Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, 2C4H12N+·2C10H5O8 −·C10H6O8, consists of a tetramethylamonium cation, an anion derived from the singly deprotonated pyromellitic acid anion, 2,4,5-carboxybenzoate (H3bta−), and one-half of a benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylic acid (H4bta) molecule, which has the centroid of the aromatic ring positioned at a crystallographic centre of inversion. The H4bta and H3bta− residues are involved in an extensive intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding network, which leads to a three-dimensional supramolecular structure containing one-dimensional channels running parallel to the [001] crystallographic direction. These channels house the tetramethylamonium cations.
Related literature
For general background on supramolecular assemblies of organic molecules mediated by hydrogen bonds, see: Dale et al. (2004 ▶); Fabelo et al. (2005 ▶); Ruiz-Pérez et al. (2004 ▶); Steed & Atwood (2000 ▶). For literature relevant to this communication and published by our group, see: Cunha-Silva et al. (2007 ▶); Paz & Klinowski (2003 ▶); Paz et al. (2002 ▶); Shi et al. (2007 ▶). For the Cambridge Structural Database, see: Allen (2002 ▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶)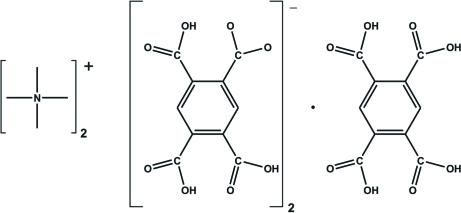
Experimental
Crystal data
2C4H12N+·2C10H5O8 −·C10H6O8
M r = 908.72
Monoclinic,
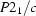
a = 9.4282 (4) Å
b = 18.7286 (8) Å
c = 11.3175 (5) Å
β = 107.053 (2)°
V = 1910.55 (14) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.13 mm−1
T = 150 (2) K
0.14 × 0.12 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1998 ▶) T min = 0.982, T max = 0.984
19608 measured reflections
3736 independent reflections
2523 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.061
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.099
S = 1.00
3736 reflections
308 parameters
5 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2; data reduction: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2005 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Bruker 2001 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807062381/sj2444sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807062381/sj2444Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯O6i | 0.959 (10) | 1.637 (11) | 2.5885 (18) | 171 (2) |
| O4—H4⋯O11ii | 0.941 (10) | 1.806 (12) | 2.7166 (19) | 162 (2) |
| O7—H7⋯O6 | 0.962 (10) | 1.483 (10) | 2.4334 (19) | 169 (2) |
| O10—H10⋯O5iii | 0.938 (10) | 1.764 (11) | 2.6890 (18) | 168 (2) |
| O12—H12⋯O8iv | 0.957 (10) | 1.600 (11) | 2.5308 (19) | 163 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 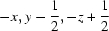 ; (ii)
; (ii) 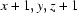 ; (iii)
; (iii) 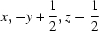 ; (iv)
; (iv) 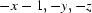 .
.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT, Portugal) for their general financial support (POCI-PPCDT/QUI/58377/2004, supported by FEDER) and for the postdoctoral and PhD research grants Nos. SFRH/BPD/14410/2003 (to LCS) and SFRH/BD/17968/2004 (to PIG.).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Crystal Engineers aim to design functional materials with overall properties which are uniquely directed by the physical and chemical properties of the employed building blocks. In this context, an important strategy used to control the self-assembly processes is based on the use of reliable intermolecular interactions, such as strong and highly directional hydrogen bonds (Steed & Atwood, 2000). Pyromellitic acid (benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylic acid, H4bta) has been widely used in the isolation of novel organic crystals, as revealed by a systematic search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.28, 3 updates - August 2007; Allen, 2002). Indeed, the four symmetrically located carboxylic acid groups confer on this organic molecule predictable and interesting supramolecular properties (Ruiz-Pérez et al., 2004; Fabelo et al., 2005; Dale et al., 2004). As part of our on-going research in the field of Crystal Engineering (Cunha-Silva et al., 2007; Shi et al., 2007), in particular in the use of organic ligands based on carboxylic acid groups (Paz & Klinowski, 2003; Paz et al., 2002), we have recently isolated the title compound, [NMe4]+2 (H3bta)-2.(H4bta), as a secondary product.
