Abstract
In the title compound, {(C10H12N3O3S)2[CdCl4]·H2O}n, the CdII atom is five-coordinate with a distorted trigonal–bipyramidal geometry formed by chloride ions. The Cd atom and two of the Cl atoms lie on a mirror plane. The cation is protonated on the amino group N atom; it is not coordinated to cadmium, but is hydrogen bonded to the chlorido ligands. Each water molecule bridges two chlorido ligands, generating ring motifs along the –Cd—Cl—Cd– chains. The isoxazole unit and the amide groups are linked through a pair of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds. The crystal structure is stabilized by N—H⋯O, O—H⋯Cl, C—H⋯N, N—H⋯Cl and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Abramenko & Sergienko (2002 ▶); Bettinetti et al. (1982 ▶); Dai et al. (2002 ▶); Fawcett et al. (1978 ▶); Haridas et al. (1984 ▶); Kagi & Vallee (1960 ▶); Kálmán et al. (1981 ▶); Kendi et al. (2000 ▶); Schaffers & Keszler (1993 ▶); Singh et al. (1984 ▶); Subashini et al. (2007 ▶); Subha Nandhini et al. (2002 ▶); Takasuka & Nakai (2001 ▶); Tao et al. (2003 ▶); Yukawa et al. (1982 ▶).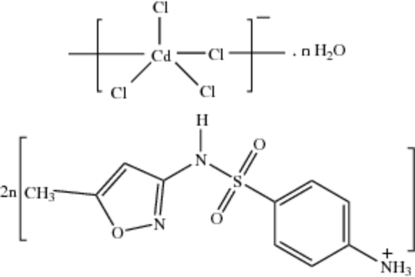
Experimental
Crystal data
(C10H12N3O3S)2[CdCl4]·H2O
M r = 780.82
Orthorhombic,
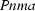
a = 15.088 (2) Å
b = 35.028 (3) Å
c = 5.562 (3) Å
V = 2939.5 (17) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 11.07 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.19 × 0.16 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Siemens AED single-crystal diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.227, T max = 0.306 (expected range = 0.157–0.212)
2834 measured reflections
2834 independent reflections
2470 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.111
S = 1.05
2834 reflections
203 parameters
4 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 1.04 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.64 e Å−3
Data collection: local program (Belletti et al., 1993 ▶); cell refinement: local program; data reduction: local program; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067190/fi2052sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067190/fi2052Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| Cd1—Cl2 | 2.4828 (17) |
| Cd1—Cl3 | 2.469 (2) |
| Cd1—Cl1i | 2.902 (2) |
| Cd1—Cl2ii | 2.4828 (17) |
| Cd1—Cl1 | 2.6688 (19) |
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl2ii | 92.51 (3) |
| Cl2—Cd1—Cl3 | 113.69 (3) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—Cl2 | 84.90 (3) |
| Cl2—Cd1—Cl2ii | 131.63 (4) |
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl2 | 92.51 (3) |
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl3 | 95.12 (5) |
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl1i | 173.60 (5) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—Cl2ii | 84.90 (3) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—Cl3 | 91.27 (5) |
| Cl2ii—Cd1—Cl3 | 113.69 (3) |
| Cd1—Cl1—Cd1iii | 173.60 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 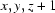 ; (ii)
; (ii) 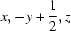 ; (iii)
; (iii) 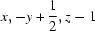 .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1W—H1W⋯Cl3i | 0.96 | 2.11 | 3.035 (5) | 161 |
| O1W—H2W⋯Cl3 | 0.95 | 2.11 | 3.036 (5) | 164 |
| N4—H4A⋯Cl2iv | 0.94 (5) | 2.26 (5) | 3.184 (4) | 171 (4) |
| N4—H4B⋯O1Wv | 0.91 (5) | 1.86 (5) | 2.758 (4) | 169 (4) |
| N4—H4B⋯O1Wiii | 0.91 (5) | 1.86 (5) | 2.758 (4) | 169 (4) |
| N4—H4C⋯Cl2vi | 0.85 (4) | 2.49 (4) | 3.196 (4) | 141 (4) |
| N4—H4C⋯O1vi | 0.85 (4) | 2.33 (5) | 2.871 (4) | 122 (4) |
| N7—H7⋯N8vii | 0.86 | 2.58 | 3.188 (5) | 129 |
| C2—H2⋯O2 | 0.93 | 2.55 | 2.911 (4) | 103 |
| C9—H9⋯O2 | 0.93 | 2.50 | 2.991 (4) | 113 |
| C9—H9⋯N8i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.354 (5) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 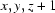 ; (iii)
; (iii) 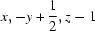 ; (iv)
; (iv) 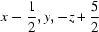 ; (v)
; (v) 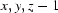 ; (vi)
; (vi) 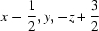 ; (vii)
; (vii) 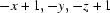 .
