Abstract
The title compound, C23H26N4O·5H2O, has noncrystallographic twofold rotation symmetry in the solid state. It crystallizes with five solvent water molecules in the asymmetric unit. Four of these water molecules are connected with each other via hydrogen-bonding interactions to form two types of centrosymmetric hexameric (H2O)6 rings. Via edge sharing of the hexamers, the water clusters thus build infinite chains that stretch parallel to the a axis. The fifth water molecule provides an additional connection between the two hexameric (H2O)6 units via hydrogen bonds to both rings. The water molecules in the channels along the a axis are also bonded via O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds to the organic units, and face-to-face π–π interactions [with centroid-to-centroid distances of 3.656 (1) Å and average face-to-face distances of 3.431 (5) Å] between the aromatic rings of adjacent molecules complete the intermolecular interactions in this structure.
Related literature
Hay et al. (1998 ▶) report the use of benzimidazole complexes to model the active site of a variety of metalloenzymes, such as carbonic anhydrase and carboxypeptidase.
Experimental
Crystal data
C23H26N4O·5H2O
M r = 464.56
Monoclinic,

a = 8.814 (5) Å
b = 25.664 (13) Å
c = 11.635 (6) Å
β = 109.06 (1)°
V = 2488 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.40 × 0.30 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.970, T max = 0.982
12521 measured reflections
4424 independent reflections
2623 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.109
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.079
wR(F 2) = 0.222
S = 1.01
4424 reflections
311 parameters
15 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1999 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL-Plus (Sheldrick, 1990 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063039/zl2082sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063039/zl2082Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1W—H1A⋯N4 | 0.93 (2) | 1.95 (4) | 2.758 (6) | 144 (5) |
| O1W—H1B⋯O3Wi | 0.92 (4) | 2.31 (5) | 2.954 (5) | 127 (5) |
| O2W—H2B⋯O4W | 0.90 (5) | 2.61 (6) | 3.308 (7) | 135 (7) |
| O2W—H2B⋯O5Wii | 0.90 (5) | 2.05 (7) | 2.770 (6) | 136 (8) |
| O3W—H3B⋯O1iii | 0.88 (5) | 2.18 (5) | 3.054 (6) | 171 (7) |
| O4W—H4B⋯O1Wi | 0.92 (8) | 2.00 (7) | 2.900 (7) | 166 (8) |
| O4W—H4A⋯O5Wii | 0.92 (7) | 2.33 (4) | 3.200 (7) | 157 (7) |
| O5W—H5B⋯N1iv | 0.90 (5) | 1.93 (5) | 2.822 (5) | 175 (6) |
| O5W—H5A⋯O3Wv | 0.90 (6) | 1.92 (6) | 2.811 (6) | 167 (6) |
| O3W—H3A⋯O2Wi | 0.91 (2) | 1.94 (2) | 2.840 (7) | 170 (6) |
| O2W—H2A⋯O1Wi | 0.90 (2) | 2.14 (5) | 2.823 (6) | 132 (5) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Science Foundation for Young Teachers of Northeast Normal University (No. 20070314) for support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
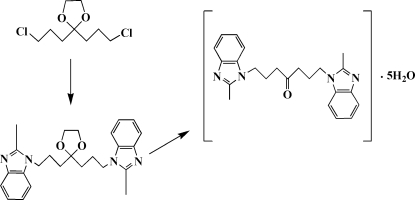
Currently there is considerable interest in the use of benzimidazole complexes to model the active site of a variety of metalloenzymes such as carbonic anhydrase and carboxypeptidase (Hay et al., 1998). In this context we prepared (Fig 4) and analyzed the title benzimidazole compound, and its structure is described here.