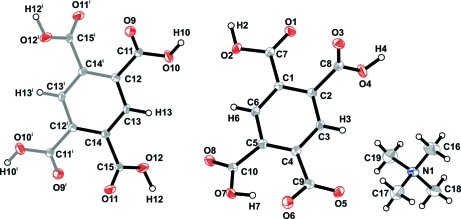
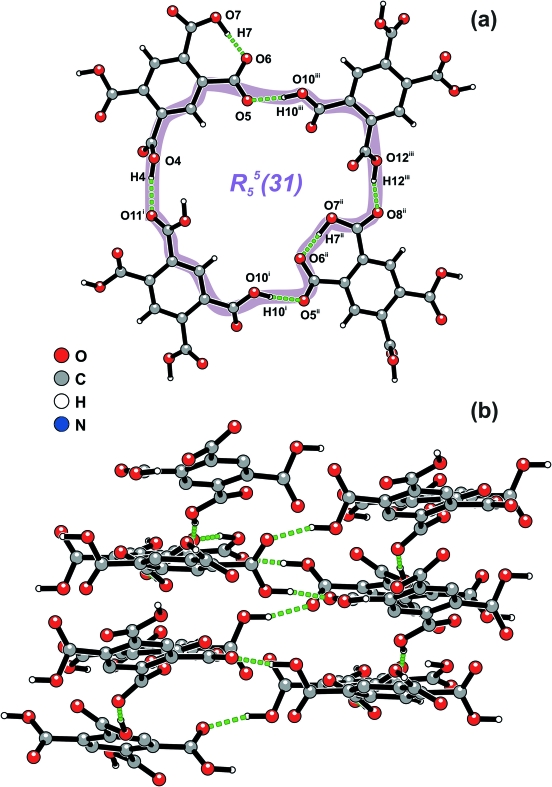
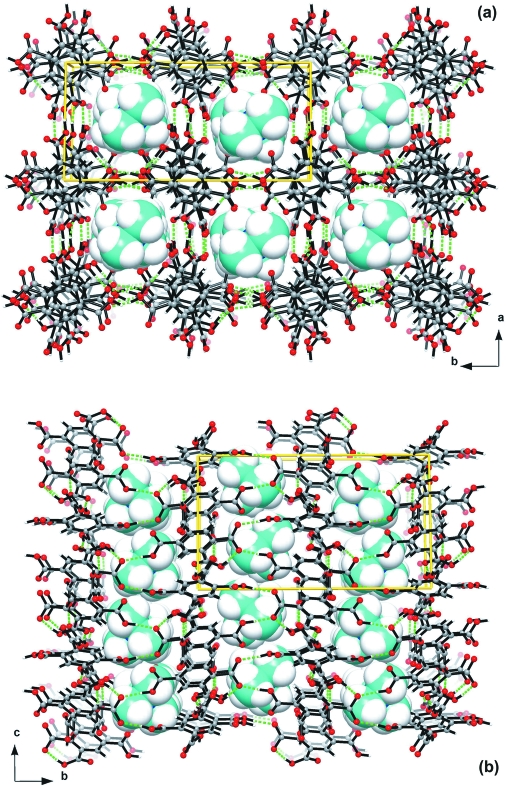
The asymmetric unit of I comprises one [NMe4]+ cation, one H3bta- anion and half of a H4bta molecule which has the centroid of the aromatic ring (Cg) positioned at a crystallographic centre of inversion (Figure 1). H3bta- anions (moiety type A) and H4bta molecules (moiety type B) close pack along the [001] direction of the unit cell in a AABAAB∞ alternate fashion, mediated by a series of weak π···π offset stacking interactions having Cg···Cg distances of 3.762 (2) Å (for A···A), 3.927 (2) Å (for A···B) and 3.910 (2) Å (for B···A). However, the crystal packing of I is essentially mediated by the extensive hydrogen bonding network composed of strong and highly directional O—H···O hydrogen bonds involving the two crystallographic independent residues of pyromellitic acid (Table 1). Indeed, while each H4bta molecule interacts with six neighbouring H3bta- anions, each H3bta- is instead connected to three H4bta plus another two symmetry-related H3bta-. The resulting complicated hydrogen bond connectivity leads to the formation of supramolecular R55(31) rings (Bernstein et al., 1995), which are further interconnected into helices running parallel to the [001] direction of the unit cell (Figure 2 and Table 1). This supramolecular arrangement distributes the H3bta- and H4bta chemical moieties in such a way that the anionic framework contains a one-dimensional channels (also running parallel to the [001] direction) which houses the charge-balancing [NMe4]+ cations (Figure 3). Besides the electrostatic interactions, these cationic moieties are further stabilized inside the channels by a series of weak C—H···O interactions, with C···O distances ranging from 3.161 (3) to 3.663 (3) Å (not shown).