.
Acknowledgments
AS thanks Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India, for the award of a Research Studentship (Ref. CCCD/ PhD-2/15504/2004).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Polynuclear d10– metal complexes have been found to exhibit intriguing structural and photoluminescent properties (Dai et al., 2002; Tao et al., 2003). Chloride-bridged cadmium(II) polymeric complexes are of considerable interest, because they may act as photoactive materials. Cadmium is found to occur naturally in at least one protein, metallothionein (Kagi & Vallee, 1960). Sulfonamides constitute an important class of antimicrobial agents. The drug, 4-[5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)aminosulfonyl] aniline [Sulfamethoxazole (SMZ)] prevents the formation of dihydrofolic acid, a compound that bacteria must be able to make in order to survive. The two polymorphs of SMZ (Bettinetti et al., 1982) have already been reported in literature. Recently, the crystal structure of sulfamethoxazole hydrochloride (Subashini et al., 2007) has been reported from our laboratory. X-ray analysis reveals that (I) possesses a polynuclear structure with the Cd atom and two of the Cl atoms on a special positions(m). The Cd atom has trigonal bipyramidal coordination geometry formed by five chloride anions. The Cd1—Cl1, Cd1—Cl2, Cd1—Cl3, and Cd—Cli bond lengths are 2.669 (2), 2.4828 (17), 2.469 (2) and 2.902 (2)Å respectively. The mean Cd—Cl distance, 2.630 (2) Å, is in agreement with the corresponding distances reported in the structures of complexes of CdCl2 with 4-hydroxy-L-proline [2.620 (2) Å] (Yukawa et al., 1982), β-alanine [2.619 (5) Å] (Subha Nandhini et al., 2002) and L– alanine [2.61 (1) Å] (Schaffers & Keszler, 1993). The Cd—Cl distances reported for tetrameric cadmium(II) complex (Fawcett et al., 1978), viz. 2.946 (6) and 2.946 (5) Å, are longer compared to those in the present structure.
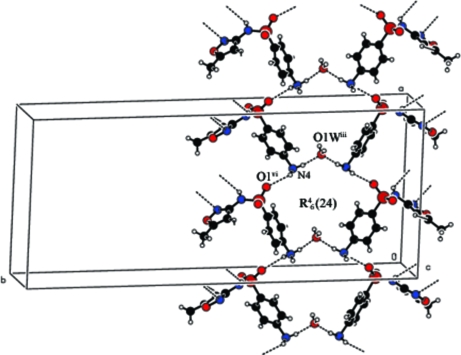
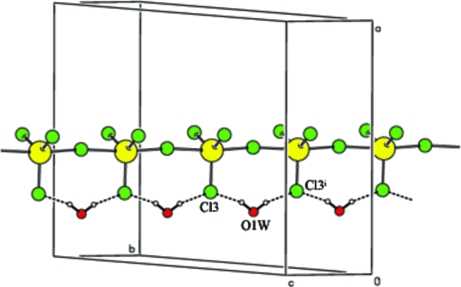
The atoms around the sulfonamide S atom in (I) are arranged in a slightly distorted tetrahedral configuration. The largest deviation is in the angle O1—S1—O2 [121.22 (17)°], but it confirms to the non-tetrahedral nature commonly observed in sulfonamides (Haridas et al., 1984; Kendi et al., 2000; Takasuka & Nakai, 2001). The S1—C1 distance of 1.760 (3)Å (I) is a normal single-bond value and matches well with those observed in other sulfonamides (Singh et al., 1984; Abramenko & Sergienko, 2002). In the present structure the dihedral angle between the isoxazole and amino phenyl plane is found to be 88.31 (18)°, whereas in neutral SMZ structures the dihedral angles are 73.1 (5)° for Form 1 and 79.6 (6)° for Form 2 (Bettinetti et al., 1982) respectively. The two torsion angles τ1 (C—C—S—N) and τ2 (C—S—N—C) defining the conformation of the sulfonamide group are reported to lie in the range 70–120° and 60–90°, respectively (Kálmán et al., 1981). The torsion angles τ1 is -81.9 (3)° (C6—C1—S1—N7) and τ2 is -73.6 (3)° (C1—S1—N7—C8). In neutral forms, the torsion angles τ1 are -76.5 (9)° (Form 1) and -78.5 (5)° (Form 2). The torsion angles τ2 are -56.1 (4)° in form 1 and -61.5 (8)° in form 2. In sulfamethoxazole hydrochloride the torsion angles are (τ1) 73.2 (3)° and (τ2) -71.2 (3)° (Subashini et al., 2007). The cation is protonated on the amine nitrogen (N4) atom. The drug is not coordinated to cadmium and the amino group (N4) of the drug is hydrogen bonded to the chloride ions. 4-ammonio group acts as a bridge between the sulfonamide oxygen atom and water molecules. Four smz cations and two water molecules are connected through N—H···O hydrogen bonds forming a 24 membered ring with graph-set R46(24) (Fig. 2). The isoxazole moiety and the amide groups are paired through a pair of N—H···N hydrogen bonds. A C—H···N hydrogen bond is observed between isoxazole carbon (C9) and nitrogen (N8). The water O1W atom does not participate in coordination with cadmium. Each water molecule bridges two chloride ions generating ring motifs along the –Cd—Cl—Cd- chains as shown in Fig 3.
