Abstract
In the title compound, C14H10Cl2N2O, which is an important synthetic precursor of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) inhibitor, the dihedral angle between the 2,6-dichlorophenyl ring and the phenyl ring is 69.4 (1)°. In the crystal structure, the molecules form centrosymmetric dimers via N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds with an R 2 2(8) motif. The dimers are connected by intermolecular C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For the starting material, see: Reich et al. (1917 ▶). For human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibitors, see: Pauwels et al. (1993 ▶). For related literature on the crystal structures of α-anilinoacetamide derivatives, see: Peeters et al. (1993 ▶); Garg et al. (1993 ▶); Opatz & Ferenc (2005 ▶). For related literature on C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, see: Taylor & Kennard (1982 ▶); Biradha et al. (1997 ▶); Batchelor et al. (2000 ▶). For related literature on C—H⋯π interactions, see: Malone et al. (1997 ▶); Tomura & Yamashita (2001 ▶); Nishio (2004 ▶). For related literature, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶); Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶); Allen (2002 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H10Cl2N2O
M r = 293.14
Triclinic,
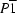
a = 7.8777 (2) Å
b = 9.1433 (3) Å
c = 10.0217 (4) Å
α = 102.170 (3)°
β = 91.795 (3)°
γ = 102.145 (2)°
V = 687.66 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 4.19 mm−1
T = 296 (1) K
0.50 × 0.40 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.229, T max = 0.818
3020 measured reflections
2808 independent reflections
2499 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.016
3 standard reflections frequency: 120 min intensity decay: 0.8%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.045
wR(F 2) = 0.135
S = 1.05
2808 reflections
173 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: CAD-4 EXPRESS (Enraf–Nonius, 1992 ▶); cell refinement: CAD-4 EXPRESS; data reduction: TEXSAN (Rigaku/MSC, 2000 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063891/kp2151sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063891/kp2151Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.08 | 2.935 (2) | 172 |
| N2—H2B⋯N1 | 0.86 | 2.37 | 2.708 (2) | 104 |
| C3—H3⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.260 (2) | 133 |
| N2—H2B⋯Cg1iii | 0.86 | 2.76 | 3.484 (2) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  . Cg1 is the centroid of the C8–C13 benzene ring.
. Cg1 is the centroid of the C8–C13 benzene ring.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the Instrument Center of the Institute for Molecular Science for the X-ray structure analysis.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound, (I), is an important synthetic precursor of α-anilinophenylaceamide derivatives, which are potent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) specific reverse transcriptase inhibitors (Pauwels et al., 1993). A search for α-anilinoaceamide structure in the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.28; Allen, 2002) revealed three examples (Peeters et al., 1993; Garg et al., 1993; Opatz & Ferenc, 2005) while no structure of an α-phenyliminoaceamide derivative, such as (I), was found. We report here the molecular and crystal structures of the title α-phenyliminoaceamide derivative (I) (Fig. 1).
The compound (I) was synthesized by the reaction of N-(2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)aniline (Reich et al., 1917) with NaCN and crystallizes in the P1 space group with one molecule in an asymmetric unit. The molecule has an E-conformation about the C7?N1 bond. The bond lengths and angles are within the normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987). Two benzene rings of (I) are planar [r.m.s. deviations of 0.0047 (C1—C6) and 0.0074 (C8—C13) Å from the least-squares planes] with a dihedral angle between their least-squares planes of 69.4 (1)°. Each benzene ring is close to be orthogonal [86.5 (2) for C1—C6 and 73.9 (1)° for C8—C13] to the plane of the amide group (C14/O1/N2). In the amide group, the intramolecular hydrogen bond between atoms N1 and N2 is observed [2.708 (2) Å].
In the crystal structure, the molecules are linked via N—H···O hydrogen bonds [2.935 (2) Å for N2—H2A···O1(-x + 1, -y + 1, -z + 1)] to form a centrosymmetric dimer with a graph-set motif (Bernstein et al., 1995) of R22(8) (Fig. 2 and Table 1). The intermolecular C—H···O [3.260 (2) Å for C3—H3···O1(-x + 1, -y + 1, -z + 2)] and C—H···π [3.484 (2) Å for N2—H2B···Cg1(-x, -y, -z + 1), Cg1 is the centroid of the benzene ring (C8—C13)] interactions are observed between the dimers (Tomura & Yamashita, 2001; Nishio, 2004). The C—H···O hydrogen bond in the crystal structure of (I) is stronger than the typical C—H···O hydrogen bonds in other structures (Taylor & Kennard, 1982; Biradha et al., 1997; Batchelor et al., 2000). The C—H···π interaction corresponds to a geometry of type III (Malone et al., 1997).
