Abstract
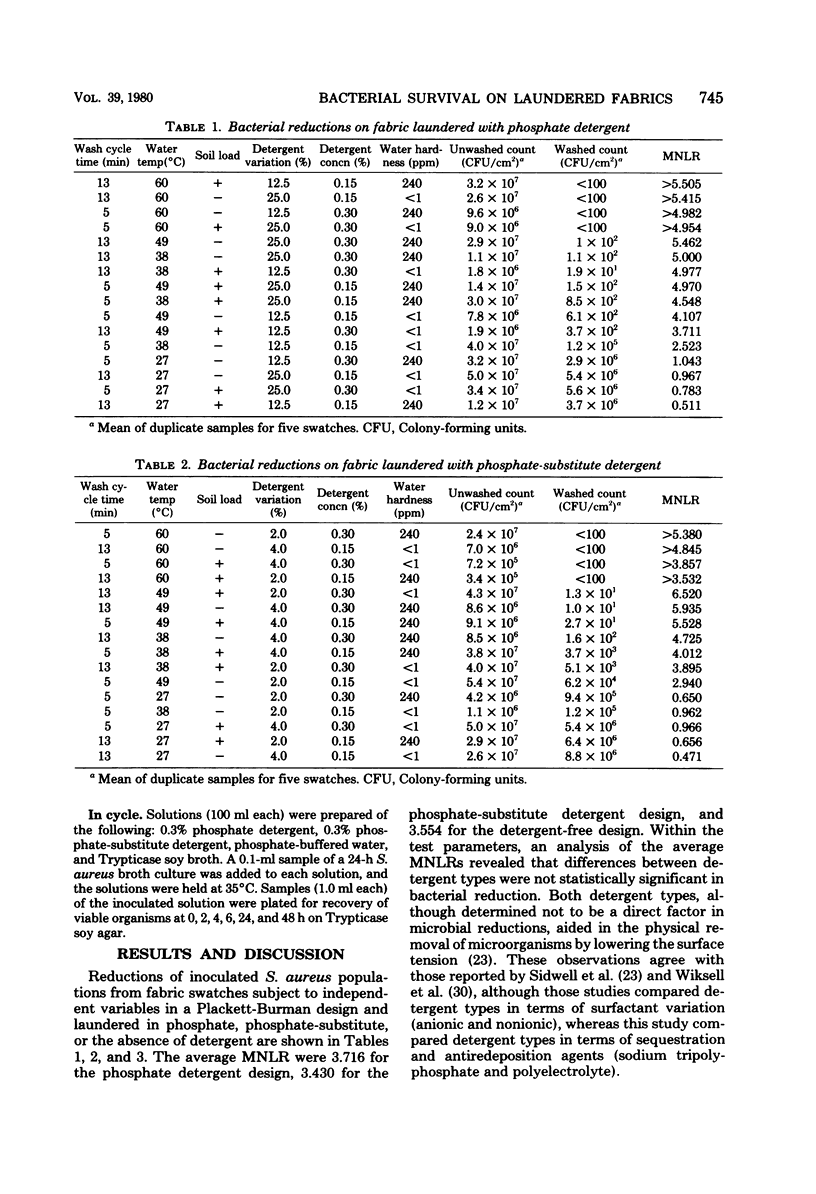
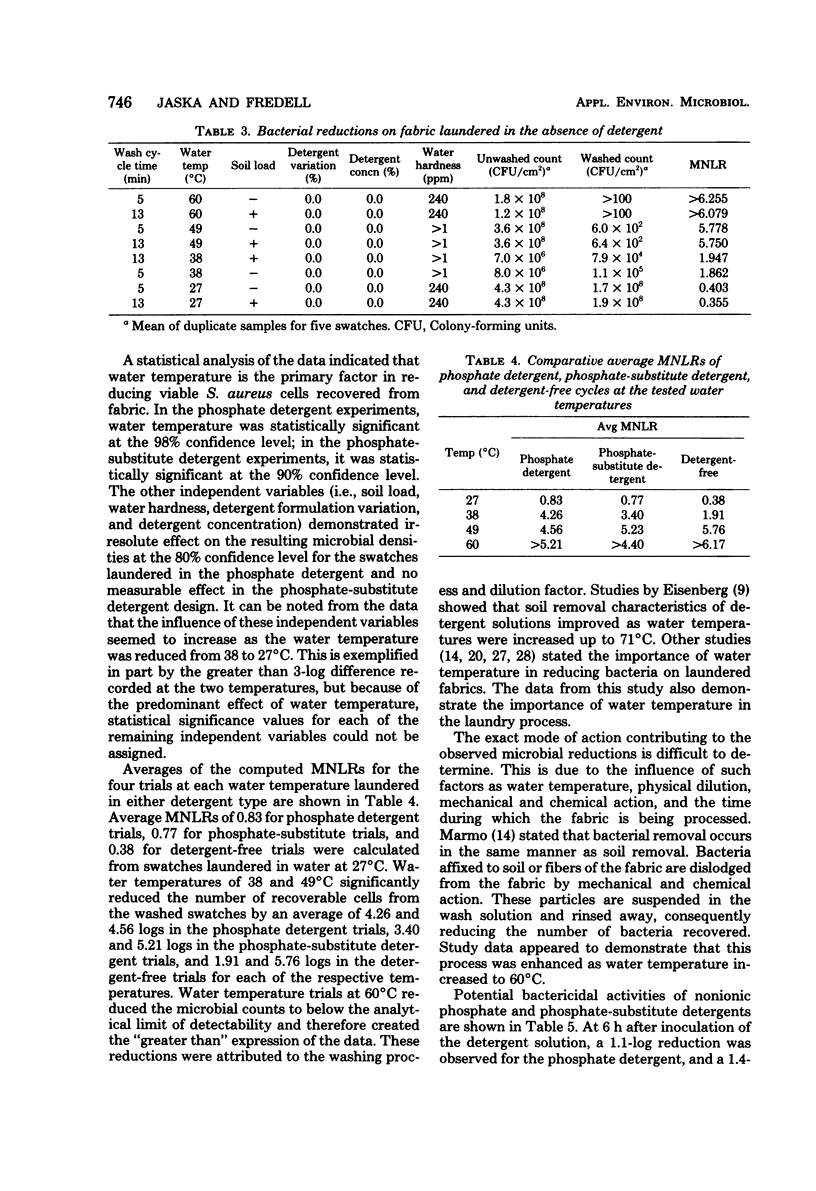
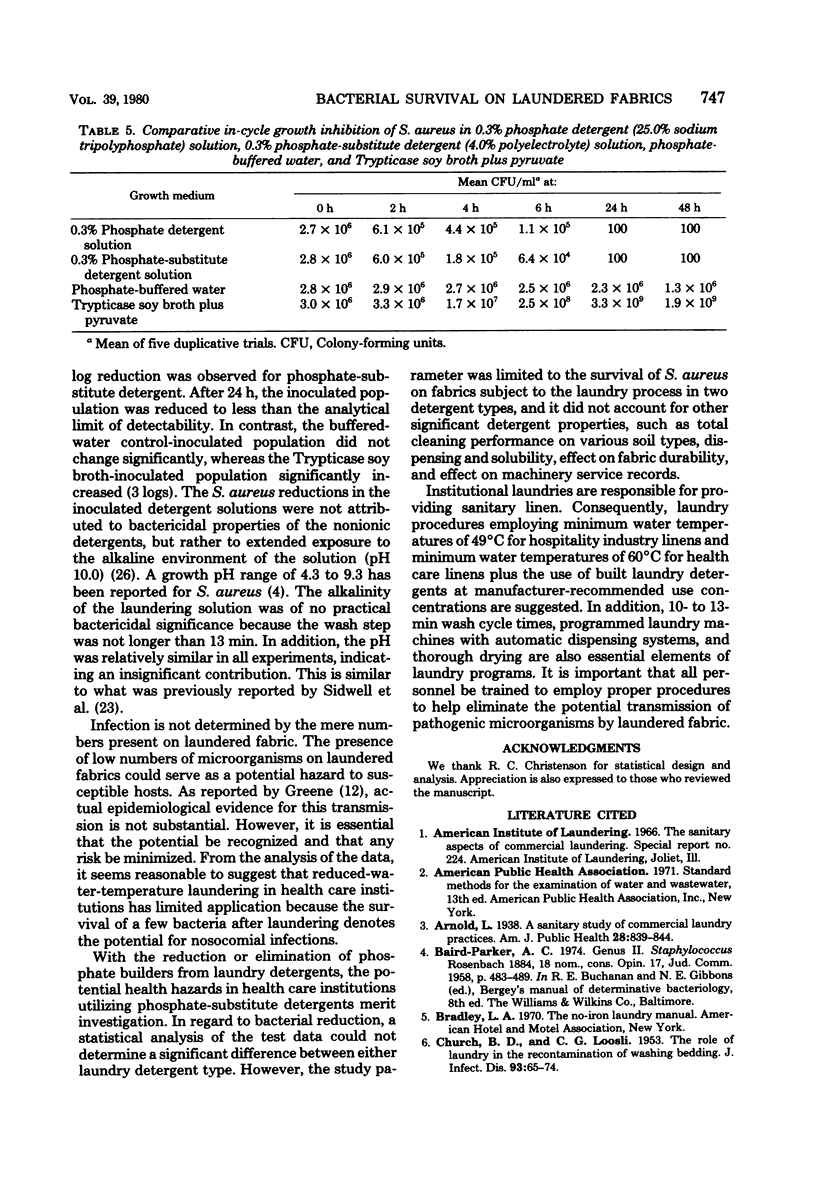
The survival of Staphylococcus aureus was determined from inoculated swatches laundered in either a phosphate or a phosphate-substitute detergent. In a Plackett-Burman design study, the independent variables of detergent type, concentration, and variation, wash water temperature, soil load, cycle time, and water hardness were assigned high and low values. Wash water temperatures of 27, 38, 49, and 60 degrees C were employed. Viable bacteria were recovered from macerated swatches. Statistical analysis disclosed that there was no practical difference in the ability of phosphate or phosphate-substitute detergents to reduce the level of S. aureus on the laundered swatches in this controlled design. Analysis did reveal that water temperature was the most significant independent variables. The remaining variables did not appear to have any practical significance upon bacterial reduction. This bacteriological study did not evaluate other essential detergent properties.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold L. A Sanitary Study of Commercial Laundry Practices. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1938 Jul;28(7):839–844. doi: 10.2105/ajph.28.7.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHURCH B. D., LOOSLI C. G. The role of the laundry in the recontamination of washed bedding. J Infect Dis. 1953 Jul-Aug;93(1):65–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/93.