Abstract
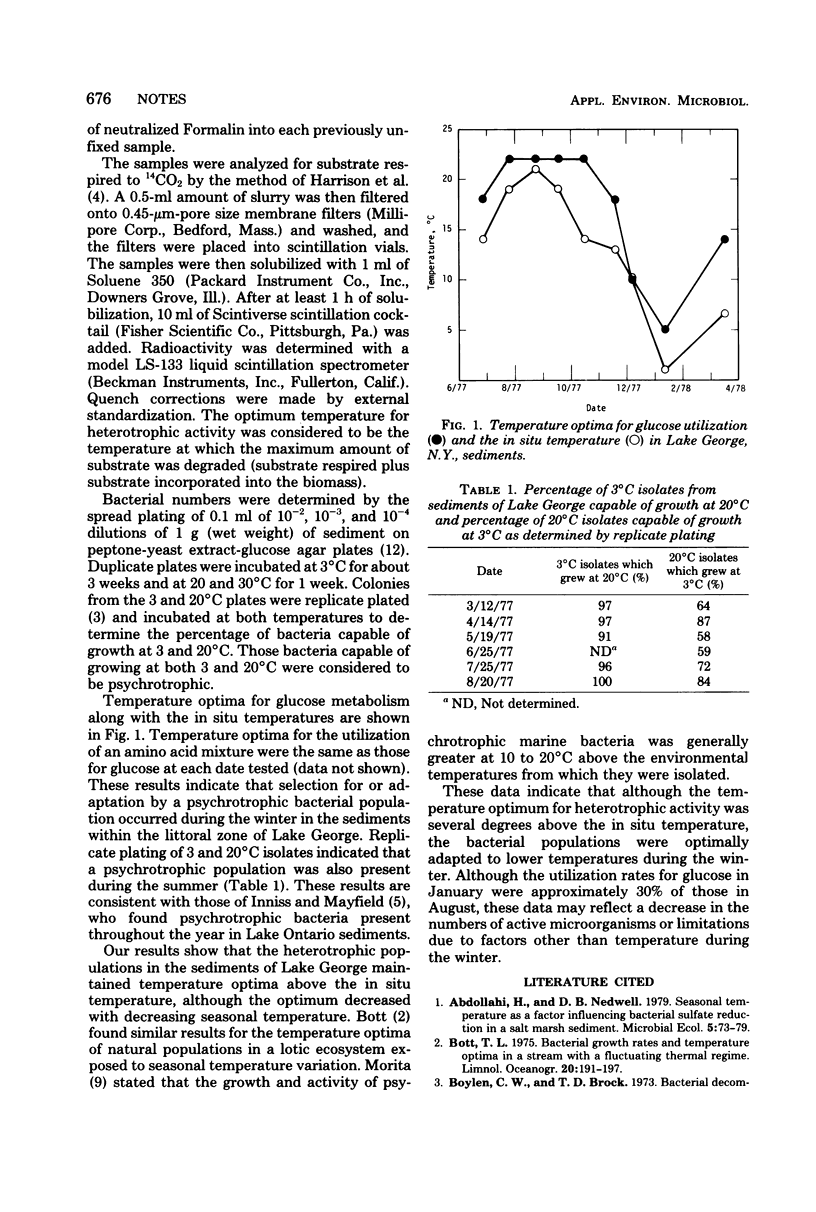
Temperature optima for the heterotrophic utilization of glucose and an amino acid mixture were determined throughout the year in sediments from Lake George, N.Y. The temperature optimum decreased with decreasing in situ temperature in the fall and winter, suggesting that selection for or adaptation by a psychrotrophic bacterial population occurred. Replicate plating of bacterial isolates from 3 and 20°C indicated that a psychrotrophic bacterial population was present in the sediments throughout the year. These results indicate that decomposition and nutrient cycling processes in the sediments within the littoral zone of Lake George were probably not completely inhibited by winter temperatures, although process rates were decreased.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Harrison M. J., Wright R. T., Morita R. Y. Method for measuring mineralization in lake sediments. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):698–702. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.698-702.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. M. Seasonal incidence of bacterial temperature types in Louisiana soil and water. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):286–288. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.286-288.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita R. Y. Psychrophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):144–167. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.144-167.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


