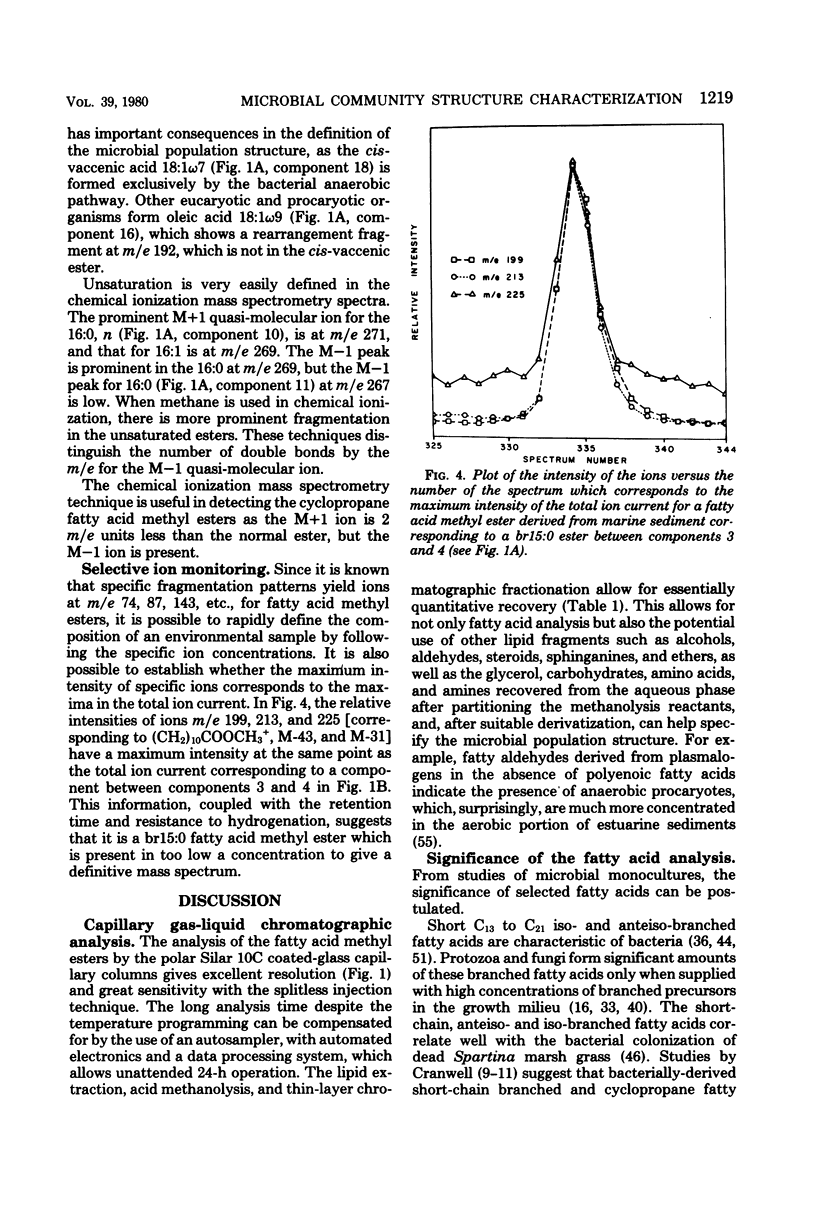
Abstract
Fatty acids are a widely studied group of lipids of sufficient taxonomic diversity to be useful in defining microbial community structure. The extraordinary resolution of glass capillary gas-liquid chromatography can be utilized to separate and tentatively identify large numbers of fatty acid methyl esters derived from the lipids of estuarine detritus and marine benthic microbiota without the bias of selective methods requiring culture or recovery of the microbes. The gas-liquid chromatographic analyses are both reproducible and highly sensitive, and the recovery of fatty acids is quantitative. The analyses can be automated, and the diagnostic technique of mass spectral fragmentation analysis can be readily applied. Splitless injection on glass capillary gas chromatographic columns detected by mass spectral selective ion monitoring provides an ultrasensitive and definitive monitoring system. Reciprocal mixtures of bacteria and fungi, when extracted and analyzed, showed progressive changes of distinctive fatty acid methyl esters derived from the lipids. By manipulating the environment of an estuarine detrital microbial community with antibiotics and culture conditions, it was possible to produce a community greatly enriched in eucaryotic fungi, as evidenced by scanning electron microscopic morphology. The fatty acid methyl esters from the lipids in the fungus-enriched detritus showed enrichment of the C18 dienoic and the C18 and C20 polyenoic esters. Manipulation of the detrital microbiota that increased the procaryotic population resulted in an absence of large structures typical of fungal mycelia or diatoms, as evidenced by scanning electron microscopy, and a significantly larger proportion of anteiso- and isobranched C15 fatty acid esters, C17 cyclopropane fatty acid esters, and the cis-vaccenic isomer of the C18 monoenoic fatty acid esters. As determined by these techniques, a marine settling community showed greater differences in bacterial as contrasted to microeucaryotic populations when compared with the microbial communities of benthic cores.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobbie R. J., Morrison S. J., White D. C. Effects of substrate biodegradability on the mass and activity of the associated estuarine microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):179–184. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.179-184.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon J. J., de Leeuw J. W., Hoek G. J., Vosjan J. H. Significance and taxonomic value of iso and anteiso monoenoic fatty acids and branded beta-hydroxy acids in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1183-1191.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio S. D., Mayberry W. R., White D. C. Muramic Acid assay in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):349–350. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.349-350.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulco A. J. The biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids by bacilli. II. Temperature-dependent biosynthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun 10;245(11):2985–2990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckers H., Melcher F. W., Schloeder U. SP 2340 in the glass capillary chromatography of fatty acid methyl esters. J Chromatogr. 