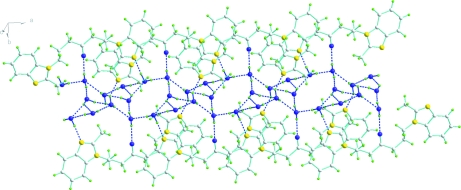
The title molecule (Fig 1) has non-crystallographic two fold symmetry with an r.m.s. deviation for both halves of 0.066 Å. It crystallizes with five lattice water molecules in the asymmetric part of the unit cell. Four of these water molecules (O1W, O2W, O3W and O5W) are connected with each other via hydrogen bonding interactions to form two types of centrosymmetric hexameric (H2O)6 rings. Via edge sharing of the hexamers the water clusters thus build infinite chains that stretch parallel to the a axis. The fifth water molecule O4W provides an additional connection between the two hexameric (H2O)6 rings via hydrogen bonds to both units. Water molecules O1W and O5W in the channels along a axis are also bonded via O—H···N hydrogen bonds to N4 and N1 of the organic unit, and all water molecules act both as donors and acceptors (Fig. 2).
Face-to-face π-π interactions between adjacent benzimidazoles made up by the atoms C1—C7, N3 and N4 and their symmetry equivalents at 1 - x, -y, 2 - z (with centroid-to-centriod distances of 3.656 (1) Å and an average face-to-face distance of 3.431 (5) Å, Fig. 3) complete the intermolecular interactions in this structure and lead to the formation of a 1-D supramolecuar chain along the a axis.
Experimental
To a solution of 1,7-dichloro-4-oxoheptane (8.3 g, 47 mmol) and ethylene glycol (2.9 g, 47 mmol) in cyclohexane (35 ml) was added 0.024 g sodium bisulfate. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 3 h with azeotropic removal of water via a Dean–Stark trap, until there was no more water created. The resulting clear solution was cooled down, washed with water twice, and then distilled. The fraction distilling between 447 K and 453 K was collected to obtain 1,11-dichloro-(5,8-dioxaspiro[4.2]undecane) as a clear liquid (5.5 g, 25 mmol, 53%).
A mixture of 2-methyl-benzimidazole (6.6 g, 50 mmol) and NaOH (2.0 g, 50 mmol) in DMSO (10 ml) was stirred at 333 K for 1 h, and then the collected distillate (5.5 g, 25 mmol) from the previous step was added. The mixture was cooled to room temperature after stirring at 333 K for 2 h, then poured into 200 ml of water and a white solid formed immediately. The compound (5,8-dioxaspiro[4.2]undecyl)bis(2-methyl-benzimidazole) was obtained in 74% yield (7.6 g, 19 mmol).
After washing with 50 ml water, the solid was transfered into 150 ml water with 10 ml HCl (12 mol l-1). The mixture was refluxed for 3.5 h, and then filtered. The obtained residue was dissolved in 100 ml me thanol, and colorless single crystals of the title compound were obtained after several days at room temperature (3.7 g, 10 mmol, 55%).
Refinement
The methyl H atoms were refined as members of rigid groups with C—H = 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(parent atom), and were allowed to rotate around the C—C bonds. Other H atoms on C atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding atoms, with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(parent atom). Water H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined as riding atoms, with an O—H distance of 0.89 (2) Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O). An anti-bumping restraint (standard deviation 0.01 Å) was used to avoid chemically not meaningful close contacts between the hydrogen atoms of the water molecules.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The water filled channels along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are represented by dashed lines.
Fig. 3.
The π-π interactions in the structure of the title compound. H atoms have been omitted for clarity. Symmetry codes: (i) 1 - x, -y, 2 - z.
Fig. 4.
The synthesis of the title compound as described in the experimental section.
