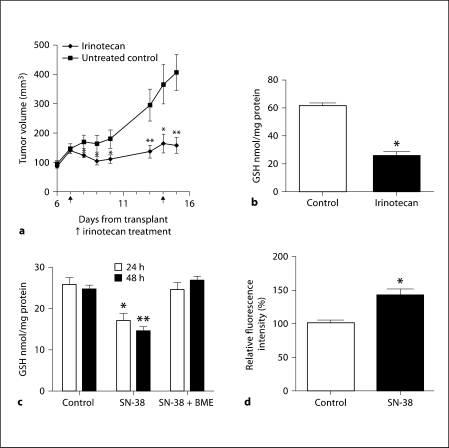
Fig. 2.
Irinotecan inhibits FaDu tumor growth with decreased GSH and increased ROS. a Effect of irinotecan on the growth of FaDu tumor xenografts. FaDu tumors were transplanted and allowed to grow for a week before being treated with the maximum tolerated dose of irinotecan (100 mg/kg/week i.v. × 2). The control and irinotecan-treated tumor volumes were measured for up to 15 days. Five different mice were used for each condition. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.009. b GSH concentrations in the FaDu tumor xenografts treated with irinotecan. Total GSH levels were determined in the tumor xenografts 24 h after the second dose of irinotecan. Five different tumor samples were used. ∗ p < 0.004. c Concentration of GSH in FaDu cells treated with SN-38. FaDu cells treated with SN-38 (0.1 μM) and GSH were analyzed after 24 and 48 h. The experiments were repeated three times with triplicate samples. BME was added to the culture medium to facilitate cystine transport via formation of mixed disulfide consisting of cysteine and BME. ∗ p < 0.02, ∗∗ p < 0.002. d Effect of SN-38 on ROS levels. FaDu cells treated with 0.1 μM SN-38 had a significantly increased accumulation of intracellular ROS compared to the untreated controls. The experiment was performed 3 times with triplicate samples. ∗ p < 0.01.