Abstract
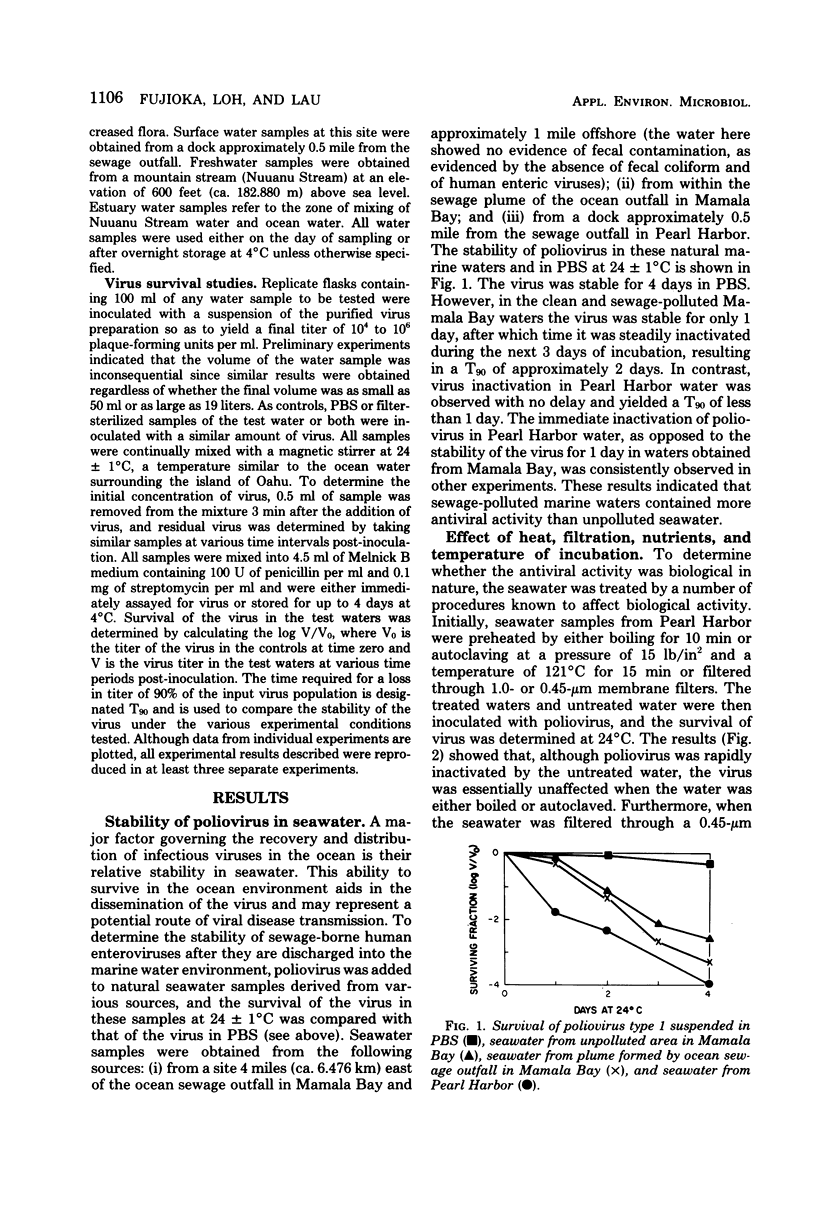
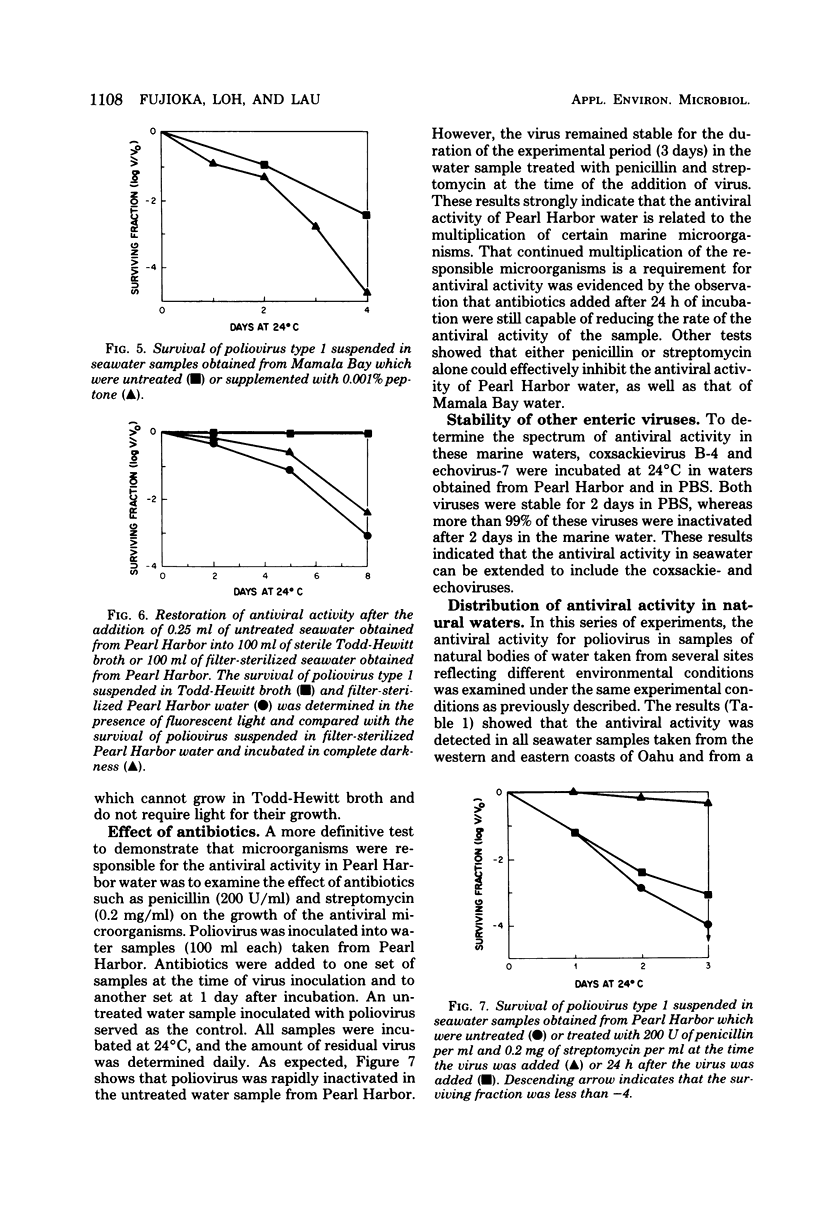
The stability of certain human enteroviruses in the Hawaiian ocean environment was examined. The present data indicated that the time for 90% reduction of poliovirus type 1 at 24 +/- 1 degree C in seawater samples obtained from different sites in Hawaii ranged from 24 to 48 h, and complete inactivation occurred within 72 to 96 h. The accumulated evidence also strongly indicated that a virus-inactivating agent(s) of a microbiological nature was present in both clean and sewage-polluted seawaters, but not in fresh, mountain stream waters. The antiviral activity was lost when the seawater samples were subjected to boiling, autoclaving, or filtration through a 0.22- or 0.45-micrometer, but not a 1.0-micrometer, membrane filter. That the antiviral activity of the seawater was related to the growth activities of microorganisms was corroborated by the observed effects of added nutrients, a lower temperature of incubation, and the presence of certain antibiotics. Other enteric viruses, such as coxsackie virus B-4 and echo virus-7, were also shown to be similarly inactivated in seawater.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gundersen K., Brandberg A., Magnusson S., Lycke E. Characterization of a marine bacterium associated with virus inactivating capacity. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(2):281–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb05165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S., Gilbert J., Hetrick F. Stability of human enteroviruses in estuarine and marine waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Aug;32(2):245–249. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.2.245-249.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Hedström C. E., Lycke E. The virus inactivating capacity of sea water. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(4):551–559. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matossian A. M., Garabedian G. A. Virucidal action of sea water. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Jan;85(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



