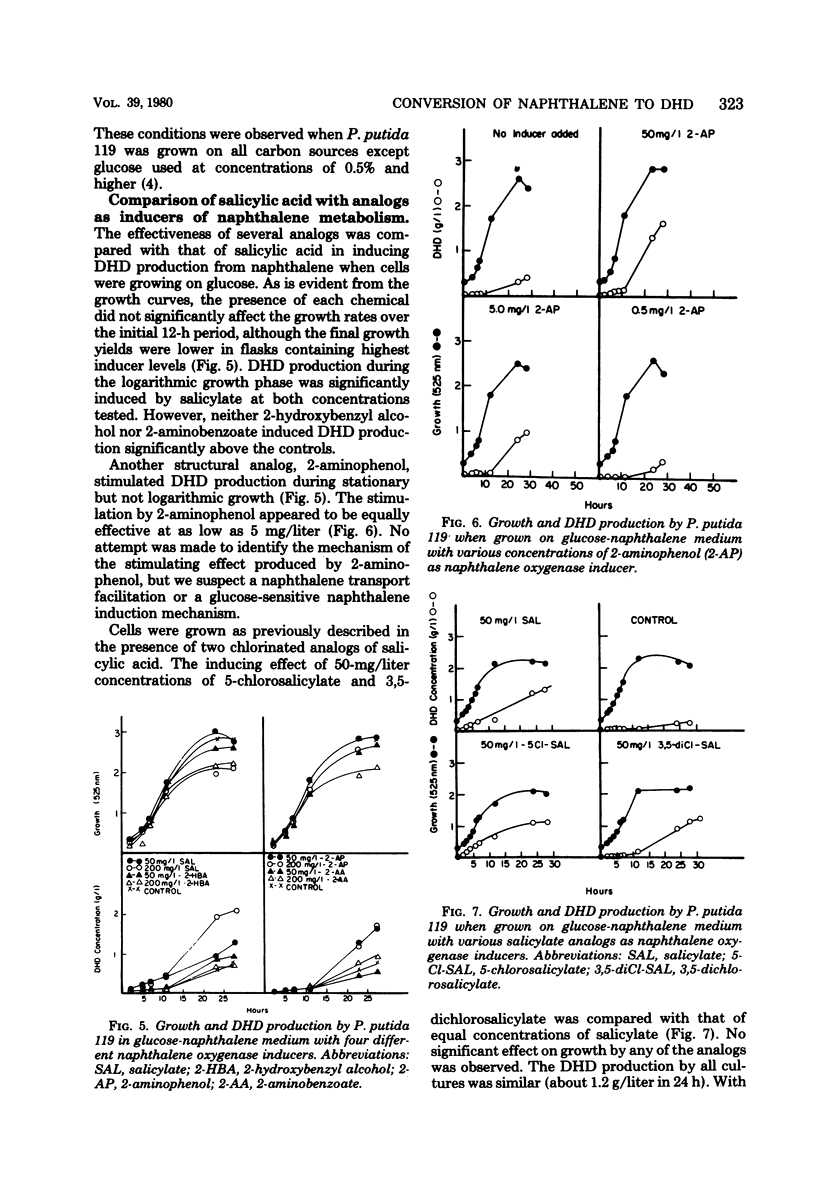
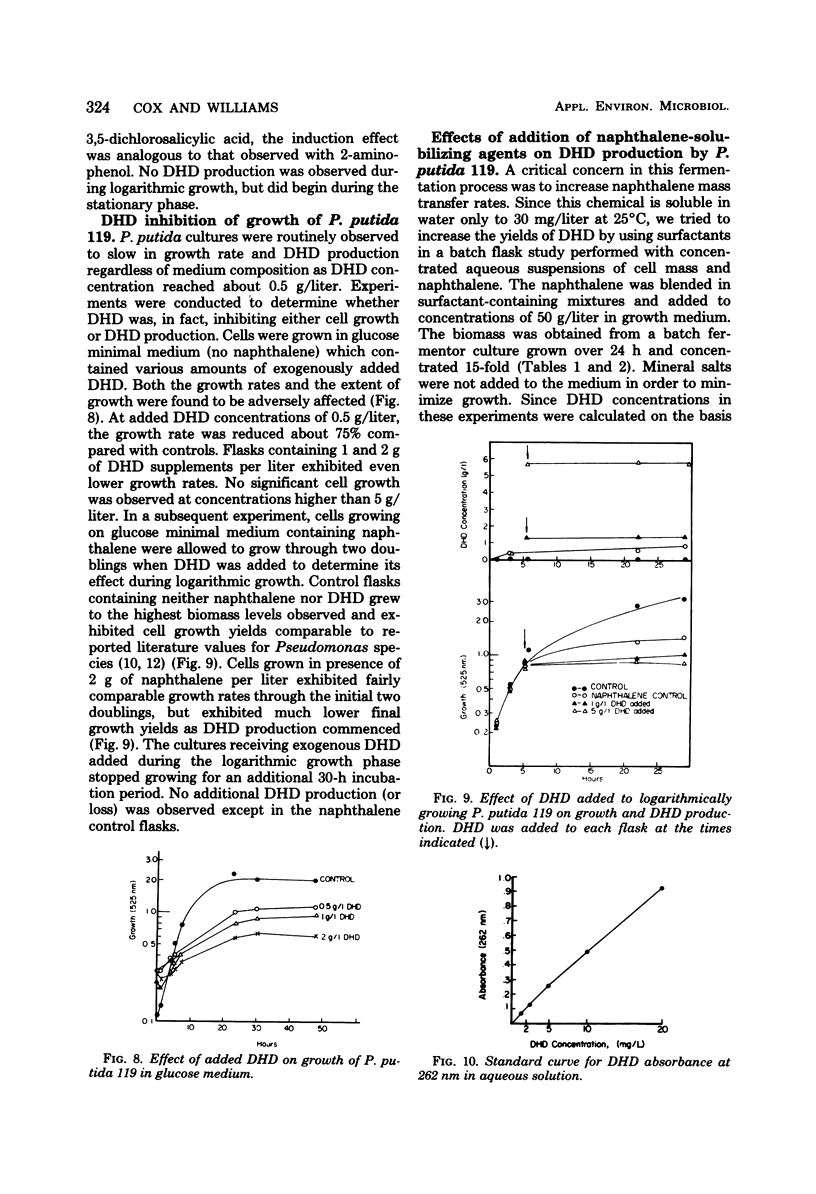
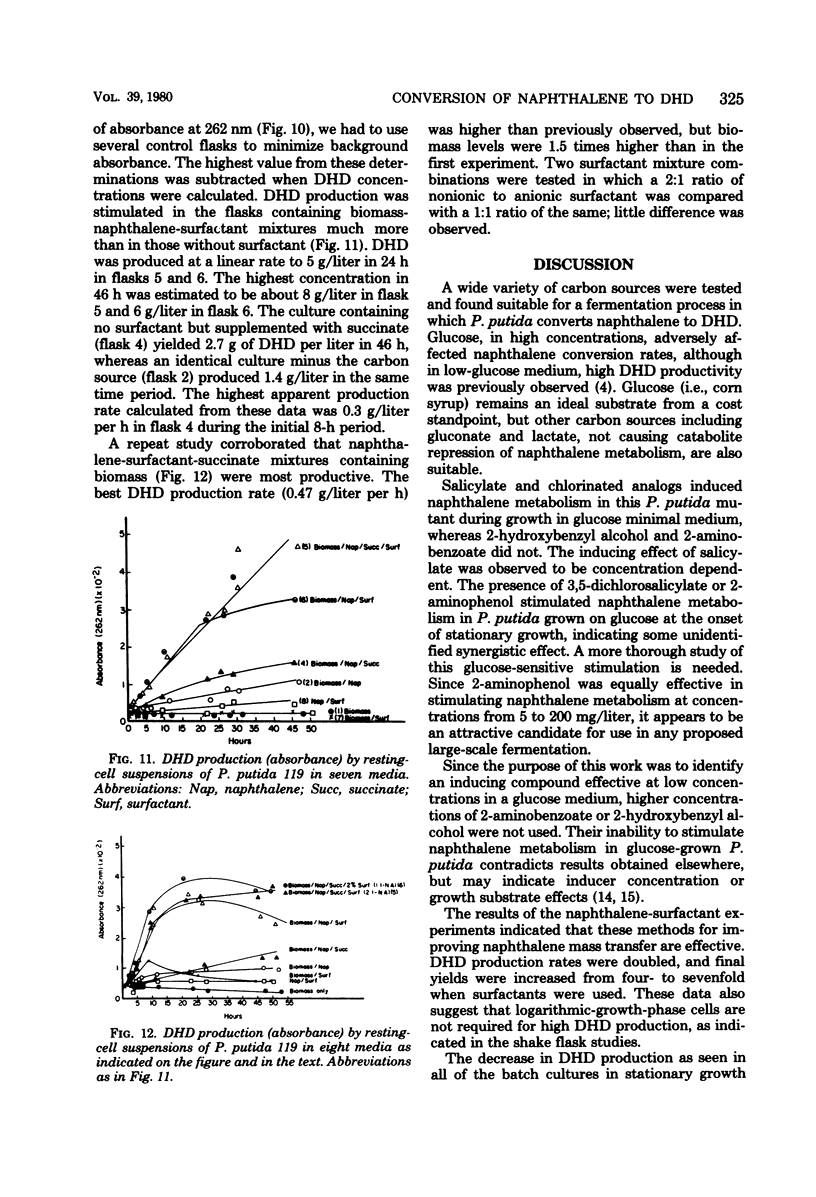
Abstract
A biological process for converting naphthalene to cis-1,2-dihydroxy-1,2-dihydronaphthalene (DHD) catalyzed by Pseudomonas putida strain 119 was optimized in flask experiments. These studies revealed the following: (i) P. putida 119 can propagate efficiently and produce DHD when supplied one of several carbon sources and naphthalene; (ii) maximum DHD production by P. putida 119 occurs in logarithmic-growth-phase cells and decreases at various rates in the stationary growth phase, depending upon the carbon source used; (iii) several analogs of salicylic acid can be used as effective inducers of naphthalene metabolism in P. putida cells growing on glucose; and (iv) the addition of chemical surfactants to naphthalene-cell (P. putida 119) mixtures stimulates DHD production.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnsley E. A. The induction of the enzymes of naphthalene metabolism in pseudomonads by salicylate and 2-aminobenzoate. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):193–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall G. F., Williams P. A. Some properties of the naphthalene oxygenase from Pseudomonas sp. NCIB 9816. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jul;67(1):117–124. doi: 10.1099/00221287-67-1-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. I., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):251–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0910251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERNLEY H. N., EVANS W. C. Oxidative metabolism of polycyclic hydrocarbons by soil Pseudomonads. Nature. 1958 Aug 9;182(4632):373–375. doi: 10.1038/182373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey A. M., Yeh H. J., Jerina D. M., Patel T. R., Davey J. F., Gibson D. T. Initial reactions in the oxidation of naphthalene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):575–584. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Jeffrey A. M., Gibson D. T. Cis-1,2-dihydroxy-1,2-dihydronaphthalene: a bacterial metabolite from naphthalene. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jan;142(1):394–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry W. R., Prochazka G. J., Payne W. J. Growth yields of bacteria on selected organic compounds. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1332–1338. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1332-1338.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel T. R., Gibson D. T. Purification and propeties of (plus)-cis-naphthalene dihydrodiol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):879–888. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.879-888.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J. Energy yields and growth of heterotrophs. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:17–52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuzzaman K. M., Barnsley E. A. The regulation of naphthalene metabolism in pseudomonads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):582–589. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuzzaman K. M., Barnsley E. A. The regulation of naphthalene oxygenase in pseudomonads. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):165–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRECCANI V., WALKER N., WILTSHIRE G. H. The metabolism of naphthalene by soil bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Dec;11(3):341–348. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-3-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER N., WILTSHIRE G. H. The breakdown of naphthalene by a soil bacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Apr;8(2):273–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-8-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



