Abstract
The title compound, C12H14N2O3, was synthesized as an intermediate for the synthesis of metamitron. The benzene ring forms dihedral angles of 86.3 (2) and 10.0 (3)° with the ethyl group and the acetylimino plane, respectively. The crystal structure involves intermolecular C—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Glaser et al. (1993 ▶); Javier et al. (2006 ▶); Pan & Gao (2007 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H14N2O3
M r = 234.25
Orthorhombic,
a = 9.3039 (19) Å
b = 15.752 (3) Å
c = 17.129 (3) Å
V = 2510.3 (8) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 153 (2) K
0.32 × 0.22 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID IP area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi 1995 ▶) T min = 0.972, T max = 0.991
18227 measured reflections
2206 independent reflections
1870 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.023
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.110
S = 1.09
2206 reflections
156 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3
Data collection: RAPID-AUTO (Rigaku 2004 ▶); cell refinement: RAPID-AUTO; data reduction: RAPID-AUTO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2001 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807060941/hg2352sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807060941/hg2352Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯O3i | 0.86 | 2.03 | 2.8737 (16) | 165 |
| C9—H9B⋯O3i | 0.97 | 2.55 | 3.2023 (19) | 124 |
Symmetry code: (i) 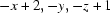 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Metamitron(Trade name: Goltix) is a widely used herbicide for the control of grass and broad-leaved weeds in sugar and red beets, fodder beet, and certain strawberry varieties. The dose rates for metamitron are 0.35–4.2 kg active ingredient/ha for all crops. The currently used weed control strategy in sugarbeet involves a mixture of herbicides(phenmedipham, ethofumesate, metamitron, chloridazon etc) to control dicotyledonus weeds. 70% wettable powderand has been used for the control of morel goosefoot chickweed Lamium barbatum etc. Metamitron can be used before and after the plantingis. It can be applied to the control of the entire crop growing period with better efficacy when it cooperate with others herbicides and pesticides(Javier et al., 2006). The title compound (I) was synthesized as an intermediate for the synthesis of metamitron. We report here the crystal structure of (I).
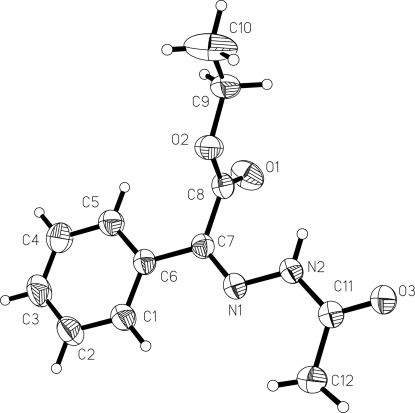
In (I) (Fig. 1), all bond lengths and angles are normal and in a good agreement with those reported previously (Glaser et al., 1993). The benzene ring plane forms dihedral angles of 86.3 (2)° and 10.0 (3)° with the ethyl plane (O1/O2/C7/C8/C9) and the acetylimino plane (O3/N1/N2/C4/C5/C6/C7/C11/C12), respectively. The crystal structure is stabilized by intermolecular C–H–O and N–H–O hydrogen bonds.
Experimental
Ethyl benzoylformate 12.1 g (6.8 mmol), was dissolved in 20 ml e thanol in a flask equipped with stirrer and reflux condenser. Acethydrazide 5.1 g(6.8 mmol) was slowly added from a dropping-funnel during 30 minutes while maintaining the temperature at 75–80°C for eight hours. Evaporation of portion of the solvent and cooling down the remaining solution in ice water yielded white crystals out after three hours (11.9 g, yield 78.9%) (Pan et al., 2007). Single crystals suitable for X-ray measurement were obtained by recrystallization from petroleum ether at room temperature.
Refinement
All H atoms were found on difference maps. All H atoms were positioned geometrically [N—H = 0.86 Å(NH). C—H = 0.93Å (CH), C—H = 0.97Å (CH2). C—H = 0.96Å (CH3). Uiso(H) = 1.5 x (Methyl) or Uiso(H) = 1.2 x (other groups)].
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 35% probability level.