Experimental
2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (0.308 g, 2 mmol) and benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylic acid (0.510 g, 2 mmol) were mixed in distilled water (ca 20 ml). Tetramethylamonium hydroxide (solution of 25%; 2 mmol) and manganese chloride tetrahydrate (0.101 g, 0.5 mmol) were added, and the resulting mixture was refluxed for 5 h. The solvent from the final pale yellow solution was allowed to slowly evaporate, at ambient temperature, over a period of 10 months. Large single-crystals of the title compound, suitable for X-ray diffraction, were directly harvested from the crystallization vial.
Refinement
H atoms associated with the carboxylic acid groups were markedly visible from difference Fourier maps and were included in the final structural model with the O—H distances restrained to 0.95 (1) Å, and assuming an isotropic displacement behaviour with Uiso fixed at 1.5 times Ueq of the parent O atom. All remaining H atoms were located at idealized positions and refined with Uiso=1.2×Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Chemical moieties composing the asymmetric unit of I (black-filled bonds), showing the labelling scheme for all atoms. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level and H-atoms are shown as small spheres with arbitrary radii. Symmetry transformation used to generate equivalent atoms:(i) -x, -y, -z.
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of the O—H···O connections between adjacent H3bta- and H4bta residues leading to (a)R55(31) rings which are further interconnected along the [001] direction of the unit cell into (b) helical chains surrounding the channels present in the crystal structure. For geometrical details on the represented hydrogen bonds (dashed green lines) see Table 1. Symmetry transformations used to generate equivalent atoms: (i) 1 + x, y, 1 + z; (ii) 1 + x, 1/2 - y, 1/2 + z; (iii) -x, 1/2 + y, 1/2 - z.
Fig. 3.
Crystal packing of the title compound viewed in perspective along the (a) [001] and (b) [100] directions of the unit cell. O—H···O hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed green lines and the [NMe4]+ cations in space-filling mode.
Crystal data
| 2C4H12N+·2C10H5O8−·C10H6O8 | F(000) = 948 |
| Mr = 908.72 | Dx = 1.580 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2577 reflections |
| a = 9.4282 (4) Å | θ = 2.9–23.2° |
| b = 18.7286 (8) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| c = 11.3175 (5) Å | T = 150 K |
| β = 107.053 (2)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1910.55 (14) Å3 | 0.14 × 0.12 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Bruker X8 KappaCCD APEXII diffractometer | 3736 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2523 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.061 |
| ω/φ scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1998) | h = −11→9 |
| Tmin = 0.982, Tmax = 0.984 | k = −22→23 |
| 19608 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0485P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3736 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 308 parameters | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 5 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. See dedicated section in the main paper |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.23459 (15) | −0.18900 (7) | 0.41351 (13) | 0.0243 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.03177 (16) | −0.19106 (7) | 0.25030 (14) | 0.0306 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.059 (2) | −0.2395 (6) | 0.241 (2) | 0.046* | |
| O3 | 0.45044 (15) | −0.07193 (7) | 0.43306 (13) | 0.0222 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.38326 (15) | −0.05971 (7) | 0.60719 (13) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.4840 (12) | −0.0655 (11) | 0.6516 (18) | 0.034* | |
| O5 | 0.07842 (15) | 0.17226 (7) | 0.47794 (13) | 0.0233 (4) | |