Experimental
Hot ethanol solution of sulfamethoxazole (Qualigens, 63 mg) and an aqueous solution of cadmium chloride (CdCl2.2H2O, 98%) (SISCO CHEM, 54 mg) were mixed in a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio. On slow evaporation light brown prismatic crystals of the title complex were formed.
Refinement
The hydrogen atoms of the aromatic groups were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H=0.93–0.96Å and Uiso(H)= 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl hydrogen atoms and 1.2 Ueq(C) for all other hydrogen atoms. The hydrogen atoms of the water molecule and ammonio group (N4) were located in a difference Fourier maps and were refined, subject to bond length restraints of 0.96 Å(O—H), 1.5Å (H..H) and 0.86Å for ammonio N—H(H4C). The highest peak in the final difference map was found at a distance of 1.04Å from Cd1 and the deepest hole was -0.64Å from Cl1.
Figures
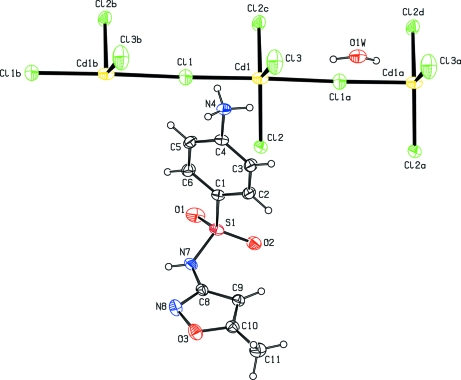
Fig. 1.
An ORTEP view of the asymmetric unit of (I) showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. Symmetry codes: (i)x,y,z + 1; (ii)x,-y + 1/2,z.
Fig. 2.
Packing view of compound (I). Symmetry codes: (iii)x,-y + 1/2,z - 1; (vi) x - 1/2,y,-z + 3/2.
Fig. 3.
Water molecules bridging chloride ions generating ring motifs along –Cd—Cl—Cd chains. Symmetry codes: (i) x,y,z + 1.
Crystal data
| (C10H12N3O3S)2[CdCl4]·H2O | F000 = 1568 |
| Mr = 780.82 | Dx = 1.764 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pnma | Cu Kα radiation λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2n | Cell parameters from 45 reflections |
| a = 15.088 (2) Å | θ = 5.1–70.1º |
| b = 35.028 (3) Å | µ = 11.07 mm−1 |
| c = 5.562 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| V = 2939.5 (17) Å3 | Prism-like, light-brown |
| Z = 4 | 0.19 × 0.16 × 0.14 mm |
Data collection
| Siemens AED single-crystal diffractometer | 2834 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine- focus sealed tube | 2470 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.0000 |
| T = 293 K | θmax = 70.1º |
| ω–2θ scans | θmin = 5.1º |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan(North et al., 1968) | h = −2→18 |
| Tmin = 0.227, Tmax = 0.306 | k = −2→42 |
| 2834 measured reflections | l = −6→6 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.111 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0706P)2 + 2.0804P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 2834 reflections | Δρmax = 1.04 e Å−3 |
| 203 parameters | Δρmin = −0.64 e Å−3 |
| 4 restraints | Extinction correction: shelxl, FC*=KFC[1+0.001XFC2Λ3/SIN(2Θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.00108 (10) |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All e.s.d.'s are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2> σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.47494 (5) | 0.09076 (2) | 0.89098 (17) | 0.0348 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.54498 (17) | 0.11258 (8) | 0.7896 (6) | 0.0526 (9) | |
| O2 | 0.47844 (16) | 0.07794 (8) | 1.1338 (5) | 0.0433 (8) | |
| O3 | 0.34703 (17) | −0.03052 (8) | 0.6783 (5) | 0.0465 (8) | |
| N4 | 0.1435 (2) | 0.18175 (9) | 0.7834 (6) | 0.0367 (9) | |