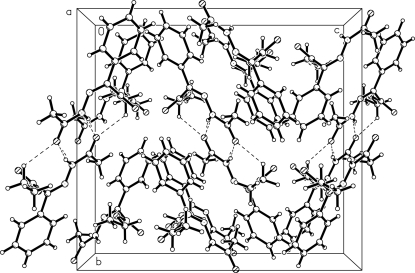
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram of the molecule of the title compound, viewed down the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C12H14N2O3 | F000 = 992 |
| Mr = 234.25 | Dx = 1.240 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 2998 reflections |
| a = 9.3039 (19) Å | θ = 2.3–21.9º |
| b = 15.752 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 17.129 (3) Å | T = 153 (2) K |
| V = 2510.3 (8) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.32 × 0.22 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS Rapid IP area-detector diffractometer | 2206 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating Anode | 1870 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.023 |
| T = 153(2) K | θmax = 25.0º |
| ω Oscillation scans | θmin = 3.2º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(ABSCOR; Higashi 1995) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.972, Tmax = 0.991 | k = −18→18 |
| 18227 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0576P)2 + 0.4358P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.110 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| S = 1.09 | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 2206 reflections | Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3 |
| 156 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.030 (2) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.98377 (12) | 0.11865 (7) | 0.70415 (6) | 0.0676 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.84719 (10) | 0.19284 (6) | 0.62123 (6) | 0.0504 (3) | |
| O3 | 1.14302 (12) | −0.00717 (6) | 0.44126 (6) | 0.0628 (3) | |
| N1 | 1.16667 (12) | 0.17432 (7) | 0.55542 (6) | 0.0456 (3) | |
| N2 | 1.11668 (13) | 0.09905 (7) | 0.52543 (6) | 0.0485 (3) | |
| H2A | 1.0369 | 0.0782 | 0.5420 | 0.058* | |
| C1 | 1.26329 (16) | 0.33271 (9) | 0.60630 (8) | 0.0514 (4) | |
| H1B | 1.3104 | 0.3071 | 0.5646 | 0.062* | |
| C2 | 1.30914 (19) | 0.41054 (10) | 0.63304 (9) | 0.0616 (4) | |
| H2B | 1.3875 | 0.4369 | 0.6096 | 0.074* | |
| C3 | 1.2401 (2) | 0.44963 (10) | 0.69408 (10) | 0.0682 (5) | |
| H3A | 1.2713 | 0.5024 | 0.7117 | 0.082* | |
| C4 | 1.1246 (2) | 0.41045 (10) | 0.72922 (10) | 0.0675 (5) | |
| H4A | 1.0776 | 0.4368 | 0.7706 | 0.081* | |
| C5 | 1.07824 (17) | 0.33195 (9) | 0.70302 (8) | 0.0538 (4) | |
| H5A | 1.0005 | 0.3057 | 0.7271 | 0.065* | |
| C6 | 1.14696 (14) | 0.29215 (8) | 0.64113 (7) | 0.0416 (3) | |
| C7 | 1.09697 (14) | 0.20901 (8) | 0.61165 (7) | 0.0405 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.97033 (15) | 0.16787 (8) | 0.65146 (7) | 0.0422 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.71683 (16) | 0.15866 (11) | 0.65747 (9) | 0.0574 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.7085 | 0.1788 | 0.7108 | 0.069* | |
| H9B | 0.7202 | 0.0971 | 0.6582 | 0.069* | |
| C10 | 0.5936 (2) | 0.18798 (17) | 0.61093 (13) | 0.1044 (9) | |
| H10A | 0.5062 | 0.1667 | 0.6334 | 0.157* | |
| H10B | 0.6029 | 0.1675 | 0.5584 | 0.157* | |
| H10C | 0.5914 | 0.2489 | 0.6107 | 0.157* | |
| C11 | 1.19254 (16) | 0.05777 (9) | 0.46999 (8) | 0.0494 (4) | |
| C12 | 1.33423 (19) | 0.09243 (12) | 0.44570 (12) | 0.0758 (5) | |
| H12A | 1.3687 | 0.0617 | 0.4011 | 0.114* | |
| H12B | 1.4015 | 0.0867 | 0.4878 | 0.114* | |
| H12C | 1.3240 | 0.1513 | 0.4325 | 0.114* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0664 (7) | 0.0730 (7) | 0.0634 (6) | −0.0111 (6) | −0.0089 (5) | 0.0261 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0413 (6) | 0.0526 (6) | 0.0575 (6) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0043 (4) | 0.0092 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0619 (7) | 0.0551 (6) | 0.0715 (7) | −0.0139 (5) | 0.0159 (5) | −0.0241 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0468 (6) | 0.0391 (6) | 0.0508 (6) | −0.0053 (5) | 0.0006 (5) | −0.0052 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0485 (7) | 0.0406 (6) | 0.0564 (7) | −0.0102 (5) | 0.0089 (5) | −0.0100 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0531 (8) | 0.0463 (8) | 0.0548 (8) | −0.0067 (6) | 0.0027 (7) | −0.0031 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0647 (10) | 0.0519 (9) | 0.0682 (10) | −0.0166 (8) | 0.0005 (8) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0787 (12) | 0.0473 (9) | 0.0785 (11) | −0.0158 (8) | −0.0044 (9) | −0.0145 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0750 (11) | 0.0591 (9) | 0.0683 (10) | −0.0048 (8) | 0.0055 (8) | −0.0229 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0539 (9) | 0.0521 (8) | 0.0553 (8) | −0.0055 (7) | 0.0032 (7) | −0.0076 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0435 (7) | 0.0372 (7) | 0.0442 (7) | 0.0002 (5) | −0.0062 (5) | −0.0004 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0406 (7) | 0.0372 (7) | 0.0436 (7) | −0.0002 (5) | −0.0036 (5) | 0.0007 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0473 (8) | 0.0376 (7) | 0.0416 (7) | −0.0023 (5) | −0.0030 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0470 (9) | 0.0641 (9) | 0.0610 (9) | −0.0050 (7) | 0.0153 (7) | −0.0018 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0464 (11) | 0.174 (3) | 0.0925 (14) | −0.0096 (13) | −0.0001 (10) | 0.0327 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0495 (8) | 0.0437 (7) | 0.0551 (8) | −0.0041 (6) | 0.0056 (6) | −0.0057 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0617 (10) | 0.0691 (11) | 0.0964 (13) | −0.0160 (8) | 0.0270 (9) | −0.0234 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C8 | 1.1964 (16) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C8 | 1.3173 (16) | C5—C6 | 1.3878 (19) |