Experimental
The compound (I) was prepared as follows: a mixture of N-(2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)aniline (Reich et al., 1917) (504 mg, 2.0 mmol) and NaCN (110 mg, 2.0 mmol) in dimethyl sulfoxide (20 ml) was stirred for 1 day at 296 K. The reaction mixture was poured into water (100 ml) and the solution was extracted with dichloromethane (100 ml × 3). The organic layer was washed with water and dried over Na2SO4. After the solvent was evaporated in vacuo, dichloromethane (10 ml) was added to the residue. The resulting colourless precipitate was collected to give 198 mg (34% yield) of (I). Physical data for (I): m.p. 510 K; 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ p.p.m.): 5.30–5.65 (br s, 1H), 6.81–7.26 (m, 8H), 7.37–7.47 (br s, 1H); MS (EI): m/z 294 (M++2), 292 (M+), 248. Colourless crystals of (I) suitable for X-ray analysis were grown from a chloroform solution.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in geometrically calculated positions and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.93 Å, N—H = 0.86 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or (N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms and H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
The packing diagram of (I). Dashed lines indicate intermolecular N—H···O, C—H···O and C—H···π interactions.
Crystal data
| C14H10Cl2N2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 293.14 | F000 = 300 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.416 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point: 510 K |
| a = 7.8777 (2) Å | Cu Kα radiation λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 9.1433 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| c = 10.0217 (4) Å | θ = 15.0–42.6º |
| α = 102.170 (3)º | µ = 4.19 mm−1 |
| β = 91.795 (3)º | T = 296 (1) K |
| γ = 102.145 (2)º | Prism, colourless |
| V = 687.66 (4) Å3 | 0.50 × 0.40 × 0.05 mm |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.016 |
| Monochromator: graphite | θmax = 74.3º |
| T = 296(1) K | θmin = 4.5º |
| ω–2θ scan | h = 0→9 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan(North et al., 1968) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.229, Tmax = 0.818 | l = −12→12 |
| 3020 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections |
| 2808 independent reflections | every 120 min |
| 2499 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | intensity decay: 0.8% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0796P)2 + 0.1897P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.135 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 2808 reflections | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
| 173 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0156 (17) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.15690 (8) | 0.38587 (7) | 0.87469 (7) | 0.0713 (2) | |
| Cl2 | 0.62681 (8) | 0.04600 (8) | 0.72009 (7) | 0.0791 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.5291 (2) | 0.42558 (17) | 0.65152 (14) | 0.0632 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.2306 (2) | 0.07483 (17) | 0.59095 (15) | 0.0472 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.3232 (2) | 0.3200 (2) | 0.47621 (16) | 0.0598 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.3588 | 0.3906 | 0.4323 | 0.072* | |
| H2B | 0.2355 | 0.2462 | 0.4425 | 0.072* | |
| C1 | 0.3973 (2) | 0.21737 (18) | 0.81031 (16) | 0.0413 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.3294 (2) | 0.3076 (2) | 0.91479 (18) | 0.0476 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.3924 (3) | 0.3366 (3) | 1.0501 (2) | 0.0611 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.3451 | 0.3986 | 1.1180 | 0.073* | |
| C4 | 0.5255 (3) | 0.2723 (3) | 1.0823 (2) | 0.0720 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.5683 | 0.2902 | 1.1732 | 0.086* | |
| C5 | 0.5971 (3) | 0.1818 (3) | 0.9828 (2) | 0.0690 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.6872 | 0.1382 | 1.0061 | 0.083* | |
| C6 | 0.5340 (3) | 0.1557 (2) | 0.8470 (2) | 0.0515 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.3324 (2) | 0.19374 (19) | 0.66374 (16) | 0.0412 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.1608 (2) | −0.0528 (2) | 0.64758 (18) | 0.0471 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.1897 (3) | −0.1957 (2) | 0.5867 (2) | 0.0622 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.2556 | −0.2065 | 0.5113 | 0.075* | |
| C10 | 0.1197 (3) | −0.3220 (3) | 0.6390 (3) | 0.0724 (7) | |
| H10 | 0.1420 | −0.4171 | 0.6000 | 0.087* | |
| C11 | 0.0181 (3) | −0.3085 (3) | 0.7476 (3) | 0.0695 (6) | |
| H11 | −0.0290 | −0.3942 | 0.7815 | 0.083* | |