| N7 | 0.46903 (19) | 0.05310 (9) | 0.7171 (5) | 0.0383 (9) | |
| N8 | 0.39733 (19) | −0.00044 (9) | 0.5779 (6) | 0.0450 (10) | |
| C1 | 0.3753 (2) | 0.11622 (9) | 0.8542 (6) | 0.0311 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.3077 (2) | 0.11213 (9) | 1.0198 (6) | 0.0376 (9) | |
| C3 | 0.2303 (2) | 0.13307 (10) | 0.9951 (6) | 0.0380 (10) | |
| C4 | 0.2224 (2) | 0.15783 (9) | 0.8048 (6) | 0.0322 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.2887 (2) | 0.16153 (10) | 0.6346 (7) | 0.0400 (10) | |
| C6 | 0.3658 (2) | 0.14054 (10) | 0.6588 (6) | 0.0403 (10) | |
| C8 | 0.4174 (2) | 0.02120 (9) | 0.7613 (6) | 0.0315 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.3822 (2) | 0.00750 (9) | 0.9784 (6) | 0.0348 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.3395 (2) | −0.02479 (9) | 0.9160 (6) | 0.0345 (9) | |
| C11 | 0.2894 (3) | −0.05362 (11) | 1.0534 (8) | 0.0500 (11) | |
| Cd1 | 0.47373 (2) | 0.25000 | 1.18772 (7) | 0.0430 (1) | |
| Cl1 | 0.48401 (11) | 0.25000 | 0.7087 (2) | 0.0541 (5) | |
| Cl2 | 0.54023 (7) | 0.18534 (3) | 1.21780 (16) | 0.0511 (3) | |
| Cl3 | 0.31017 (11) | 0.25000 | 1.2016 (3) | 0.0795 (7) | |
| O1W | 0.2295 (3) | 0.25000 | 1.7017 (8) | 0.0513 (14) | |
| H2 | 0.31420 | 0.09530 | 1.14790 | 0.0450* | |
| H3 | 0.18440 | 0.13040 | 1.10560 | 0.0460* | |
| H4A | 0.119 (3) | 0.1815 (15) | 0.938 (10) | 0.073 (15)* | |
| H4B | 0.165 (3) | 0.2055 (13) | 0.753 (7) | 0.046 (11)* | |
| H4C | 0.118 (3) | 0.1707 (14) | 0.666 (7) | 0.076 (17)* | |
| H5 | 0.28150 | 0.17800 | 0.50500 | 0.0480* | |
| H6 | 0.41080 | 0.14270 | 0.54540 | 0.0480* | |
| H7 | 0.50050 | 0.05320 | 0.58820 | 0.0460* | |
| H9 | 0.38720 | 0.01830 | 1.13060 | 0.0420* | |
| H11A | 0.22950 | −0.05460 | 0.99580 | 0.0750* | |
| H11B | 0.28950 | −0.04690 | 1.22070 | 0.0750* | |
| H11C | 0.31670 | −0.07820 | 1.03310 | 0.0750* | |
| H1W | 0.26750 | 0.25000 | 1.83940 | 0.13 (4)* | |
| H2W | 0.26530 | 0.25000 | 1.56040 | 0.08 (2)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0272 (4) | 0.0305 (4) | 0.0468 (5) | 0.0038 (3) | −0.0006 (3) | −0.0050 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0300 (12) | 0.0449 (15) | 0.083 (2) | −0.0033 (11) | 0.0069 (12) | −0.0036 (14) |
| O2 | 0.0447 (13) | 0.0426 (14) | 0.0427 (13) | 0.0104 (11) | −0.0108 (11) | −0.0063 (11) |
| O3 | 0.0442 (14) | 0.0511 (15) | 0.0441 (14) | −0.0099 (12) | 0.0004 (11) | −0.0139 (11) |
| N4 | 0.0343 (15) | 0.0302 (15) | 0.0456 (18) | 0.0058 (12) | −0.0034 (13) | −0.0003 (13) |
| N7 | 0.0427 (16) | 0.0326 (15) | 0.0395 (15) | 0.0050 (11) | 0.0113 (12) | −0.0059 (12) |
| N8 | 0.0426 (15) | 0.0549 (19) | 0.0374 (16) | −0.0080 (14) | 0.0044 (13) | −0.0087 (14) |
| C1 | 0.0283 (14) | 0.0255 (14) | 0.0394 (16) | 0.0020 (12) | 0.0004 (12) | −0.0023 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0384 (16) | 0.0345 (16) | 0.0400 (17) | 0.0067 (14) | 0.0072 (14) | 0.0087 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0338 (16) | 0.0388 (17) | 0.0415 (17) | 0.0041 (13) | 0.0080 (14) | 0.0067 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0295 (15) | 0.0242 (15) | 0.0428 (17) | 0.0005 (11) | −0.0017 (13) | −0.0026 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0436 (18) | 0.0335 (16) | 0.0429 (17) | 0.0035 (14) | 0.0070 (15) | 0.0110 (15) |
