Abstract
In the title compound, C12H12O4, the dihedral angle between the plane through the phenyl ring and the mean plane of the side chain is approximately 14°. The molecules, which contain an intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond, are linked end-to-end by weak C—H⋯O intermolecular hydrogen-bonding contacts, forming infinite one-dimensional chain systems in the crystal structure.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Davey & Ribbons (1975 ▶); Emerson et al. (1991 ▶); Aliev et al. (2000a
▶,b
▶); Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶); Desiraju & Steiner (2001 ▶).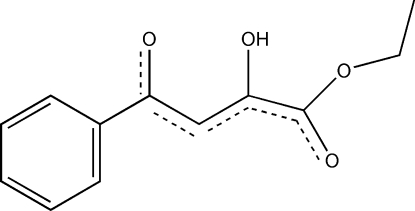
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H12O4
M r = 220.22
Monoclinic,

a = 9.872 (4) Å
b = 13.498 (5) Å
c = 8.843 (3) Å
β = 105.464 (6)°
V = 1135.7 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 294 (2) K
0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.975, T max = 0.981
6252 measured reflections
2316 independent reflections
1405 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.049
wR(F 2) = 0.151
S = 1.02
2316 reflections
147 parameters
2 restraints
H-atom parameters constraned
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1998 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807061223/si2049sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807061223/si2049Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2A⋯O1 | 0.82 | 1.80 | 2.518 (2) | 146 |
| C5—H5⋯O3i | 0.93 | 2.67 | 3.405 (3) | 137 |
| C11—H11A⋯O1ii | 0.97 | 2.68 | 3.571 (4) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (No. 07JCYBJC09300).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
1,3-Diketones are substrates for carbon-carbon bond hydrolysis by beta-ketolases. The 2,4-diketo acids examined for hydrolysis by acetopyruvate hydrolase from rat liver (EC 3.7.1.5) all have aliphatic side chains.(Davey & Ribbons, 1975) The acetopyruvate hydrolases cleave 2,4-diketopentanoic acid into pyruvate and acetate (Emerson et al., 1991). Cleavage of analogues such as 2,4-diketo-4-phenylbutanoic acid was not reported. In order to discover the hydrolysis process of analogues, the title compound was synthesized.
In the title compound, the C—O and C—C bond lengths are in the normal range, and the dihedral angle between the plane of the phenyl ring and the mean plane of the side chain is approximately 14 °. The corresponding torsion angle C1—C6—C7—C8 is -14.0 (3) °. The molecule contains the typical O—H···O intra-molecular hydrogen bond graph set S(6) (Bernstein et al., 1995). As shown in Figure 2, these monomers are associated end-to-end to form the R22(10) ring system, which is generated by different weak C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1). These hydrogen bonds connect the molecules due to translational symmetry to assembly a chain system along the c direction. Similarly, the S(6) intra-molecular hydrogen bond type is also observed in 2-hydroxy-4-oxo-4-phenyl-3(Z)-butenic acid and 4-hydroxy-2-oxo-6-phenyl-3(Z),5(E)-hexadienic acid, but the monomer of the former is extended by the R22(8) (Bernstein et al. 1995) inter-molecular H-bonds, related by a centre of inversion to form a two-dimensional layer with head-to-tail packing architecture (Aliev et al., 2000a,b). Head-to-tail packing is also observed in the structure of the title compound, and long H···O distances (Table 1) in weak intermolecular C—H···O contacts are extensively discussed in the literature (Desiraju & Steiner, 2001).
Experimental
Sodium (2.3 g, 103 mmol) was added to absolute ethanol (133 ml). The mixture was cooled to -273 K and a mixture of diethyl oxalate (14.0 g, 96 mmol) and the ketone (96 mmol) was added slowly over a period of 20 min. A precipitate formed and stirring was continued for 4 h at room temperature. The precipitate was filtered, washed with absolute ethanol (20 ml) and dissolved in 2 N sulfuric acid (150 ml) and ether-extracted (3x150 ml), dried over Na2SO4 and ether removed. The residue was distilled under reduced pressure. The residue was recrystallized from ethanol and single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray measurements were obtained by recrystallization from acetone at room temperature. Elemental analysis (%) calcd for 1, C18H22CuN4O8: C 65.45, H 5.49; found: C 65.52, H 5.54.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding with distances C–H = 0.93–0.97 Å, and O–H = 0.82 Å. The respective Uiso(H)=1.2Ueq(aromatic C and CH2), Uiso(H)=1.5Ueq(CH3), Uiso(H)=1.5(Ueq)(hydroxyl O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
An ORTEP view of the labelled title molecule with 30% thermal ellipsoids. The intramolecular hydrogen bond is indicated by a dashed line.