| C12 | −0.0139 (3) | −0.1682 (3) | 0.8058 (3) | 0.0649 (6) | |
| H12 | −0.0836 | −0.1594 | 0.8790 | 0.078* | |
| C13 | 0.0564 (3) | −0.0396 (2) | 0.7570 (2) | 0.0541 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.0340 | 0.0551 | 0.7971 | 0.065* | |
| C14 | 0.4032 (2) | 0.3250 (2) | 0.59550 (17) | 0.0449 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0733 (4) | 0.0624 (4) | 0.0828 (4) | 0.0283 (3) | 0.0142 (3) | 0.0118 (3) |
| Cl2 | 0.0702 (4) | 0.0934 (5) | 0.0848 (4) | 0.0427 (3) | 0.0105 (3) | 0.0191 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0780 (10) | 0.0577 (8) | 0.0474 (7) | −0.0110 (7) | −0.0061 (6) | 0.0245 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0523 (8) | 0.0469 (8) | 0.0428 (7) | 0.0070 (6) | 0.0000 (6) | 0.0155 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0740 (11) | 0.0567 (9) | 0.0480 (9) | −0.0007 (8) | −0.0090 (8) | 0.0272 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0463 (9) | 0.0404 (8) | 0.0378 (8) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0029 (6) | 0.0173 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0520 (10) | 0.0424 (9) | 0.0467 (9) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0090 (7) | 0.0140 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0704 (13) | 0.0610 (12) | 0.0400 (9) | −0.0096 (10) | 0.0083 (9) | 0.0088 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0816 (16) | 0.0808 (15) | 0.0419 (10) | −0.0152 (12) | −0.0111 (10) | 0.0235 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0646 (13) | 0.0763 (14) | 0.0678 (14) | 0.0035 (11) | −0.0171 (11) | 0.0352 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0499 (10) | 0.0551 (10) | 0.0519 (10) | 0.0081 (8) | 0.0004 (8) | 0.0212 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0460 (9) | 0.0432 (8) | 0.0376 (8) | 0.0105 (7) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0153 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0473 (9) | 0.0468 (9) | 0.0468 (9) | 0.0041 (7) | −0.0047 (7) | 0.0173 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0667 (13) | 0.0526 (11) | 0.0663 (12) | 0.0107 (9) | 0.0070 (10) | 0.0136 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0703 (14) | 0.0477 (11) | 0.1013 (19) | 0.0132 (10) | −0.0044 (13) | 0.0231 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0565 (12) | 0.0630 (13) | 0.0950 (17) | 0.0009 (10) | −0.0058 (11) | 0.0445 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0530 (11) | 0.0709 (14) | 0.0712 (13) | −0.0013 (10) | 0.0054 (10) | 0.0318 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0493 (10) | 0.0518 (10) | 0.0596 (11) | 0.0028 (8) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0175 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0550 (10) | 0.0440 (9) | 0.0380 (8) | 0.0095 (7) | 0.0051 (7) | 0.0154 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C2 | 1.737 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| Cl2—C6 | 1.728 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.388 (3) |
| O1—C14 | 1.228 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.273 (2) | C7—C14 | 1.519 (2) |
| N1—C8 | 1.420 (2) | C8—C13 | 1.391 (3) |
| N2—C14 | 1.322 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.389 (3) |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C9—C10 | 1.385 (3) |
| N2—H2B | 0.8600 | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.385 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.371 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.389 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C7 | 1.496 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.371 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.381 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.367 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.384 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.372 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N1—C8 | 120.81 (14) | N1—C7—C14 | 117.73 (14) |
| C14—N2—H2A | 120.0 | C1—C7—C14 | 115.27 (14) |
| C14—N2—H2B | 120.0 | C13—C8—C9 | 119.52 (18) |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 120.0 | C13—C8—N1 | 121.59 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.04 (16) | C9—C8—N1 | 118.78 (18) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 121.51 (16) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.5 (2) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 121.38 (16) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.2 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.56 (19) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.2 |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 118.54 (17) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.8 (2) |