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon G. J., Sidwell R. W., McNeil E. Quantitative studies on fabrics as disseminators of viruses. II. Persistence of poliomyelitis virus on cotton and wool fabrics. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):183–188. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.183-188.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene V. W. Microbiological contamination control in hospitals. 6. Roles of central service and the laundry. Hospitals. 1970 Jan 1;44(1):98–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond A. L. Phosphate replacements: problems with the washday miracle. Science. 1971 Apr 23;172(3981):361–363. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3981.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholes P. S. Bacteria in laundered fabrics. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1970 Nov;60(11):2175–2180. doi: 10.2105/ajph.60.11.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPILLARD M. A. LAUNDERING CAN BREAK THE INFECTION CHAIN. Mod Hosp. 1964 Oct;103:102–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Dixon G. J., McNeil E. Quantitative studies on fabrics as disseminators of viruses. 3. Persistence of vaccinia virus on fabrics impregnated with a virucidal agent. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):921–927. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.921-927.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Dixon G. J., Westbrook L., Forziati F. H. Quantitative studies on fabrics as disseminators of viruses. V. Effect of laundering on poliovirus-contaminated fabrics. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Feb;21(2):227–234. doi: 10.1128/am.21.2.227-234.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley F. W. The Influence of Changes in Concentration of Sodium Hydroxide upon Its Bactericidal Activity. J Bacteriol. 1946 Jun;51(6):779–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.51.6.779-785.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter W. G., Schillinger J. E. Bacterial survival in laundered fabrics. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):368–373. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.368-373.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzler T. F., Quan T. J., Schatzle K. Critical analysis of the microflora of toweling. Am J Public Health. 1971 Feb;61(2):376–393. doi: 10.2105/ajph.61.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiksell J. C., Pickett M. S., Hartman P. A. Survival of microorganisms in laundered polyester-cotton sheeting. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):431–435. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.431-435.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkoff L. J., Dixon G. J., Westbrook L., Happich W. F. Potentially infectious agents associated with shearling bedpads: effect of laundering with detergent-disinfectant combinations on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):647–652. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.647-652.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkoff L. J., Westbrook L., Dixon G. J. Factors affecting the persistence of Staphylococcus aureus on fabrics. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Feb;17(2):268–274. doi: 10.1128/am.17.2.268-274.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