| O2—C9 | 1.4650 (17) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| O3—C11 | 1.2251 (16) | C6—C7 | 1.4787 (18) |
| N1—C7 | 1.2832 (17) | C7—C8 | 1.5078 (19) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3733 (15) | C9—C10 | 1.471 (2) |
| N2—C11 | 1.3501 (18) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.377 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.391 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9300 | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.373 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.486 (2) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9300 | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.378 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (2) | ||
| C8—O2—C9 | 116.34 (11) | C6—C7—C8 | 118.16 (11) |
| C7—N1—N2 | 118.50 (11) | O1—C8—O2 | 125.51 (13) |
| C11—N2—N1 | 120.12 (11) | O1—C8—C7 | 122.55 (12) |
| C11—N2—H2A | 119.9 | O2—C8—C7 | 111.94 (11) |
| N1—N2—H2A | 119.9 | O2—C9—C10 | 107.46 (13) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.50 (14) | O2—C9—H9A | 110.2 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 119.8 | C10—C9—H9A | 110.2 |
| C6—C1—H1B | 119.8 | O2—C9—H9B | 110.2 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.52 (15) | C10—C9—H9B | 110.2 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 119.7 | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.5 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 119.7 | C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.78 (15) | C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.1 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.1 | C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.10 (15) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.0 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.0 | O3—C11—N2 | 119.22 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.51 (15) | O3—C11—C12 | 121.86 (13) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.7 | N2—C11—C12 | 118.92 (13) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.7 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.59 (12) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.07 (12) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.33 (12) | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 118.33 (12) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 123.46 (11) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C7—N1—N2—C11 | −175.43 (12) | C1—C6—C7—N1 | 2.49 (19) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.5 (2) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.87 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.4 (3) | C1—C6—C7—C8 | −179.93 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 (3) | C9—O2—C8—O1 | 1.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.3 (3) | C9—O2—C8—C7 | −178.08 (11) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.2 (2) | N1—C7—C8—O1 | 85.17 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.90 (14) | C6—C7—C8—O1 | −92.28 (16) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.2 (2) | N1—C7—C8—O2 | −94.86 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 179.29 (13) | C6—C7—C8—O2 | 87.69 (14) |
| N2—N1—C7—C6 | −177.00 (11) | C8—O2—C9—C10 | −174.94 (15) |
| N2—N1—C7—C8 | 5.56 (19) | N1—N2—C11—O3 | −176.56 (13) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | −178.46 (12) | N1—N2—C11—C12 | 3.6 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···O3i | 0.86 | 2.03 | 2.8737 (16) | 165 |
| C9—H9B···O3i | 0.97 | 2.55 | 3.2023 (19) | 124 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG2352).
References
- Glaser, R., Chen, G. S. & Barnes, C. L. (1993). J. Org. Chem.58, 7446–7455.
- Higashi, T. (1995). ABSCOR Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Javier, M., Sergio, A. & Salvador, G. (2006). Anal. Chim. Acta, 565, 255–260.
- Pan, Z. W. & Gao, H. X. (2007). Pesticides, 46, 166–167.
- Rigaku (2004). RAPID-AUTO Version 3.0. Rigaku Corporation, Takyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2001). SHELXTL Version 5.0. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807060941/hg2352sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807060941/hg2352Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report