Fig. 2.
View of the one-dimensional weak hydrogen bonded chain structure.
Crystal data
| C12H12O4 | F000 = 464 |
| Mr = 220.22 | Dx = 1.288 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1800 reflections |
| a = 9.872 (4) Å | θ = 2.6–26.2º |
| b = 13.498 (5) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 8.843 (3) Å | T = 294 (2) K |
| β = 105.464 (6)º | Block, yellow |
| V = 1135.7 (7) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2316 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1405 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.028 |
| T = 294(2) K | θmax = 26.4º |
| phi and ω scans | θmin = 2.1º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −12→11 |
| Tmin = 0.975, Tmax = 0.981 | k = −16→15 |
| 6252 measured reflections | l = −9→10 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.151 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0635P)2 + 0.3304P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2316 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 147 parameters | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Extinction correction: none |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.58450 (15) | 0.67082 (13) | 0.25001 (17) | 0.0695 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.43270 (15) | 0.65232 (14) | 0.43639 (17) | 0.0714 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.4506 | 0.6651 | 0.3531 | 0.107* | |
| O3 | 0.62879 (18) | 0.56869 (16) | 0.80268 (18) | 0.0871 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.40548 (14) | 0.61835 (11) | 0.71546 (15) | 0.0558 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.9543 (2) | 0.62744 (16) | 0.4355 (3) | 0.0589 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.9547 | 0.6290 | 0.5407 | 0.071* | |
| C2 | 1.0792 (2) | 0.6156 (2) | 0.3952 (3) | 0.0708 (7) | |
| H2 | 1.1633 | 0.6099 | 0.4732 | 0.085* | |
| C3 | 1.0797 (3) | 0.61223 (19) | 0.2404 (3) | 0.0726 (7) | |
| H3 | 1.1636 | 0.6025 | 0.2136 | 0.087* | |
| C4 | 0.9558 (3) | 0.6232 (2) | 0.1241 (3) | 0.0721 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.9566 | 0.6216 | 0.0192 | 0.087* | |
| C5 | 0.8304 (2) | 0.63658 (17) | 0.1634 (3) | 0.0603 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.7473 | 0.6453 | 0.0849 | 0.072* | |
| C6 | 0.8285 (2) | 0.63697 (14) | 0.3204 (2) | 0.0479 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.6913 (2) | 0.64484 (15) | 0.3590 (2) | 0.0490 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.6759 (2) | 0.62196 (16) | 0.5096 (2) | 0.0516 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.7552 | 0.6022 | 0.5926 | 0.062* | |
| C9 | 0.5473 (2) | 0.62671 (15) | 0.5400 (2) | 0.0497 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.5333 (2) | 0.60126 (17) | 0.7012 (2) | 0.0536 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.3828 (2) | 0.5971 (2) | 0.8685 (2) | 0.0641 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.4489 | 0.6341 | 0.9496 | 0.077* | |
| H11B | 0.3962 | 0.5270 | 0.8920 | 0.077* | |
| C12 | 0.2353 (3) | 0.6269 (2) | 0.8617 (3) | 0.0833 (8) | |
| H12A | 0.2239 | 0.6966 | 0.8405 | 0.125* | |
| H12B | 0.2164 | 0.6126 | 0.9604 | 0.125* | |
| H12C | 0.1710 | 0.5906 | 0.7799 | 0.125* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0472 (9) | 0.1101 (13) | 0.0500 (9) | 0.0117 (8) | 0.0109 (7) | 0.0164 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0429 (9) | 0.1209 (15) | 0.0501 (9) | 0.0102 (8) | 0.0119 (7) | 0.0166 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0623 (11) | 0.1483 (18) | 0.0514 (10) | 0.0333 (11) | 0.0161 (8) | 0.0217 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0470 (8) | 0.0774 (10) | 0.0453 (8) | 0.0045 (7) | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0043 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0463 (12) | 0.0808 (16) | 0.0507 (12) | 0.0012 (11) | 0.0151 (10) | 0.0017 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0464 (13) | 0.1006 (19) | 0.0671 (15) | 0.0019 (12) | 0.0183 (11) | 0.0075 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0546 (15) | 0.0928 (19) | 0.0803 (17) | 0.0009 (13) | 0.0353 (13) | 0.0072 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0713 (17) | 0.0946 (19) | 0.0593 (14) | −0.0037 (13) | 0.0326 (13) | 0.0025 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0531 (13) | 0.0767 (16) | 0.0518 (13) | 0.0000 (11) | 0.0150 (10) | 0.0068 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0455 (12) | 0.0522 (12) | 0.0480 (11) | −0.0005 (9) | 0.0159 (9) | 0.0019 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0419 (11) | 0.0555 (12) | 0.0492 (12) | 0.0020 (9) | 0.0117 (9) | −0.0019 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0420 (12) | 0.0697 (14) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0090 (9) | 0.0101 (9) | 0.0013 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0448 (11) | 0.0597 (13) | 0.0430 (11) | 0.0042 (9) | 0.0093 (9) | −0.0018 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0456 (12) | 0.0693 (14) | 0.0455 (12) | 0.0050 (10) | 0.0115 (10) | −0.0013 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0679 (15) | 0.0823 (16) | 0.0462 (12) | 0.0021 (12) | 0.0220 (11) | 0.0012 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0776 (18) | 0.104 (2) | 0.0825 (18) | 0.0151 (15) | 0.0469 (15) | 0.0085 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C7 | 1.274 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C9 | 1.299 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.394 (3) |