| O6 | −0.07866 (16) | 0.17604 (7) | 0.28878 (13) | 0.0261 (4) | |
| O7 | −0.27358 (15) | 0.09642 (7) | 0.17213 (13) | 0.0201 (3) | |
| H7 | −0.1913 (17) | 0.1273 (9) | 0.2101 (18) | 0.030* | |
| O8 | −0.32512 (15) | −0.01671 (7) | 0.19026 (13) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| O9 | 0.22586 (15) | 0.16081 (7) | 0.01694 (14) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| O10 | −0.00003 (15) | 0.19454 (7) | 0.02169 (13) | 0.0226 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.038 (2) | 0.2382 (7) | 0.004 (2) | 0.034* | |
| O11 | −0.34327 (15) | −0.06460 (7) | −0.22544 (13) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| O12 | −0.39830 (15) | 0.00769 (8) | −0.08721 (14) | 0.0270 (4) | |
| H12 | −0.5011 (12) | 0.0024 (12) | −0.1315 (18) | 0.041* | |
| C1 | 0.0979 (2) | −0.08162 (9) | 0.34901 (17) | 0.0127 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.2037 (2) | −0.03525 (10) | 0.42177 (17) | 0.0129 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.1658 (2) | 0.03604 (10) | 0.43179 (17) | 0.0136 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.2361 | 0.0669 | 0.4851 | 0.016* | |
| C4 | 0.0279 (2) | 0.06330 (9) | 0.36590 (17) | 0.0134 (4) | |
| C5 | −0.0786 (2) | 0.01648 (10) | 0.29062 (17) | 0.0137 (4) | |
| C6 | −0.0402 (2) | −0.05506 (10) | 0.28629 (17) | 0.0137 (4) | |
| H6 | −0.1123 | −0.0870 | 0.2379 | 0.016* | |
| C7 | 0.1305 (2) | −0.15936 (10) | 0.34274 (18) | 0.0158 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.3601 (2) | −0.05876 (10) | 0.48645 (19) | 0.0160 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.0077 (2) | 0.14282 (10) | 0.38080 (19) | 0.0161 (4) | |
| C10 | −0.2354 (2) | 0.03281 (10) | 0.21461 (18) | 0.0157 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.1018 (2) | 0.14644 (10) | 0.01977 (17) | 0.0142 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.0487 (2) | 0.07093 (10) | 0.01737 (17) | 0.0123 (4) | |
| C13 | −0.0993 (2) | 0.05489 (10) | −0.04131 (17) | 0.0132 (4) | |
| H13 | −0.1680 | 0.0928 | −0.0691 | 0.016* | |
| C14 | −0.1490 (2) | −0.01526 (10) | −0.06025 (17) | 0.0123 (4) | |
| C15 | −0.3083 (2) | −0.02798 (10) | −0.13252 (18) | 0.0141 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.46132 (18) | 0.23095 (8) | 0.82066 (15) | 0.0209 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.5398 (3) | 0.17774 (12) | 0.9150 (2) | 0.0412 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.6108 | 0.2024 | 0.9837 | 0.062* | |
| H16B | 0.5929 | 0.1438 | 0.8775 | 0.062* | |
| H16C | 0.4675 | 0.1520 | 0.9459 | 0.062* | |
| C17 | 0.5693 (3) | 0.27012 (13) | 0.7714 (2) | 0.0380 (6) | |
| H17A | 0.5170 | 0.3070 | 0.7135 | 0.057* | |
| H17B | 0.6169 | 0.2366 | 0.7284 | 0.057* | |
| H17C | 0.6449 | 0.2925 | 0.8398 | 0.057* | |
| C18 | 0.3829 (3) | 0.28289 (12) | 0.8791 (2) | 0.0363 (6) | |
| H18A | 0.3321 | 0.3185 | 0.8178 | 0.054* | |
| H18B | 0.4551 | 0.3068 | 0.9480 | 0.054* | |
| H18C | 0.3101 | 0.2576 | 0.9100 | 0.054* | |
| C19 | 0.3527 (3) | 0.19388 (13) | 0.7173 (2) | 0.0407 (7) | |
| H19A | 0.2768 | 0.1710 | 0.7480 | 0.061* | |
| H19B | 0.4039 | 0.1576 | 0.6827 | 0.061* | |
| H19C | 0.3054 | 0.2286 | 0.6531 | 0.061* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0200 (8) | 0.0142 (8) | 0.0316 (9) | 0.0039 (6) | −0.0034 (7) | −0.0003 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0315 (9) | 0.0129 (8) | 0.0342 (9) | 0.0053 (7) | −0.0112 (7) | −0.0103 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0235 (8) | 0.0284 (9) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0075 (7) | −0.0020 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0156 (8) | 0.0316 (9) | 0.0170 (8) | 0.0017 (7) | −0.0018 (6) | 0.0010 (7) |
| O5 | 0.0261 (9) | 0.0126 (7) | 0.0266 (8) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0007 (7) | −0.0038 (6) |
| O6 | 0.0302 (9) | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0286 (9) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0044 (7) | 0.0043 (6) |