| C6 | 0.0387 (17) | 0.0375 (18) | 0.0447 (19) | 0.0020 (14) | 0.0112 (15) | 0.0072 (15) |
| C8 | 0.0287 (14) | 0.0343 (15) | 0.0314 (15) | 0.0091 (12) | −0.0009 (12) | −0.0036 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0388 (16) | 0.0329 (16) | 0.0328 (16) | 0.0068 (13) | −0.0004 (13) | −0.0014 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0292 (14) | 0.0356 (16) | 0.0388 (17) | 0.0064 (12) | −0.0008 (13) | −0.0018 (14) |
| C11 | 0.0441 (19) | 0.045 (2) | 0.061 (2) | −0.0010 (16) | 0.0025 (18) | 0.0030 (18) |
| Cd1 | 0.0368 (2) | 0.0306 (2) | 0.0615 (3) | 0.0000 | 0.0019 (2) | 0.0000 |
| Cl1 | 0.0672 (9) | 0.0529 (8) | 0.0422 (7) | 0.0000 | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0000 |
| Cl2 | 0.0724 (6) | 0.0427 (5) | 0.0383 (5) | 0.0192 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | −0.0018 (4) |
| Cl3 | 0.0402 (7) | 0.1403 (19) | 0.0581 (9) | 0.0000 | 0.0057 (6) | 0.0000 |
| O1W | 0.052 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.065 (3) | 0.0000 | 0.000 (2) | 0.0000 |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cd1—Cl2 | 2.4828 (17) | N7—H7 | 0.8599 |
| Cd1—Cl3 | 2.469 (2) | C1—C6 | 1.388 (5) |
| Cd1—Cl1i | 2.902 (2) | C1—C2 | 1.382 (5) |
| Cd1—Cl2ii | 2.4828 (17) | C2—C3 | 1.386 (4) |
| Cd1—Cl1 | 2.6688 (19) | C3—C4 | 1.374 (5) |
| S1—C1 | 1.760 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.383 (5) |
| S1—O1 | 1.421 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.383 (5) |
| S1—O2 | 1.424 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.404 (5) |
| S1—N7 | 1.638 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.347 (4) |
| O3—N8 | 1.413 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.475 (5) |
| O3—C10 | 1.342 (4) | C2—H2 | 0.9299 |
| O1W—H1W | 0.9567 | C3—H3 | 0.9306 |
| O1W—H2W | 0.9536 | C5—H5 | 0.9296 |
| N4—C4 | 1.461 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9298 |
| N7—C8 | 1.384 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9303 |
| N8—C8 | 1.306 (5) | C11—H11A | 0.9595 |
| N4—H4A | 0.94 (5) | C11—H11B | 0.9598 |
| N4—H4B | 0.91 (5) | C11—H11C | 0.9611 |
| N4—H4C | 0.85 (4) | ||
| Cd1···H1Wiii | 3.6654 | N8···H7xi | 2.5778 |
| Cd1···H2W | 3.7665 | C3···O1xii | 3.293 (5) |
| Cd1···H4Aiv | 3.86 (5) | C4···O1xii | 3.155 (4) |
| Cd1···H4Av | 3.86 (5) | C4···O1Wvi | 3.281 (4) |
| Cd1···H1Wvi | 3.6654 | C4···O1Wiii | 3.281 (4) |
| Cd1···H2Wii | 3.7665 | C5···O1Wvi | 3.247 (4) |
| Cl1···Cd1iii | 2.902 (2) | C5···O1Wiii | 3.247 (4) |
| Cl1···N4vii | 3.392 (4) | C8···C11xv | 3.516 (6) |
| Cl1···N4viii | 3.392 (4) | C8···N8xi | 3.450 (5) |
| Cl1···Cl2iii | 3.648 (2) | C8···C9x | 3.500 (5) |
| Cl2···N4vii | 3.196 (4) | C9···O2 | 2.991 (4) |
| Cl2···N4v | 3.184 (4) | C9···N8i | 3.354 (5) |
| Cl3···O1Wiii | 3.035 (5) | C9···C8x | 3.500 (5) |
| Cl3···O1Wvi | 3.035 (5) | C10···O2x | 3.330 (4) |
| Cl3···O1Wii | 3.036 (5) | C11···C8xvi | 3.516 (6) |
| Cl3···O1W | 3.036 (5) | C11···N8xvi | 3.397 (6) |
| Cl2···H3v | 3.0659 | C11···O1x | 3.357 (5) |
| Cl2···H4Cvii | 2.49 (4) | C8···H11Axv | 2.9089 |
| Cl2···H4Av | 2.26 (5) | H1W···H4Bi | 2.2477 |
| Cl2···H6i | 3.0601 | H1W···Cd1i | 3.6654 |