Crystal data
| C23H26N4O·5H2O | F000 = 1000 |
| Mr = 464.56 | Dx = 1.240 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 4407 reflections |
| a = 8.814 (5) Å | θ = 1.6–25.3º |
| b = 25.664 (13) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 11.635 (6) Å | T = 293 (2) K |
| β = 109.06 (1)º | Block, colorless |
| V = 2488 (2) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.30 × 0.25 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4424 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2623 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.109 |
| T = 293(2) K | θmax = 25.3º |
| ω scans | θmin = 1.6º |
| Absorption correction: empirical (using intensity measurements)(SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.970, Tmax = 0.982 | k = −24→30 |
| 12521 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.079 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.222 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0646P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4424 reflections | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 311 parameters | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
| 15 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.011 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.7657 (6) | 0.03465 (19) | 0.9184 (5) | 0.0691 (15) | |
| H1 | 0.8154 | 0.0179 | 0.8693 | 0.083* | |
| C2 | 0.6000 (5) | 0.03845 (18) | 0.8828 (4) | 0.0554 (13) | |
| C3 | 0.5296 (5) | 0.06379 (18) | 0.9592 (4) | 0.0551 (13) | |
| C4 | 0.6183 (6) | 0.08559 (19) | 1.0686 (5) | 0.0670 (14) | |
| H4 | 0.5697 | 0.1026 | 1.1180 | 0.080* | |
| C5 | 0.7824 (7) | 0.0810 (2) | 1.1012 (5) | 0.0804 (17) | |
| H5 | 0.8467 | 0.0950 | 1.1747 | 0.096* | |
| C6 | 0.8542 (6) | 0.0558 (2) | 1.0266 (6) | 0.0785 (17) | |
| H6 | 0.9655 | 0.0534 | 1.0513 | 0.094* | |
| C7 | 0.3447 (6) | 0.0363 (2) | 0.7922 (4) | 0.0603 (13) | |
| C8 | 0.1824 (2) | 0.02679 (8) | 0.70124 (17) | 0.0900 (19) | |
| H8A | 0.1014 | 0.0396 | 0.7326 | 0.135* | |
| H8B | 0.1675 | −0.0099 | 0.6858 | 0.135* | |
| H8C | 0.1742 | 0.0446 | 0.6269 | 0.135* | |
| C9 | −0.8388 (2) | 0.22467 (8) | 0.63617 (17) | 0.0538 (13) | |
| C10 | −0.9846 (2) | 0.24529 (8) | 0.63617 (17) | 0.0691 (15) | |
| H10 | −1.0804 | 0.2309 | 0.5863 | 0.083* | |
| C11 | −0.9873 (2) | 0.28737 (8) | 0.71070 (17) | 0.0743 (16) | |
| H11 | −1.0849 | 0.3012 | 0.7107 | 0.089* | |
| C12 | −0.8442 (2) | 0.30882 (8) | 0.78523 (17) | 0.0753 (16) | |
| H12 | −0.8460 | 0.3370 | 0.8351 | 0.090* | |
| C13 | −0.6984 (2) | 0.28820 (8) | 0.78522 (17) | 0.0648 (14) | |
| H13 | −0.6027 | 0.3026 | 0.8351 | 0.078* | |
| C14 | −0.6957 (2) | 0.24613 (8) | 0.71069 (17) | 0.0497 (12) | |
| C15 | −0.6463 (6) | 0.18141 (19) | 0.6109 (4) | 0.0615 (14) | |
| C16 | −0.5526 (6) | 0.1420 (2) | 0.5672 (5) | 0.0935 (19) | |
| H16A | −0.6243 | 0.1222 | 0.5018 | 0.140* | |
| H16B | −0.4981 | 0.1190 | 0.6327 | 0.140* | |
| H16C | −0.4752 | 0.1595 | 0.5389 | 0.140* | |
| C17 | −0.4031 (5) | 0.22546 (18) | 0.7553 (4) | 0.0645 (15) | |
| H17A | −0.3820 | 0.2618 | 0.7778 | 0.077* | |
| H17B | −0.3447 | 0.2165 | 0.7005 | 0.077* | |
| C18 | −0.3436 (5) | 0.19203 (18) | 0.8684 (4) | 0.0582 (13) | |
| H18A | −0.4014 | 0.2013 | 0.9234 | 0.070* | |
| H18B | −0.3664 | 0.1558 | 0.8459 | 0.070* | |
| C19 | −0.1661 (5) | 0.19827 (19) | 0.9332 (4) | 0.0640 (14) | |
| H19A | −0.1407 | 0.2351 | 0.9376 | 0.077* | |
| H19B | −0.1423 | 0.1857 | 1.0158 | 0.077* | |
| C20 | −0.0576 (5) | 0.17074 (18) | 0.8769 (5) | 0.0549 (13) | |
| C21 | 0.1192 (5) | 0.17729 (19) | 0.9435 (4) | 0.0640 (14) | |