| O7 | 0.0165 (8) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0230 (8) | 0.0021 (6) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0015 (6) |
| O8 | 0.0126 (8) | 0.0185 (8) | 0.0333 (9) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0016 (7) | −0.0031 (7) |
| O9 | 0.0148 (8) | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0406 (9) | −0.0036 (6) | 0.0067 (7) | 0.0040 (7) |
| O10 | 0.0218 (8) | 0.0110 (8) | 0.0369 (9) | −0.0001 (6) | 0.0116 (7) | 0.0006 (7) |
| O11 | 0.0166 (8) | 0.0250 (8) | 0.0204 (8) | −0.0002 (6) | −0.0022 (6) | −0.0061 (7) |
| O12 | 0.0100 (7) | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0360 (9) | 0.0011 (7) | 0.0024 (7) | −0.0143 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0145 (11) | 0.0107 (10) | 0.0143 (10) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0065 (9) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0133 (10) | 0.0132 (10) | 0.0123 (10) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0042 (9) | 0.0031 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0135 (11) | 0.0121 (10) | 0.0145 (10) | −0.0021 (8) | 0.0030 (9) | −0.0011 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0169 (11) | 0.0121 (10) | 0.0126 (10) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.0064 (9) | 0.0004 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0130 (10) | 0.0132 (10) | 0.0161 (10) | −0.0005 (8) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0005 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0150 (11) | 0.0124 (10) | 0.0139 (10) | −0.0030 (8) | 0.0044 (9) | −0.0014 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0160 (11) | 0.0141 (11) | 0.0165 (11) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0036 (9) | −0.0016 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0180 (11) | 0.0073 (10) | 0.0215 (12) | −0.0026 (9) | 0.0038 (9) | −0.0008 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0140 (11) | 0.0128 (10) | 0.0227 (11) | −0.0015 (9) | 0.0071 (10) | 0.0013 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0146 (11) | 0.0160 (11) | 0.0161 (11) | 0.0020 (9) | 0.0038 (9) | −0.0022 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0134 (11) | 0.0142 (10) | 0.0122 (10) | 0.0012 (9) | −0.0008 (8) | 0.0023 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0127 (10) | 0.0126 (10) | 0.0129 (10) | −0.0013 (8) | 0.0056 (8) | −0.0016 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0126 (10) | 0.0115 (10) | 0.0153 (10) | 0.0037 (8) | 0.0037 (8) | 0.0030 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0102 (10) | 0.0137 (10) | 0.0134 (10) | −0.0010 (8) | 0.0041 (8) | −0.0001 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0121 (10) | 0.0090 (10) | 0.0199 (12) | 0.0011 (8) | 0.0028 (9) | 0.0045 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0201 (10) | 0.0169 (9) | 0.0256 (10) | −0.0021 (8) | 0.0064 (8) | 0.0002 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0388 (15) | 0.0307 (14) | 0.0453 (16) | 0.0095 (12) | −0.0015 (13) | 0.0120 (12) |
| C17 | 0.0345 (14) | 0.0419 (15) | 0.0453 (16) | −0.0130 (12) | 0.0239 (13) | −0.0084 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0479 (16) | 0.0242 (13) | 0.0494 (17) | 0.0059 (11) | 0.0342 (14) | 0.0049 (11) |
| C19 | 0.0358 (15) | 0.0397 (15) | 0.0369 (15) | −0.0158 (12) | −0.0043 (12) | −0.0037 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C7 | 1.205 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.392 (3) |
| O2—C7 | 1.320 (2) | C5—C10 | 1.507 (3) |
| O2—H2 | 0.959 (10) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C8 | 1.205 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.498 (3) |
| O4—C8 | 1.319 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.391 (3) |
| O4—H4 | 0.941 (10) | C12—C14i | 1.395 (3) |
| O5—C9 | 1.236 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.390 (3) |
| O6—C9 | 1.280 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| O7—C10 | 1.296 (2) | C14—C12i | 1.395 (3) |
