Figure 2.
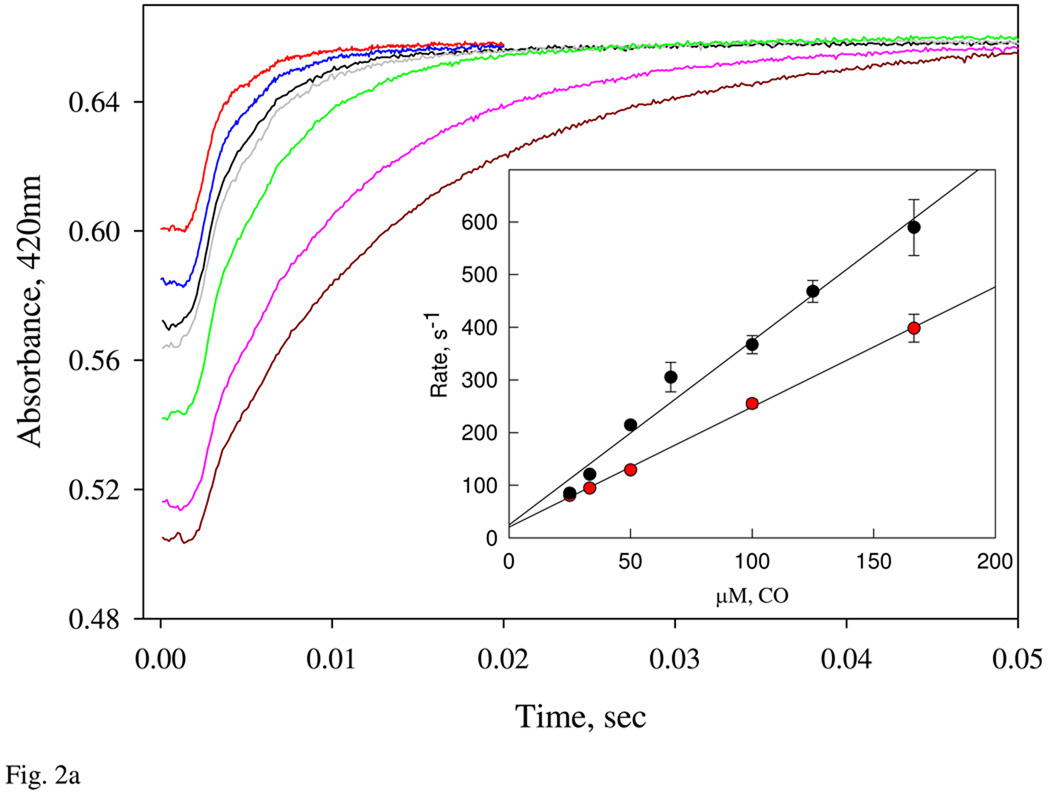
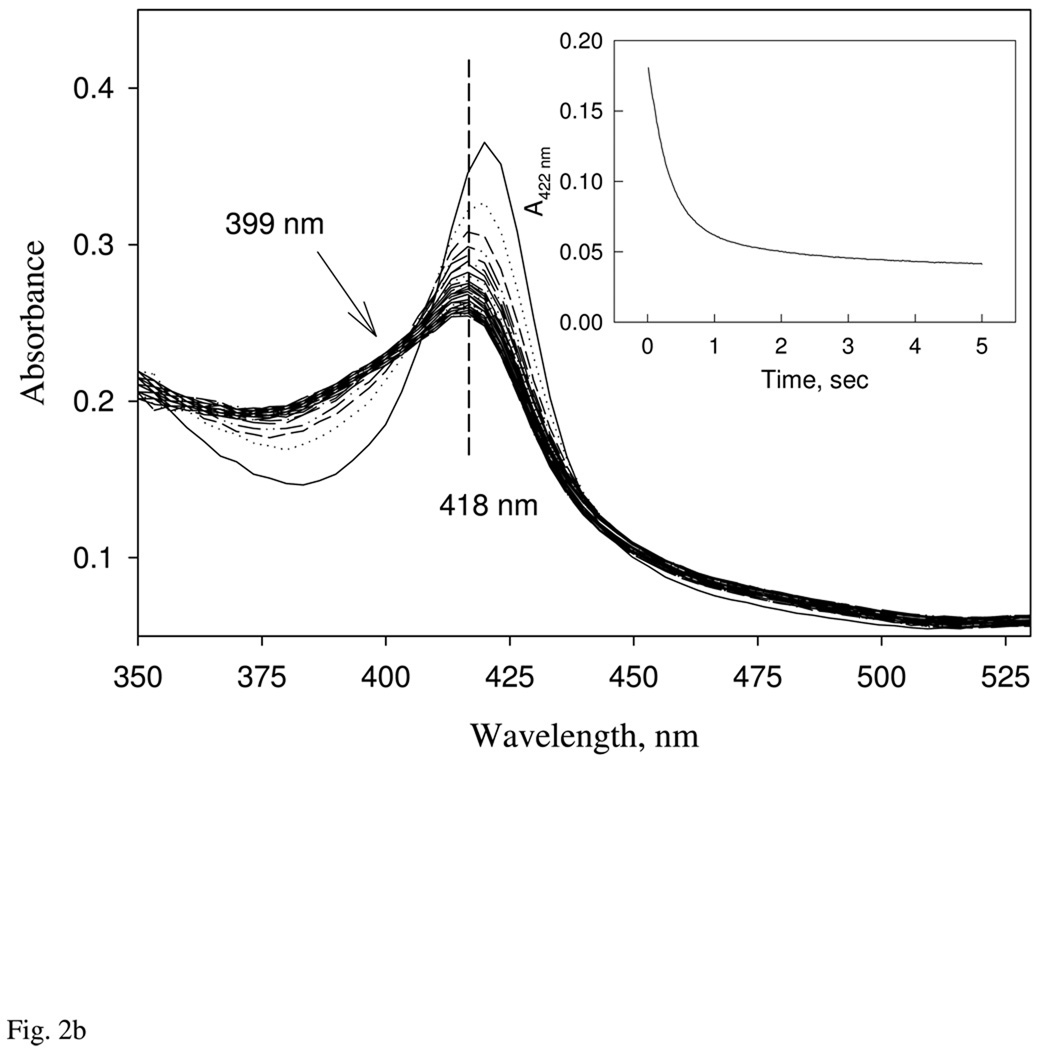
A: Kinetics of CO binding to the ferrous Ns H-NOX. Ferrous Ns H-NOX, 5 µM, prepared in an anaerobic tonometer was reacted with CO in a stopped-flow at 24 °C. CO was prepared in anaerobic buffer at concentrations varying from 25 to 166 µM. One-exponential change of absorbance at 420 nm was used to determine the observed rates and used for calculation of the 2nd-order on rate constant (Inset). Two sets of experiments using two different batches of sensor protein were conducted (red and black circles). Standard deviation of at least triplicates at each concentration was shown by the significant bar. B: Determination of the dissociation rate constant of CO binding. CO-ferrous Ns H-NOX complex was pre-formed by mixing 4 µM sensor with 1 mM CO in an anaerobic glass tonometer, and then reacted with 1 mM NO solution. The CO-dissociation rate was followed by diode array or single wavelength stopped-flow at 422 nm (Inset) for 8s data collection at 24 °C. Kinetic data were fit to 2- exponential function.