| O2—H2A | 0.8200 | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C10 | 1.199 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.486 (3) |
| O4—C10 | 1.321 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.415 (3) |
| O4—C11 | 1.458 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.367 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.381 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9572 |
| C1—C6 | 1.386 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.509 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.496 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.371 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.383 (3) | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C9—O2—H2A | 109.5 | C8—C7—C6 | 122.28 (18) |
| C10—O4—C11 | 116.17 (16) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.88 (19) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.5 (2) | C9—C8—H8A | 118.4 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.7 | C7—C8—H8A | 120.8 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.7 | O2—C9—C8 | 123.66 (19) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.2 (2) | O2—C9—C10 | 116.41 (18) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C8—C9—C10 | 119.93 (18) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.9 | O3—C10—O4 | 125.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.2 (2) | O3—C10—C9 | 122.62 (19) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | O4—C10—C9 | 112.41 (17) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | O4—C11—C12 | 107.37 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.1 (2) | O4—C11—H11A | 110.2 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C12—C11—H11A | 110.2 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 | O4—C11—H11B | 110.2 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.1 (2) | C12—C11—H11B | 110.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.92 (19) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 122.10 (19) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.96 (19) | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C8 | 119.81 (18) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 117.88 (18) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.6 (4) | O1—C7—C8—C9 | 0.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.7 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −177.77 (19) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.7 (4) | C7—C8—C9—O2 | −0.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.3 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.55 (19) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.4 (3) | C11—O4—C10—O3 | 1.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 176.9 (2) | C11—O4—C10—C9 | −179.21 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 2.3 (3) | O2—C9—C10—O3 | 173.6 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −176.0 (2) | C8—C9—C10—O3 | −6.3 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | 167.8 (2) | O2—C9—C10—O4 | −6.0 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | −13.9 (3) | C8—C9—C10—O4 | 174.08 (19) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −14.0 (3) | C10—O4—C11—C12 | 176.8 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 164.3 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2A···O1 | 0.82 | 1.80 | 2.518 (2) | 146 |
| C5—H5···O3i | 0.93 | 2.67 | 3.405 (3) | 137 |
| C11—H11A···O1ii | 0.97 | 2.68 | 3.571 (4) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y, z−1; (ii) x, y, z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SI2049).
References
- Aliev, Z. G., Shurov, S. N., Nekrasov, D. D., Podvintsev, I. B. & Atovmyan, L. O. (2000a). Zh. Strukt. Khim.41, 1255–1260.
- Aliev, Z. G., Shurov, S. N., Nekrasov, D. D., Podvintsev, I. B. & Atovmyan, L. O. (2000b). J. Struct. Chem, 41, 1041–1045.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker, (1998). SMART-NT and SAINT-NT Version 5.1. Bruker AXS Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Davey, J. F. & Ribbons, D. W. (1975). J. Biol. Chem.250, 3826–3830. [PubMed]
- Desiraju, G. R. & Steiner, T. (2001). The Weak Hydrogen Bond in Structural Chemistry and Biology, pp. 100–112. IUCr Monograph on Crystallography 9. Oxford University Press.
- Emerson, D. W., Titus, R. L. & Gonzáles, R. M. (1991). J. Org. Chem.56, 5301–5307.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807061223/si2049sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807061223/si2049Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