| O7—H7 | 0.962 (10) | C14—C15 | 1.503 (3) |
| O8—C10 | 1.231 (2) | N1—C19 | 1.482 (3) |
| O9—C11 | 1.210 (2) | N1—C18 | 1.489 (3) |
| O10—C11 | 1.321 (2) | N1—C16 | 1.489 (3) |
| O10—H10 | 0.938 (10) | N1—C17 | 1.489 (3) |
| O11—C15 | 1.217 (2) | C16—H16A | 0.9800 |
| O12—C15 | 1.298 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9800 |
| O12—H12 | 0.957 (10) | C16—H16C | 0.9800 |
| C1—C6 | 1.380 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.395 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C7 | 1.494 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.395 (3) | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C8 | 1.507 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.392 (3) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C19—H19A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.415 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.9800 |
| C4—C9 | 1.517 (3) | C19—H19C | 0.9800 |
| C7—O2—H2 | 111.2 (15) | C14i—C12—C11 | 120.69 (16) |
| C8—O4—H4 | 112.9 (13) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.57 (17) |
| C10—O7—H7 | 106.7 (12) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.2 |
| C11—O10—H10 | 105.5 (13) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.2 |
| C15—O12—H12 | 114.8 (13) | C13—C14—C12i | 119.26 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.85 (17) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.14 (16) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 120.19 (17) | C12i—C14—C15 | 122.53 (16) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 120.92 (17) | O11—C15—O12 | 126.05 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.21 (17) | O11—C15—C14 | 122.25 (17) |
| C1—C2—C8 | 122.22 (16) | O12—C15—C14 | 111.59 (16) |
| C3—C2—C8 | 118.52 (17) | C19—N1—C18 | 109.77 (18) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.91 (17) | C19—N1—C16 | 109.59 (17) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.0 | C18—N1—C16 | 109.03 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.0 | C19—N1—C17 | 108.99 (17) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.80 (17) | C18—N1—C17 | 109.11 (17) |
| C3—C4—C9 | 115.37 (17) | C16—N1—C17 | 110.34 (18) |
| C5—C4—C9 | 125.82 (17) | N1—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.12 (17) | N1—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 113.39 (17) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C10 | 128.46 (17) | N1—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 123.02 (18) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 118.5 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 118.5 | N1—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—O2 | 124.56 (18) | N1—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 123.77 (18) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 111.67 (17) | N1—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O3—C8—O4 | 126.17 (19) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O3—C8—C2 | 123.43 (18) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O4—C8—C2 | 110.35 (16) | N1—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| O5—C9—O6 | 123.75 (17) | N1—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O5—C9—C4 | 118.97 (17) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O6—C9—C4 | 117.23 (17) | N1—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O8—C10—O7 | 120.75 (18) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O8—C10—C5 | 118.01 (17) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O7—C10—C5 | 121.19 (17) | N1—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| O9—C11—O10 | 124.15 (18) | N1—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| O9—C11—C12 | 122.01 (17) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| O10—C11—C12 | 113.81 (16) | N1—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C14i | 119.16 (16) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 119.71 (16) | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.7 (3) | C1—C2—C8—O4 | −111.46 (19) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −175.72 (17) | C3—C2—C8—O4 | 70.9 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C8 | −175.85 (17) | C3—C4—C9—O5 | −28.3 (3) |