| H21A | 0.1390 | 0.1687 | 1.0283 | 0.077* | |
| H21B | 0.1459 | 0.2138 | 0.9401 | 0.077* | |
| C22 | 0.2331 (5) | 0.14550 (19) | 0.8985 (4) | 0.0629 (14) | |
| H22A | 0.1977 | 0.1470 | 0.8104 | 0.075* | |
| H22B | 0.3391 | 0.1611 | 0.9286 | 0.075* | |
| C23 | 0.2449 (5) | 0.08920 (19) | 0.9373 (4) | 0.0656 (14) | |
| H23A | 0.2737 | 0.0873 | 1.0251 | 0.079* | |
| H23B | 0.1413 | 0.0725 | 0.9021 | 0.079* | |
| N1 | −0.8030 (5) | 0.18326 (15) | 0.5730 (3) | 0.0632 (11) | |
| N2 | −0.5748 (4) | 0.21841 (15) | 0.6929 (3) | 0.0551 (11) | |
| N3 | 0.3650 (4) | 0.06156 (15) | 0.8987 (4) | 0.0570 (11) | |
| N4 | 0.4803 (5) | 0.02109 (15) | 0.7805 (4) | 0.0659 (12) | |
| O1 | −0.1070 (3) | 0.14430 (13) | 0.7855 (3) | 0.0654 (10) | |
| O1W | 0.5198 (5) | −0.06286 (16) | 0.6451 (4) | 0.1008 (14) | |
| H1A | 0.548 (7) | −0.0316 (14) | 0.687 (4) | 0.151* | |
| H1B | 0.455 (7) | −0.052 (2) | 0.570 (3) | 0.151* | |
| O2W | 0.2025 (6) | 0.02126 (17) | 0.3906 (5) | 0.1258 (18) | |
| H2A | 0.308 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.425 (5) | 0.189* | |
| H2B | 0.155 (7) | 0.0522 (16) | 0.366 (8) | 0.189* | |
| O3W | 0.7904 (5) | 0.08554 (17) | 0.5440 (4) | 0.0971 (13) | |
| H3A | 0.780 (8) | 0.0512 (11) | 0.559 (6) | 0.146* | |
| H3B | 0.825 (8) | 0.099 (3) | 0.618 (3) | 0.146* | |
| O4W | 0.2093 (7) | 0.1308 (3) | 0.2426 (5) | 0.153 (2) | |
| H4A | 0.129 (7) | 0.126 (4) | 0.276 (8) | 0.229* | |
| H4B | 0.289 (7) | 0.109 (3) | 0.289 (8) | 0.229* | |
| O5W | 0.5163 (4) | 0.39697 (15) | 0.9246 (3) | 0.0828 (12) | |
| H5A | 0.457 (6) | 0.404 (3) | 0.973 (5) | 0.124* | |
| H5B | 0.576 (6) | 0.3710 (17) | 0.968 (5) | 0.124* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.056 (3) | 0.058 (4) | 0.097 (4) | 0.009 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
| C2 | 0.054 (3) | 0.047 (3) | 0.069 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.025 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C3 | 0.050 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.005 (2) | 0.012 (3) | 0.010 (3) |
| C4 | 0.067 (3) | 0.058 (4) | 0.071 (4) | 0.008 (3) | 0.015 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C5 | 0.066 (4) | 0.078 (4) | 0.082 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.003 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C6 | 0.048 (3) | 0.082 (4) | 0.097 (5) | −0.002 (3) | 0.010 (3) | 0.004 (4) |
| C7 | 0.053 (3) | 0.067 (4) | 0.059 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C8 | 0.063 (3) | 0.108 (5) | 0.086 (4) | 0.009 (3) | 0.005 (3) | −0.006 (3) |
| C9 | 0.050 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.055 (3) | −0.003 (2) | 0.008 (2) | −0.001 (3) |
| C10 | 0.045 (3) | 0.084 (4) | 0.071 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.008 (3) | 0.012 (3) |
| C11 | 0.065 (3) | 0.076 (4) | 0.084 (4) | 0.022 (3) | 0.026 (3) | 0.007 (3) |
| C12 | 0.082 (4) | 0.062 (4) | 0.086 (4) | 0.015 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C13 | 0.064 (3) | 0.057 (4) | 0.070 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C14 | 0.050 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.056 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C15 | 0.064 (3) | 0.052 (4) | 0.067 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.019 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C16 | 0.085 (4) | 0.096 (5) | 0.100 (4) | 0.011 (3) | 0.030 (3) | −0.026 (4) |
| C17 | 0.047 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.088 (4) | −0.001 (2) | 0.013 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C18 | 0.042 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.068 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.015 (2) | −0.003 (3) |