| Cl3···H1Wiii | 2.1149 | H1W···H4Bix | 2.2477 |
| Cl3···H2W | 2.1074 | H1W···Cl3i | 2.1149 |
| Cl3···H5i | 3.0652 | H1W···Cl3i | 2.1149 |
| Cl3···H5ix | 3.0652 | H1W···Cd1i | 3.6654 |
| Cl3···H2Wii | 2.1074 | H2···O2 | 2.5528 |
| Cl3···H1Wvi | 2.1149 | H2···H11Axvi | 2.4923 |
| S1···H9 | 3.1577 | H2W···Cd1 | 3.7665 |
| O1···C11x | 3.357 (5) | H2W···Cl3 | 2.1074 |
| O1···C3vii | 3.293 (5) | H2W···H4Bix | 2.4223 |
| O1···N4vii | 2.871 (4) | H2W···H5ix | 2.5525 |
| O1···C4vii | 3.155 (4) | H2W···Cl3 | 2.1074 |
| O1W···N4i | 2.758 (4) | H2W···H4Bi | 2.4223 |
| O1W···C4i | 3.281 (4) | H2W···H5i | 2.5525 |
| O1W···Cl3i | 3.035 (5) | H2W···Cd1 | 3.7665 |
| O1W···Cl3 | 3.036 (5) | H3···H4A | 2.2464 |
| O1W···C5ix | 3.247 (4) | H3···Cl2xiv | 3.0659 |
| O1W···C5i | 3.247 (4) | H4A···H3 | 2.2464 |
| O1W···Cl3i | 3.035 (5) | H4A···Cd1xiv | 3.86 (5) |
| O1W···N4ix | 2.758 (4) | H4A···Cl2xiv | 2.26 (5) |
| O1W···Cl3 | 3.036 (5) | H4A···Cd1xvii | 3.86 (5) |
| O1W···C4ix | 3.281 (4) | H4B···H5 | 2.4332 |
| O2···C9 | 2.991 (4) | H4B···O1Wvi | 1.86 (5) |
| O2···C10x | 3.330 (4) | H4B···O1Wiii | 1.86 (5) |
| O1···H4Cvii | 2.33 (5) | H4B···H1Wiii | 2.2477 |
| O1···H11Cx | 2.6035 | H4B···H2Wiii | 2.4223 |
| O1···H6 | 2.6564 | H4B···H1Wvi | 2.2477 |
| O1W···H5ix | 2.8589 | H4B···H2Wvi | 2.4223 |
| O1W···H5i | 2.8589 | H4C···Cl2xii | 2.49 (4) |
| O1W···H4Bix | 1.86 (5) | H4C···O1xii | 2.33 (5) |
| O1W···H4Bi | 1.86 (5) | H5···H2Wiii | 2.5525 |
| O2···H7i | 2.6925 | H5···Cl3iii | 3.0652 |
| O2···H2 | 2.5528 | H5···O1Wiii | 2.8589 |
| O2···H9 | 2.5019 | H5···Cl3vi | 3.0652 |
| O3···H11Biii | 2.7496 | H5···O1Wvi | 2.8589 |
| O3···H7xi | 2.8496 | H5···H4B | 2.4332 |
| N4···Cl1xii | 3.392 (4) | H5···H2Wvi | 2.5525 |
| N4···Cl2xii | 3.196 (4) | H6···O1 | 2.6564 |
| N4···Cl1xiii | 3.392 (4) | H6···Cl2iii | 3.0601 |
| N4···O1xii | 2.871 (4) | H7···O3xi | 2.8496 |
| N4···O1Wvi | 2.758 (4) | H7···N8xi | 2.5778 |
| N4···Cl2xiv | 3.184 (4) | H7···O2iii | 2.6925 |
| N4···O1Wiii | 2.758 (4) | H9···O2 | 2.5019 |
| N7···N8xi | 3.188 (5) | H9···N8i | 2.5776 |
| N8···C8xi | 3.450 (5) | H9···S1 | 3.1577 |
| N8···C9iii | 3.354 (5) | H11A···N8xvi | 2.7545 |
| N8···N7xi | 3.188 (5) | H11A···C8xvi | 2.9089 |
| N8···C11xv | 3.397 (6) | H11A···H2xv | 2.4923 |
| N8···N8xi | 3.217 (4) | H11B···O3i | 2.7496 |
| N8···H11Axv | 2.7545 | H11C···O1x | 2.6035 |
| N8···H9iii | 2.5776 | ||
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl2ii | 92.51 (3) | S1—C1—C2 | 120.0 (2) |
| Cl2—Cd1—Cl3 | 113.69 (3) | C1—C2—C3 | 120.1 (3) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—Cl2 | 84.90 (3) | C2—C3—C4 | 118.9 (3) |
| Cl2—Cd1—Cl2ii | 131.63 (4) | N4—C4—C3 | 119.7 (3) |
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl2 | 92.51 (3) | C3—C4—C5 | 121.6 (3) |
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl3 | 95.12 (5) | N4—C4—C5 | 118.7 (3) |
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl1i | 173.60 (5) | C4—C5—C6 | 119.5 (3) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—Cl2ii | 84.90 (3) | C1—C6—C5 | 119.3 (3) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—Cl3 | 91.27 (5) | N7—C8—C9 | 129.9 (3) |
| Cl2ii—Cd1—Cl3 | 113.69 (3) | N8—C8—C9 | 112.7 (3) |
| Cd1—Cl1—Cd1vi | 173.60 (7) | N7—C8—N8 | 117.4 (3) |