| C7—C1—C2—C8 | 6.7 (3) | C5—C4—C9—O5 | 152.83 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −3.6 (3) | C3—C4—C9—O6 | 149.16 (18) |
| C8—C2—C3—C4 | 174.08 (17) | C5—C4—C9—O6 | −29.7 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 2.6 (3) | C6—C5—C10—O8 | 22.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | −176.26 (17) | C4—C5—C10—O8 | −155.63 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.1 (3) | C6—C5—C10—O7 | −155.23 (17) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | 178.88 (17) | C4—C5—C10—O7 | 26.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | 177.89 (18) | O9—C11—C12—C13 | −146.62 (19) |
| C9—C4—C5—C10 | −3.3 (3) | O10—C11—C12—C13 | 31.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.0 (3) | O9—C11—C12—C14i | 25.7 (3) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 178.48 (17) | O10—C11—C12—C14i | −156.07 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.9 (3) | C14i—C12—C13—C14 | −1.2 (3) |
| C10—C5—C6—C1 | 179.95 (17) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 171.26 (17) |
| C6—C1—C7—O1 | −163.87 (19) | C12—C13—C14—C12i | 1.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | 13.5 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −175.65 (17) |
| C6—C1—C7—O2 | 16.4 (3) | C13—C14—C15—O11 | 123.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | −166.19 (17) | C12i—C14—C15—O11 | −53.6 (3) |
| C1—C2—C8—O3 | 71.0 (3) | C13—C14—C15—O12 | −53.2 (2) |
| C3—C2—C8—O3 | −106.6 (2) | C12i—C14—C15—O12 | 130.02 (19) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O6ii | 0.96 (1) | 1.64 (1) | 2.5885 (18) | 171 (2) |
| O4—H4···O11iii | 0.94 (1) | 1.81 (1) | 2.7166 (19) | 162 (2) |
| O7—H7···O6 | 0.96 (1) | 1.48 (1) | 2.4334 (19) | 169 (2) |
| O10—H10···O5iv | 0.94 (1) | 1.76 (1) | 2.6890 (18) | 168 (2) |
| O12—H12···O8v | 0.96 (1) | 1.60 (1) | 2.5308 (19) | 163 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x+1, y, z+1; (iv) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (v) −x−1, −y, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SJ2444).
References
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Version 3.1d. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2001). SHELXTL. Version 6.12. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2005). SAINT-Plus Version 7.23a. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2006). APEX2. Version 2.1-RC13. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cunha-Silva, L., Mafra, L., Ananias, D., Carlos, L. D., Rocha, J. & Paz, F. A. A. (2007). Chem. Mater.19, 3527–3538.
- Dale, S. H., Elsegood, M. R. J., Hemmings, M. & Wilkinson, A. L. (2004). CrystEngComm, 6, 207–214.
- Fabelo, O., Cañadillas-Delgado, L., Delgado, F. S., Lorenzo-Luis, P., Laz, M. M., Julve, M. & Ruiz-Pérez, C. (2005). Cryst. Growth Des.5, 1163–1167.
- Paz, F. A. A., Bond, A. D., Khimyak, Y. Z. & Klinowski, J. (2002). New J. Chem.26, 381–383.
- Paz, F. A. A. & Klinowski, J. (2003). CrystEngComm, 5, 238–244.
- Ruiz-Pérez, C., Loreno-Luis, P. A., Hernández-Molina, M., Laz, M. M., Gili, P. & Julve, M. (2004). Cryst. Growth Des.4, 57–61.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1998). SADABS. Version 2.01. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Shi, F.-N., Cunha-Silva, L., Sá Ferreira, R. A., Mafra, L., Trindade, T., Carlos, L. D., Paz, F. A. A. & Rocha, J. (2007). J. Am. Chem. Soc. doi:10.1021/ja074119k. In the press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Steed, J. W. & Atwood, J. L. (2000). Supramolecular Chemistry. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807062381/sj2444sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807062381/sj2444Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report