1977 Jun 11;136(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)86285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORN E. D., GREENBLATT C. L., LEES A. M. SYNTHESIS OF UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS IN THE SLIME MOLD PHYSARUM POLYCEPHALUM AND THE ZOOFLAGELLATES LEISHMANIA TARENTOLAE, TRYPANOSOMA LEWISI, AND CRITHIDIA SP.: A COMPARATIVE STUDY. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. Bacterial lipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1964;2:17–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. N. Fatty acid composition of unicellular strains of blue-green algae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):827–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.827-834.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. N., Rippka R., Stanier R. Y. Fatty acid composition and physiological properties of some filamentous blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;83(3):216–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00645123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. D., White D. C. Muramic acid as a measure of microbial biomass in estuarine and marine samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):777–783. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.777-783.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. D., White D. C., Taylor C. W. Use of lipid composition and metabolism to examine structure and activity of estuarine detrital microflora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1177–1183. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1177-1183.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knivett V. A., Cullen J. Some factors affecting cyclopropane acid formation in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):771–776. doi: 10.1042/bj0960771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier M. P. Lipids in bacterial taxonomy - a taxonomist's view. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):109–210. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr A. G., Ingraham J. L. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE COMPOSITION OF FATTY ACIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1260-1267.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H., Holz G. G., Jr Biosynthesis of lipids by kinetoplastid flagellates. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):5000–5007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary W. M. The chemistry of microbial lipids. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1975 Oct;4(1):41–63. doi: 10.3109/10408417509105486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. L., Van Baalen C., Maurer L. Fatty acids in eleven species of blue-green algae: geochemical significance. Science. 1967 Feb 10;155(3763):707–708. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3763.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N. Lipid composition as a guide to the classification of bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1974;17(0):63–108. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70555-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. The fatty acid composition of some entomophthoraceae : II. The occurrence of branched-chain fatty acids inConidiobolus denaesporus Drechsl. Lipids. 1968 Jul;3(4):368–372. doi: 10.1007/BF02530941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Cox R. H. Indentification and localization of the fatty acids in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1079–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1079-1088.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]