| O1—S1—N7 | 103.85 (17) | C8—C9—C10 | 104.3 (3) |
| O1—S1—C1 | 108.46 (16) | C9—C10—C11 | 133.4 (3) |
| O2—S1—N7 | 107.94 (16) | O3—C10—C11 | 116.8 (3) |
| O1—S1—O2 | 121.22 (17) | O3—C10—C9 | 109.8 (3) |
| O2—S1—C1 | 107.56 (16) | C1—C2—H2 | 119.91 |
| N7—S1—C1 | 107.03 (15) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.02 |
| N8—O3—C10 | 108.9 (3) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.56 |
| H1W—O1W—H2W | 108.68 | C4—C3—H3 | 120.52 |
| S1—N7—C8 | 125.2 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.25 |
| O3—N8—C8 | 104.4 (3) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.28 |
| H4A—N4—H4C | 121 (4) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.37 |
| C4—N4—H4A | 104 (3) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.33 |
| H4B—N4—H4C | 116 (4) | C8—C9—H9 | 127.81 |
| H4A—N4—H4B | 109 (4) | C10—C9—H9 | 127.93 |
| C4—N4—H4B | 104 (3) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.45 |
| C4—N4—H4C | 100 (3) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.51 |
| C8—N7—H7 | 117.52 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.42 |
| S1—N7—H7 | 117.31 | C10—C11—H11A | 109.53 |
| S1—C1—C6 | 119.3 (2) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.49 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.6 (3) | C10—C11—H11C | 109.44 |
| O1—S1—N7—C8 | 171.7 (3) | O3—N8—C8—C9 | −0.8 (4) |
| O2—S1—N7—C8 | 41.8 (3) | S1—C1—C6—C5 | −177.8 (3) |
| C1—S1—N7—C8 | −73.7 (3) | S1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.0 (3) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | −150.0 (3) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.5 (5) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | 29.6 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.7 (5) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | −17.2 (3) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (5) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | 162.3 (3) | C2—C3—C4—N4 | −176.5 (3) |
| N7—S1—C1—C2 | 98.6 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.8 (5) |
| N7—S1—C1—C6 | −81.9 (3) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.6 (5) |
| N8—O3—C10—C11 | −179.5 (3) | N4—C4—C5—C6 | 176.7 (3) |
| C10—O3—N8—C8 | 0.5 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.2 (5) |
| N8—O3—C10—C9 | 0.0 (4) | N8—C8—C9—C10 | 0.8 (4) |
| S1—N7—C8—N8 | 158.6 (3) | N7—C8—C9—C10 | −178.6 (3) |
| S1—N7—C8—C9 | −22.0 (5) | C8—C9—C10—O3 | −0.5 (4) |
| O3—N8—C8—N7 | 178.7 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 178.9 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y, z+1; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z; (iii) x, y, z−1; (iv) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z+5/2; (v) x+1/2, y, −z+5/2; (vi) x, −y+1/2, z−1; (vii) x+1/2, y, −z+3/2; (viii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ix) x, −y+1/2, z+1; (x) −x+1, −y, −z+2; (xi) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (xii) x−1/2, y, −z+3/2; (xiii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, −z+3/2; (xiv) x−1/2, y, −z+5/2; (xv) −x+1/2, −y, z−1/2; (xvi) −x+1/2, −y, z+1/2; (xvii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, −z+5/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1W—H1W···Cl3i | 0.96 | 2.11 | 3.035 (5) | 161 |