| C19 | 0.047 (3) | 0.066 (4) | 0.074 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.015 (3) | −0.008 (3) |
| C20 | 0.059 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.059 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.014 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C21 | 0.044 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.078 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.010 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C22 | 0.048 (3) | 0.064 (4) | 0.078 (4) | 0.010 (2) | 0.023 (3) | 0.012 (3) |
| C23 | 0.052 (3) | 0.067 (4) | 0.080 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.015 (3) |
| N1 | 0.054 (2) | 0.062 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.008 (2) | −0.012 (2) |
| N2 | 0.044 (2) | 0.055 (3) | 0.063 (3) | 0.0036 (19) | 0.012 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| N3 | 0.046 (2) | 0.063 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.0081 (19) | 0.016 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| N4 | 0.059 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.070 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.017 (2) | −0.008 (2) |
| O1 | 0.057 (2) | 0.070 (3) | 0.066 (2) | 0.0025 (17) | 0.0161 (17) | −0.0130 (19) |
| O1W | 0.073 (3) | 0.117 (3) | 0.113 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.031 (2) | −0.033 (3) |
| O2W | 0.099 (3) | 0.099 (4) | 0.187 (5) | −0.008 (3) | 0.057 (4) | −0.019 (3) |
| O3W | 0.080 (3) | 0.098 (3) | 0.106 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.020 (2) | −0.023 (3) |
| O4W | 0.135 (5) | 0.180 (6) | 0.129 (4) | −0.010 (4) | 0.023 (4) | 0.042 (4) |
| O5W | 0.079 (3) | 0.077 (3) | 0.080 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C6 | 1.359 (7) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.385 (6) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C17—N2 | 1.460 (5) |
| C2—N4 | 1.382 (6) | C17—C18 | 1.513 (6) |
| C2—C3 | 1.400 (6) | C17—H17A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.376 (6) | C17—H17B | 0.9700 |
| C3—N3 | 1.392 (5) | C18—C19 | 1.507 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.376 (6) | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.388 (7) | C19—C20 | 1.501 (6) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C19—H19A | 0.9700 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C19—H19B | 0.9700 |
| C7—N4 | 1.306 (6) | C20—O1 | 1.216 (5) |
| C7—N3 | 1.358 (6) | C20—C21 | 1.506 (6) |
| C7—C8 | 1.496 (5) | C21—C22 | 1.513 (6) |
| C8—H8A | 0.9600 | C21—H21A | 0.9700 |
| C8—H8B | 0.9600 | C21—H21B | 0.9700 |
| C8—H8C | 0.9600 | C22—C23 | 1.507 (6) |
| C9—N1 | 1.386 (4) | C22—H22A | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.390 (3) | C22—H22B | 0.9700 |
| C9—C14 | 1.390 (3) | C23—N3 | 1.461 (5) |
| C10—C11 | 1.390 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | C23—H23B | 0.9700 |
| C11—C12 | 1.390 (3) | O1W—H1A | 0.93 (2) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9300 | O1W—H1B | 0.92 (4) |
| C12—C13 | 1.390 (3) | O2W—H2A | 0.90 (2) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | O2W—H2B | 0.90 (5) |
| C13—C14 | 1.390 (3) | O3W—H3A | 0.91 (2) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9300 | O3W—H3B | 0.88 (5) |
| C14—N2 | 1.352 (4) | O4W—H4A | 0.92 (7) |
| C15—N1 | 1.307 (6) | O4W—H4B | 0.92 (8) |
| C15—N2 | 1.348 (6) | O5W—H5A | 0.90 (6) |
| C15—C16 | 1.496 (7) | O5W—H5B | 0.90 (5) |
| C16—H16A | 0.9600 | ||