| C1—C2—Cl1 | 118.89 (14) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.6 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.7 | C12—C11—C10 | 119.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.7 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.14 (19) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C11—C12—C13 | 120.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.4 (2) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.3 | C12—C13—C8 | 119.6 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.3 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.2 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 121.2 (2) | C8—C13—H13 | 120.2 |
| C1—C6—Cl2 | 118.90 (14) | O1—C14—N2 | 124.57 (16) |
| C5—C6—Cl2 | 119.94 (18) | O1—C14—C7 | 119.44 (15) |
| N1—C7—C1 | 126.95 (15) | N2—C14—C7 | 115.98 (16) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.1 (3) | C6—C1—C7—N1 | 79.6 (2) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −177.07 (16) | C2—C1—C7—C14 | 79.1 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—Cl1 | −179.37 (13) | C6—C1—C7—C14 | −97.79 (19) |
| C7—C1—C2—Cl1 | 3.6 (2) | C7—N1—C8—C13 | 60.6 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.7 (3) | C7—N1—C8—C9 | −123.2 (2) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.54 (15) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −2.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.6 (3) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | −178.79 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.4 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 2.0 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.1 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.5 (4) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 178.08 (17) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.5 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—Cl2 | −178.50 (13) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | 0.0 (3) |
| C7—C1—C6—Cl2 | −1.5 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 1.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.3 (3) | N1—C8—C13—C12 | 177.73 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—Cl2 | 178.32 (17) | N1—C7—C14—O1 | −164.09 (18) |
| C8—N1—C7—C1 | 2.0 (3) | C1—C7—C14—O1 | 13.6 (3) |
| C8—N1—C7—C14 | 179.41 (16) | N1—C7—C14—N2 | 15.0 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7—N1 | −103.5 (2) | C1—C7—C14—N2 | −167.32 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···O1i | 0.86 | 2.08 | 2.935 (2) | 172 |
| N2—H2B···N1 | 0.86 | 2.37 | 2.708 (2) | 104 |
| C3—H3···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.260 (2) | 133 |
| N2—H2B···Cg1iii | 0.86 | 2.76 | 3.484 (2) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2; (iii) −x, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: KP2151).
References
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Batchelor, E., Klinowski, J. & Jones, W. (2000). J. Mater. Chem.10, 839–848.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Biradha, K., Nangia, A., Desiraju, G. R., Carrellb, C. J. & Carrell, H. L. (1997). J. Mater. Chem.7, 1111–1122.
- Enraf–Nonius (1992). CAD-4 EXPRESS Version 5.1. Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Garg, S. N., Agarwal, S. K., Fidelis, K., Hossain, M. B. & van der Helm, D. (1993). J. Nat. Prod.56, 539–544. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst.39, 453–457.
- Malone, J. F., Murray, C. M., Charlton, M. H., Docherty, R. & Lavery, A. J. (1997). J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans.93, 3429–3436.
- Nishio, M. (2004). CrystEngComm, 6, 130–158.
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Opatz, T. & Ferenc, D. (2005). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 121–126.
- Pauwels, R., Andries, K., Debyser, Z., Van Daele, P., Schols, D., Stoffels, P., De Vreese, K., Woestenborghs, R., Vandamme, A. M., Janssen, C. G. M., Anné, J., Cauwenbergh, G., Desmyter, J., Heykants, J., Janssen, M. A. C., De Clercq, E. & Janssen, P. A. J. (1993). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 1711–1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Peeters, O. M., Blaton, N. M. & De Ranter, C. J. (1993). Acta Cryst. C49, 1961–1963.
- Reich, S., Salzmann, R. & Kawa, D. (1917). Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr.21, 217–225.
- Rigaku/MSC (2000). TEXSAN Version 1.11. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Taylor, R. & Kennard, O. (1982). J. Am. Chem. Soc.104, 5063–5070.
- Tomura, M. & Yamashita, Y. (2001). Chem. Lett. pp. 532–533.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063891/kp2151sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063891/kp2151Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