| O1W—H2W···Cl3 | 0.95 | 2.11 | 3.036 (5) | 164 |
| N4—H4A···Cl2xiv | 0.94 (5) | 2.26 (5) | 3.184 (4) | 171 (4) |
| N4—H4B···O1Wiii | 0.91 (5) | 1.86 (5) | 2.758 (4) | 169 (4) |
| N4—H4B···O1Wvi | 0.91 (5) | 1.86 (5) | 2.758 (4) | 169 (4) |
| N4—H4C···Cl2xii | 0.85 (4) | 2.49 (4) | 3.196 (4) | 141 (4) |
| N4—H4C···O1xii | 0.85 (4) | 2.33 (5) | 2.871 (4) | 122 (4) |
| N7—H7···N8xi | 0.86 | 2.58 | 3.188 (5) | 129 |
| C2—H2···O2 | 0.93 | 2.55 | 2.911 (4) | 103 |
| C9—H9···O2 | 0.93 | 2.50 | 2.991 (4) | 113 |
| C9—H9···N8i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.354 (5) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y, z+1; (xiv) x−1/2, y, −z+5/2; (iii) x, y, z−1; (vi) x, −y+1/2, z−1; (xii) x−1/2, y, −z+3/2; (xi) −x+1, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FI2052).
References
- Abramenko, V. L. & Sergienko, V. S. (2002). Russ. J. Inorg. Chem.47, 905–914.
- Belletti, D., Cantoni, A. & Pasquinelli, G. (1993). Gestione on Line di Diffractometro a Cristallo Singolo Siemens AED con Personal Computer Internal Report 1-93. Centro di Studio per la Strutturistica Diffrattometrica del CNR Parma, Italy.
- Bettinetti, G. P., Giordano, F., La Manna, A., Giuseppetti, G. & Tadini, C. (1982). Cryst. Struct. Commun 11, 821–828.
- Dai, J.-C., Wu, X.-T., Fu, Z.-Y., Cui, C.-P., Wu, S.-M., Du, W.-X., Wu, L.-M., Zhang, H.-H. & Sun, Q.-Q. (2002). Inorg. Chem.41, 1391–1396. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, T. G., Ou, C. C., Potenza, J. A. & Schugar, H. J. (1978). J. Am. Chem. Soc.100, 2058–2062.
- Haridas, M., Tiwari, R. K. & Singh, T. P. (1984). Acta Cryst. C40, 658–660.
- Kagi, J. H. R. & Vallee, B. L. J. (1960). J. Biol. Chem.235, 3460–3460.
- Kálmán, A., Czugler, M. & Argay, Gy. (1981). Acta Cryst. B37, 868–877.
- Kendi, E., Özbey, S., Bozdağ, O. & Ertan, R. (2000). Acta Cryst. C56, 457–458. [DOI] [PubMed]
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Schaffers, K. I. & Keszler, D. A. (1993). Acta Cryst. C49, 1156–1158.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXL97 and SHELXS97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Singh, T. P., Patel, U. & Haridas, M. (1984). Acta Cryst. C40, 2088–2091.
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Subashini, A., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Cantoni, A. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4312–o4313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Subha Nandhini, M., Krishnakumar, R. V., Sivakumar, K. & Natarajan, S. (2002). Acta Cryst. E58, m307–m309. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Takasuka, M. & Nakai, H. (2001). Vib. Spectrosc.25, 197–204.
- Tao, J., Yin, X., Jiang, Y.-B., Yang, L.-F., Huang, R.-B. & Zheng, L.-S. (2003). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 2678–2682.
- Yukawa, Y., Inomata, Y., Takeuchi, T., Shimoi, M. & Ouchi, A. (1982). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 55, 3135–3137.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067190/fi2052sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067190/fi2052Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report