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.6 (5) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 120.7 | N2—C17—C18 | 111.8 (4) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 120.7 | N2—C17—H17A | 109.3 |
| N4—C2—C1 | 132.0 (5) | C18—C17—H17A | 109.3 |
| N4—C2—C3 | 109.0 (4) | N2—C17—H17B | 109.3 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.0 (5) | C18—C17—H17B | 109.3 |
| C4—C3—N3 | 131.9 (5) | H17A—C17—H17B | 107.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 122.7 (4) | C19—C18—C17 | 112.6 (4) |
| N3—C3—C2 | 105.4 (4) | C19—C18—H18A | 109.1 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 116.6 (5) | C17—C18—H18A | 109.1 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 121.7 | C19—C18—H18B | 109.1 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 121.7 | C17—C18—H18B | 109.1 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.4 (5) | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.8 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C20—C19—C18 | 115.9 (4) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C20—C19—H19A | 108.3 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 121.6 (5) | C18—C19—H19A | 108.3 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.2 | C20—C19—H19B | 108.3 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.2 | C18—C19—H19B | 108.3 |
| N4—C7—N3 | 112.7 (4) | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.4 |
| N4—C7—C8 | 125.0 (4) | O1—C20—C19 | 123.2 (4) |
| N3—C7—C8 | 122.3 (4) | O1—C20—C21 | 121.8 (4) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C19—C20—C21 | 115.0 (4) |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C20—C21—C22 | 117.0 (4) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C20—C21—H21A | 108.1 |
| C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C22—C21—H21A | 108.1 |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C20—C21—H21B | 108.1 |
| H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C22—C21—H21B | 108.1 |
| N1—C9—C10 | 131.51 (17) | H21A—C21—H21B | 107.3 |
| N1—C9—C14 | 108.49 (18) | C23—C22—C21 | 113.7 (4) |
| C10—C9—C14 | 119.99 (18) | C23—C22—H22A | 108.8 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.00 (18) | C21—C22—H22A | 108.8 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 | C23—C22—H22B | 108.8 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 | C21—C22—H22B | 108.8 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.00 (18) | H22A—C22—H22B | 107.7 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 | N3—C23—C22 | 111.1 (4) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 | N3—C23—H23A | 109.4 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 119.99 (18) | C22—C23—H23A | 109.4 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 120.0 | N3—C23—H23B | 109.4 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 120.0 | C22—C23—H23B | 109.4 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.00 (18) | H23A—C23—H23B | 108.0 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 120.0 | C15—N1—C9 | 104.4 (3) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 | C15—N2—C14 | 105.6 (3) |
| N2—C14—C13 | 132.77 (18) | C15—N2—C17 | 127.5 (4) |
| N2—C14—C9 | 107.23 (18) | C14—N2—C17 | 126.8 (4) |
| C13—C14—C9 | 120.01 (18) | C7—N3—C3 | 106.6 (4) |
| N1—C15—N2 | 114.3 (4) | C7—N3—C23 | 128.3 (4) |
| N1—C15—C16 | 123.4 (5) | C3—N3—C23 | 124.4 (4) |
| N2—C15—C16 | 122.3 (5) | C7—N4—C2 | 106.3 (4) |
| C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 | H1A—O1W—H1B | 102 (3) |
| C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 | H2A—O2W—H2B | 106 (4) |
| H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 | H3A—O3W—H3B | 103 (7) |
| C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 | H4A—O4W—H4B | 102 (7) |
| H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 | H5A—O5W—H5B | 99 (6) |
| C6—C1—C2—N4 | −179.8 (5) | C21—C22—C23—N3 | −175.9 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.1 (7) | N2—C15—N1—C9 | −0.7 (5) |
| N4—C2—C3—C4 | −179.8 (4) | C16—C15—N1—C9 | 179.7 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.5 (7) | C10—C9—N1—C15 | −178.9 (2) |
| N4—C2—C3—N3 | −0.7 (5) | C14—C9—N1—C15 | 0.2 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—N3 | 179.5 (4) | N1—C15—N2—C14 | 0.8 (5) |
| N3—C3—C4—C5 | −179.4 (5) | C16—C15—N2—C14 | −179.6 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.6 (7) | N1—C15—N2—C17 | 177.5 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.4 (8) | C16—C15—N2—C17 | −2.9 (8) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.1 (8) | C13—C14—N2—C15 | 178.8 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (9) | C9—C14—N2—C15 | −0.6 (3) |
| N1—C9—C10—C11 | 179.1 (2) | C13—C14—N2—C17 | 2.1 (5) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.0 | C9—C14—N2—C17 | −177.3 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.0 | C18—C17—N2—C15 | −85.2 (6) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.0 | C18—C17—N2—C14 | 90.8 (5) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.0 | N4—C7—N3—C3 | 1.7 (5) |
| C12—C13—C14—N2 | −179.4 (2) | C8—C7—N3—C3 | −179.4 (4) |
| C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0.0 | N4—C7—N3—C23 | 172.2 (4) |
| N1—C9—C14—N2 | 0.3 (2) | C8—C7—N3—C23 | −8.9 (7) |
| C10—C9—C14—N2 | 179.52 (18) | C4—C3—N3—C7 | 178.4 (5) |
| N1—C9—C14—C13 | −179.26 (19) | C2—C3—N3—C7 | −0.5 (5) |
| C10—C9—C14—C13 | 0.0 | C4—C3—N3—C23 | 7.4 (8) |
| N2—C17—C18—C19 | 179.3 (4) | C2—C3—N3—C23 | −171.5 (4) |
| C17—C18—C19—C20 | −76.8 (5) | C22—C23—N3—C7 | −88.9 (6) |
| C18—C19—C20—O1 | −0.8 (7) | C22—C23—N3—C3 | 80.1 (5) |
| C18—C19—C20—C21 | −179.7 (4) | N3—C7—N4—C2 | −2.1 (5) |
| O1—C20—C21—C22 | −5.5 (7) | C8—C7—N4—C2 | 179.0 (4) |
| C19—C20—C21—C22 | 173.4 (4) | C1—C2—N4—C7 | −178.6 (5) |
| C20—C21—C22—C23 | −77.5 (5) | C3—C2—N4—C7 | 1.7 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1W—H1A···N4 | 0.93 (2) | 1.95 (4) | 2.758 (6) | 144 (5) |
| O1W—H1B···O3Wi | 0.92 (4) | 2.31 (5) | 2.954 (5) | 127 (5) |
| O2W—H2B···O4W | 0.90 (5) | 2.61 (6) | 3.308 (7) | 135 (7) |
| O2W—H2B···O5Wii | 0.90 (5) | 2.05 (7) | 2.770 (6) | 136 (8) |
| O3W—H3B···O1iii | 0.88 (5) | 2.18 (5) | 3.054 (6) | 171 (7) |
| O4W—H4B···O1Wi | 0.92 (8) | 2.00 (7) | 2.900 (7) | 166 (8) |
| O4W—H4A···O5Wii | 0.92 (7) | 2.33 (4) | 3.200 (7) | 157 (7) |
| O5W—H5B···N1iv | 0.90 (5) | 1.93 (5) | 2.822 (5) | 175 (6) |
| O5W—H5A···O3Wv | 0.90 (6) | 1.92 (6) | 2.811 (6) | 167 (6) |
| O3W—H3A···O2Wi | 0.91 (2) | 1.94 (2) | 2.840 (7) | 170 (6) |
| O2W—H2A···O1Wi | 0.90 (2) | 2.14 (5) | 2.823 (6) | 132 (5) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iii) x+1, y, z; (iv) x+3/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (v) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZL2082).
References
- Bruker (1997). SMART Version 5.622. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (1999). SAINT Version 6.02. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Hay, R. W., Clifford, T. & Lightfoot, P. (1998). Polyhedron, 17, 3575–3581.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1990). SHELXTL-Plus Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063039/zl2082sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063039/zl2082Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report